0 L E D Technology
Alireza Afzal aghaei
B.Sc. computer science
Damghan university
Whats OLED?
- An OLED is any light emitting diode (LED) which emissive electroluminescent layer is composed of a film of organic compounds
- Electroluminescence is a process in which a material emits light in response to electrical field applied across it
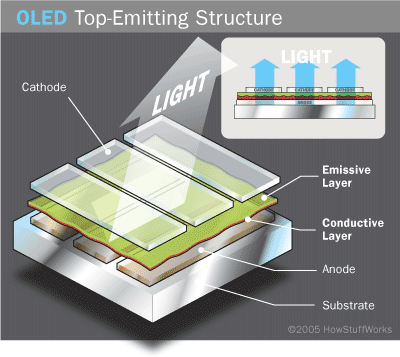
OLED Architecture
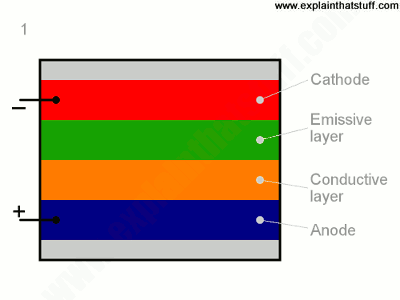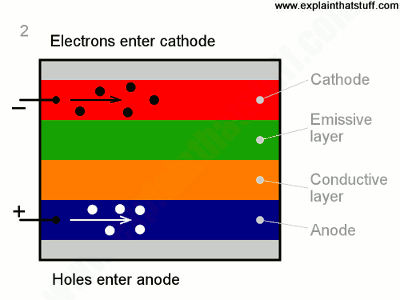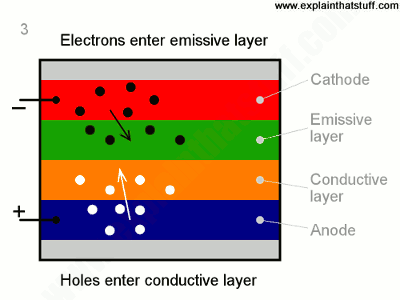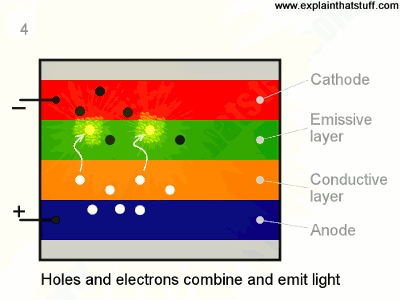
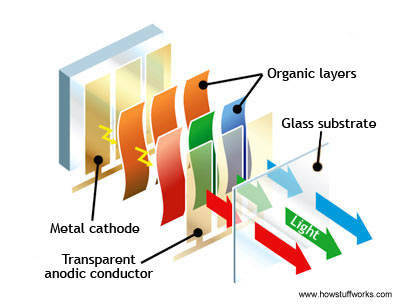
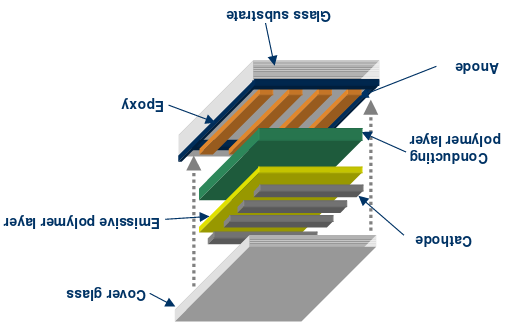
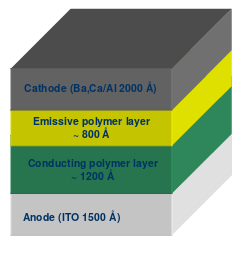
- Cathode: The cathode injects electrons into emissive layer.
- Emissive layer: This layer is made of polyfluorene that transport electrons from the cathode. This is where light is made.
- Conducting layer: This layer is made of polyaniline that transport "holes" from the anode.
- Anode: It is kept transparent. Usually made up of Indium tin oxide (ITO) that removes electrons.
- Substrate: The substrate supports the OLED.
Oled Structure
WORKING PRINCIPLE
- A voltage is applied across the anode and cathode.
- Current flows from cathode to anode through the organic layers.
- Electrons flow to emissive layer from the cathode.
- Electrons are removed from conductive layer leaving holes.
- Holes jump into emissive layer .
- Electron and hole combine and light emitted.
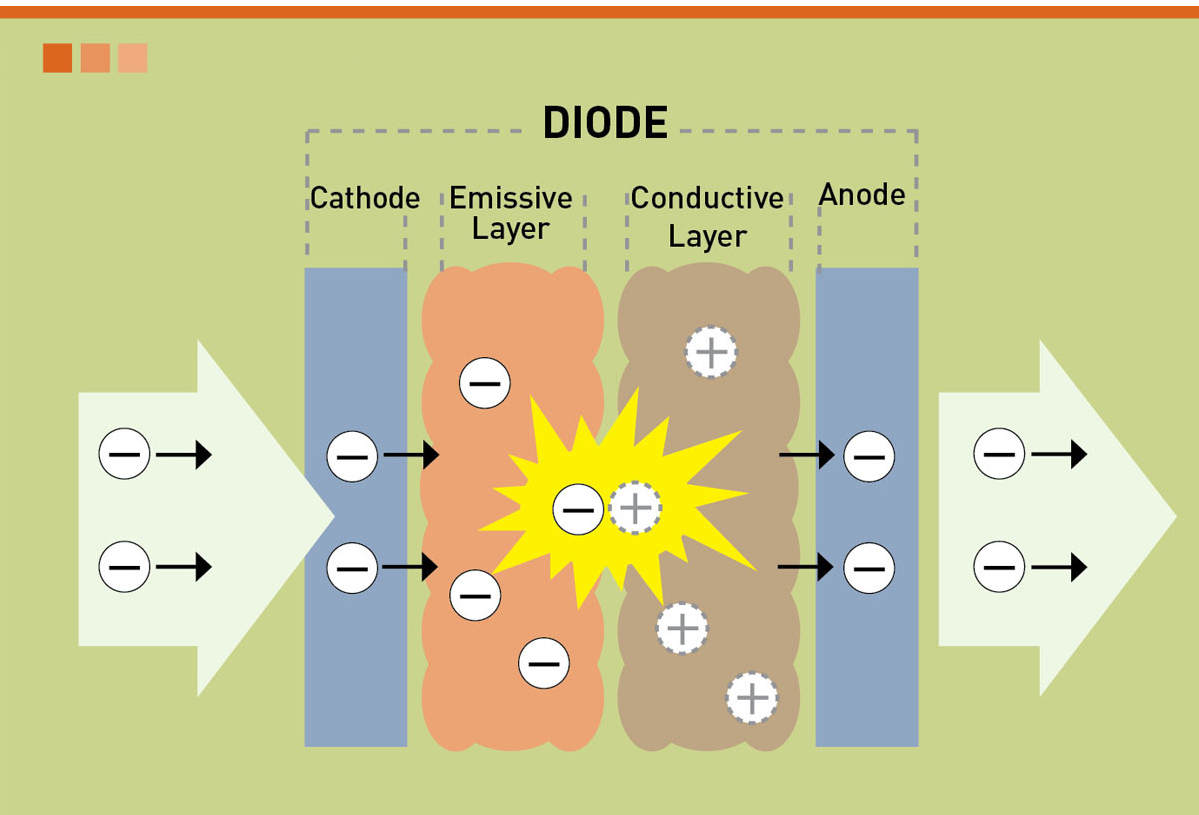
WORKING PRINCIPLE
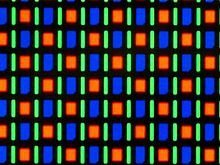
Display & Pixel Structure
Pixel
Display
Types of OLEDs
- Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED)
- Light Emitting polymers (LEP)
Types of OLEDs
- Passive-matrix OLED
- Active-matrix OLED
- Transparent OLED
- Top-emitting OLED
- Foldable OLED
- White OLED
Passive-matrix OLED
- Perpendicular cathode/anode strip orientation
- Light emitted at intersections(pixels)
- Easy to make
- Large power consumption
- Best for small screens
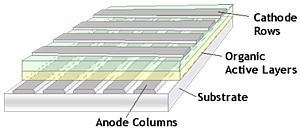
Active-matrix OLED
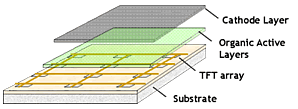
- Full layers of cathode and anode
- Anode overlays a TFT
- Requires less power
- Suitable for large screens
- Newer AMOLED technologies
- Super AMOLED
- Super Amoled Plus
- Super AMOLED HD
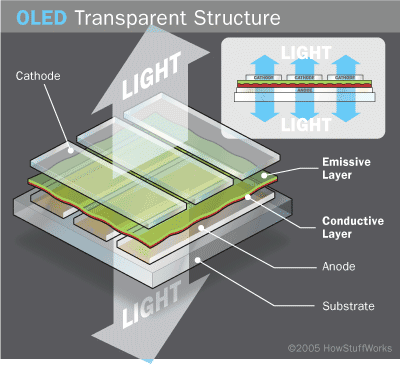
Transparent OLED
- Transparent substrate,cathode and anode
- Emits light bi-directionally
- Passive or Active matrix OLED
- Useful for head-up displays
- Transparent projector screens
- Glasses
Top-Emitting OLED
- Non Transparent or reflective substrate
- Transparent cathode
- Used with Active matrix device
- Smart Card displays
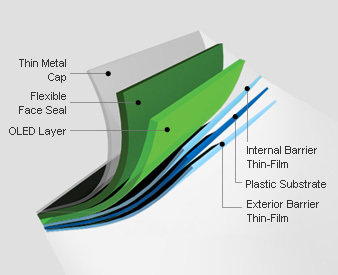
Foldable OLED
- Substrates made of very flexible metallic foils or plastics
- Very lightweight and durable reduces breakage
- Attached to fabrics to create "smart" clothing
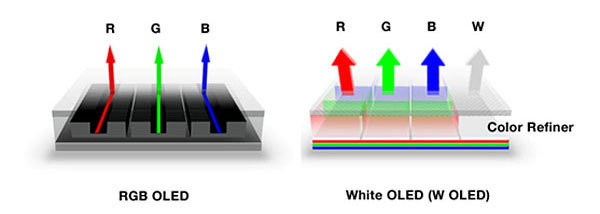
WHite OLED
- Emits bright white light.
- Replace fluorescent lights.
- Reduce energy cost for lighting.
- True Color Qualities.
Applications
- TVs
- Cell Phone screens
- Computer Screens
- Keyboards (Optimus Maximus)
- Lights
- Portable Device displays
advantages
- Thinner, lighter and more flexible.
- Plastic substrates rather then glass.
- Able to display "True Black" picture
- High resolution (<5um pixel size) and fast switching (1-10um).
- Do not require backlight, light generated.
- Low voltage, low power and emissive source.
- Larger sized displays.
- Brighter- good day light visibility.
- Larger viewing angles -170°
- Safer for environment
Disadvantages
- Lifetime
- White, Red, Green 46,000-230,000 hours.
- About 5-25 years.
- Blue 14,000 hours.
- About 1.6 years.
- White, Red, Green 46,000-230,000 hours.
- Expensive.
- Manufactoring
- Susceptible to water.
- Overcome multi-billion dollar LCD market.
future of oled
- Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode (QLED)
-
Advantages:
-
emitting brighter
-
more vibrant
-
more diverse colors
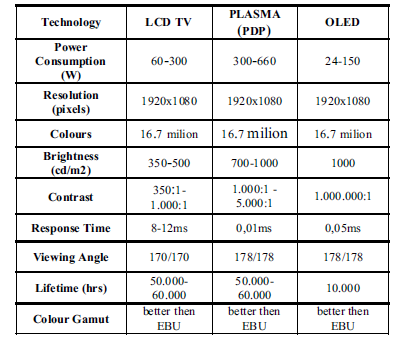
lcd vs. Plasma vs. oled
Resources
- http://www.ewh.ieee.org/soc/cpmt/presentations/cpmt0401a.pdf
- http://www.slideshare.net/skrishnabhagavan1993/oled-technology-25369915
- http://www.slideshare.net/aadishchopra/oled-46947976
- http://www.slideshare.net/kevinpatel10/oled-all-you-need-to-know
- http://www.slideshare.net/nikhil2akhil/oled-technology-37597952
- http://www.slideshare.net/RohitBuddabathina/oled-technology-45945851
- http://www.explainthatstuff.com/how-oleds-and-leps-work.html
- http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/oled.htm