Image formats
and how to extract figures from papers to create awesome presentations
(
)
FELIPE DELESTRO
Phd student - IBENS
Bioinformatics Platform
https://slides.com/delestro/image-formats/live
Follow the presentation live
image quality is of great importance
-
Helps you to clearly convey a message
-
Shows dedication to the work
-
Holds the attention of the public
Before anything else,
we need to know how
images are displayed





additive color model
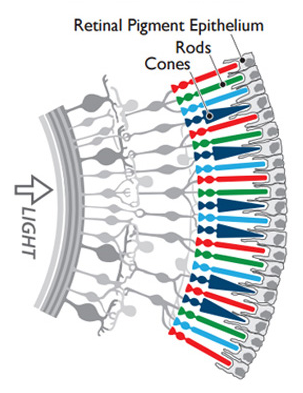


subtractive color model



To better understand the relationship of size between pixels on screen and on printed paper, follow this tutorial
Raster
Vector
&
Not all images are created equal Delestro, Bioinfo Seminar (2017)

raster
raster
raster
vector

raster
vector
raster
vector

raster
vector
raster
vector


raster
vector


raster
vector


Right software for the right task
RASTER
- Photoshop
- GIMP
Vector
- Illustrator
- Inkscape
Raster formats
JPG
PNG
GIF
TIFF
JPG

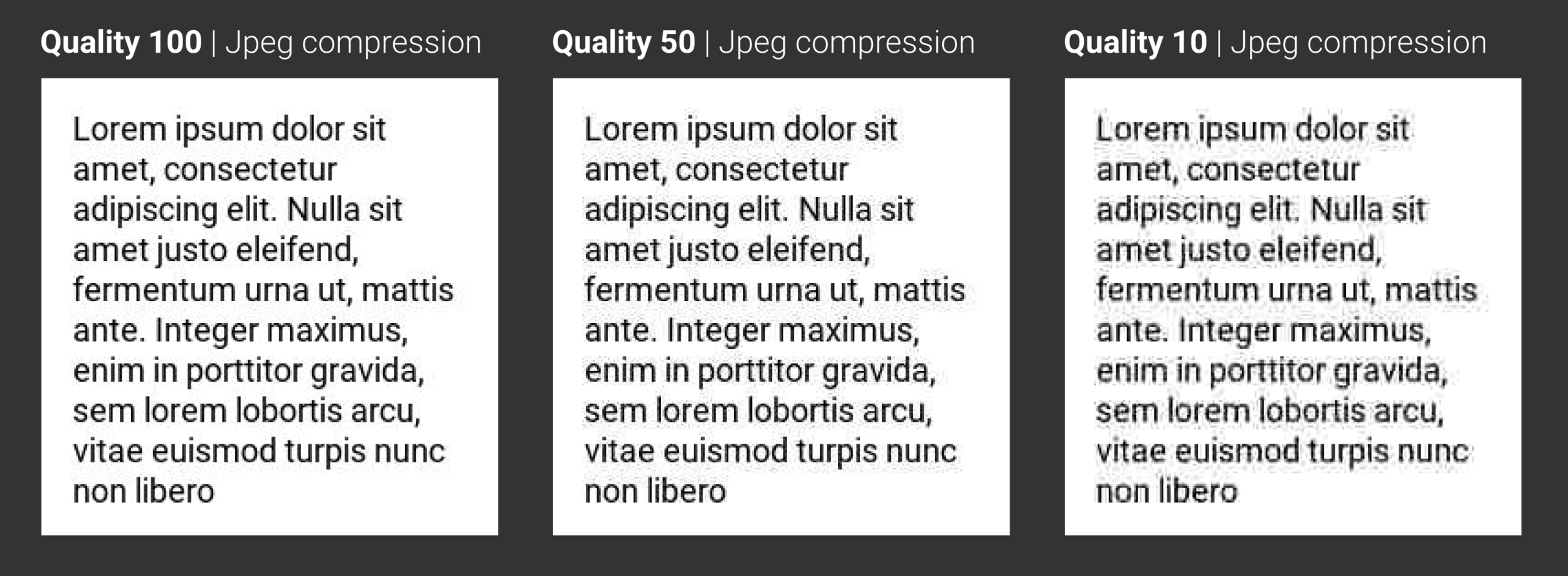
JPEG (/ˈdʒeɪpɛɡ/ jay-peg)[1] is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality.[2]
Colors
R
G
B
JPG images in color are in fact composed of three different images (or channels) one for each of the base colors: red, green and blue
Each channel usually has 8-bit values, meaning that they can range from 0 to 255




LOSSY compression
The format allows compression of the image by reducing quality, using frequency filters on blocks of fixed size

LOSSY compression
The format allows compression of the image by reducing quality, using frequency filters on blocks of fixed size

LOSSY compression
The format allows compression of the image by reducing quality, using frequency filters on blocks of fixed size

LOSSY compression
The format allows compression of the image by reducing quality, using frequency filters on blocks of fixed size

LOSSY compression
The format allows compression of the image by reducing quality, using frequency filters on blocks of fixed size

JPG | Quality 100
JPG | Quality 25
1024x1024 px (1.5 MB)
1024x1024 px (0.13 MB)




JPG | Quality 100
JPG | Quality 25
200x200 px (106 kB)
200x200 px (52 kB)
JPG | Quality 100
JPG | Quality 25
250x250 px (26.2 kB)
250x250 px (4.4 kB)



PNG

Portable Network Graphics (PNG /ˈpɪŋ/[2][3]) is a raster graphics file format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was created as an improved, non-patented replacement for Graphics Interchange Format (GIF), and is the most widely used lossless image compression format on the Internet.[4]
Colors
Colors are kept the same way as on JPG files, but on extra channel, usually called alpha, for transparency



+
=

PNG USES LOSSLESS COMPRESSION
This means that the file size is reduced, but without quality loss


JPG Quality 100 (26.2 kB)
PNG (7.9 kB)

PNG - 1024x1024 px (1.7 MB)

JPG Q100 - 1024x1024 px (1.5 MB)
GIF

The Graphics Interchange Format (better known by its acronym GIF /ˈdʒɪf/ jif or /ˈɡɪf/ ghif) is a bitmap image format that was developed by US-based software writer Steve Wilhite while working at the internet service provider CompuServe in 1987[1] and has since come into widespread usage on the World Wide Web due to its wide support and portability.
Colors
Instead of channels, GIFs use an indexed color system. It supports a maximum of 256 colors !


JPG Q100 - 1024x1024 px (1.5 MB)
GIF - 1024x1024 px (0.54 MB)


JPG
GIF
TIFF

Tagged Image File Format, abbreviated TIFF or TIF, is a computer file format for storing raster graphics images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry,[1] and photographers. The TIFF format is widely supported by image-manipulation applications, by publishing and page layout applications, and by scanning, faxing, word processing, optical character recognition and other applications.[2]
PREcise & versatile
-
Multi-page file
-
Meatadata on the file
-
Lossless compression (or no compression at all)
-
Higher bit-rates (up to 32 bit)
MULTIPAGE FILES
other
formats
...
...
Metadata on the file
BitsPerPixel = 16
DimensionOrder = XYCZT
IsInterleaved = false
IsRGB = false
LittleEndian = true
PixelType = uint16
Series 0 Name = CSU561/CSU491
SizeC = 2
SizeT = 400
SizeX = 256
SizeY = 512
SizeZ = 45
Binning = 1
BitsPerSample = 16
CalibrationUnits = um
CameraBin = 1x1
Channel #0 _IllumSetting_ = CSU561
Channel #0 _MagSetting_ = Pixel
Channel #1 _IllumSetting_ = CSU561
Channel #1 _MagSetting_ = Pixel
Lossless compression
(or no compression at all)

JPG Q100 - 1024x1024 px (1.5 MB)

TIFF RGB - 1024x1024 px (3.2 MB)
HIGHER BIT RATES
8 bit → 0 to 255
16 bit→ 0 to 65535
32 bit float→ -3.4E+38 to +3.4E+38
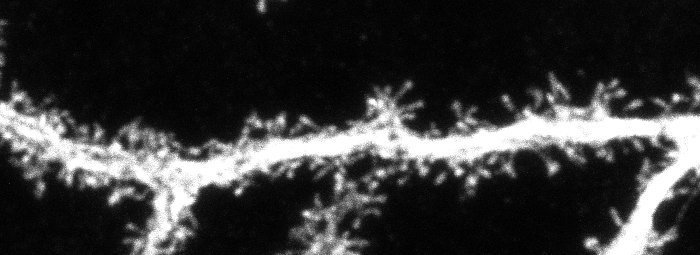
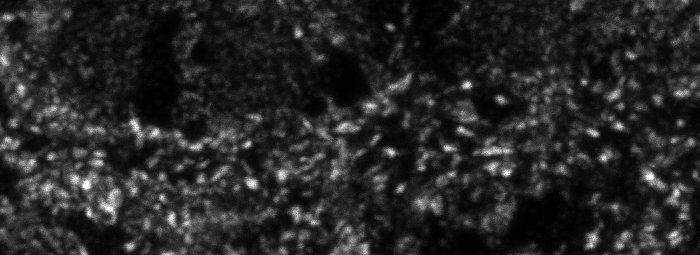
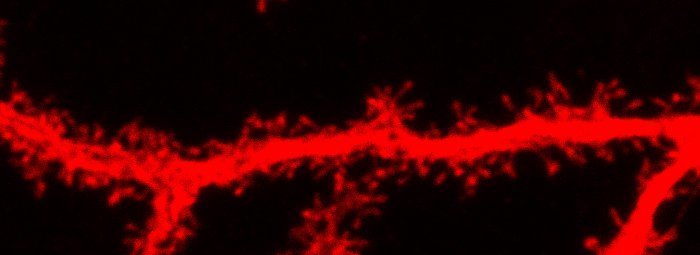
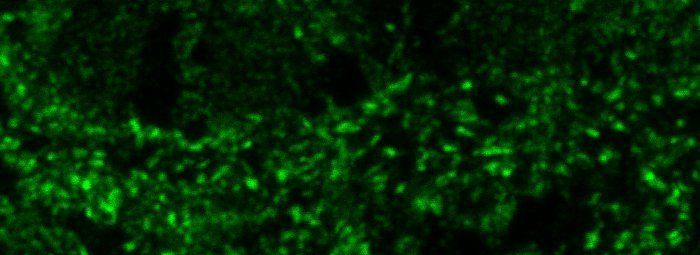





Tiff file with 2 pages
RGB output


RASTER SUMMARY
-
JPG
Photography or big images, where the accuracy is not important -
PNG
Images with higher quality, or when transparency is needed -
GIF
Short animations -
TIFF
Data analysis
Vector formats
SVG
EPS
AI



Every vector format supports EMBEDDED raster images


one single file
You can always export an vector file as raster, and for compatibility sometimes this is a good idea
Just remember to export in a high resolution/DPI !
The differences between vectorial file formats are more related to the editing capabilities of the software than to the final result itself






basic vector capabilities
AI

Adobe Illustrator Artwork (AI) is a proprietary file format developed by Adobe Systems for representing single-page vector-based drawings in either the EPS or PDF formats. The .ai filename extension is used by Adobe Illustrator.

eps

Encapsulated PostScript (EPS) is a DSC-conforming PostScript document with additional restrictions which is intended to be usable as a graphics file format. In other words, EPS files are more-or-less self-contained, reasonably predictable PostScript documents that describe an image or drawing and can be placed within another PostScript document.
SVG

Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an XML-based vector image format for two-dimensional graphics with support for interactivity and animation. The SVG specification is an open standard developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) since 1999. SVG images and their behaviors are defined in XML text files. This means that they can be searched, indexed, scripted, and compressed.
SVG format allows animations and interactivity

The Portable Document Format (commonly referred to as PDF) is a file format used to present documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems.[2] Each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a fixed-layout flat document, including the text, fonts, graphics, and other information needed to display it.
VECTOR SUMMARY
-
AI
Adobe Illustrator only. Not possible even to visualize correctly outsite the software -
EPS
Compatibility mode vector file, mostly used before PDF was a standard -
SVG
Versatile and open format. Editable using open software and widely used over the web -
PDF
Solution for visualising files across platforms. Limited editing capabilities
Now that we now all this, how can we extract figures from papers with the highest possible quality ?
tip: it is not using print screen
