Crowdsourced
profiling and testing
presented by Giorgio Natili
Mobile tea #4
Rome, 22 may 2013
Title
about me

e-mail: g.natili@gnstudio.com
twitter: @giorgionatili
blog: webplatform.io (coming soon!)
community: codeinvaders.net
Agenda
- Crowdsource testing:
- how it works
- pro and cons
- Apps testing and profiling:
- Types of testing
- Profiling
- Key challenges
- Overview of the crowdsource testing platforms
- Workflow integration
Crowdsourcing
- The practice of obtaining needed services, ideas, or content by soliciting contributions from a large group of people (i.e. the crowd)
- Obtain great results with a small effort by a a group of individuals
- Crowdsourcing is an online, distributed problem-solving and production model
Types of crowdsourcing
- Crowdvoting
- Crowdsourcing creative work
- Crowdsearching
- Crowdfunding
- Crowdsource testing
- Many others...
the landscape
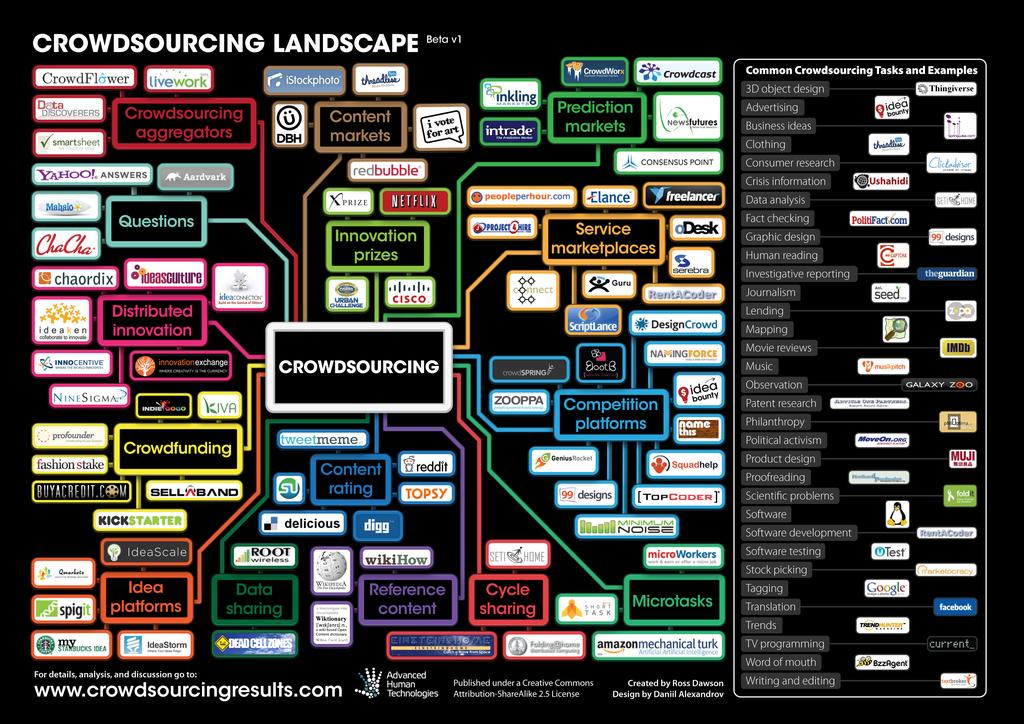
crowdsourced testing
or for brevity
crowdtesting
THE CROWD

Crowdtesting
- A way of testing software based upon crowdsourcing
- The tests are executed by testers from different countries
- Testers are not hired as consultants
- Most of the testing platforms are clouds based
- Testers are usually paid per verified bug
- Tests are executed on real platforms and are more reliable
how it works
- There are three main actors working together in a crowdtesting environment:
- A test platform
- Testers
- Companies
- There are several activities to perform:
- Select the right testers
- Profile the testing platforms
- Write meaningful tests
- Get consistent feedback
Advantages
- The tests are executed on a great number of platforms
- The tests are reliable because executed on real devices
- It's a low costs solution because tests are paid per bug
- Testers are not influenced by any company concerns
- Tests include languages and locales
- Tests can be executed faster
variety of in-context data
Users are ready 24/7 all around the world to test:
- Network density
- App response on specific devices
- Different battery states on the device
- Different types of network (Wi-Fi, 4G, etc.)
human errors
- Software testing is not an exact science. Like programming, it is subject to human error
- By working with a greater number of testers, you are effectively diminishing the likelihood that your software testing team may miss an important issue during the testing period
Disadvantages
- The confidentiality of the project is compromised due to the usage of external resources
- Communication can be difficult due to the crowdsourcing itself
- Due to the usual business model testers should find easily low impact bugs rather than critical ones (usually more complex to find)
- Management and planning is not easy
outsource testing
- Outsourced testers belong to the same organization
- There is a company responsible for the quality of testing
- Testers are paid for their job also if they don't find bugs
apps
testing + profiling
Metrics matter

apps testing
- No one really wants to do it! It's time consuming, expensive and it's boring!
- The goal of testing efforts is not to find errors instead should be to understand the quality of the app
- It's a process that should be parallel to development
- Can be done through emulators, services but over all using physical devices
functional testing
- Functional testing ensures that the application is working as per the requirements
- Most of the test conducted for this is driven by the user interface and call flows
- Have to be defined upon the software requirements
- Should be automated as much as possible
- Should help to create a test suite classified as regression tests
Usability testing
- Carried out to verify if the app is achieving its goals and getting a favorable response from users
- How much steps are required to complete tasks
- How does the person feel about the tasks completed
- How much does the user remember afterwards or after periods of non-use
- It's not a way to gather opinions on an app
interrupt testing
- Incoming and outgoing SMS and MMS
- Incoming and outgoing calls
- Incoming notifications
- Battery Removal
- Cable insertion and removal for data transfer
- Network outage and recovery
screen resolutions
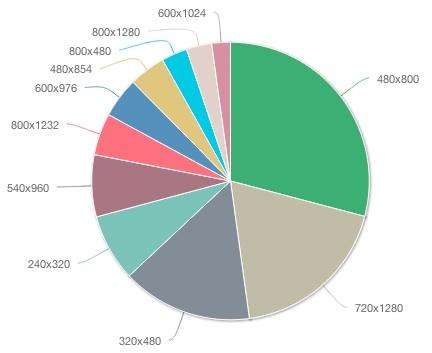
apps profiling
- Performance is a concern for all but the simplest of applications
- Making apps perform well seems a simple enough ask, but it can be something of a black art
- Profiling an app allows to glean valuable metrics, such as memory usage of a given object and execution times of specific methods,
- Through the analysis of these metrics it's possible to improve apps performances
Performances
- Determine how a system performs in terms of responsiveness and stability
- Check the performance and behavior of the app in normal conditions and particular ones (low battery, bad network, etc.)
- Understand the upper limits of capacity of an app within the system (Stress testing)
memory leaks
- Memory leakage happens when an app is unable to manage the memory it is allocated
- The best result is poor performance of the app and the overall slowdown of the system
- As mobile devices have significant constraints of available memory, memory leakage testing is crucial for the proper functioning of an application
challenges
- Variety of Mobile Devices, input methods and hardware capabilities
- Diversity in Mobile Platforms/OS
- Mobile network operators- There are over 400 mobile network operators in the world
- The variety of devices makes executing the test script (Scripting) a key challenge
crowdtesting
platforms
overview
utest
Web site http://www.utest.com
- Supported kinds of apps:
- Web
- Desktop
- Mobile
-
Supported testing types:
- Functional Testing
- Security Testing
- Load Testing
- Localization testing
- Usability Testing
utest
-
Pros:
- Integrated with bugzilla, google code, mantis, redmine, rally, etc.
- Good user interface to manage projects and test cases
-
Cons:
- Unusable web site
- High prices not clearly reported (anyway here the wizards you may be interested to http://www.utest.com/wizard-usability/, http://www.utest.com/wizard-localization/, etc.)
passbrains
Web site http://www.passbrains.com
- Supported kinds of apps:
- Mobile
- Web
- Enterprise (WAT!)
-
Supported testing types:
- Functional Testing
- Security Testing
- Compatibility Testing
- Localization testing
- Usability Testing
passbrains
-
Pros:
- You can be a customer and a tester with the same account
- Customers are supported when defining needs and goals
- Fixed (and reasonable) prices
-
Cons:
- No integration with third party tools
- You need a couple of days to start your test project
99tests
Web site http://www.99tests.com
- Supported kinds of apps:
- Web
- Mobile
- Tablets
-
Supported testing types:
- Functional Testing
- Security Testing
- Performance Testing
99tests
-
Pros:
- Registration process and profile update is easy
- Customers create test cases as contest
- Fixed and transparent prices
-
Cons:
- No integration with third party tools
pay4bugs
Web site http://www.pay4bugs.com
- Supported kinds of apps (iOS only):
- Web
- Native
-
Supported testing types:
- Functional Testing
- Security Testing
- Performance Testing
pay4bugs
-
Pros:
- Registration process and profile update is easy
- Customers can specify a price per bug
- Testers can join projects arbitrarily
-
Cons:
- The total cost is made up by a monthly subscription plus a fee per bug
- No integration with third party tools
applover
Web site http://applover.me
- Supported kinds of apps (Android only):
- Native
-
Supported testing types: (user driven)
- Functional Testing
- Security Testing
- Performance Testing
applover
-
Pros:
- It's a community, there is no cost
- Testers do tests because are passionate
-
Cons:
- There is no way to be sure about the quality of tests
- Tests cannot have a time range
- No integration with third party tools
FeedbackArmy
Web site http://feedbackarmy.com
- Supported kinds of apps:
- Web
- Mobile
- Desktop
- Even more... (WAT!)
-
Supported testing types:
- Functional Testing
- Security Testing
- Load Testing
- Even more... (WAT!)
Feedbackarmy
-
Pros:
- It's a community, there is no cost
- Testers do tests because are passionate
-
Cons:
- There is no way to be sure about the quality of tests
- Tests cannot have a time range
- No integration with third party tools
Workflow integration
building blocks
- Phabricator www.phabricator.org
- GitHub www.github.com
- Mechanical Turk www.mturk.com
- Arcanist http://goo.gl/qTLC0
Developer flow (1/3)
- Pick up a task from Phabricator
- Create a new branch using the task id in the name (e.g. git branch feature-ID) and move to it (e.g. git branch checkout feature-ID)
- Work on it and add or remove the files to the new commit using the commands git add or git del filename
- Commit the changes to current branch using the command git commit -a -m ‘your commit message’
developer flow (2/3)
- Run the command
arc diff
and fill the information required
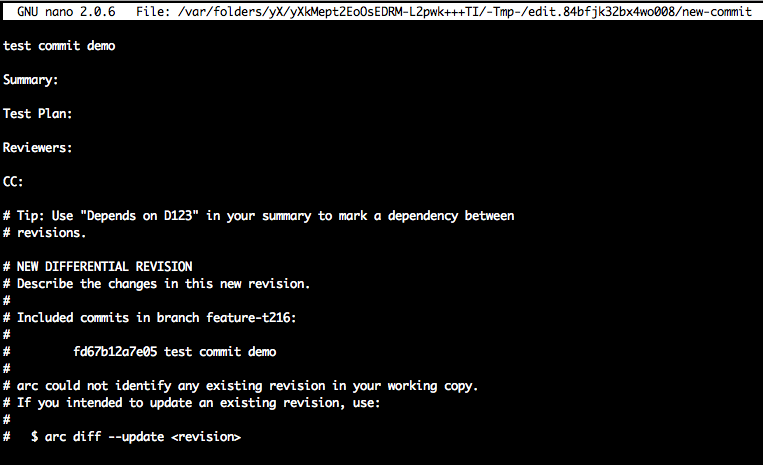
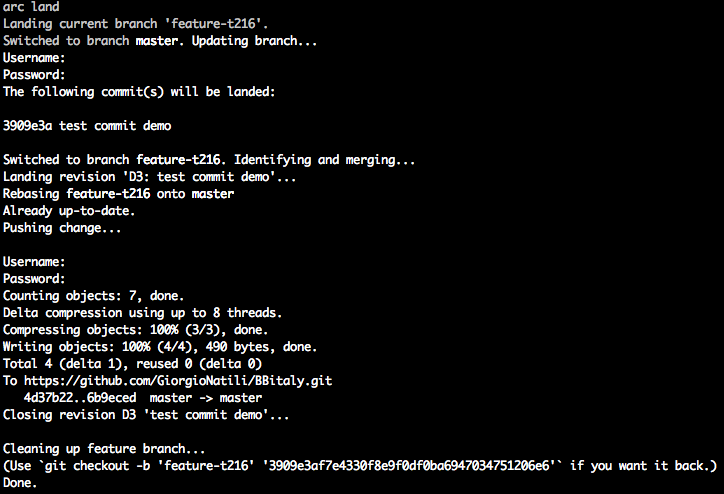
developer flow (3/3)
- Wait the review is performed and eventually make the changes to the code
- Run the command
arc land
once the review has been accepted
system workflow
- On each review submitted Phabricator eventually runs tests and do a build using Jenkins
- Potential error handling (review workflow)
- A weekly build is deployed using the last working Jenkins build (mturk)
drawbacks
- It's not user friendly
- It's a set of scripts that will be released open source at the end of July 2013
- It requires coding and system administration competencies
-
It requires developers are able to use the command line tool
THANKS!
e-mail: g.natili@gnstudio.com
twitter: @giorgionatili