A monad is just a monoid in the category of endofunctors.
what's the problem ?
I know some
of these words
Category theory
Category theory is used to formalize mathematics and its concepts as a collection of objects and arrows (also called morphisms). Category theory can be used to formalize concepts of other high-level abstractions such as set theory, field theory, and group theory.
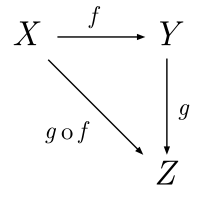
category theory
Several terms used in category theory, including the term "morphism", differ from their uses within mathematics itself.
In category theory, a "morphism" obeys a set of conditions specific to category theory itself. Thus, care must be taken to understand the context in which statements are made.
WTF is a category ??
In mathematics, a category is an algebraic structure that comprises "objects" that are linked by "arrows".

That'd be great
YEAAAH, IF YOU COULD ACTUALLY DEFINE WHAT THIS IS ABOUT.
wtf is a morphism ??
In many fields of mathematics, morphism refers to a structure-preserving mapping from one mathematical structure to another.
In set theory, morphisms are functions; in linear algebra, linear transformations; in group theory, group homomorphisms; in topology, continuous functions, and so on.
In category theory, morphism is a broadly similar idea, but somewhat more abstract: the mathematical objects involved need not be sets, and the relationship between them may be something more general than a map.
Type system
a type is a classification identifying one of various types of data,that determines the possible values for that type; the operations that can be done on values of that type [...]
functions
a function is a relation between a set of inputs and a set of permissible outputs with the property that each input is related to exactly one output.
function
val id = (x: Int) => xval sqrt = (x: Int) => x * xval random = () => scala.util.Random.nextIntval const = (x: Int) => 42
A monad is just a monoid in the category of endofunctors.
what's the problem ?
FUNCTOR
A functor is a type of mapping between categories, which is applied in category theory. Functors can be thought of as homomorphisms between categories. In the category of small categories, functors can be thought of more generally as morphisms.
functor
let's implement that!
endofunctor
Endofunctor: A functor that maps a category to itself.
A monad is just a monoid in the category of endofunctors.
what's the problem ?
monoid
a monoid is an algebraic structure with a single associative binary operation and an identity element.
Monoid
LET'S IMPLEMENT THAT!
A monad is just a monoid in the category of endofunctors.
what's the problem ?
MONAD
a monad is an (endo-)functor, together with two natural transformations.
natural transformation provides a way of transforming one functor into another while respecting the internal structure
Monad
LET'S IMPLEMENT THAT!
A monoid is...
-
A set, S
-
An operation, • : S × S -> S
-
An element of S, e : 1 -> S
A monad is...
-
An endofunctor, T : X -> X
-
A natural transformation, μ : T × T -> T,
-
A natural transformation, η : I -> T