Term Paper Guideline
Political Economics I
OSIPP, Osaka University
1 December, 2017
Masa Kudamatsu
1
2
3
4
Term Paper Structure
Research question and its motivation
Conceptual framework
Data
Empirical method
For theory
For empirics
Model
Proposition(s)
Anecdotal evidence
Now I explain each item in detail
with my own papers as examples:
1
Research question and its motivation
Clearly state your research question
Be specific.
Don't ask a question like
"How can we make politicians accountable?" or
"What's the cause and consequence of ...?"
Then explain why this question is important and original
Does it help us understand how to improve people's welfare?
What is the gap in the literature?
1
Research question and its motivation
Clearly state your research question
Then explain why this question is important and original
e.g.
Has democratization in Africa reduced infant mortality?
(NOT "Does democracy improve people's welfare?")
e.g.
Infant mortality in Africa is high: 100 per 1,000 live births
There is no convincing evidence of the impact of democracy on living standards
1
Research question and its motivation
Clearly state your research question
Then explain why this question is important and original
e.g.
e.g.
It's a big mystery why non-democratic China manages to sustain economic growth over several decades
There is very little evidence on political selection in non-democratic countries
Who becomes a top politician in China?
(NOT "What's the political factor for growth in China?")
2
Conceptual framework
For empirics
Set up a simple and stupid model
to derive predictions testable with your data
Or at least verbally explain
why your hypothesis to test can be correct
Key: Avoid introducing variables you don't observe
You may need to consult other disciplines
e.g. Medicine if you're looking at health outcomes
2
Conceptual framework
For empirics
e.g.
The median voter theorem
probabilistic voting model, and
political agency model
all predict democratization induces politicians
to pick policies favored by the poor
In Africa, one such policy is to reduce infant mortality
2
Conceptual framework
For empirics
e.g.
Build a career concern model without moral hazard
to derive a prediction:
Top politicians promote the best-performing officials
among those connected to themselves
(I do not observe Chinese politicians' behavior)
3
Data
For empirics
Data source (who collected the data?)
Sample construction
Which areas?
What period?
Sampling method if it's a survey data
If you drop some observations from the original data, why?
Variables to be used in the analysis
3
Data
For empirics
Data source
Sample construction
Which areas: 28 African countries
What period: 1960-2004
Sampling method: Babies born to a nationally representative sample of women in each country around 2000
Variables to be used in the analysis
Indicator of death within 12 months after birth
Demographic and Health Surveys
3
Data
For empirics
Data source
Sample construction
Which areas: 31 Chinese provinces
What period: 1993-2009
Sampling method: Provincial party secretaries and governors in office with data from China Vitae (check sample selection bias in terms of provincial economic growth rate)
Variables to be used in the analysis
Indicator of promotion to higher positions in Beijing
Indicator of being a former colleague of top politicians
China Vitae (Online database of Chinese politicians' CV)
4
For empirics
Equations to be estimated
Dependent variable
Treatment variable
Controls
Empirical method
Estimation methods
OLS, 2SLS, SUR, Probit, GMM, etc.
How standard errors are calculated
Statistics to be reported in the table
F-test for the equality of coefficients
4
For empirics
Equations to be estimated
Empirical method
Estimation methods
OLS (mother fixed effects estimation)
Standard errors clustered at the country level
Also report p-value from wild cluster bootstrap-t of Cameron et al (2008)
Statistics to be reported in the table
F-test for the equality of \(\gamma_1\) and \(\gamma_2\)
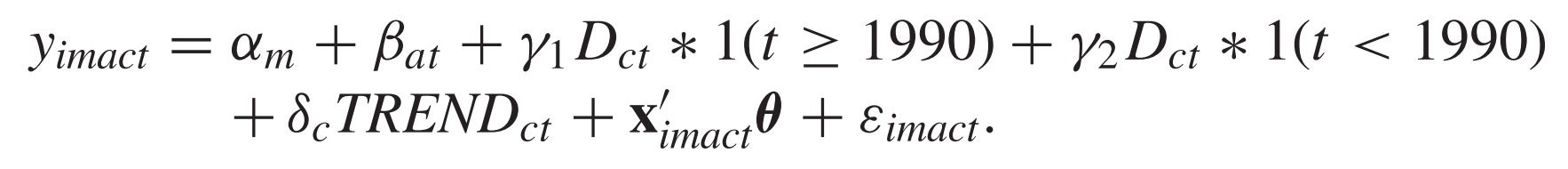
4
For empirics
Equations to be estimated
Empirical method
Estimation methods
OLS (Probit and Logit in the appendix)
Standard errors clustered at the province level
Also report p-value from wild cluster bootstrap-t of Cameron et al (2008)
Statistics to be reported in the table
n.a.
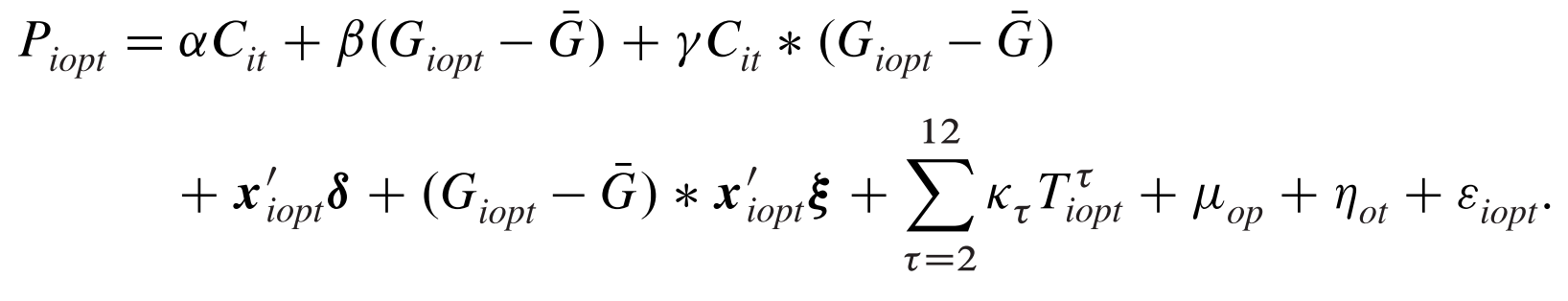
2
Model
For theory
Set up a simple and stupid model
Don't start with a general model
Make it more and more specific
and stop just before you don't get any interesting result
See Varian (1997) for detail
3
Proposition(s)
4
Anecdotal evidence
For theory
Applied theory should be relevant for reality
Find anecdotal evidence consistent with your proposition(s) from
History (e.g. papers written by Acemoglu and Robinson)
Correlations found in empirical papers in economics
(of course, better if it's causal evidence)
Mass media reports
If unavailable, be ready to run a few regressions on your own
Reference
Presentation
Follow this guideline
prepared by LSE faculty members
in the field of development/political economics
This will help you in the future as well
when you present your research at a conference etc.