The Complex Nature of Traits
by Leo Brueggeman
for the Personal Genome Learning Center

Background
a lightning tour of genetics

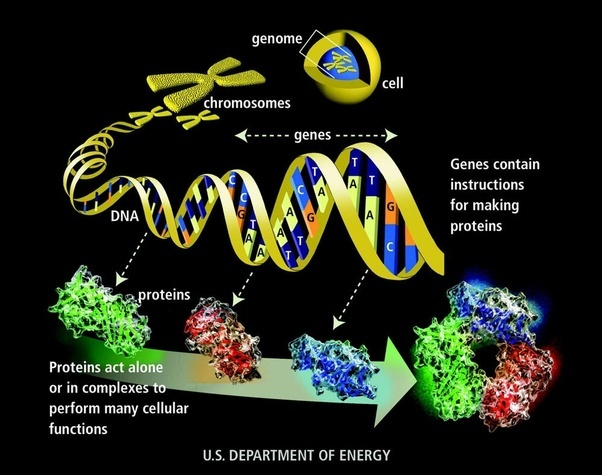
The human genome
- 23 pairs of chromosomes
- 3 billion bases
- 22000 genes
- 1/1350 bases different btw individuals
SNPs
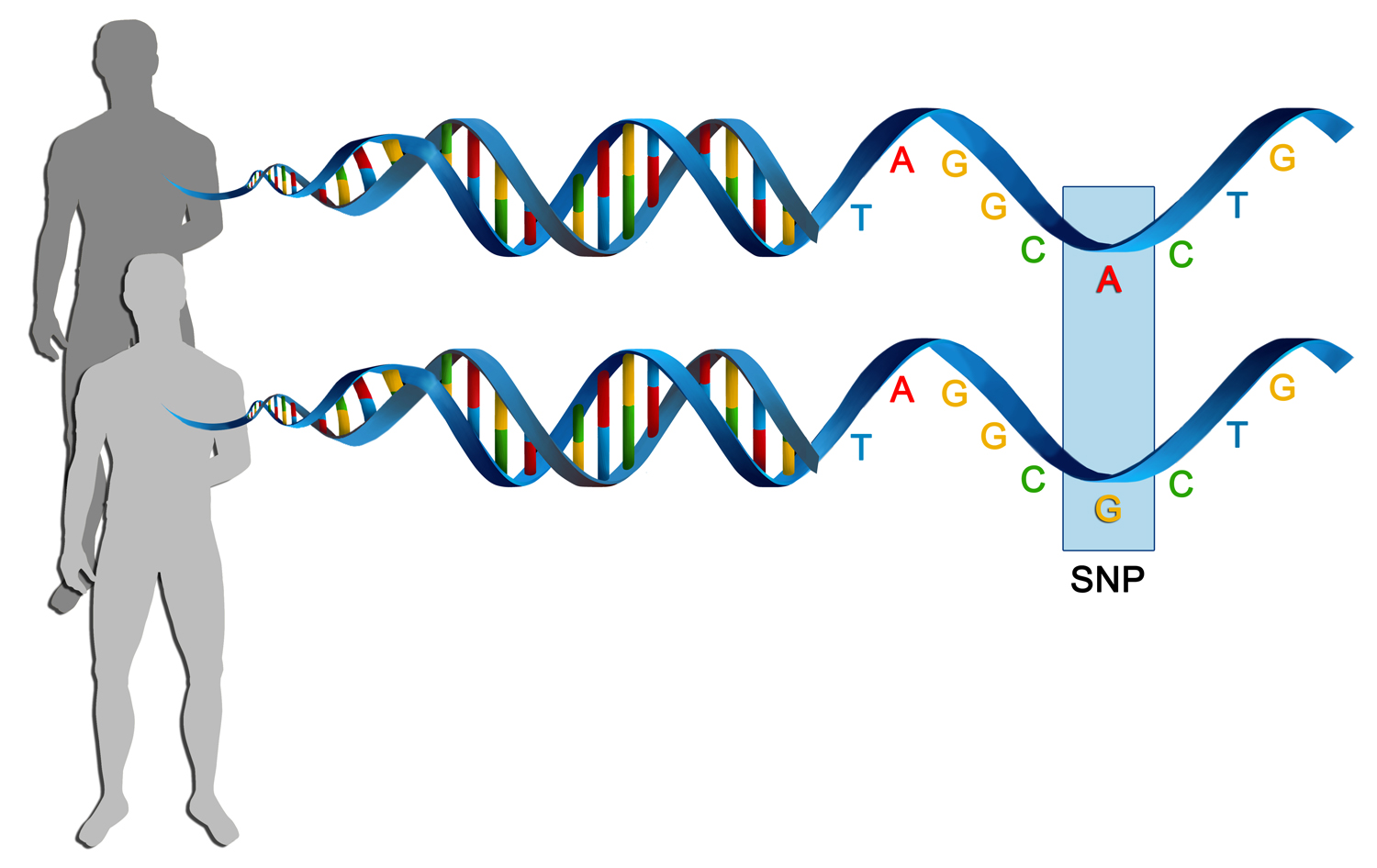
300 million total SNPs (1 every 300 bases)!
SNPs


at Broad Institute
SNPs - traits
height
AA
AG
GG
height
AA
AG
GG
SNPs - disease
AA
AG
GG
Dx
No dx
A
| 6 | 20 |
|---|---|
| 20 | 6 |
G
Dx
No dx
OR = 11.1
Odds Ratio (OR):
20/6
6/20
SNPs - disease
AA
AG
GG
Dx
No dx
OR = 11.1
Prevalence of disease: 2%
Prevalence of disease w/ SNP: 2% * 11.1 = 22.2%
GWAS Era
GWAS everything
GWAS everything

500K people, 4203 traits

1mil people

5mil people
SNPs (outliers)
- Breast cancer:
- OR = 3.6-6.9
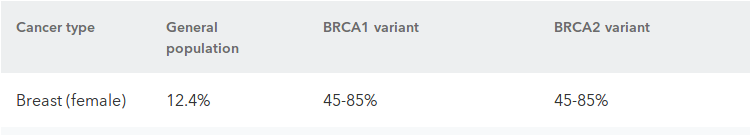
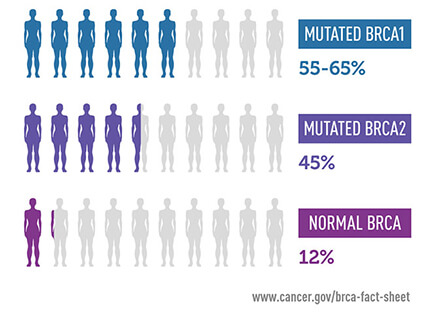

SNPs (outliers)
- Alzheimer's Disease:
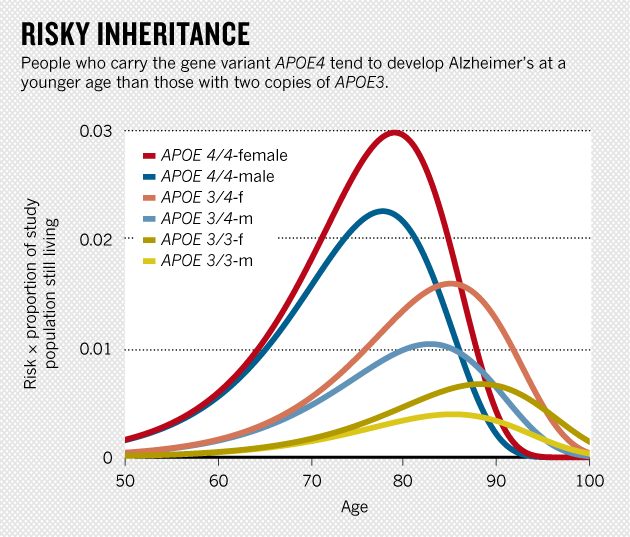
ApoE4 OR:
one copy = 3
two copies = 14.5
10-15% of population
from Scientific American
SNPs (outliers)
- Warfarin processing:
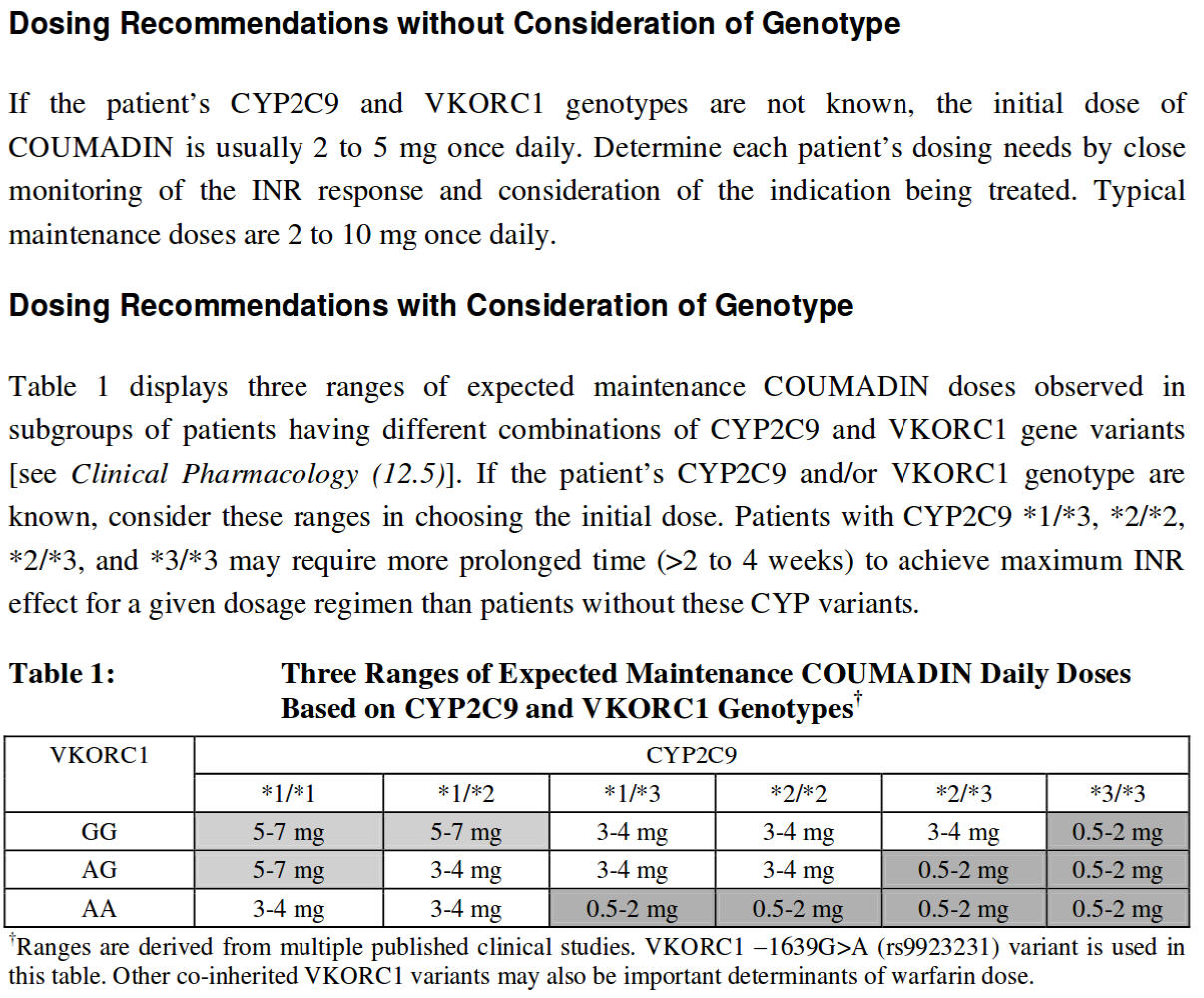
Results (typical)

- Schizophrenia is ~80% genetic
- 37K cases, 113K controls
Results (typical)

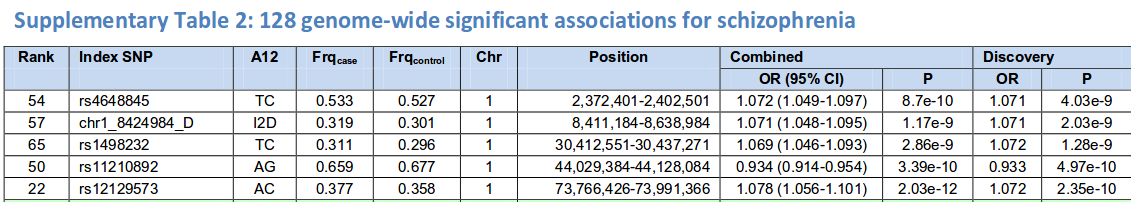
Results (typical)


Results (typical)


Rate of schizophrenia: 0.25% - 0.64%
rate * 1.32 = 0.33% - 0.84%
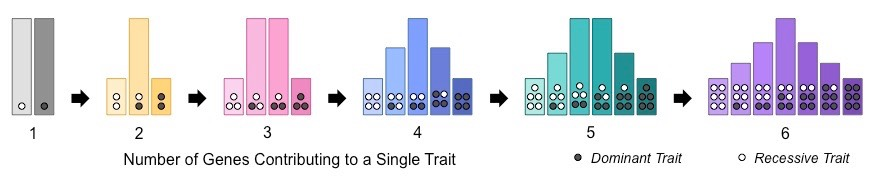
Complex traits
Traits
albinism
wet/dry earwax
lactase persistence
eye color
hair color
height
weight
intelligence
schizophrenia
cancer
Height as a trait
- 60-80% genetic
- 50% from SNPs
- Top SNPs found through GWAS only explain <1% of height variability, individually

Height as a trait
- 60-80% genetic
- 50% from SNPs
- Top SNPs found through GWAS only explain <1% of height variability, individually

Idea:
Look at the effects of multiple SNPs together
Polygenic Risk Scores

To calculate polygenic risk scores, add up ORs for every SNP you have
Assuming I have one of each SNP above, my PRS is 1.07 + 1.07 + 1.07 + .933 + 1.07 = 5.213
Polygenic Risk Scores
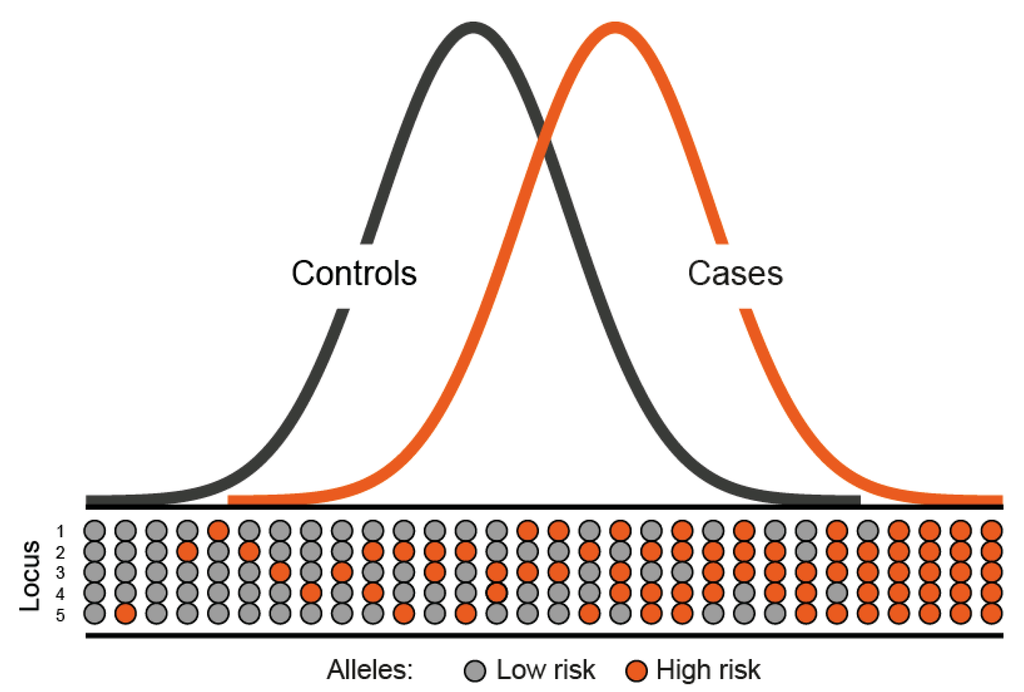
from Whiffin et al
Polygenic Risk Scores

from Whiffin et al
Risk?
80/100 => 80% chance of case-status
80 cases
20 ctls
Height as a trait
- 60-80% genetic
- 50% from SNPs
- Top SNPs found through GWAS only explain <1% of height variability, individually
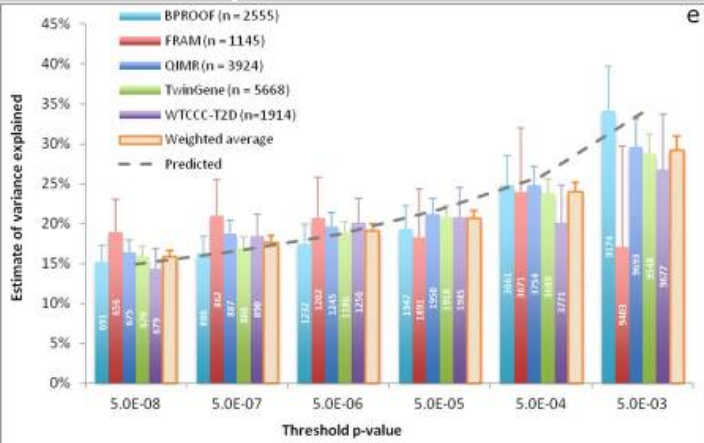
from Wood et al
- Using 10,000 SNPs, a polygenic risk score model explained 30% of height variability
Height as a trait
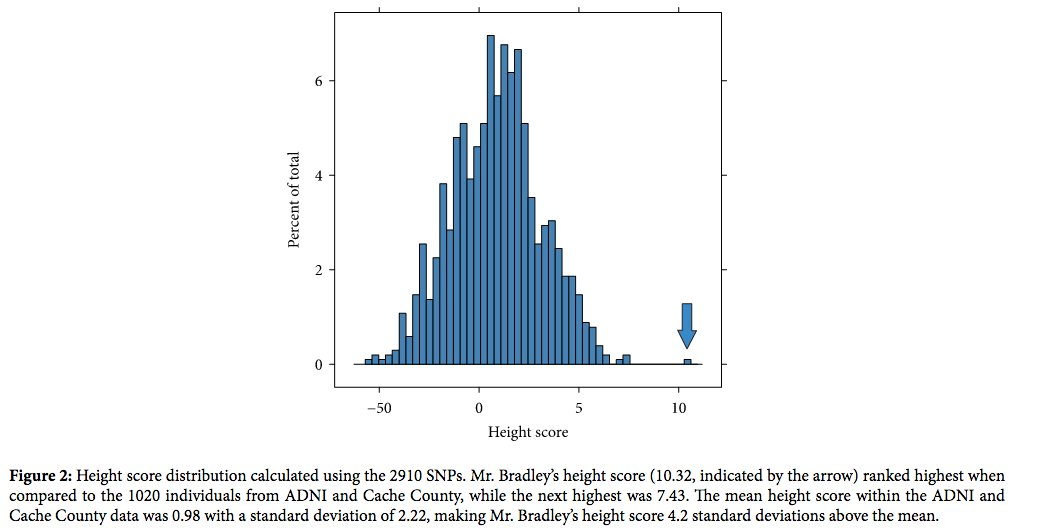

from Sexton et al
Weight as a trait
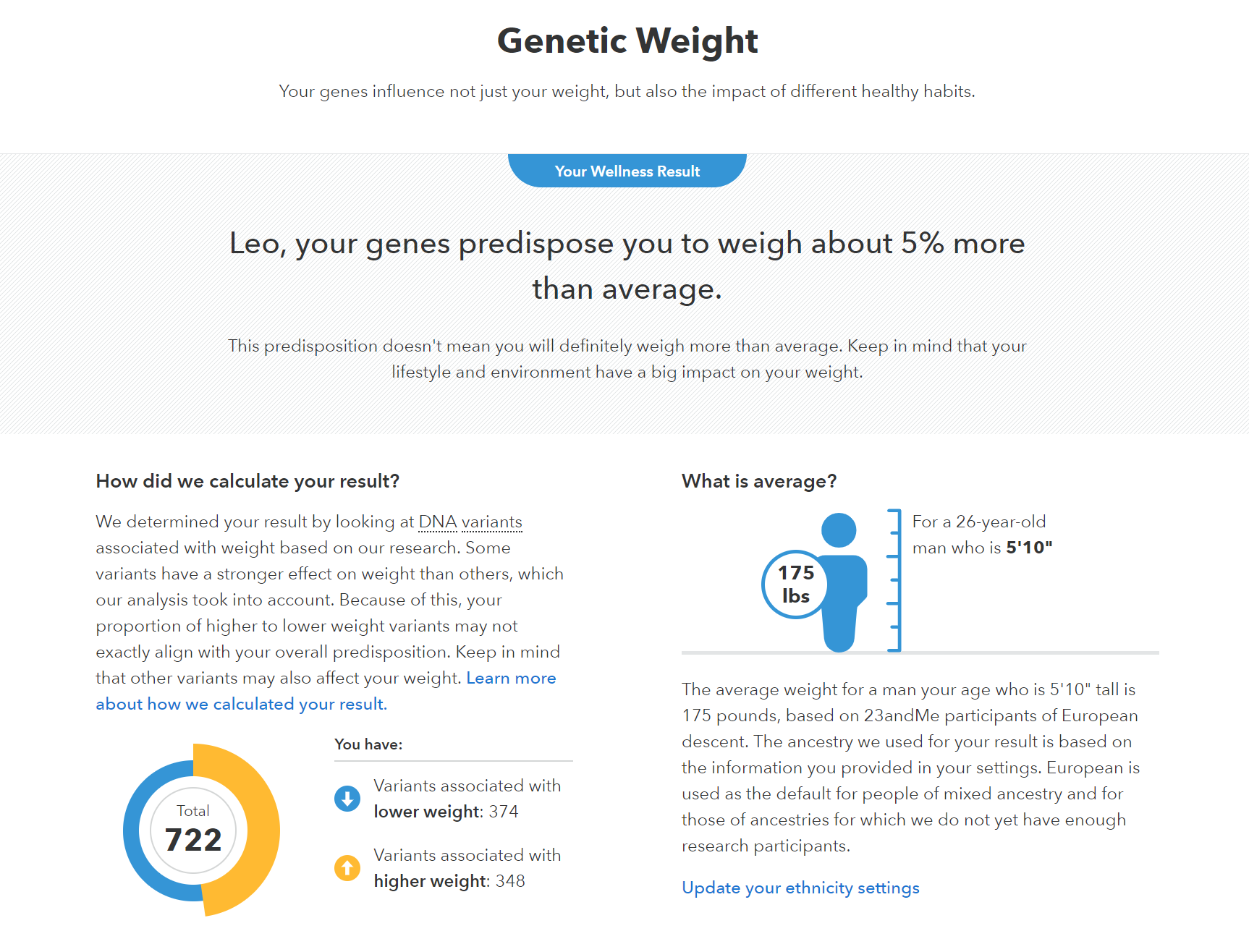

Polygenic Risk Scores
Potential in Medicine
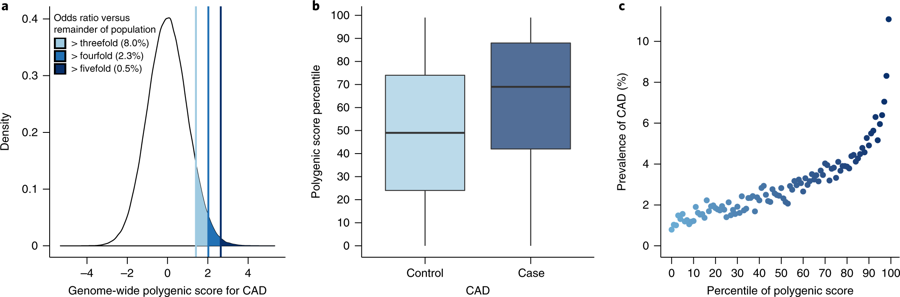
from Khera et al
Coronary artery disease
Potential in Medicine
from Khera et al
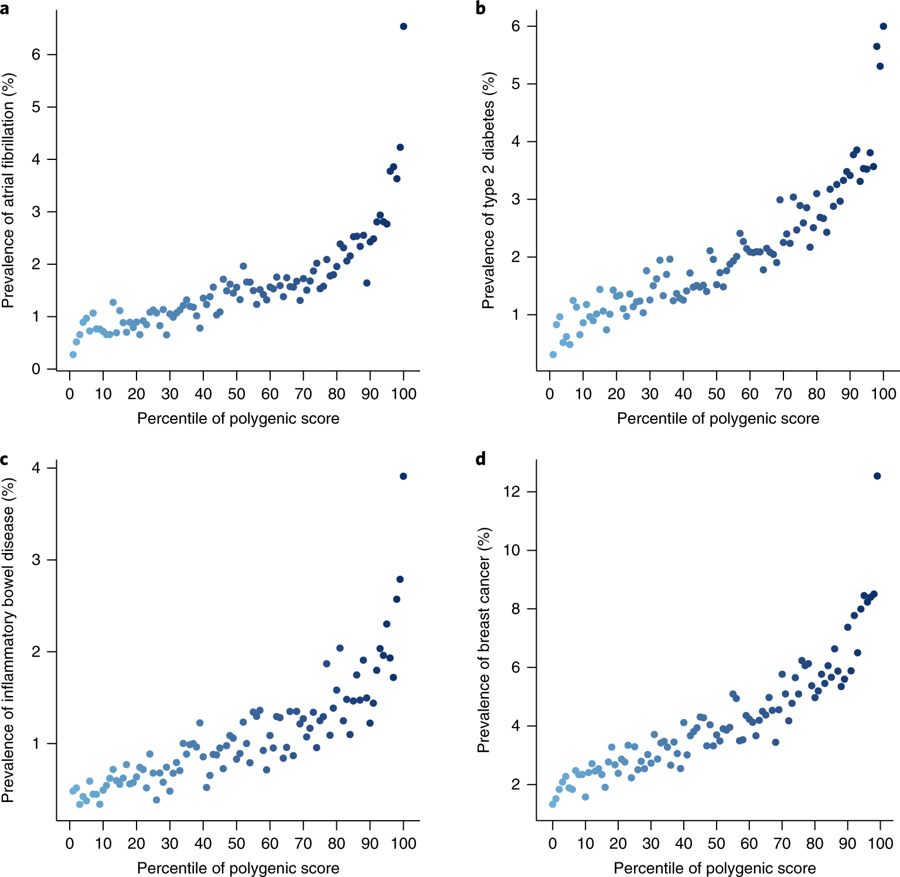
Afib
T2D
B.C.
IBD


PRS for you

PRSs for DTC genetics users

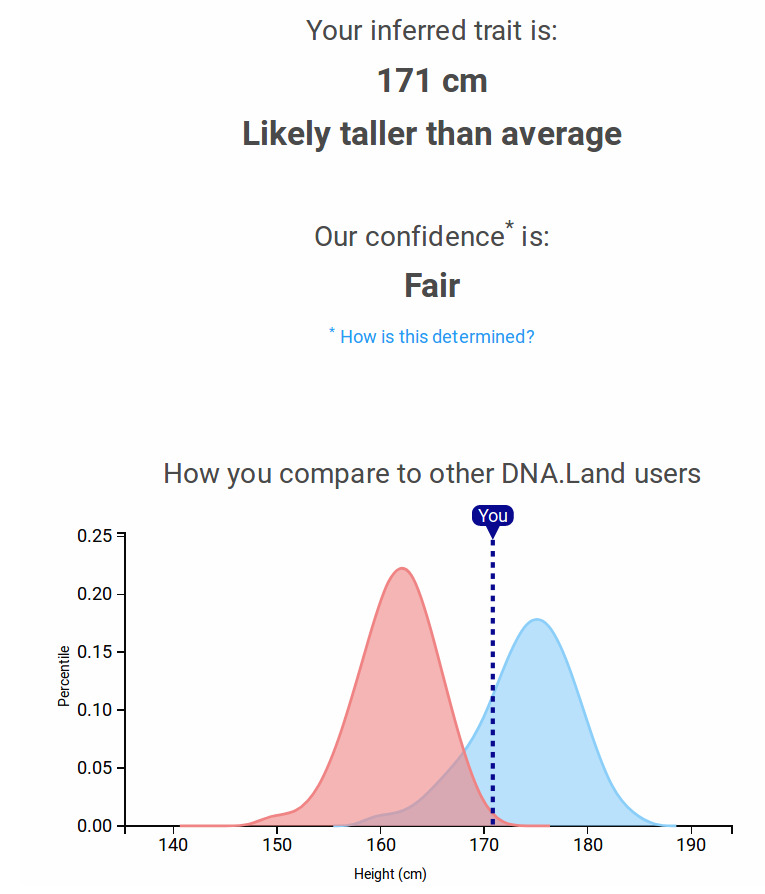
PRSs for DTC genetics users
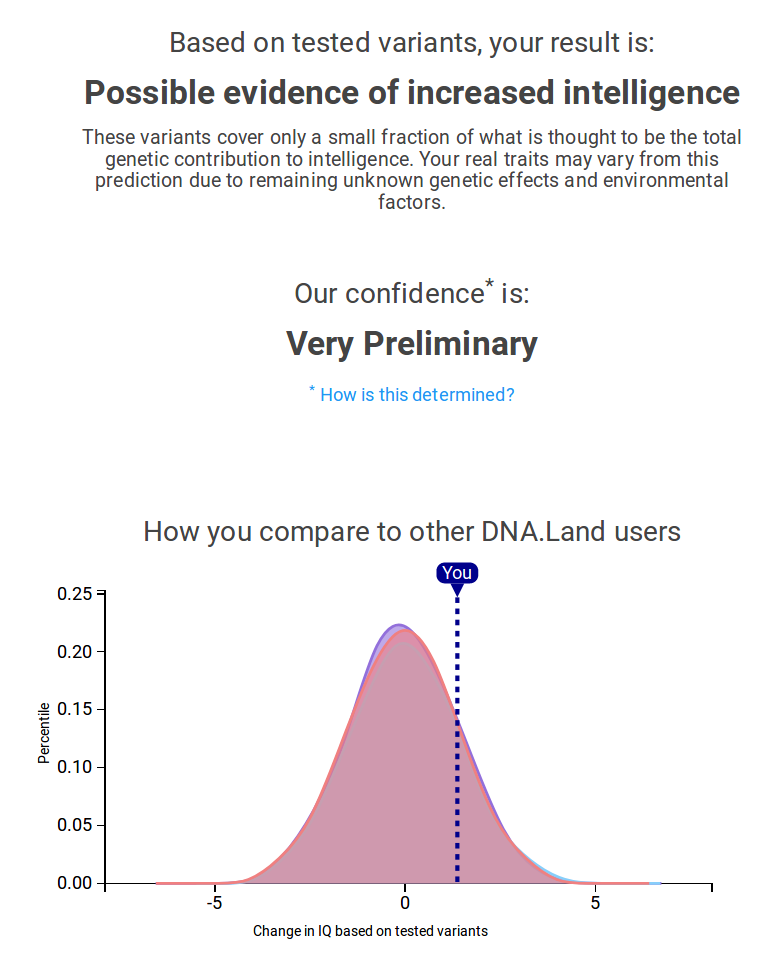

PRSs for DTC genetics users

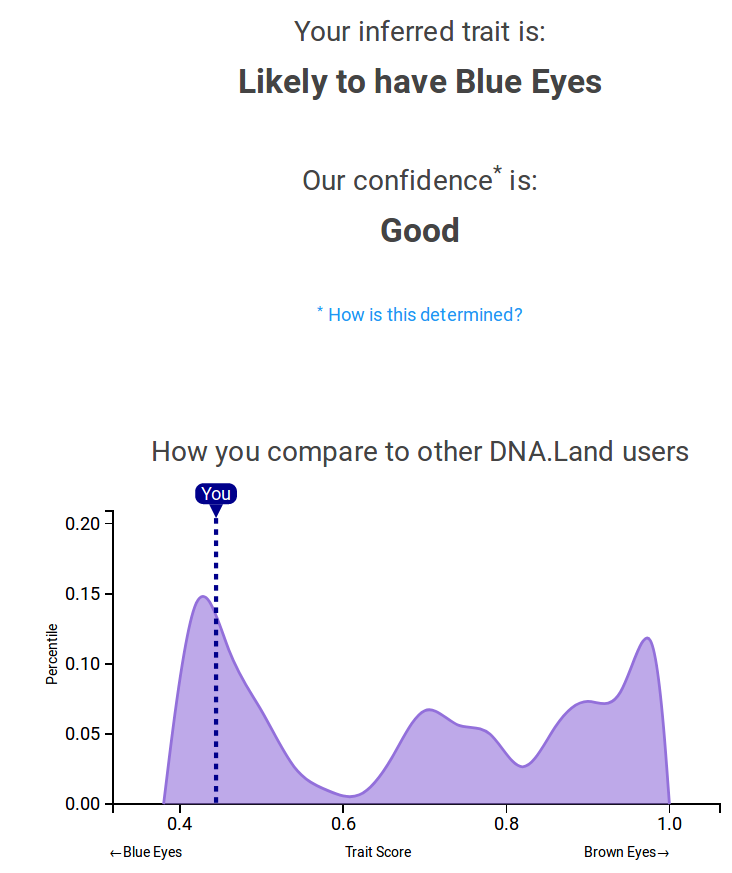
How to interpret



Intelligence:
80% genetic,
~5% of variation explained
Eye color:
100% genetic,
~100% of variation explained
Height:
80% genetic,
~20% of variation explained
"Variation explained"
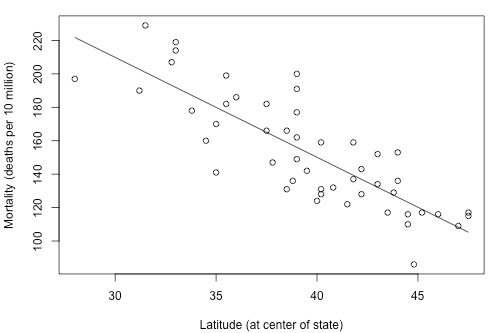
Polygenic Risk Score
Polygenic Risk Score
Brown eyes
Blue eyes
IQ
PRS for personality and psych disorders
History of personality
Sir Francis Galton founded the lexical hypothesis of personality (1884):
Important personality characteristics will eventually become part of language

History of personality
- Gordon Allport and Henry Odbert collected 4,504 adjectives relating to personality (1936)
- Raymond Cattell eliminates synonyms creating 171 terms (1940), found 16 factors
- Reduced to 5 factors by Ernest Tupes and Raymond Christal (1960s)
- In 1980s, Lewis Goldberg and others championed the five-factor model

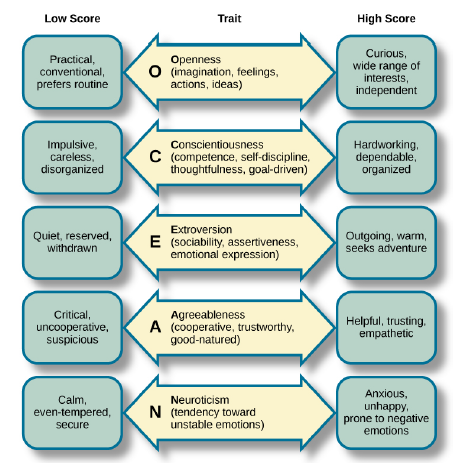
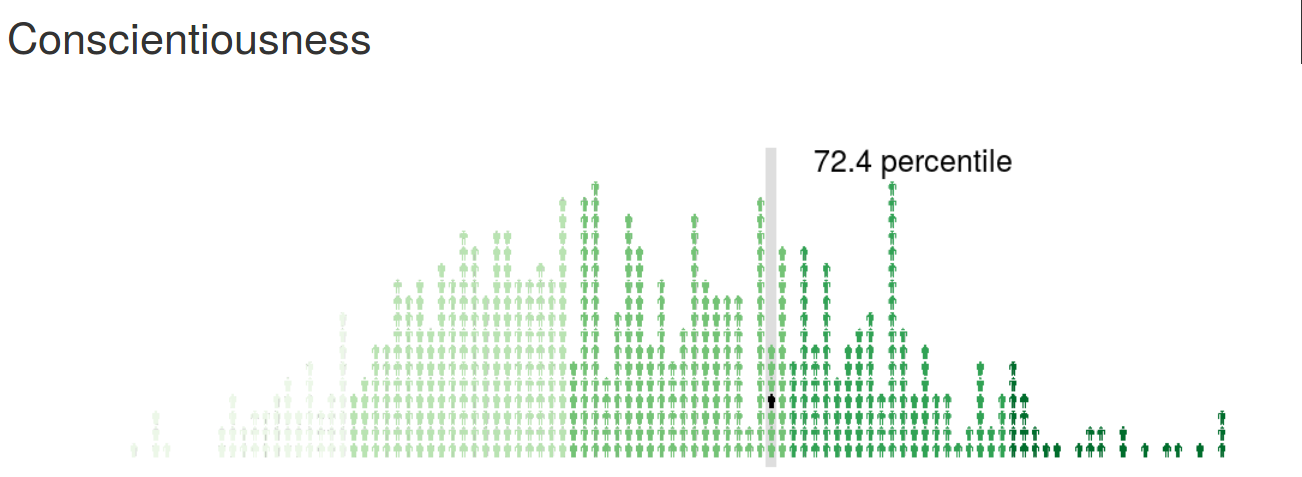
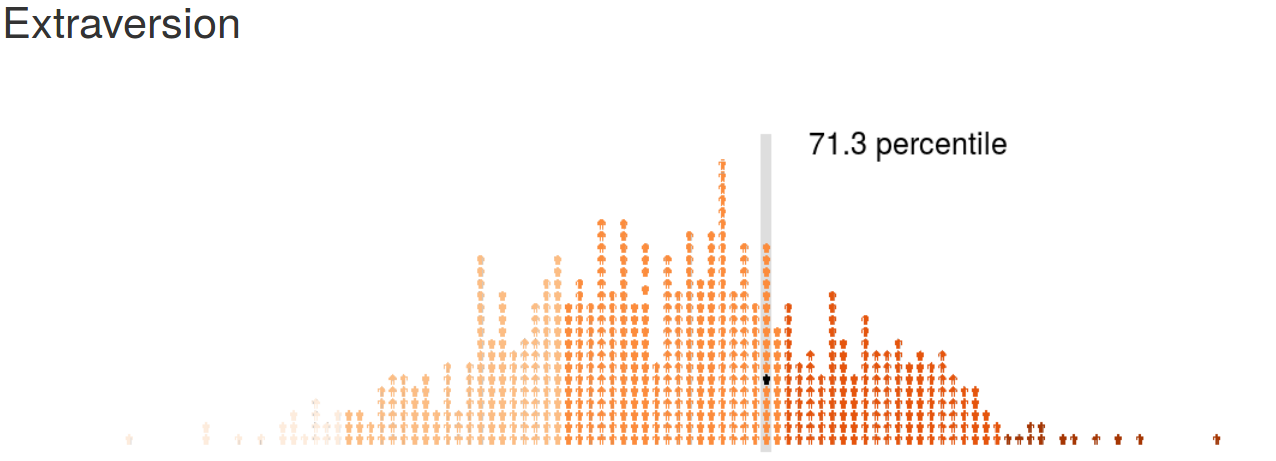
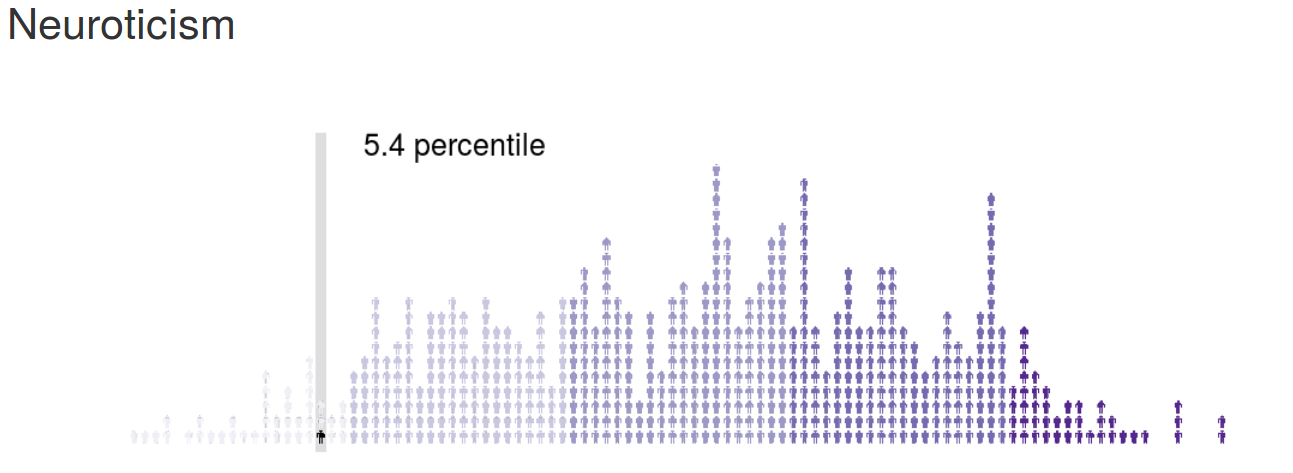
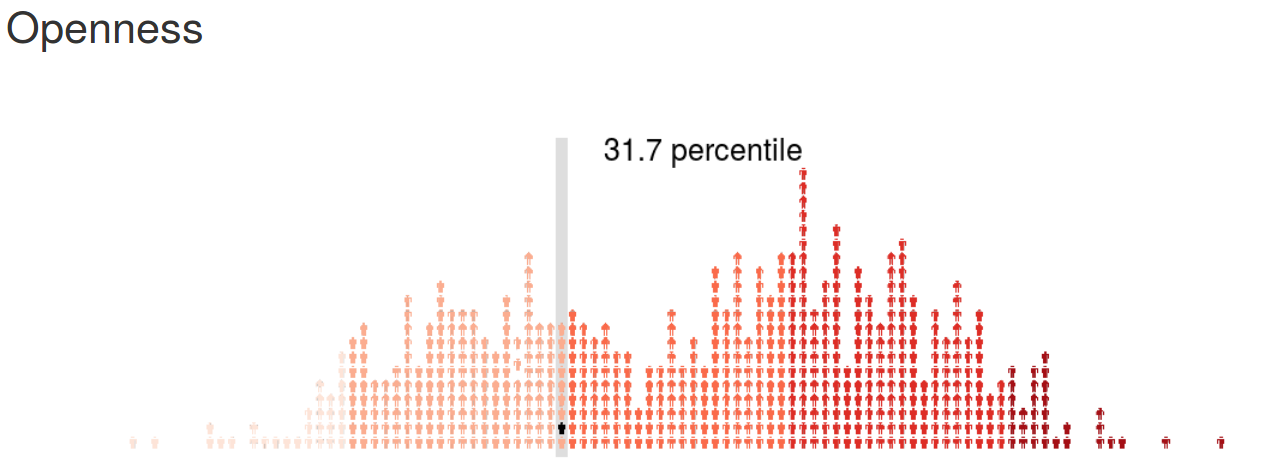
The Big Five
5-10% genetic
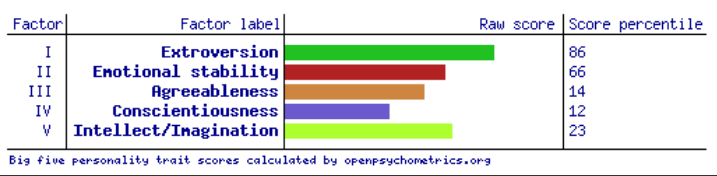
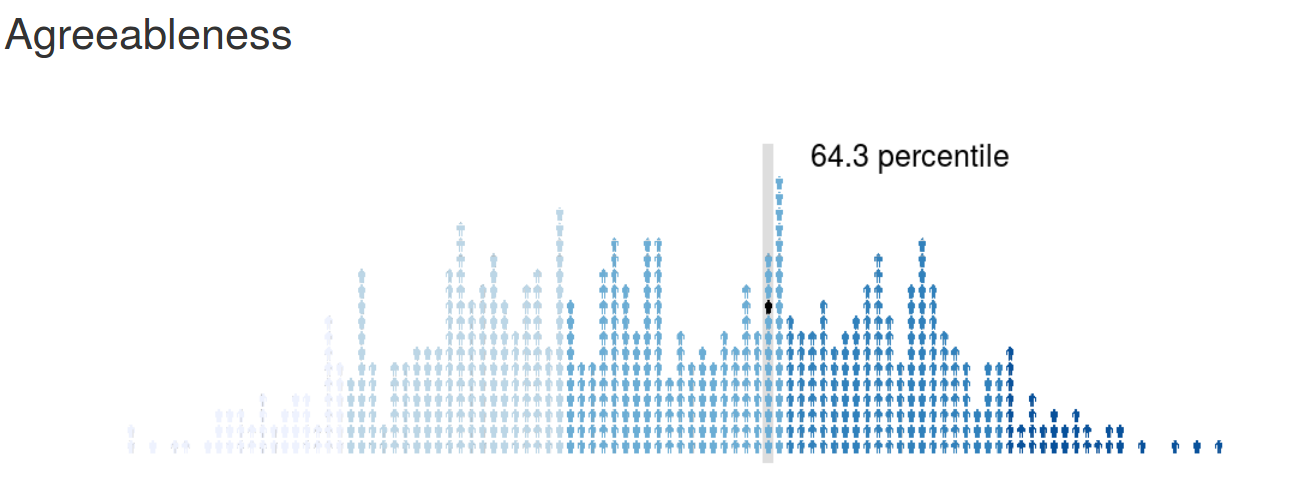
psychRisk
http://leobrueg.shinyapps.io/psychRisk
psychRisk

psychRisk
Additional Resources
DNA.land: dna.land
Impute.me: impute.me
psychRisk: http://leobrueg.shinyapps.io/psychRisk
This presentation: slides.com/leoo/deck-8/
Me: leo-brueggeman@uiowa.edu
@LeoBman
