Future Teachers'
Critical thinking & multi-literacy

Florent Michelot
Le 29 novembre 2019


Beyond Fake News
-
Boy & Michelat (1986): Among professional categories, teachers were among the most open to certain beliefs
- Ede (2000), Genovese (2005): Despite the increasing accessibility to science, paranormal beliefs are still strong
Teachers are not immune...


Boy et Michelat (1986)
Critical thnking definition based on russel
Ability to draw on a wide range of skills, dispositions and attitudes that form an intellectual and moral virtue that allows both the revision of one's own judgments and reject inappropriate assumptions.

A comparative study with 3 French-speaking nations


A comparative study with 3 French-speaking nations
The theorical presupposition of the research

3 tools
-
CritTSE : a scale to measure critical thinking self-efficacy
- Based on Confidence subscale of the CriTT (Stupple & al., 2017)
-
MASE : a scale to measure metaliteracic assessment (i.e. reconceptualisation of information literacy) self-efficacy
- Based on Evaluate information aspects of Metaliteracy Goals & Objectives (Mackey & Jacobson, 2018)
-
CT score : a "measurement" critical thinking test
- Based on a reducted HCTA short version (Halpern, 2016)


self-efficacy seems to have a slight effect
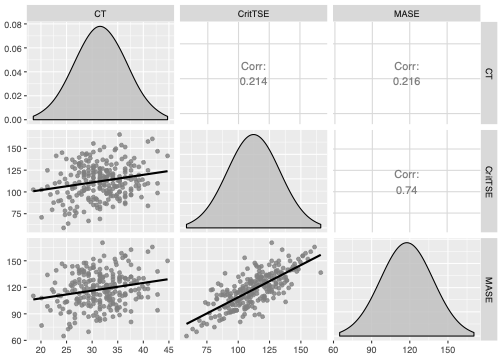
CT
CT self-efficacy
CT self-efficacy
Metaliteracy self-efficacy
However, french-speaking Quebecers self-efficacy is good
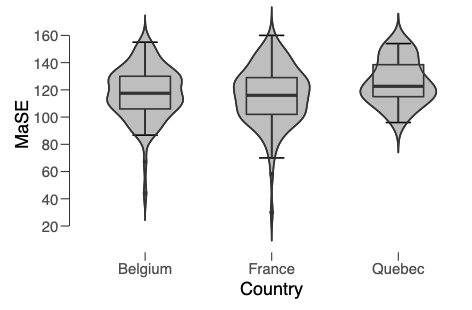
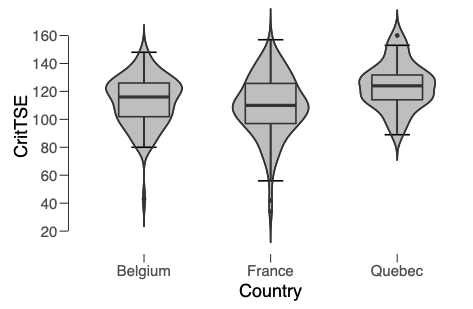
... and the level of critical thinking is affected

By complicating the model...
Critical thinking score can be partially explained with:
- Country (Be, Fr, QC)
- Type of training (professional, disciplinary)
- Self-efficacy
- ... and the anticipation of becoming a teacher
Results
Critical thinking score is particularly influenced:
- positively by self-efficacy
- negatively by professional training
- positively by studying in Qc



other preliminary results
- Perception of Social Media in terms of information quality:
- The perception is much more negative in disciplinary training compared to vocationnal training
- Social Media are universally seen as very useful tools to work / study
- Quebeckers have a positive image of traditional media
- There are doubts: "I tend to trust [...] I often take for granted that they have to check their information before sharing it"
- Many said that evaluating information on the web was easier: "I find it easier to evaluate information on the web because Fake news are more easily identifiable"
Great humility among students
Students seem to have good reflexes:
- cross-checking information
- source evaluation
- search for sophisms: "I remain on the lookout for fallacious reasoning as the argument of the straw man"
and some "know-how"
Is there a deficit in training?

