Plugin development for elasticsearch


Simply explained
by geek & poke
-
Why plugins
-
Getting started with a simple plugin
-
How they fit into Elasticsearch architecture
-
Examples walkthrough
-
Development
-
Testing
-
Distribution
-
-
Limitations
-
Not covered
Why plugins
-
If there is no configuration option for your need
-
If you need unexposed (but public) API
-
To enforce specific behaviour
-
If scripting is simply not enough
-
Site plugin vs JVM Plugin
Here
Plugin == JVM Plugin
-
For example:
-
Creating a new REST endpoint
-
Custom mapping
-
Custom analyzer
-
Transport layer manipulation
-
HTTP layer manipulation
-
Getting started with a simple plugin
-
Plugins are written in Java (1.7+)
-
They live within a node (or transport client)
-
They can access all internals
-
They can make a node stop working (or even worse)
public class MyPlugin extends AbstractPlugin {
private final Settings settings;
public MyPlugin(Settings settings) {
this.settings = settings;
}
@Override
public String name() {
return "MyPlugin";
}
@Override
public String description() {
return "This is the description for my plugin";
}
}-
Extend AbstractPlugin class
-
... but it does not anything useful yet
public class MyPlugin extends AbstractPlugin {
...
//Define own modules
@Override
public Collection<Class<? extends Module>> modules() {
return ImmutableList.of(MyModule.class);
}
//Define own services
@Override
public Collection<Class<? extends LifecycleComponent>> services() {
return ImmutableList.of(MyService.class);
}
}-
So lets define our own modules
-
or services which do something meaningful
public class MyPlugin extends AbstractPlugin {
...
//Define own modules
@Override
public void processModule(Module module) {
if ((module instanceof RestModule)) {
((RestModule)module).addRestAction(MyRestAction.class);
}
if ((module instanceof ???)) {
((???)module).doModuleSpecificStuffHere();
}
}
}-
or do something with core modules
-
to accomplish your needs
plugin=org.company.es.plugins.MyPlugin-
Add es-plugin.properties to src/main/resources
-
Jar it, then zip it with all dependencies included
-
Maven can do that for you
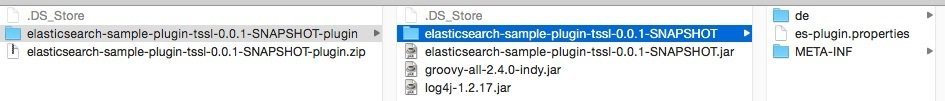
Main artefact
Your code
Dependecies
How they fit into Elasticsearch architecture
-
Elasticsearch is build upon Google guice 2.0
-
pronounced "juice"
-
Dependency injection
-
Inversion of control
-
-
Guice code is copied in ES codebase (slightly modified for lower memory footprint)
-
So elasticsearch is build upon guice modules
-
... and services because of
-
Modules start up, but they don't shut down
-
Modules should be tested
-
Modules can be overridden
-
-
Services have a lifecycle
-
Interesting core modules (for plugins)
-
ActionModule
-
AnalysisModule
-
HttpServerModule
-
RestModule
-
ScriptModule
-
TransportModule
-
-
Interesting core services (for plugins)
-
ClusterService
-
TransportService
-
NettyTransport
-
IndicesService
-
Examples walkthrough
-
Audit Plugin
-
Capture index changes
-
Write them into elasticsearch
-
(Make them visible through kibana)
-
-
Transport SSL/TLS Plugin
-
Implement and enforce SSL/TLS encryption for transport protocol
-
Development
by geek & poke
-
Audit Plugin
-
AuditService registers listener on ShardIndexingService
-
Write changes into elasticsearch via BulkProcessor
-
public class AuditService extends AbstractLifecycleComponent<AuditService>{
...
@Inject
public AuditService(Settings settings,
IndicesService indicesService,
Client client,
ClusterService clusterService,
TransportFlushAction tfa) {
super(settings);
this.indicesService = indicesService;
this.clusterService = clusterService;
...
}
@Override
protected void doStart() throws ElasticsearchException {
...
this.indicesService.indicesLifecycle().addListener(auditIndicesLsListener);
}-
Define a new service called AuditService
-
Register a indices lifecycle listener
Dependency Injection by guice
IndicesLifecycle.Listener auditIndicesLsListener =
new IndicesLifecycle.Listener() {
@Override
public void afterIndexShardStarted(final IndexShard indexShard) {
if (indexShard.routingEntry().primary()
&& !indexShard.indexService().index().name().equals(auditIndexName)) {
AuditIndexOpListener auditListener =
new AuditIndexOpListener(indexShard);
indexShard.indexingService().addListener(auditListener);
}
}-
If a shard starts, register an IndexingOperationListener
class AuditIndexOpListener extends IndexingOperationListener {
private final IndexShard indexShard;
public AuditIndexOpListener(IndexShard indexShard) {
this.indexShard = indexShard;
}
@Override
public void postIndex(Index index) {
String nodeName = indexShard.nodeName();
String indexName = indexShard.indexService().index().name();
Change change = new Change(nodeName, indexName, ...);
//store it in elasticsearch (or anywhere else)
IndexRequest ir = new IndexRequest().source(change.sourceAsMap());
addToBulkIndex(ir);
}
}-
Let the IndexingOperationListener store the change in elasticsearch (or anywhere else)
public class AuditModule extends AbstractModule {
@Override
protected void configure() {
//nothing to bind here
}
@Override
public void processModule(Module module) {
if ((module instanceof ActionModule)) {
((ActionModule)module).registerAction(FlushAction.INSTANCE,
TransportFlushAction.class);
}
if ((module instanceof RestModule)) {
((RestModule)module).addRestAction(AuditRestAction.class);
}
}
}-
Define the AuditModule (not covered today)
-
API for flushing outstanding bulk requests
public class AuditPlugin extends AbstractPlugin {
...
public String name() {
return "AuditPlugin";
}
public String description() {
return "This is the description for the AuditPlugin";
}
@Override
public Collection<Class<? extends Module>> modules() {
return ImmutableList.of(AuditModule.class);
}
@Override
public Collection<Class<? extends LifecycleComponent>> services() {
return ImmutableList.of(AuditService.class);
}
}-
Last but not least define the AuditPlugin itself
plugin=de.saly.es.example.audit.plugin.AuditPlugin-
Add es-plugin.properties
-
Transport SSL Plugin
-
Elasticsearch uses Netty for tcp communication
-
Extend NettyTransport and inject SslHandler into pipeline
-
Replace original Netty transport in TransportModule
-
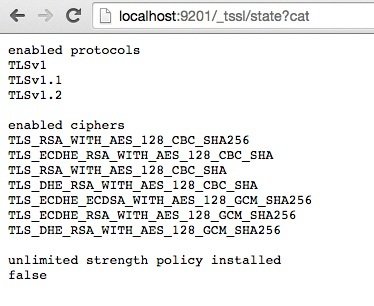
Expose some SSL/TLS related informations through a new REST API
-
public class SSLNettyTransport extends NettyTransport {
@Override
public ChannelPipelineFactory configureServerChannelPipelineFactory(String name,
Settings settings) {
return new SSLServerChannelPipelineFactory(this, name, settings, this.settings);
}
protected class SSLServerChannelPipelineFactory extends SecureServerChannelPipelineFactory {
public SSLServerChannelPipelineFactory(NettyTransport nettyTransport, String name,
Settings sslsettings, Settings essettings) {
super(nettyTransport, name, sslsettings);
}
@Override
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = super.getPipeline();
SSLEngine engine = ...
SslHandler sslHandler = new SslHandler(engine);
pipeline.addFirst("ssl_server", sslHandler);
return pipeline;
}
}
}-
Extend NettyTransport and do some netty pipeline magic
public class TSslPlugin extends AbstractPlugin {
...
public void onModule(TransportModule transportModule) {
transportModule.setTransport(SSLNettyTransport.class, name());
}
public void onModule(RestModule restModule) {
restModule.addRestAction(TSslRestAction.class);
}
}-
Replace transport in TransportModule
-
Register a custom rest action for ssl infos
public class TSslRestAction extends BaseRestHandler{
@Inject
public TSslRestAction(Settings settings, Client client,
RestController controller) {
super(settings, controller, client);
controller.registerHandler(Method.GET, "/_tssl/state", this);
controller.registerHandler(Method.POST, "/_tssl/state", this);
}
@Override
protected void handleRequest(RestRequest request, RestChannel channel,
Client client) throws Exception {
XContentBuilder builder = JsonXContent.contentBuilder();
builder.startObject();
builder.field("enabled_protocols", SecurityUtil.ENABLED_SSL_PROTOCOLS);
builder.field("enabled_chipers", SecurityUtil.ENABLED_SSL_CIPHERS);
builder.endObject();
channel.sendResponse(new BytesRestResponse(RestStatus.OK, builder));
}
}-
Register a handler for an endpoint
-
Send a JSON response
plugin=de.saly.es.example.tssl.plugin.TSslPlugin
version=${project.version}-
Add es-plugin.properties
-
Call the new REST endpoint
Testing
-
Unittests
-
Randomized testing by extending ElasticsearchIntegrationTest
-
https://github.com/tlrx/elasticsearch-test
-
Extend MultiJvmUnitTest
-
Start nodes directly in the test method
-
-
Test in real elasticsearch node/cluster
Always test with multiple nodes (cluster scenario)
-
If you want use the randomized testing suite, include test dependencies in pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId>
<artifactId>lucene-test-framework</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<type>test-jar</type>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>Distribution
-
Use Maven for building plugins
-
because ES is using Maven
-
-
Plugins are best published in maven central
-
Or distributed as .zip file
# Install from maven central
bin/plugin --install de.saly/elasticsearch-sample-plugin-tssl/1.1
# Install from a .zip file
bin/plugin --url file:///Users/.../elasticsearch-sample-plugin-tssl-1.1.zip \
--install elasticsearch-sample-plugin-tssl
-
src/main/assemblies/plugin.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<assembly>
<id>plugin</id>
<formats>
<format>zip</format>
</formats>
<includeBaseDirectory>false</includeBaseDirectory>
<dependencySets>
<dependencySet>
<outputDirectory>/</outputDirectory>
<useProjectArtifact>true</useProjectArtifact>
<useTransitiveFiltering>true</useTransitiveFiltering>
<excludes>
<exclude>org.elasticsearch:elasticsearch</exclude>
</excludes>
</dependencySet>
</dependencySets>
</assembly>-
Use maven-assembly-plugin
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<appendAssemblyId>false</appendAssemblyId>
<outputDirectory>${project.build.directory}/releases/</outputDirectory>
<descriptors>
<descriptor>${basedir}/src/main/assemblies/plugin.xml</descriptor>
</descriptors>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>!!
-
Plugin related configuration options in elasticsearch.yml
# Load this plugin from the classpath
# (does only makes sense if plugins.load_classpath_plugins is false)
# Order is respected
plugin.types: org.company.MyPlugin,com.guhgle.FantasticPlugin
# If a plugin listed here is not installed for current node, the node will not start.
plugin.mandatory: mapper-attachments,lang-groovy
# If its true (which is the default) load all plugins which are in the classpath
# No order guarantee
plugins.load_classpath_plugins: true
Limitations
-
No trust model (yet)
-
Plugins are allowed to do anything
-
With ES 2.0 maybe Java SecurityManager will be utilised
-
-
No isolation
-
Same classloader for ES and all plugins
-
Plugins can interfere with others
-
-
Shade your dependencies
-
Install plugins on as few nodes as possible
-
Consider using dedicated plugin nodes
Not covered
today
-
Creating a custom transport request/response
-
Manipulating the HTTP layer
-
Plugin scopes
-
(Rest)ActionFilter
-
Custom analyzers
-
Custom mapping types
-
Site plugins
-
... maybe there will be a Part II of this talk
by geek & poke
System.exit(0);