Maxim Salnikov
@webmaxru
For Production
In 1-2-3

Part3
Maxim Salnikov
@webmaxru
For Production
In 1-2-3

Part 1
Permanent link:
If you want to code during the session
We need a laptop/desktop with installed (latest stable versions):
- Git
- Node
- NPM
Browsers (latest stable versions):
- Chrome / Firefox / Edge
Quick start
npm install serve -g
git clone https://github.com/webmaxru/pwa-for-production
cd pwa-for-production
git checkout part-1-init
npm install
serve
Recommended to copy code snippets from
Optional
Maxim Salnikov

-
PWA Slack organizer
-
PWA Oslo / PWA Oslo meetups organizer
-
PWA speaker and trainer
Full-Stack Developer, PWAdvocate



Agenda
-
What is a PWA and what advantages does it provide?
-
Browser APIs and specifications we use in PWA and compatibility chart
-
Requirements for our Minimum Viable Product PWA
-
Application shell architecture
-
Service Worker and browser storage foundations
-
Implementing a naive version of the application shell
-
How to test Service Workers
-
Making our app installable
What is PWA at all?
Progressive web apps use modern web APIs along with traditional progressive enhancement strategy to create cross-platform web applications.
These apps work everywhere and provide several features that give them the same user experience advantages as native apps.

UX advantages?
Smart networking + Offline
Proper app experience
Staying notified
Other cool things
}
Service Worker API
Web App Manifest
Predictable caching
Postpone networking while offline
Receiving and showing notifications
Service Worker API
Is there anything REALLY new?
Adding payment methods JIT
Full-scale offline mode
Networking optimizations
install, activate, fetch, backgroundfetchsuccess, backgroundfetchfail, backgroundfetchclick
sync
push, notificationclick
paymentrequest
Cross-platform?
Browser
Desktop
Mobile








Flagged


OS






works everywhere*
* but not everything**

natively
** use progressive enhancement strategy







Platforms / browsers support
Support: detailed

Web API Confluence
APIs actively used in PWAs
-
Service Worker API
-
Cache API
-
IndexedDB
-
Fetch
-
Clients API
-
Broadcast Channel API
-
Push API
-
Notifications API
-
Local Storage
-
Session Storage
-
XMLHttpRequest
-
DOM
Not available in service worker:
Even more capable web
-
Writable Files API
-
WebHID API
-
Scheduled Task / Notification API
-
Web Share Target API
-
Wake Lock API
-
Cookie Store API
-
User Idle Detection API
-
...

Project Fugu
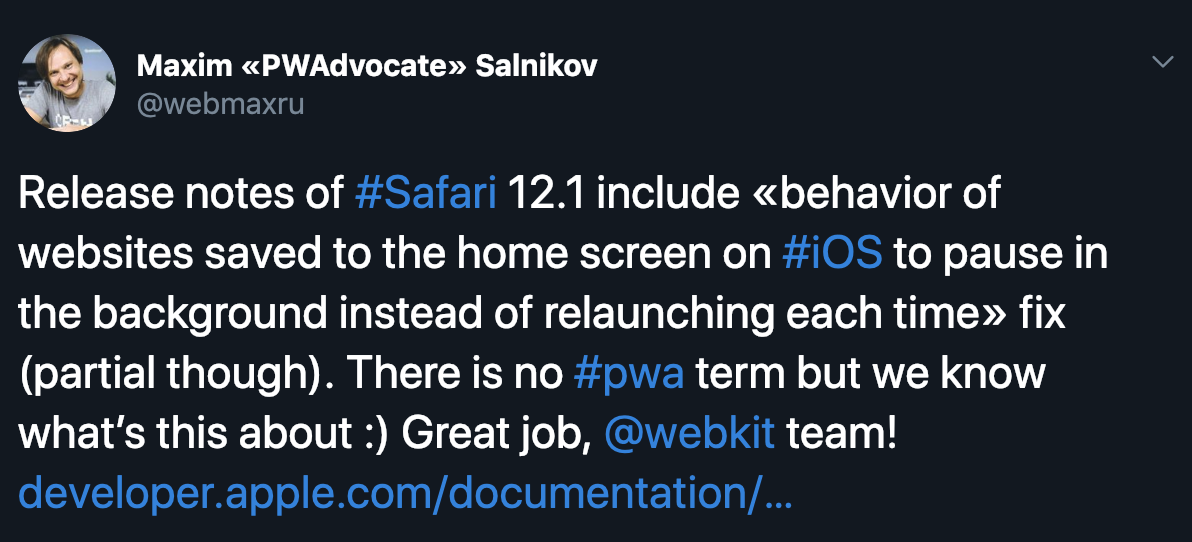
#WSH?
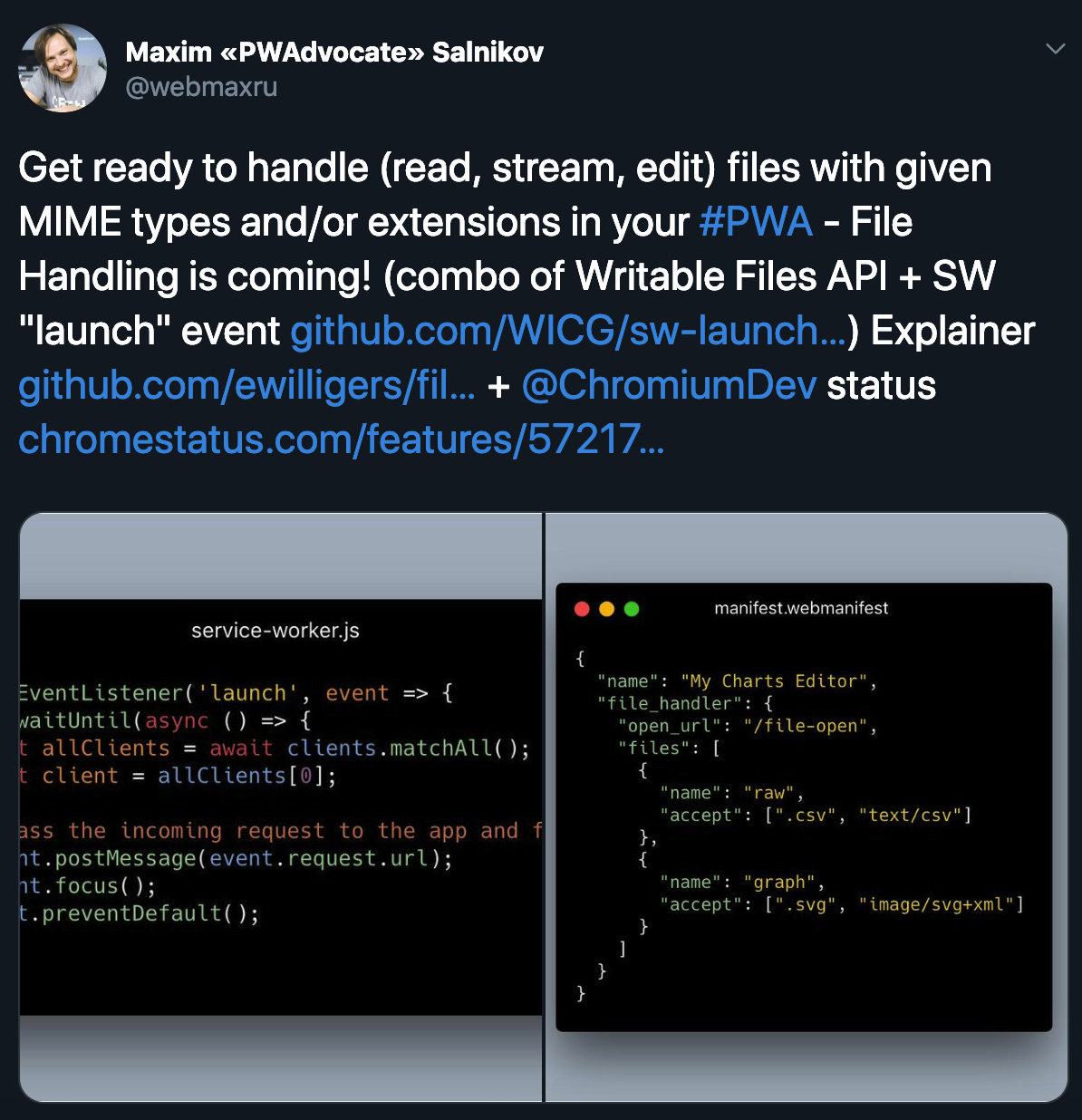
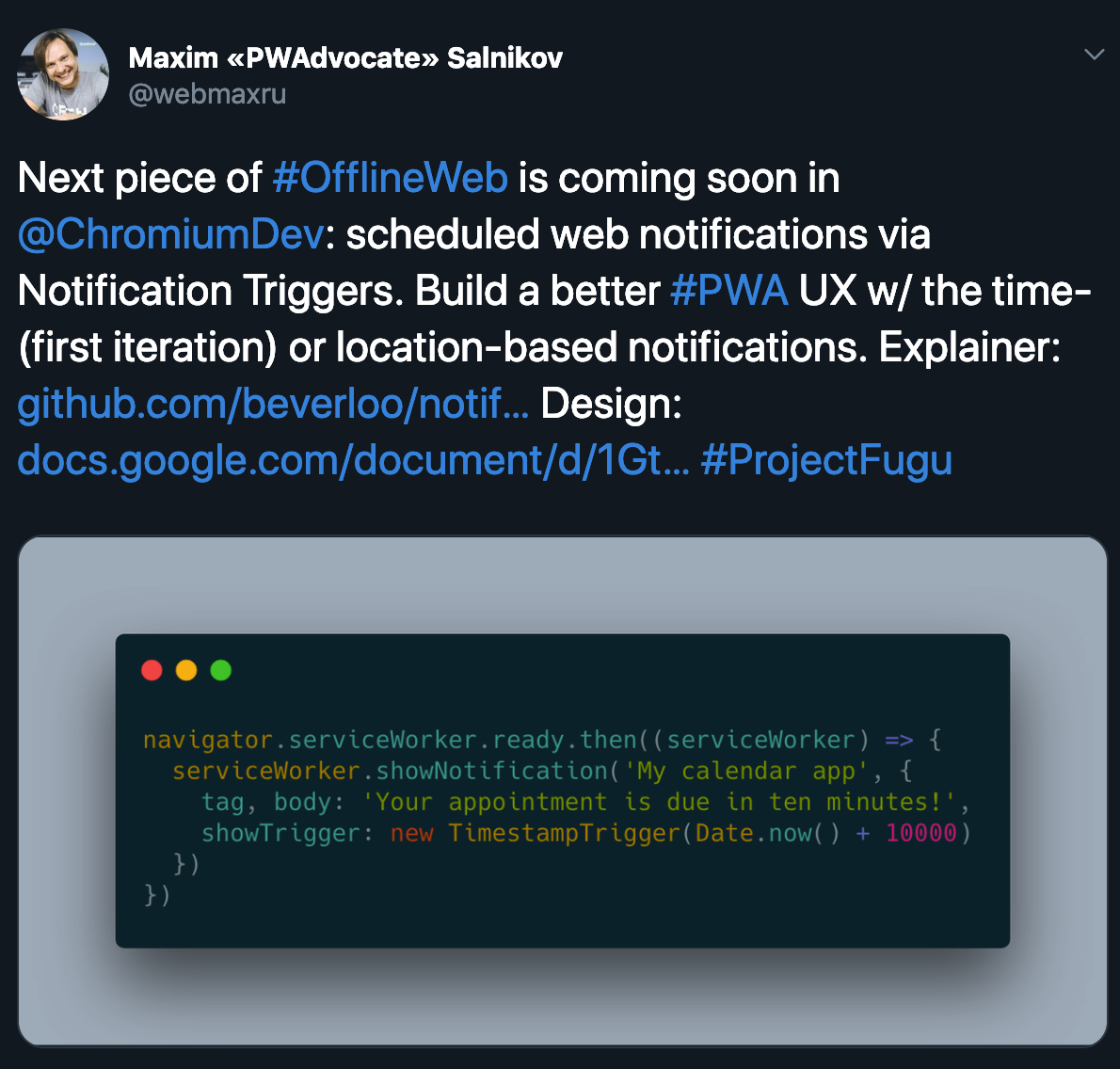
Minimum viable PWA
=
+
Application shell
Web App Manifest
Fast, responsive, mobile-first
Served via HTTPS


Let's build an App Shell
My App
-
Define the set of assets required to show the minimum viable UI
Service worker
-
install: put the assets into Cache Storage
-
activate: clear Cache Storage from the previous app version assets
-
fetch: if the asset is in Cache Storage serve it from there. Otherwise — download and serve it (and cache it)
Build time
-
Register service worker the way it does not affect the app loading performance
Website/webapp
Service Worker


Service Worker 101
Logically
Physically
-file(s)
Website
Service-worker
Browser/OS

Event-driven worker
Lifecycle
'install'
Parsed
Installing
Activating
Redundant
'activate'
Waiting
Active
Coding time
Managing cache
self.addEventListener('install', (event) => {
// Put app's html/js/css to cache
})self.addEventListener('activate', (event) => {
// Wipe previous version of app files from cache
})In the real world
-
Can't add opaque responses directly
-
Redirected requests should be managed
-
Always creating a new version of cache and deleting the old one is not optimal
-
Control over cache size is required
-
Cache invalidation for runtime caching is complex
-
...
Intercepting requests
self.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
if (event.request.url.indexOf('/api') != -1) {
event.respondWith(
// Network-First Strategy
)
} else {
event.respondWith(
// Cache-First Strategy
)
}
})In the real world
-
All kinds of fallbacks needed for the strategies
-
There are more complex strategies like Stale-While-Revalidate
-
Good to have routing
-
Good to have the possibility to provide some extra settings for different resource groups
-
...
Improve
Don't interfere
Don't break

Making an "app" from the website
=
+
Application shell
Web App Manifest
Fast, responsive, mobile-first
Served via HTTPS


For the manual install on Chrome 72 on Mac
-
Not already installed
-
Meets engagement heuristics
-
Proper Web App Manifest
-
Service worker with fetch event
-
Not "prefer related applications"
Installation criteria
-
short_name or name
-
icons must include a 192px and a 512px sized icons
-
start_url
-
display must be one of: fullscreen, standalone, or minimal-ui
MVP Web App Manifest
Test on your [mobile] device
Coding time
On iOS




with PWACompat
}
Resources
Specification
Explainer
Polyfill
Generator
In the next session...
-
Implementing complex algorithms
-
Adopting best practices
-
Focusing on YOUR task
-
Following specifications updates
-
Handling edge cases
Tools help with

Building a proper offline experience using Workbox
1) What are the cons and challenges of the manually written service workers
2) Introducing Workbox
3) Automating application shell lifecycle: from building to serving
4) Organizing a proper UX for the app update
5) Runtime caching: strategies
6) What is background sync and how to implement it using Workbox
7) Proper registration of Workbox in your app
Thank you!
Maxim Salnikov
@webmaxru
Questions?
Maxim Salnikov
@webmaxru

-
Application shell
-
Runtime caching
-
Replaying failed network requests
-
Offline Google Analytics
-
Broadcasting updates
Have our own service worker!
Working modes
-
Workbox CLI
-
Webpack plugin
-
Node module
# Installing the Workbox Node module
$ npm install workbox-build --save-devBuild script
// We will use injectManifest mode
const {injectManifest} = require('workbox-build')
// Sample configuration with the basic options
var workboxConfig = {...}
// Calling the method and output the result
injectManifest(workboxConfig).then(({count, size}) => {
console.log(`Generated ${workboxConfig.swDest},
which will precache ${count} files, ${size} bytes.`)
})workbox-build-inject.js
Workbox manifest
[
{
"url": "index.html",
"revision": "34c45cdf166d266929f6b532a8e3869e"
},
{
"url": "favicon.ico",
"revision": "b9aa7c338693424aae99599bec875b5f"
},
...
]Build script configuration
// Sample configuration with the basic options
var workboxConfig = {
globDirectory: 'dist/angular-pwa/',
globPatterns: [
'**/*.{txt,png,ico,html,js,json,css}'
],
swSrc: 'src/service-worker.js',
swDest: 'dist/angular-pwa/service-worker.js'
}
workbox-build-inject.js
Source service worker
// Importing Workbox itself from Google CDN
importScripts('https://googleapis.com/workbox-sw.js');
// Precaching and setting up the routing
workbox.precaching.precacheAndRoute([])
src/service-worker.js
1
2
Build flow integration
{
"scripts": {
"build-prod": "ng build --prod &&
node workbox-build-inject.js"
}
}package.json
Better app update UX
App version updates
v1
v2
v1
v1
v2
Deployed
Displayed
v2
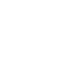
A new version of the app is available. Click to refresh.
const updateChannel = new BroadcastChannel('app-shell');
updateChannel.addEventListener('message', event => {
// Inform about the new version & prompt to reload
});Option #1: BroadcastChannel
updates.component.ts
workbox.precaching.addPlugins([
new workbox.broadcastUpdate.Plugin('app-shell')
]);src/service-worker.js
3
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
navigator.serviceWorker
.register('/service-worker.js')
}Option #2: Service worker lifecycle
index.html
Requirements
-
Feature detection
-
Registration after app fully loaded and UI rendered
-
Hook into service worker lifecycle update event
-
Was the service worker updated?
-
Was the app itself updated?
register-service-worker
import { register } from 'register-service-worker'
platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(AppModule)
.then( () => {
register('/service-worker.js', {
})
})main.ts
$ npm install register-service-worker updated (registration) {
// Inform & prompt
}3
Runtime caching
Strategies and plugins
workbox.routing.registerRoute(
new RegExp('/app/v2/'),
workbox.strategies.networkFirst()
);src/service-worker.js
workbox.routing.registerRoute(
new RegExp('/images/'),
workbox.strategies.cacheFirst({
plugins: [...]
})
);Push notifications
Notifications handling
self.addEventListener('push', (event) => {
self.registration.showNotification(...)
})src/service-worker.js
self.addEventListener('notificationclick', (event) => {
// React on notification actions
})self.addEventListener('notificationclose', (event) => {
// React on notification closing
})Summary
-
Framework-agnostic
-
Rich functionality
-
Maximum flexible configuration
-
Full power of our own service worker

Setup -> Configure -> Code
Get what you want
-
1900+ developers
-
Major browsers/frameworks/libs reps