Joint Optimization of an Autoencoder for Clustering and Embedding
Ahcène Boubekki
Michael Kampffmeyer
Ulf Brefeld
Robert Jenssen
UiT The Arctic
University of Norway
Leuphana University
Questions
-
Can we approx. k-means with an NN?
-
How to jointly learn an embedding?
Clustering Module
step by step
Step by step: Assumptions
Assumptions of k-means
Hard clustering
Null co-variances
Equally likely clusters
Relaxations
Soft assignments
Isotropic co-variances
Dirichlet prior on
Isotropic GMM
Step by step: Gradient Descent
Isotropic GMM with Dirchlet prior
Gradient Descent fails :(
Algorithmical trick
After an M-step:
Simplification due to the prior
Step by step: Where is the AE?
Current Objective function:
Computational trick
AE ⇒ reconstruction
Clustering Module
Loss Function
Reconstruction
Sparsity + Reg.
Sparsity + Merging
Dir. Prior
Network
Clustering Module: Evaluation
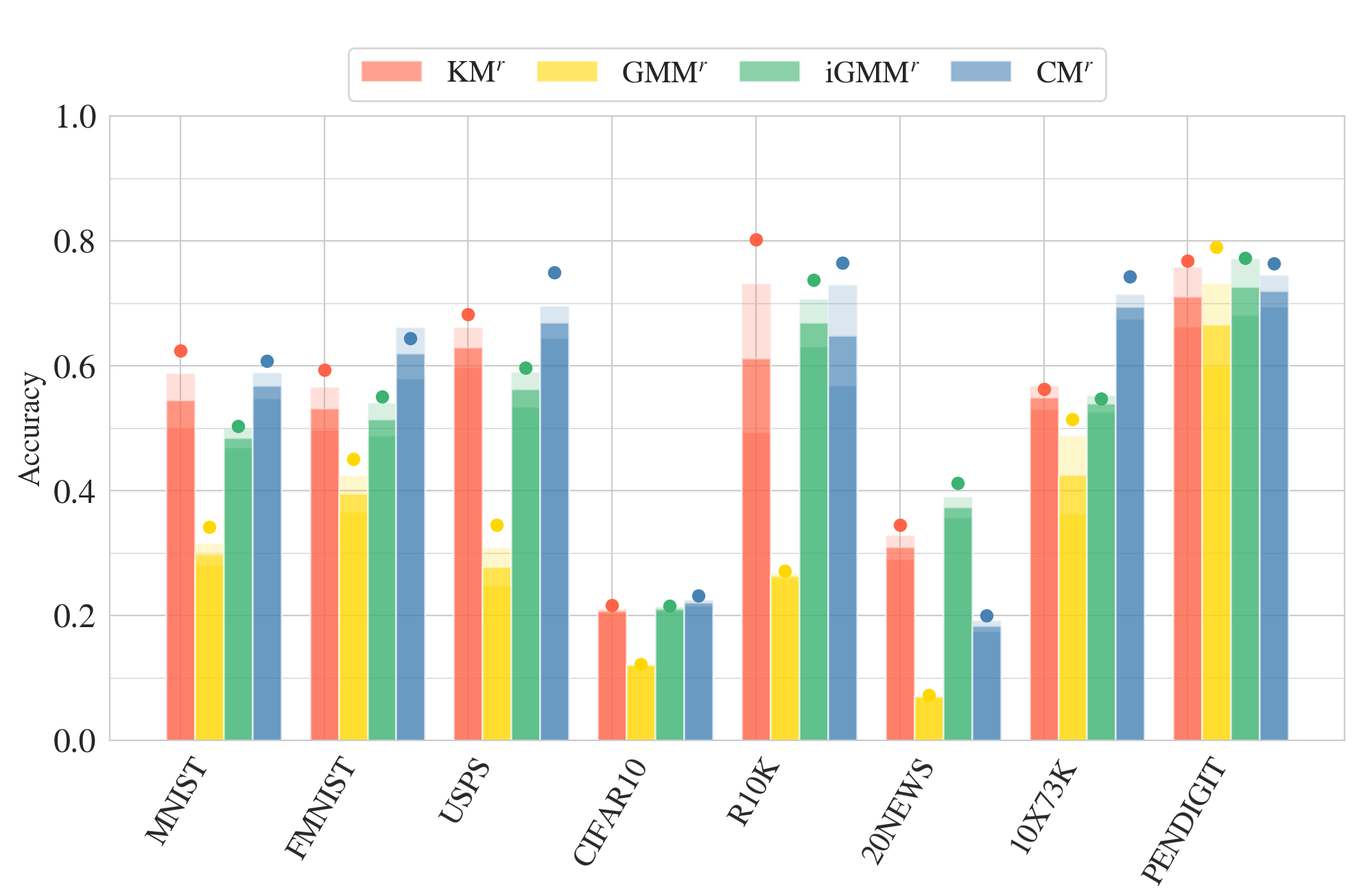
Baselines:
Best run
Average
St.Dev
k-means
GMM
iGMM
Accuracy
Clustering Module: Summary
YES
Limitations
Isotropy assumption
Linear partitions only
Tied co-variances
Spherical co-variances
we can cluster à la k-means using a NN
What is the solution?
Kernels!
Feature maps
Clustering Module
and Feature Maps
AE-CM: Introduction
CM
Invertible feature maps to avoid collapsing
Maps are learned using a neural network
AE-CM
AE-CM
Loss Function
Lagrange
does not
meet expectations
CM
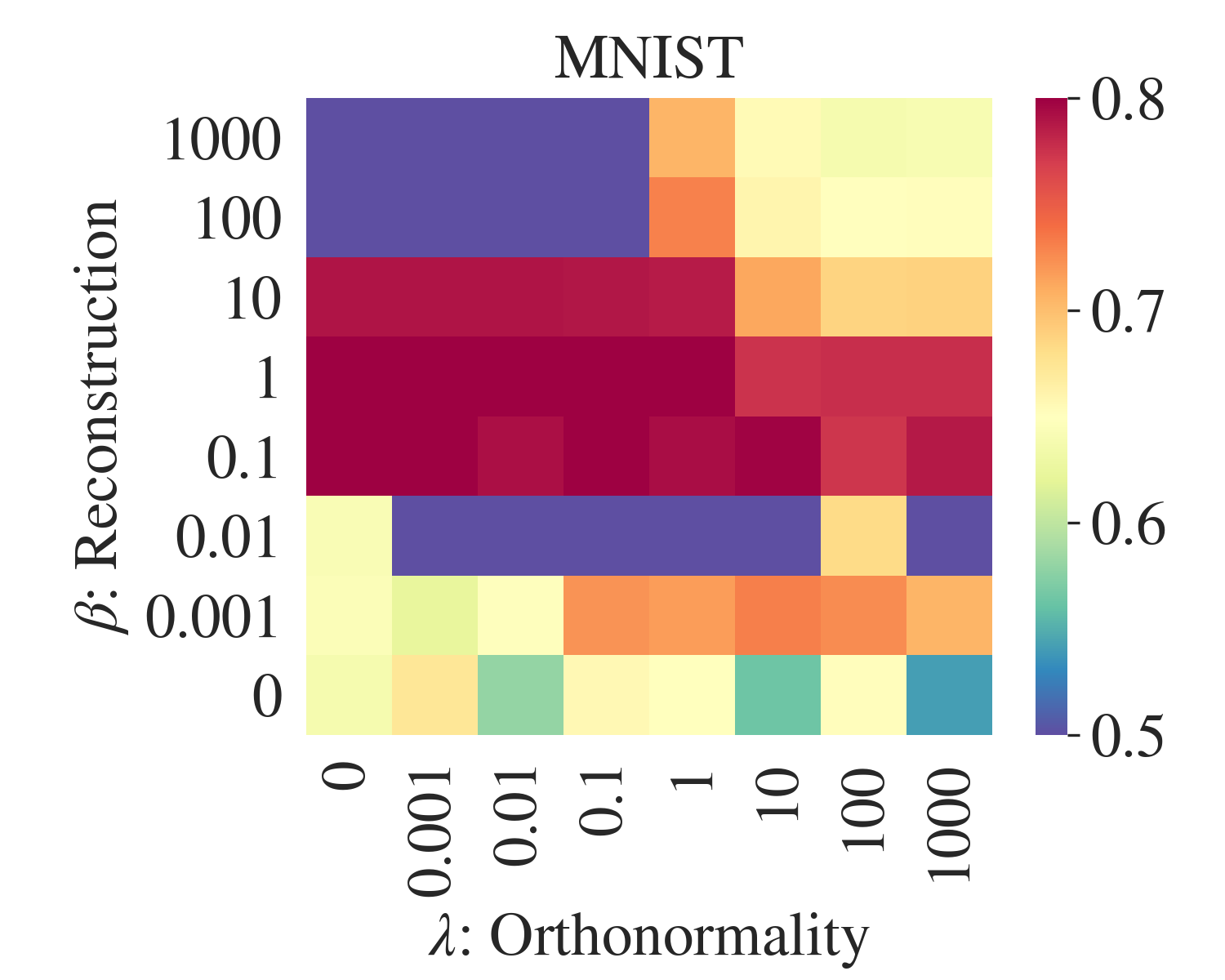
Orthonormal
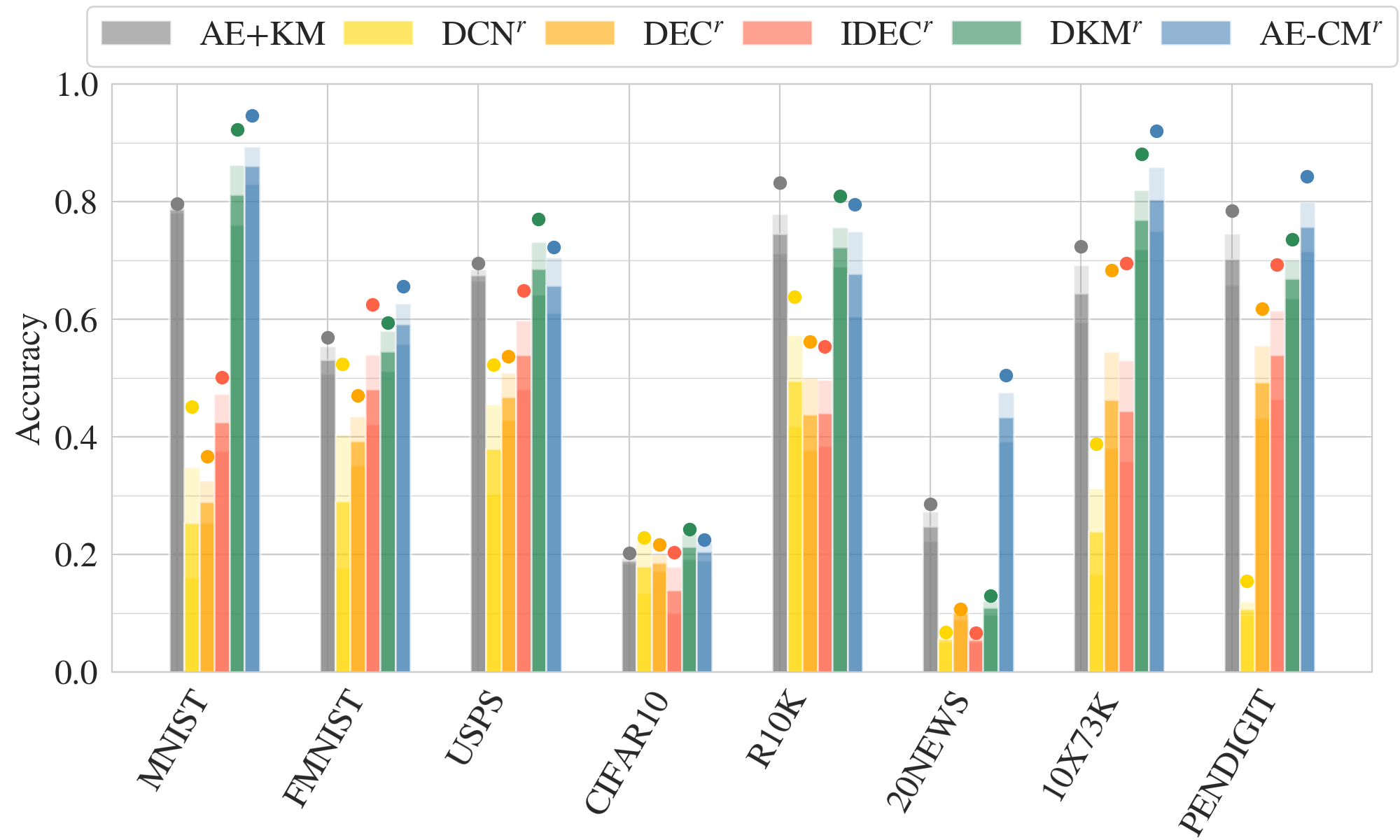
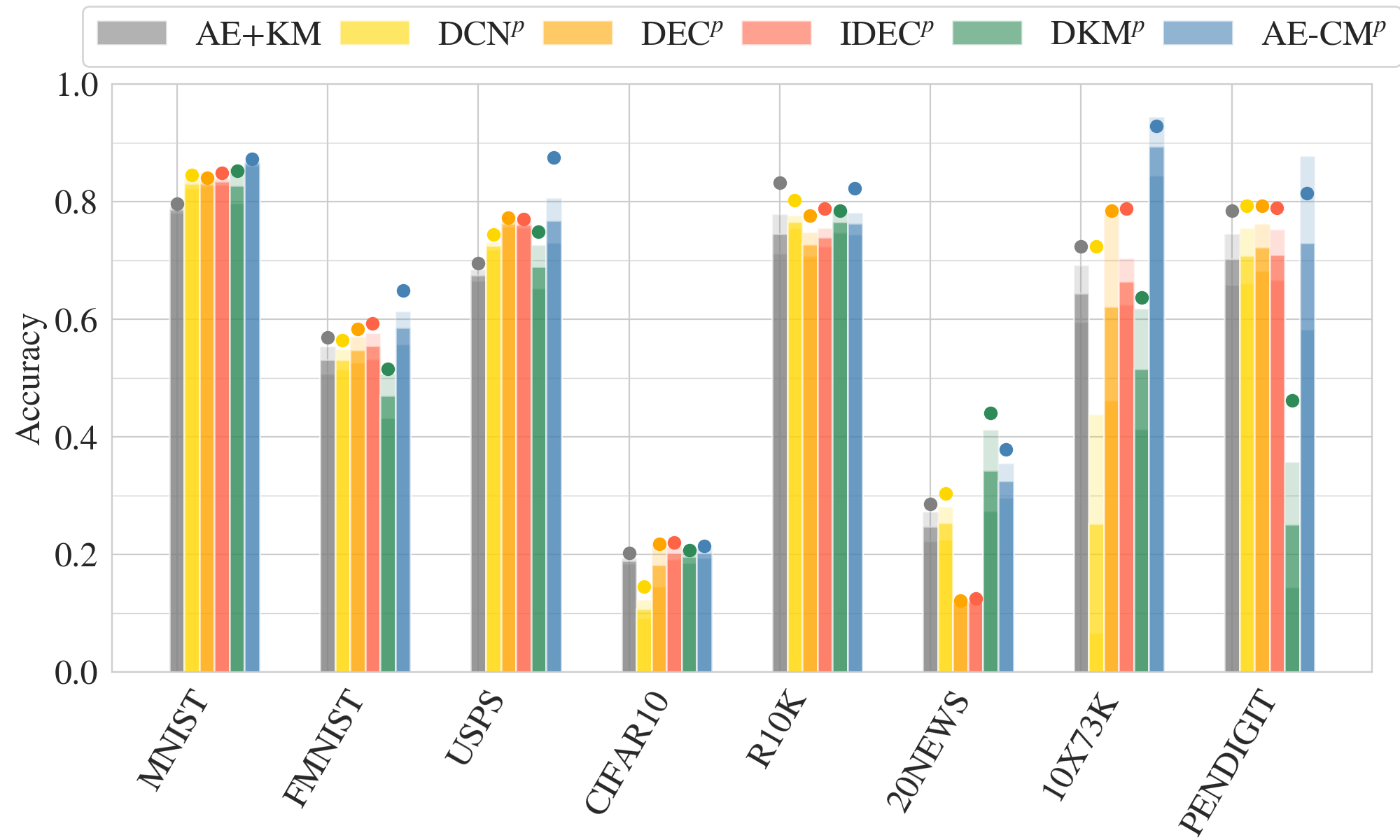
AE-CM: Baselines
AE+KM:
DCN:
Initialization:
- Pre-train DAE
- Centroids and hard assignments from k-means in feature space
Alternate:
- Minimize NN for reconstruction DAE and k-means
- Update hard assignments
- Update centroids
End-to-end autoencoder + k-means
DEC:
Initialization:
- Pre-train DAE
- Centroids and soft assignments from k-means in feature space
- Discard decoder
Alternate:
- t-SNE like loss on DAE
- Update centroids
IDEC:
Same but keep the decoder
DKM:
centroids in ad-hoc matrix
Loss = reconstruction DAE + c-means-like term
Annealing of Softmax temperature
AE+KM:
(2017) DCN:
(2016) DEC:
(2017) IDEC:
(2020) DKM:
Check paper for GAN and VAE baselines
Fully connected layers
AE-CM: Evaluation with random initialization
AE-CM: Evaluation initalized with AE+KM
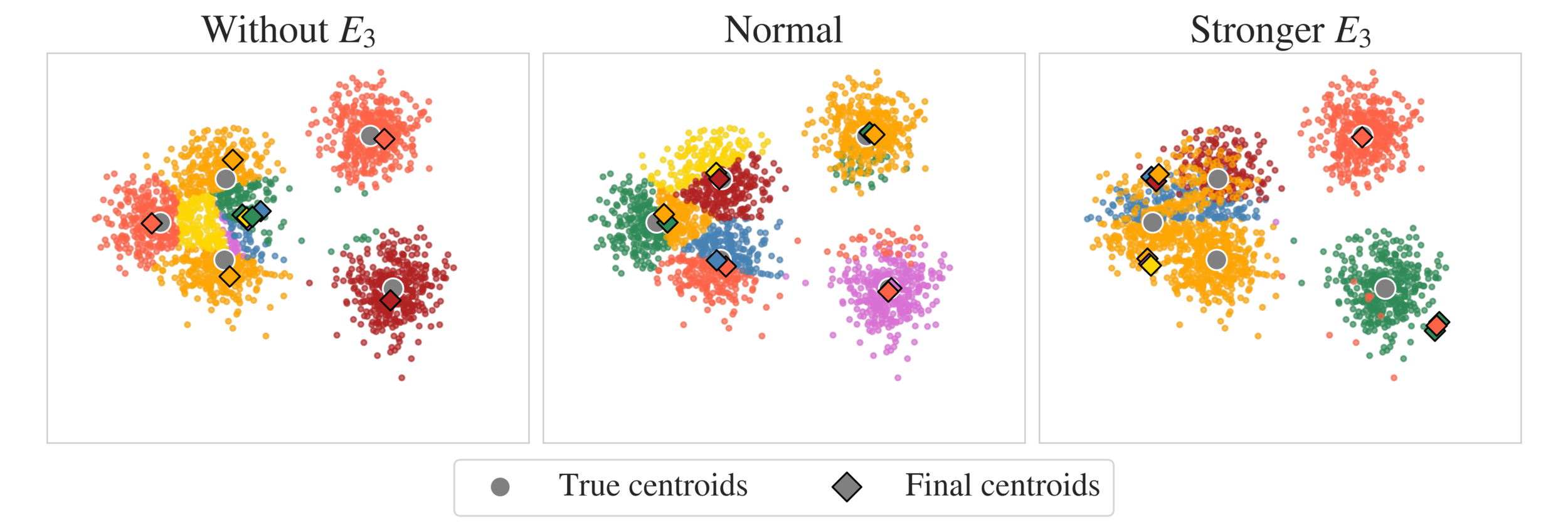
AE-CM: Toy example
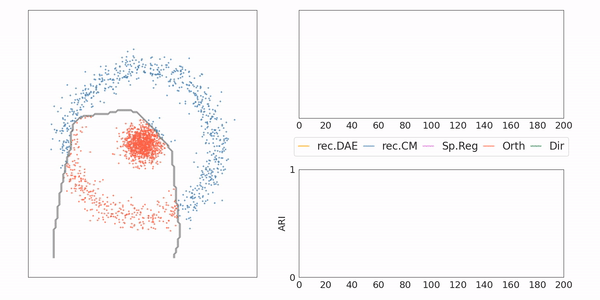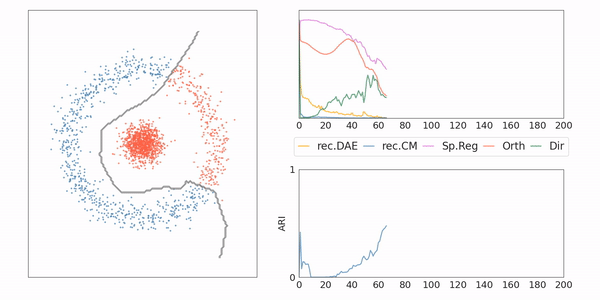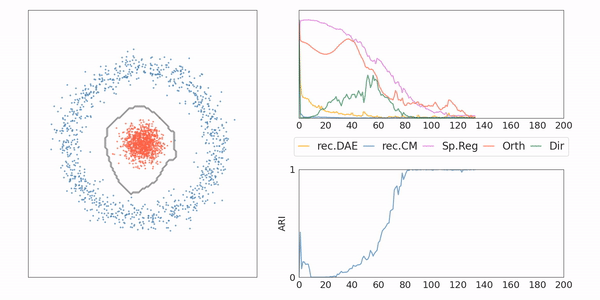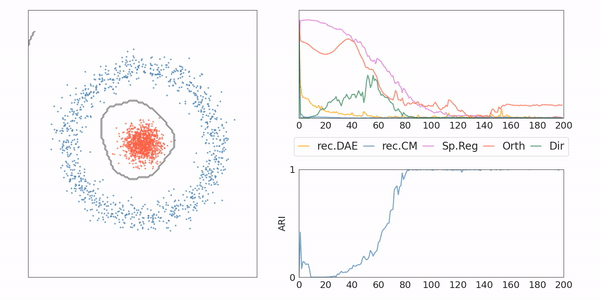
AE-CM: Generative Model

Conclusion
Conclusion
YES
What is next?
Can we approx. k-means with a NN?
Can we jointly learn an embedding?
YES
Improve stability by acting on assignments.
Softmax annealing, Gumbel-Softmax, VAE
Try more complex architectures.
More applications.
Normalize the loss
Joint Optimization of an Autoencoder for Clustering and Embedding
Ahcène Boubekki
Michael Kampffmeyer
Ulf Brefeld
Robert Jenssen
UiT The Arctic
University of Norway
Leuphana University
Ekstra
Clustering Module: Implementation
Initialization
Random
k-means++
Finalization
Averaging epoch
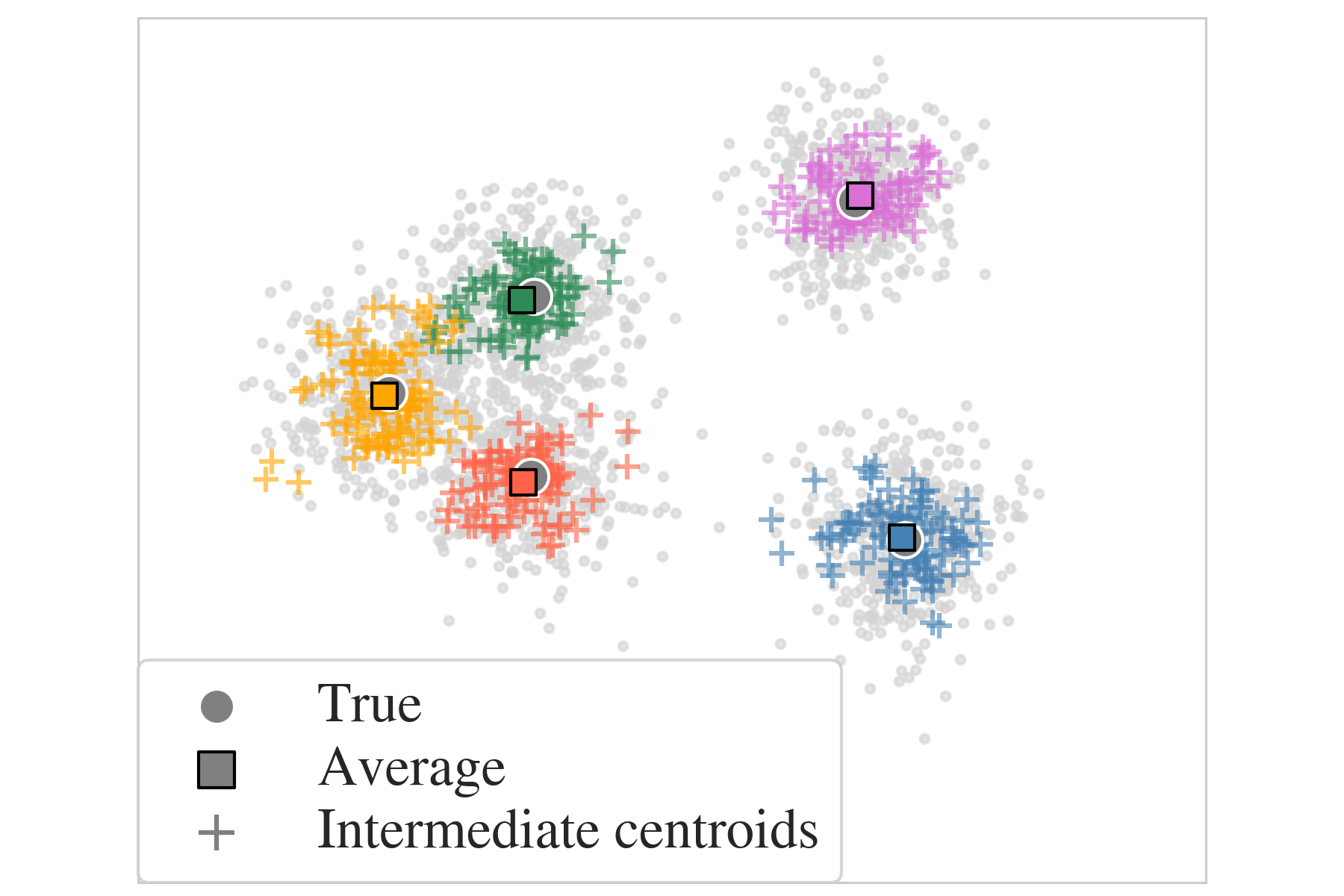
Clustering Module: Hyperparameters
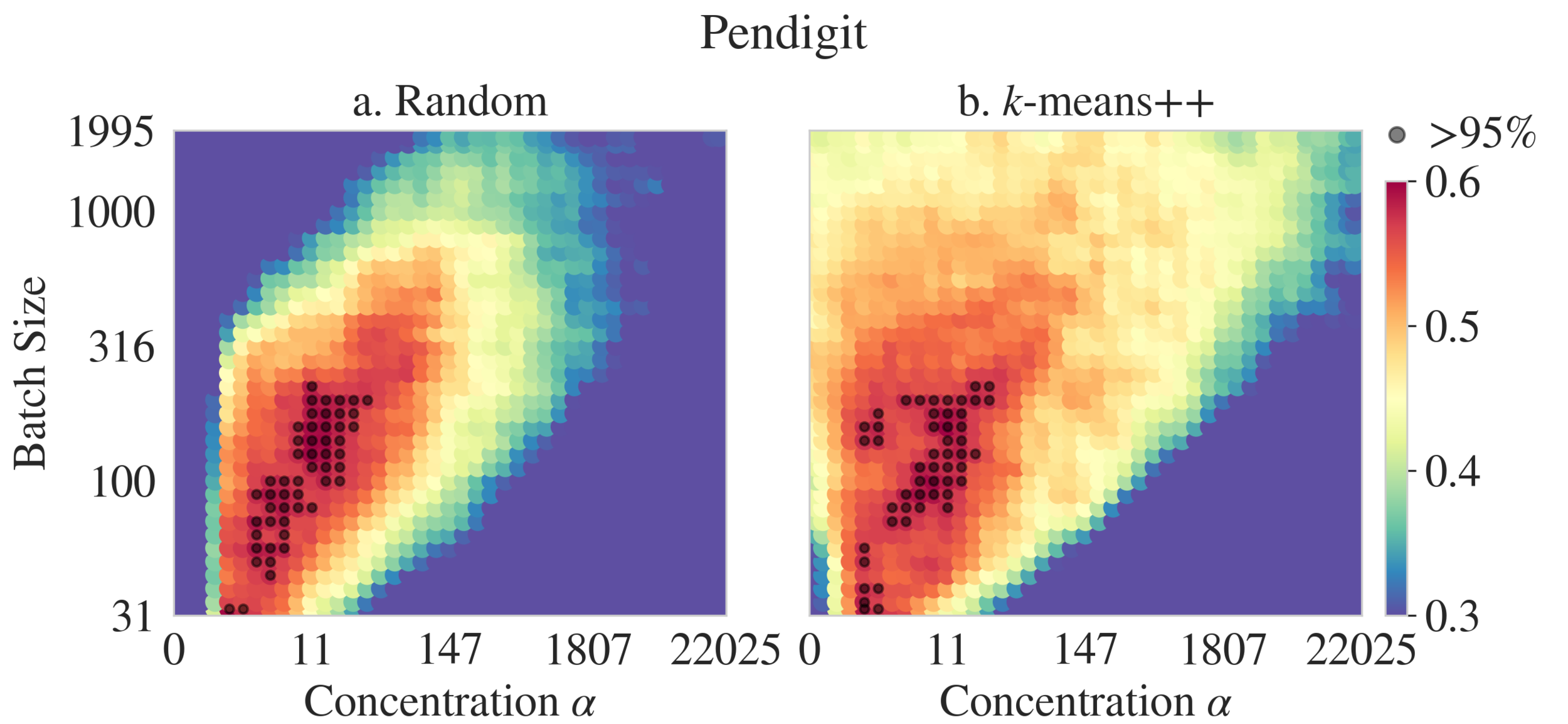
CM: Prior
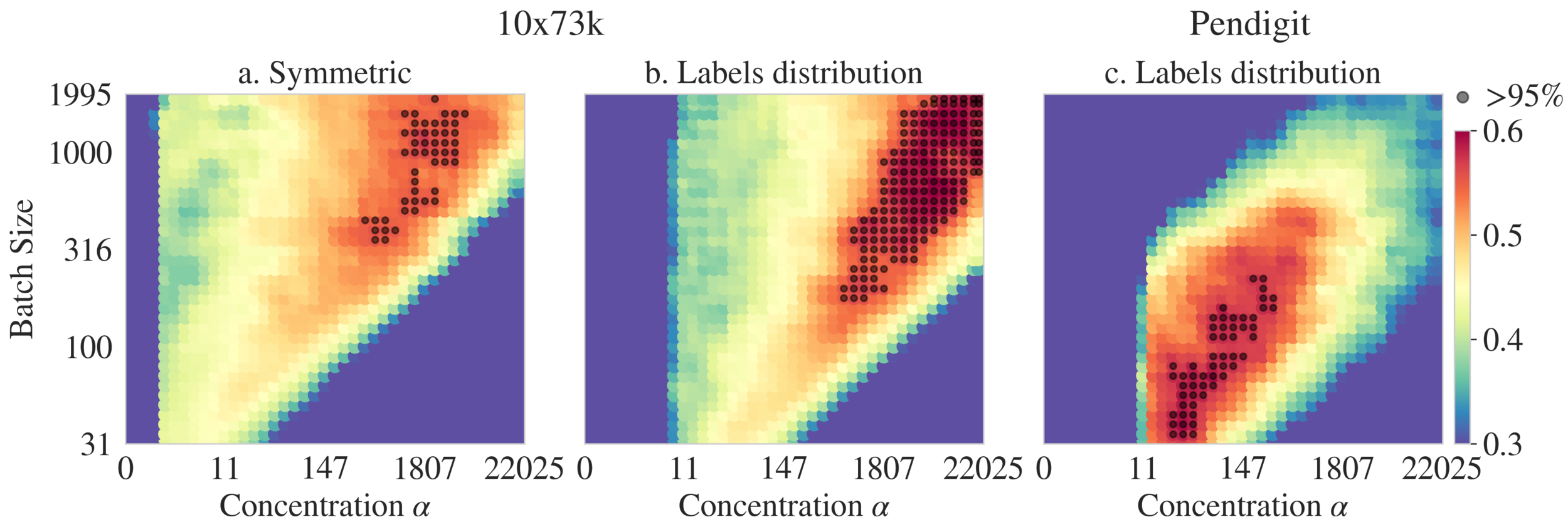


CM: E3
AE-CM: Beta vs Lambda
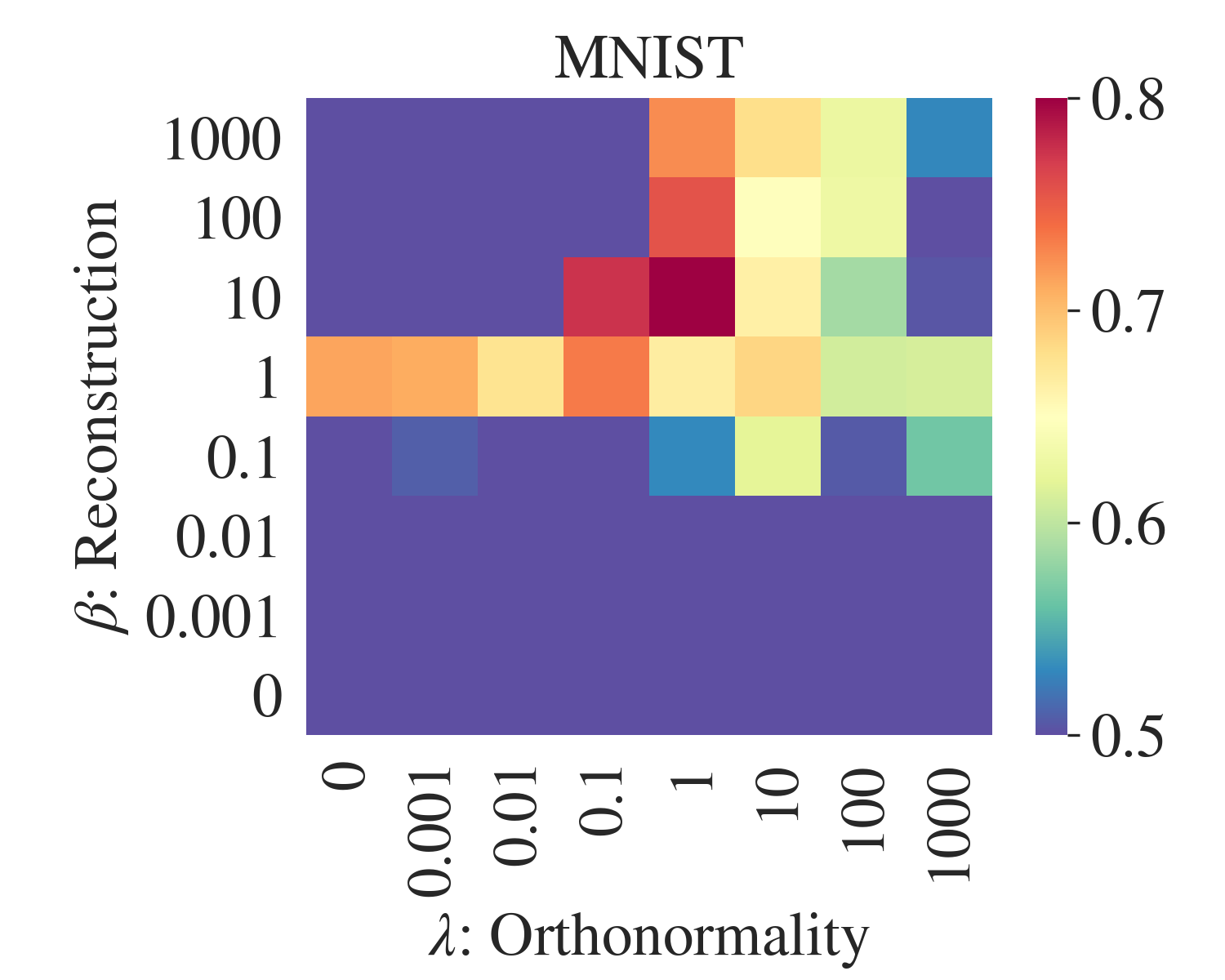
AE-CM+pre
AE-CM+rand
Motivation
To use NN to learn an embedding suitable for k-means/GMM
suitable
Linearly separable