Ahcène Boubekki
Multiple
Linear Regression with Interactions and
Dummy Variables
Topic Definition
Topic Definition
Multiple Linear Regression with Interactions and Dummy Variables
Multiple Linear Regression with Interactions and Dummy Variables
Linear Regression
Multiple
Dummy Variables
Interactions
Response is
a linear transformation
of the predictor.
Response is
a linear combination
of several predictors.
Response is
a linear combination
of several predictors,
some being binary.
Response is
a linear combination
and products
of several predictors,
some being binary.
Multiple Linear Regression with Interactions and Dummy Variables,
target audience is class of first semester statistics students
at the basic level.
Do not discuss optimization.
Only simple statistics/metrics
PISA x Socio-economics and Climate?
Setting
X
Predictor / Explanatory Variables
Y
Response / Outcome (Observation)
Ŷ
Prediction
y-ŷ
Residual
R2
R-square = square of Pearson correlation ρ
ρ
Pearson correlation
Data and Problem
Hypthesis:
The MATH PISA score (2022) per country can be explained by social, environmental and economical variables
The Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) is the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development's (OECD) programme measuring 15-year-olds’ ability to use their reading, mathematics and science knowledge and skills to meet real-life challenges.
https://www.oecd.org/en/about/programmes/pisa.html
Linear Regression
Variables:
MATH: PISA (2022) score of 79 countries
YU20: Youth Unemployment rate in ~2020 (WorldBank)


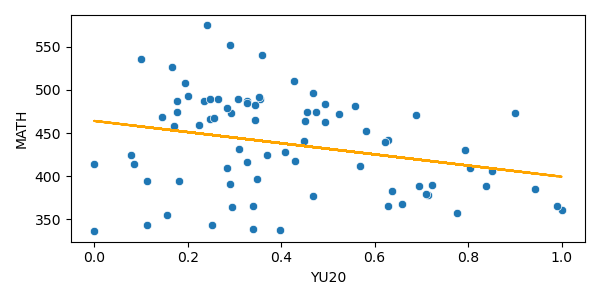
Linear Regression?
MATH ~ YU20
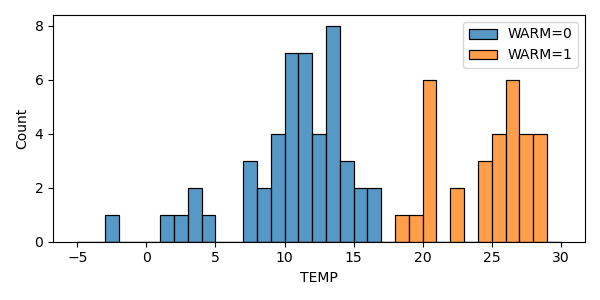
WARM {0,1}: average yearly temperature ≥ 18°C (WorldBank)
Not so good
What if we add another variable?
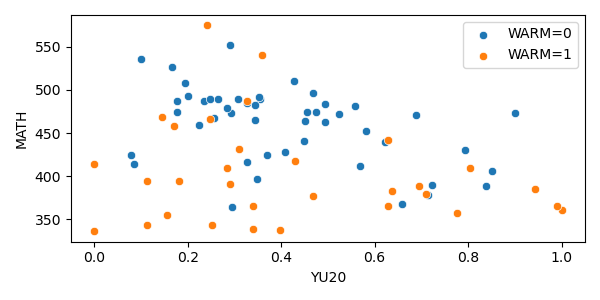
Interaction and Dummy Variable
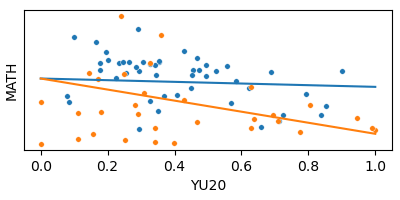
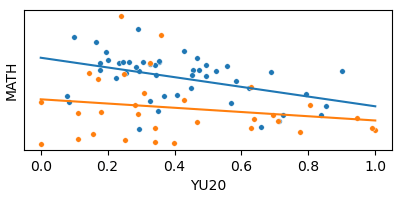
Model 2: Interaction
MATH ~ YU20 + YU20×WARM
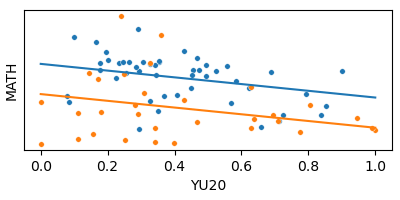
Model 1: Dummy Variable
MATH ~ YU20 + WARM
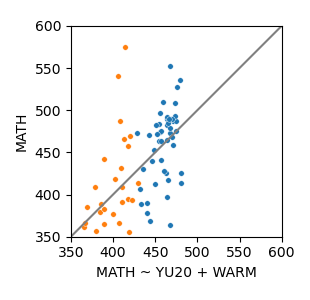
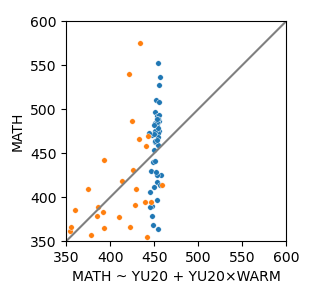
Model 3: Both
MATH ~ YU20 + YU20×WARM + WARM
Same slope
Different intercepts
Dummy Variable
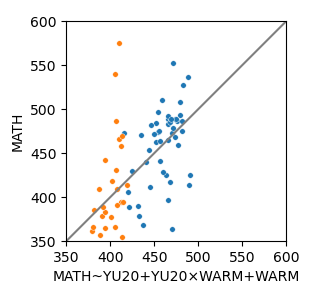
Different slopes
Same intercept
Model Selection
Model Selection

↑: accounting for
the number of predictors
↓:
Akaike/Bayesian
Information Criteria
↑: proportion of the variance explained
↓: sum of squared residuals
Model Selection
==============================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 497.3029 15.255 32.599 0.000 466.913 527.693
YU20 -91.1878 33.065 -2.758 0.007 -157.057 -25.318
WARM -78.0385 21.575 -3.617 0.001 -121.017 -35.060
YU20:WARM 51.3942 44.789 1.147 0.255 -37.831 140.619==============================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
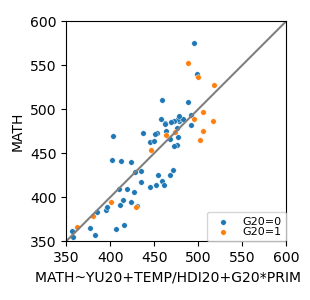
Intercept 472.2815 12.770 36.984 0.000 446.825 497.738
YU20 -55.1106 14.126 -3.901 0.000 -83.270 -26.952
TEMP -19.5058 1.660 -11.749 0.000 -22.815 -16.196
TEMP:HDI20 21.4286 2.106 10.176 0.000 17.231 25.626
G20 117.0291 33.314 3.513 0.001 50.619 183.439
PRIM 46.7952 21.065 2.221 0.029 4.802 88.788
G20:PRIM -252.5079 76.412 -3.305 0.001 -404.833 -100.182
MATH ~ YU20 + YU20×WARM + WARM
MATH ~ YU20 + TEMP + TEMP×HDI20 + G20 + G20×PRIM + PRIM
Summary
Summary
Multiple Linear Regression with interactions and dummy variables:
It is a linear regression with more than one predictor, including binary ones, and products between predictors.
Model Selection:
Pay attention to the p-values of the coefficients.
Favor low SSR, high adjusted R2, low AIC/BIC.
Favor homoscedastic and normally distributed residuals.
Remark:
The regressed lines do not always match that of stratified models (one model per dummy combination).
Linear Regression
Linear Regression
Model:
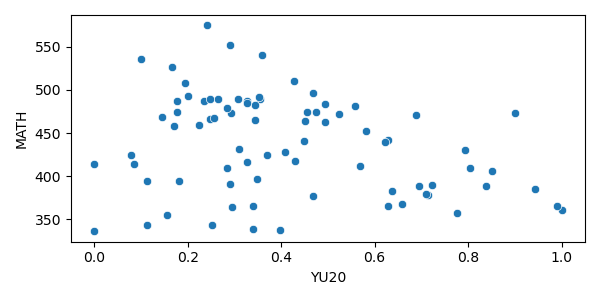

Linear Regression

Model Selection:
Proportion of the variance
in MATH predicted by YU20.
Higher is better.
Standard Error measures the average deviation to the regression line.
Lower is better.
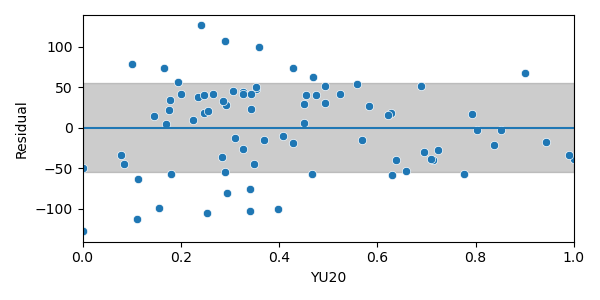
- Independent from each other;
- Homoscedastic, (variance indep. of YE20);
- Normally distributed (low skewness ).
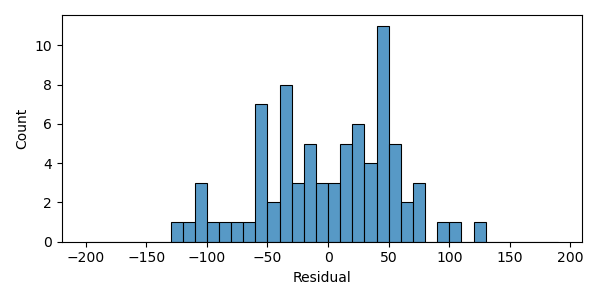
Residuals should be:
Not very satisfying...
Data and Problem
Variables:
MATH: average PISA2022 score of 79 countries
YU20: Youth Unemployment rate in ~2020 (WorldBank)

Ahcène Boubekki