Beyond Java 8
Angie Jones
https://angiejones.tech
https://TestAutomationU.com
@techgirl1908
Java Champion
Senior Director, Developer Relations
Applitools & Test Automation University

@techgirl1908

@techgirl1908

@techgirl1908
@techgirl1908
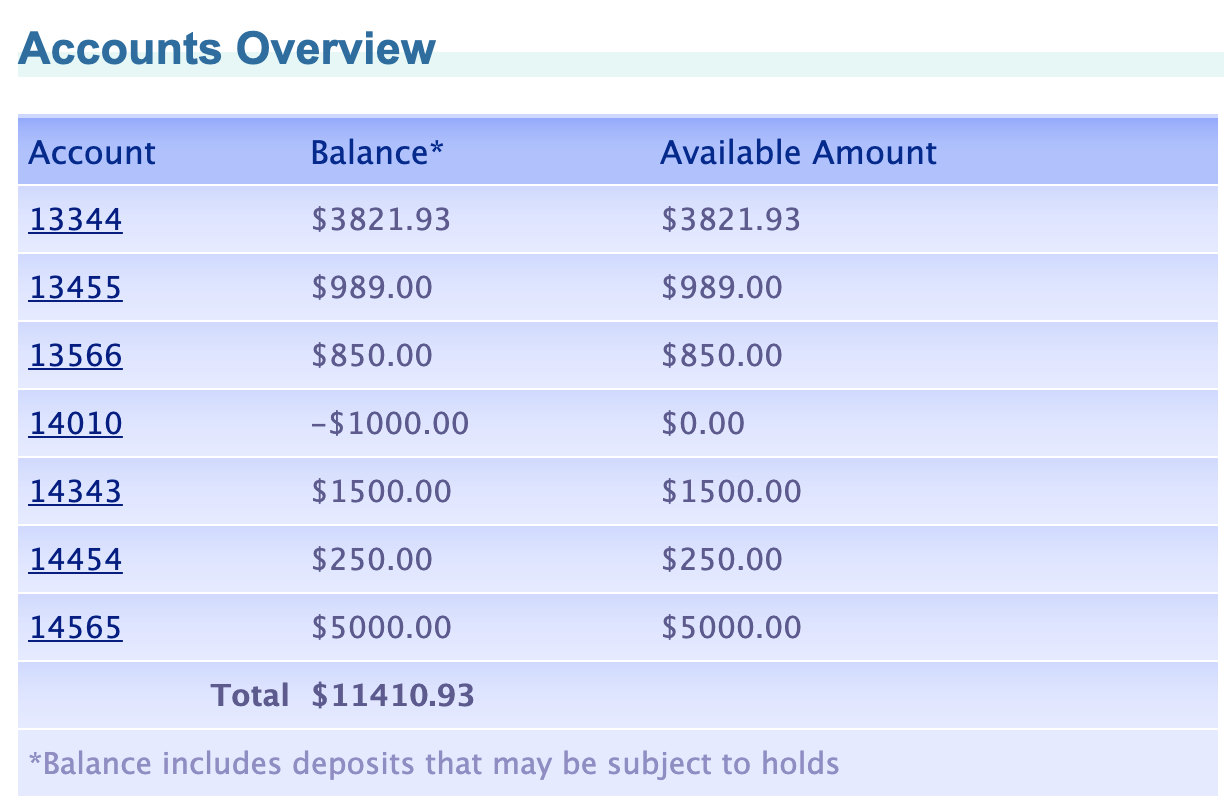
@Test
public void accountsListed() {
AccountsOverviewPage accountsOverviewPage =
page.login(username, password);
List<String> actualAccounts =
accountsOverviewPage.getAccounts();
List<Account> accounts = APIUtil.getAccounts(
Customers.getCustomerId(username));
List<String> expectedAccounts = new ArrayList();
for(Account account : accounts){
expectedAccounts
.add(String.valueOf(account.id()));
}
assertEquals(expectedAccounts, actualAccounts);
}@techgirl1908
@Test
public void accountsListed() {
AccountsOverviewPage accountsOverviewPage =
page.login(username, password);
List<String> actualAccounts =
accountsOverviewPage.getAccounts();
List<Account> accounts = APIUtil.getAccounts(
Customers.getCustomerId(username));
List<String> expectedAccounts = new ArrayList();
for(Account account : accounts){
expectedAccounts
.add(String.valueOf(account.id()));
}
assertEquals(expectedAccounts, actualAccounts);
}@techgirl1908
@Test
public void accountsListed() {
var accountsOverviewPage =
page.login(username, password);
List<String> actualAccounts =
accountsOverviewPage.getAccounts();
List<Account> accounts = APIUtil.getAccounts(
Customers.getCustomerId(username));
List<String> expectedAccounts = new ArrayList();
for(Account account : accounts){
expectedAccounts
.add(String.valueOf(account.id()));
}
assertEquals(expectedAccounts, actualAccounts);
}TYPE INFERENCE FOR LOCAL VARIABLES
@techgirl1908
Java is still a statically typed language
@techgirl1908
Initialization is required
var accountsOverviewPage;@techgirl1908
Only works for local variables
public class MyTests {
var accountsOverviewPage =
page. login(username, password);
@Test
public void accountsListed() {}
}@techgirl1908
Not allowed in headers
public class MyTests {
public MyTests(var data){}
}@techgirl1908
Naming is even more important now
var x = getX();@techgirl1908
Everything doesn't need to be a var!
var numberOfAccounts = 5;@techgirl1908
@Test
public void accountsListed() {
var accountsOverviewPage =
page.login(username, password);
var actualAccountIdsList =
accountsOverviewPage.getAccounts();
var accountsList =
APIUtil.getAccounts(
Customers.getCustomerId(username));
var expectedAccountIdsList = new ArrayList<String>();
for(var account : accountsList){
expectedAccountIdsList
.add(String.valueOf(account.id()));
}
assertEquals(expectedAccountIdsList, actualAccountIdsList);
}TYPE INFERENCE FOR LOCAL VARIABLES
@techgirl1908
@Test
public void accountsListed() {
var accountsOverviewPage =
page.login(username, password);
var actualAccountIdsList =
accountsOverviewPage.getAccounts();
var accountsList =
APIUtil.getAccounts(
Customers.getCustomerId(username));
var expectedAccountIdsList = new ArrayList<String>();
for(var account : accountsList){
expectedAccountIdsList
.add(String.valueOf(account.id()));
}
assertEquals(expectedAccountIdsList, actualAccountIdsList);
}@techgirl1908

@techgirl1908
public List<String> getAccounts(){
List<WebElement> accountCells =
driver.findElements(accountColumn);
List<String> accounts = new ArrayList();
for(WebElement element : accountCells){
accounts.add(element.getText());
}
return accounts;
}@techgirl1908
public List<String> getAccounts(){
return driver.findElements(accountColumn)
.stream()
.map(WebElement::getText)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}@techgirl1908
public List<String> getAccounts(){
return driver.findElements(accountColumn)
.stream()
.map(WebElement::getText)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}return driver.findElements(accountColumn)
.stream()
.map(e -> e.getText())
.collect(Collectors.toList());@techgirl1908
@Test
public void accountsListed() {
var accountsOverviewPage =
page.login(username, password);
var actualAccountIdsList =
accountsOverviewPage.getAccounts();
String customerId = Customers.getCustomerId(username);
var expectedAccountIdsList =
APIUtil.getAccounts(customerId)
.stream()
.map(Account::getId)
.map(String::valueOf)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
assertEquals(expectedAccountIdsList, actualAccountIdsList);
}@techgirl1908
New line for
each method call
driver.findElements(accountColumn).stream().map(WebElement::getText).collect(Collectors.toList());driver.findElements(accountColumn)
.stream()
.map(WebElement::getText)
.collect(Collectors.toList());@techgirl1908
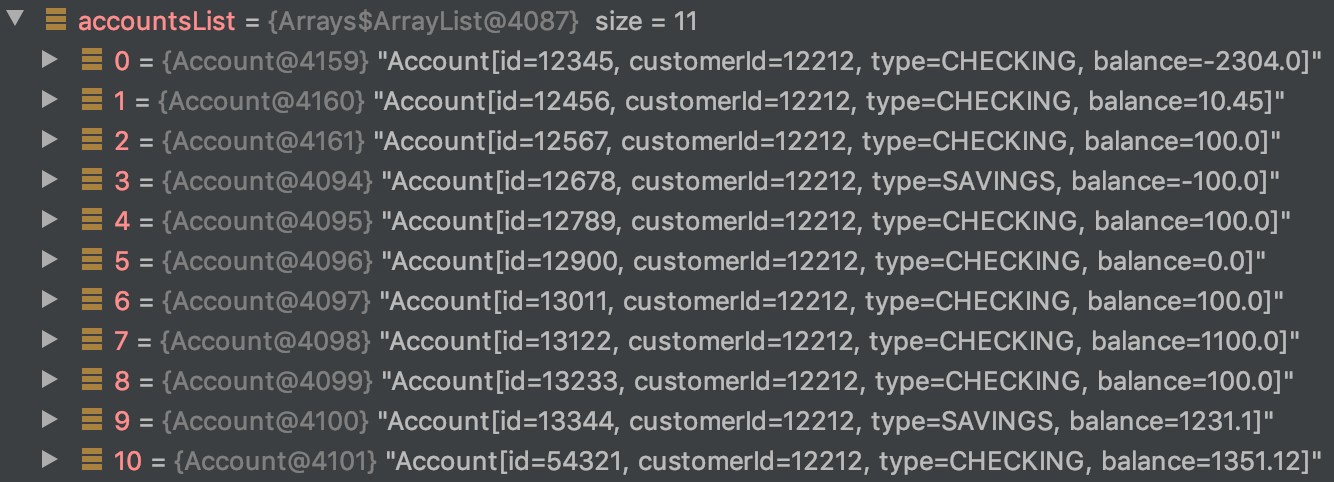
var accountsList = APIUtil.getAccounts(customerId);
var checkingAccountsList = accountsList
.stream()
.takeWhile(account -> account.type().equals("CHECKING"))
.collect(Collectors.toList());takeWhile()
var accountsList = APIUtil.getAccounts(customerId);
var checkingAccountsList = accountsList
.stream()
.takeWhile(account -> account.type().equals("CHECKING"))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
takeWhile()
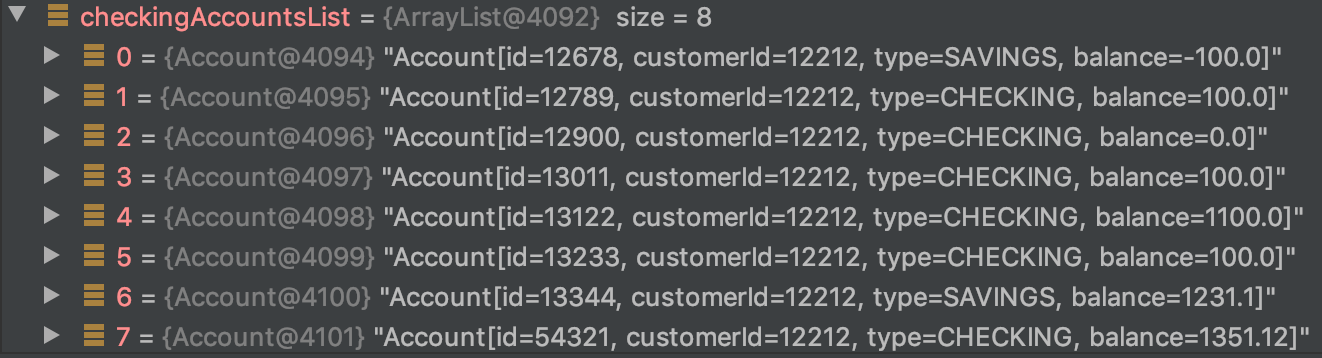
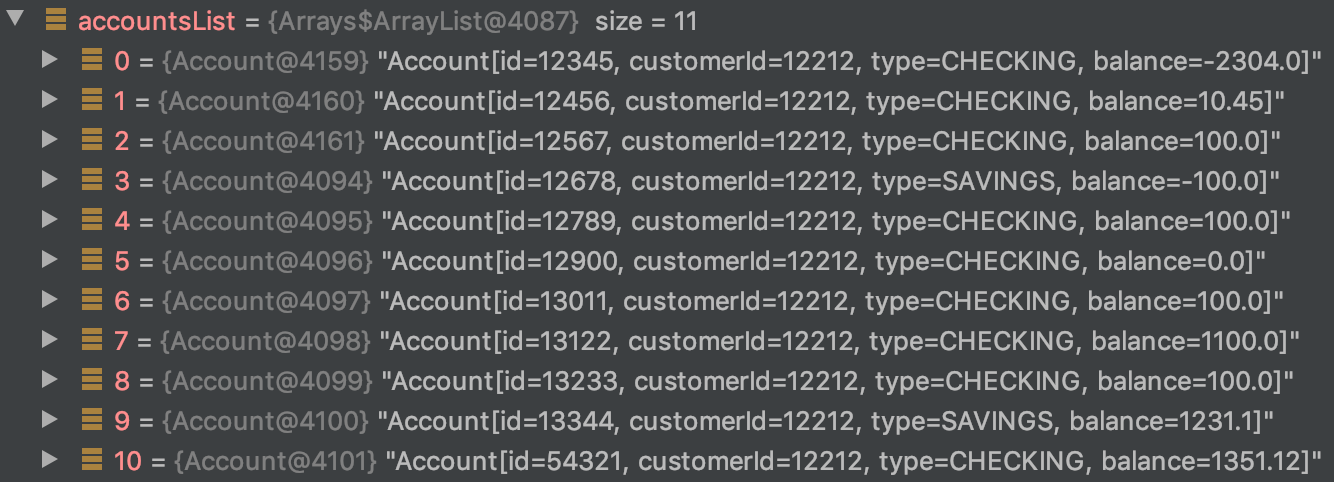
var accountsList = APIUtil.getAccounts(customerId);
var checkingAccountsList = accountsList
.stream()
.dropWhile(account -> account.type().equals("CHECKING"))
.collect(Collectors.toList());dropWhile()
var accountsList = APIUtil.getAccounts(customerId);
var checkingAccountsList = accountsList
.stream()
.dropWhile(account -> account.type().equals("CHECKING"))
.collect(Collectors.toList());dropWhile()
dropWhile()


Sort for deterministic results
var accountsList = APIUtil.getAccounts(customerId);
var checkingAccountsList = accountsList
.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Account::type))
.takeWhile(account -> account.type().equals("CHECKING"))
.collect(Collectors.toList());@techgirl1908
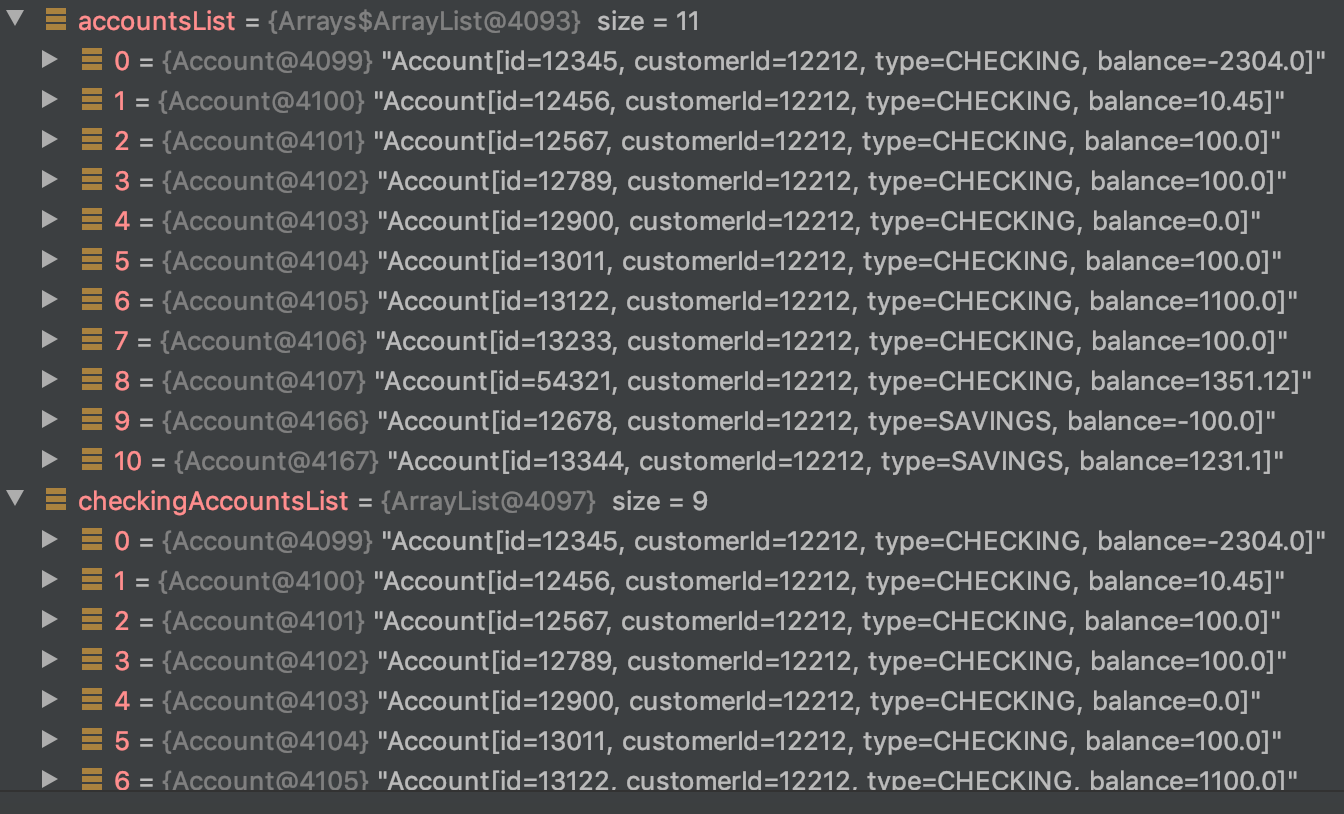
takeWhile() on sorted collection

dropWhile() on sorted collection
@techgirl1908
How does this differ from filter?
@techgirl1908
@Test
public void accountsListed() {
var accountsOverviewPage =
page.login(username, password);
var actualAccountIdsList =
accountsOverviewPage.getAccounts();
String customerId = Customers.getCustomerId(username);
var expectedAccountIdsList =
APIUtil.getAccounts(customerId)
.stream()
.map(Account::getId)
.map(String::valueOf)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
assertEquals(expectedAccountIdsList, actualAccountIdsList);
}@techgirl1908
public static String getCustomerId(String name){
String id;
switch(name){
case "john":
id = "12212";
break;
case "mary":
id = "4847474";
break;
case "tom":
id = "293743";
break;
default:
id = "";
break;
}
return id;
}@techgirl1908
SWITCH EXPRESSIONS
@techgirl1908
public static String getCustomerId(String name) {
String id = switch(name){
case "john" -> "12212";
case "mary" -> "4847474";
case "tom" -> "293743";
default -> "";
};
return id;
}public static String getCustomerId(String name){
return switch(name){
case "john" -> "12212";
case "mary" -> "4847474";
case "tom" -> "293743";
default -> "";
};
}SWITCH EXPRESSIONS
@techgirl1908
public static String getCustomerId(String name) {
return switch (name) {
case "john": yield "12212";
case "mary": yield "4847474";
case "tom" : yield "293743";
default : yield "";
};
}SWITCH EXPRESSIONS
@techgirl1908
public static String getCustomerId(String name){
return switch(name){
case "john", "demo" -> "12212";
case "mary" -> "4847474";
case "tom" -> "293743";
default -> "";
};
}SWITCH EXPRESSIONS
@techgirl1908
public static String getCustomerId(String name){
return switch(name){
case "john" -> {
System.out.println("Hi John");
yield "12212";
}
case "mary" -> "4847474";
case "tom" -> "293743";
default -> "";
};
}SWITCH EXPRESSIONS
@techgirl1908
Cannot mix and match -> and :yield
return switch(name){
case "john" -> "12212";
case "mary": yield "4847474";
case "tom" -> "293743";
default -> "";
};@techgirl1908
Can throw Exceptions
return switch(name){
case "john" -> "12212";
case "mary" -> "4847474";
case "tom" -> "293743";
default -> throw new InvalidNameException();
};@techgirl1908
When to use expressions vs statements?
@techgirl1908
@Test
public void accountsListed() {
var accountsOverviewPage =
page.login(username, password);
var actualAccountIdsList =
accountsOverviewPage.getAccounts();
String customerId = Customers.getCustomerId(username);
var expectedAccountIdsList =
APIUtil.getAccounts(customerId)
.stream()
.map(Account::getId)
.map(String::valueOf)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
assertEquals(expectedAccountIdsList, actualAccountIdsList);
}@techgirl1908
public class APIUtil {
public static List<Account> getAccounts(String customerId){
return Arrays.asList(given()
.header(new Header("Accept", "application/json"))
.get(format(GET_ACCOUNTS, customerId))
.as(Account[].class));
}
}@techgirl1908
[
{
"id": 13344,
"customerId": 12212,
"type": "CHECKING",
"balance": 4022.93
},
{
"id": 13455,
"customerId": 12212,
"type": "CHECKING",
"balance": 1000
}
]@techgirl1908
public class Account {
private int id;
private int customerId;
private String type;
private double balance;
public int getId() { return id; }
public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; }
public int getCustomerId() { return customerId; }
public void setCustomerId(int customerId) {
this.customerId = customerId;
}
public String getType() { return type; }
public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; }
public double getBalance() { return balance; }
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}@techgirl1908
public record Account(
int id,
int customerId,
String type,
double balance){}RECORDS
@techgirl1908
public record Account(
int id,
int customerId,
String type,
double balance
){
@Override
public String toString(){
return "I've overriden this!";
}
}
RECORDS
@techgirl1908
Records can be instantiated
Account account = new Account(
13344, 12212, "CHECKING", 4033.93);
@techgirl1908
Records are immutable
Account account = new Account(
13344, 12212, "CHECKING", 4033.93);
account.setType("SAVINGS");@techgirl1908
Accessors don't start with get
Account account = new Account(
13344, 12212, "CHECKING", 4033.93);
double balance = account.balance();@techgirl1908
Inheritance is not supported.
record CheckingAccount() extends Accounts
{
}@techgirl1908
Records can implement interfaces
@techgirl1908
public interface AccountInterface {
void someMethod();
}
public record Account(
int id,
int customerId,
String type,
double balance) implements AccountInterface
{
public void someMethod(){
}
}@techgirl1908
@Test
public void accountsListed() {
var accountsOverviewPage =
page.login(username, password);
var actualAccountIdsList =
accountsOverviewPage.getAccounts();
String customerId = Customers.getCustomerId(username);
var expectedAccountIdsList =
APIUtil.getAccounts(customerId)
.stream()
.map(Account::getId)
.map(String::valueOf)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
assertEquals(expectedAccountIdsList, actualAccountIdsList);
}@techgirl1908
[
{
"id": 13344,
"customerId": 12212,
"type": "CHECKING",
"balance": 4022.93
},
{
"id": 13455,
"customerId": 12212,
"type": "CHECKING",
"balance": 1000
}
]@techgirl1908
String response =
"[\n" +
" {\n" +
" \"id\": 13344,\n" +
" \"customerId\": 12212,\n" +
" \"type\": \"CHECKING\",\n" +
" \"balance\": 4022.93\n" +
" },\n" +
" {\n" +
" \"id\": 13455,\n" +
" \"customerId\": 12212,\n" +
" \"type\": \"CHECKING\",\n" +
" \"balance\": 1000\n" +
" }\n" +
"]"; @techgirl1908
public String getAccounts_mocked(){
return """
[
{
"id": 13344,
"customerId": 12212,
"type": "CHECKING",
"balance": 3821.93
},
{
"id": 13455,
"customerId": 12212,
"type": "LOAN",
"balance": 989
}
]
""";
}TEXT BLOCKS
@techgirl1908
Text cannot begin on
same line as """
System.out.println(""" Hey y'all! """);
System.out.println("""
Hey y'all!""");
System.out.println("""
Hey y'all!
"""); @Test
public void accountsListed() {
var accountsOverviewPage =
page.login(username, password);
var actualAccountIdsList =
accountsOverviewPage.getAccounts();
String customerId = Customers.getCustomerId(username);
var expectedAccountIdsList =
APIUtil.getAccounts(customerId)
.stream()
.map(Account::getId)
.map(String::valueOf)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
assertEquals(expectedAccountIdsList, actualAccountIdsList);
}@techgirl1908
public static List<String> getAccountIds_mocked(){
return Arrays.asList("13344", "13455", "13566", "14010");
}public static List<String> getAccountIds_mocked(){
return List.of("13344", "13455", "13566", "14010");
}COLLECTION CONVENIENCE METHOD
@techgirl1908
Map users = new HashMap();
users.put("john", 123);
users.put("alice", 456);
users.put("sue", 789);Map users = Map.of("john", 123, "alice", 456, "sue", 789);COLLECTION CONVENIENCE METHOD
@techgirl1908
The of() method creates immutable collections
@techgirl1908
Map users = Map.of(
"john", 123,
"alice", 456,
"sue", 789);users.put("bob", 000);users.remove("alice");COLLECTION CONVENIENCE METHOD
@techgirl1908
Thank you!
@techgirl1908
Beyond Java 8
Angie Jones
https://angiejones.tech
https://TestAutomationU.com
@techgirl1908
Java Champion
Senior Director, Developer Relations
Applitools & Test Automation University
