Quantum Monte Carlo approaches for strongly correlated systems
Variational Monte Carlo
Stochastic multireference perturbation theory
Auxiliary field QMC



Outline
- Sampling and the sign problem in AFQMC
- Reducing noise using selected CI wave functions
- Convergence of phaseless errors
- Jastrow symmetry projected states in VMC
- Auxiliary field QMC
- Variational MC
- Ongoing work
Free projection QMC
Projection QMC methods:
- Better \(|\psi\rangle\) approximates \(|\Psi_0\rangle\), faster the convergence with \(\tau\)
Mixed energy estimator:
Trial states: Selected CI, CCSD, Jastrow, MPS, ...
- Noise in QMC sampling worsens exponentially with \(\tau\)
Sampling in AFQMC
Exponentiating \(\hat{H}\): \([\hat{K}, \hat{V}] \neq 0\)
- Exponentiating \(\hat{K}\): orbital transformation
where \(|\phi\rangle\) and \(|\phi'\rangle\) are nonorthogonal determinants.
- Exponentiating \(\hat{V} = \frac{1}{2}\sum_{\gamma} \left(L^{\gamma}_{pr}\hat{a}_p^{\dagger}\hat{a}_r\right)^2\):
\(x_{\gamma}\): auxiliary field
Motta and Zhang (2017), 1711.02242
(Thouless, 1960)
(Stratonovich, 1957)
Sample Gaussian auxiliary fields \(X\), propagate, and measure
CCSD as \(|\psi_r\rangle\): sampling Slater determinants from CCSD
commuting ph excitations \(\rightarrow\) no Trotter error


\((\text{H}_2\text{O})_2\), (16e, 80o)
The sign problem

Contour shift:
In AFQMC:
Baer, Head-Gordon, Neuhauser (1998)


Zero variance principle
If \(|\psi_l\rangle\) is the exact ground state, then \(N\) and \(D\) are perfectly correlated, \(\langle\psi_0|\hat{H}|\phi_i\rangle = E_0 \langle\psi_0|\phi_i\rangle\), and the energy estimator has zero variance. More accurate \(|\psi_l\rangle\ \rightarrow\ \) higher \(\text{Cov}(N, D)\).

\((\text{H}_2\text{O})_2\), (16e, 80o)
Selected configuration interaction: put the most important configurations in the state using particle-hole excitations and diagonalize

Selected CI local energy algorithm
If \(|\psi_l\rangle\) is a Slater determinant: \(|\psi_l\rangle = |\psi_0\rangle\)
If \(|\psi_l\rangle\) is a selected CI wave function: \(|\psi_l\rangle = \sum_i^{N_d} c_i |\psi_i\rangle\)
Naive way: calculating local energy of each Slater determinant as above costs \(O(N_dN^4)\)



Generalized Wick's theorem

consider \(|\psi_l\rangle = c_{ptqu}\hat{a}_t^{\dagger}\hat{a}_p\hat{a}_u^{\dagger}\hat{a}_q|\psi_0\rangle\) (double excitations)
\(O(N^4 + N_dN)\)

\((\text{H}_2\text{O})_2\), (16e, 80o)
\([\text{Cu}_2\text{O}_2]^{2+}\) isomerization


kcal/mol

Phaseless AFQMC

\(\text{H}_{50}\) (50e, 50o)
Gets rid of the sign problem, but has a systematic trial dependent bias
Active space trial states

\(\text{H}_{10}\) (10e, 50o)
Outline
- Sampling and the sign problem in AFQMC
- Reducing noise using selected CI wave functions
- Convergence of phaseless errors
- Jastrow symmetry projected states in VMC
- Auxiliary field QMC
- Variational MC
- Ongoing work
Variational Monte Carlo (VMC)
Strategy:
- Parametrize the wave function: \(|\psi(\mathbf{p})\rangle\), choose initial \(\mathbf{p}\)
- Calculate energy and gradient: Markov chain Monte Carlo
- Optimize: smart gradient descent to change parameters

Ground state minimizes
McMillan (1965)
Symmetry projection in VMC
Symmetry breaking \(\rightarrow\) more variational freedom
Projection in VMC by restricting random walk to the symmetry sector

Correlates doublons and holons, can describe Mott insulating behavior
Symmetries: spin, complex conjugation, number, ...
Break the symmetry under a projector, to retain good quantum numbers
Jastrow factor:
| d (Bohr) | Exact (DMRG) | Jastrow-KSzPfaffian | Green's function MC |
| 1.6 | -0.5344 | -0.5337 | -0.5342 |
| 1.8 | -0.5408 | -0.5400 | -0.5406 |
| 2.5 | -0.5187 | -0.5180 | -0.5185 |
H\( _{50} \) linear chain (50e, 50o)
Hartree/particle
| U/t | Benchmark energy | Jastrow- KSzGHF |
Green's function MC |
| 2 | -1.1962 | -1.1920 | -1.1939 |
| 4 | -0.8620 | -0.8566 | -0.8598 |
| 8 | -0.5237 | -0.5183 | -0.5221 |
2D Hubbard: 98 sites (half filling)

Density-density correlation function: 18 site 2D Hubbard model (\(U/t=4\))
Outline
- Sampling and the sign problem in AFQMC
- Reducing noise using selected CI wave functions
- Convergence of phaseless errors
- Jastrow symmetry projected states in VMC
- Auxiliary field QMC
- Variational MC
- Ongoing work
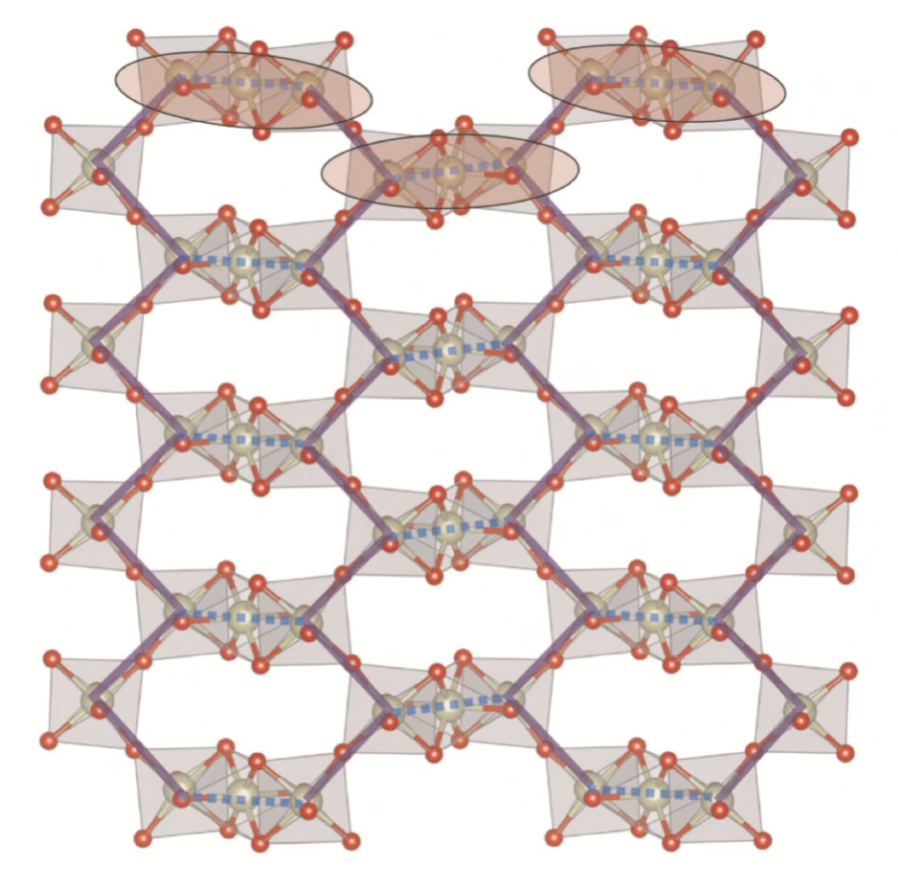
Quantum spin liquid in \(\text{Ba}_4\text{Ir}_3\text{O}_{10}\)?
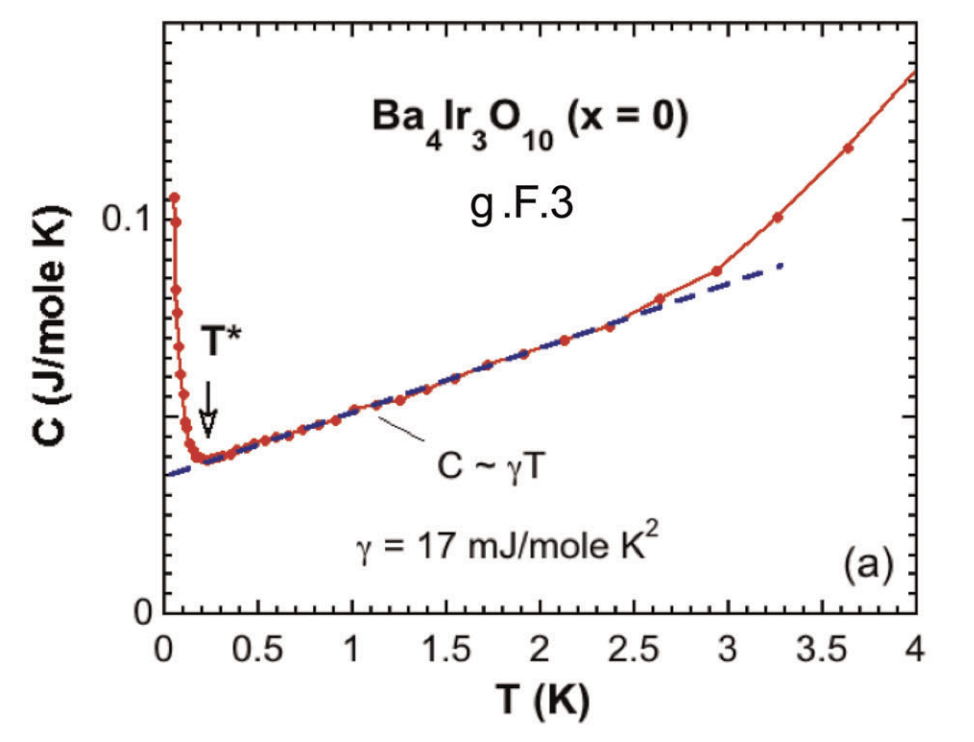
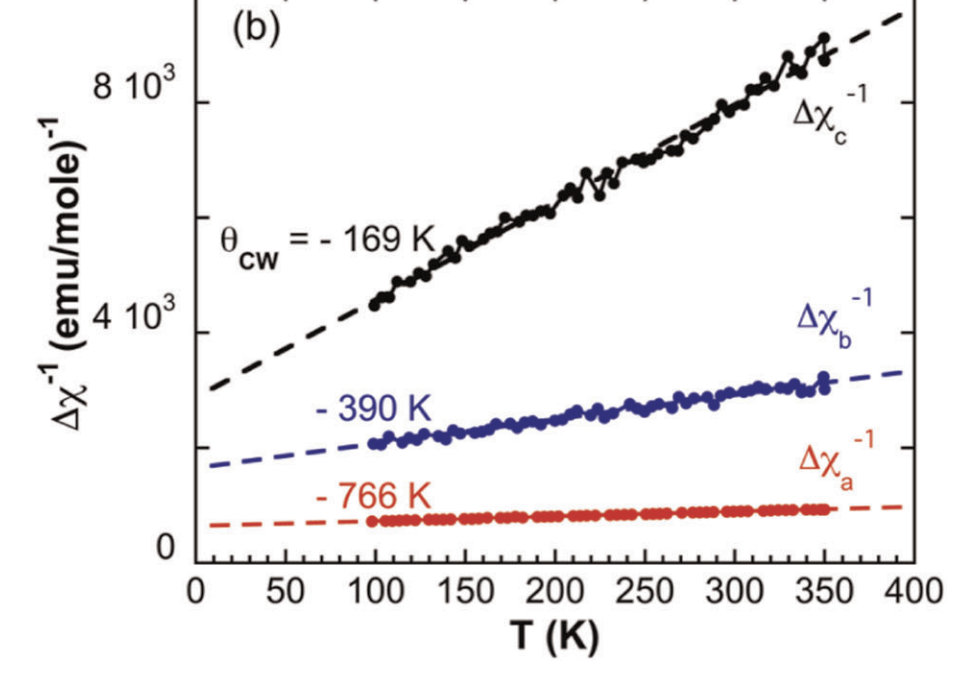
inverse susceptibility
heat capacity
- Insulator with T-linear heat capacity
- Interactions ~ 500 K but orders at 0.2 K
- 2D but not geometrically frustrated
G. Cao, et al. (2020) 1901.04125
Ab initio wave function calculations
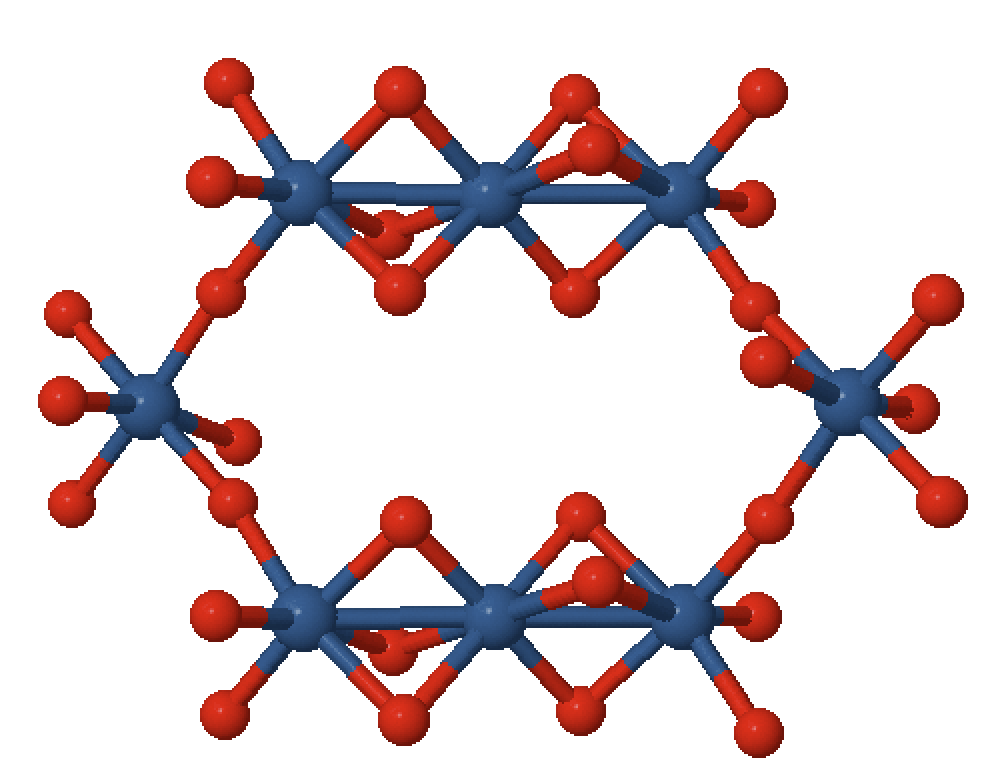
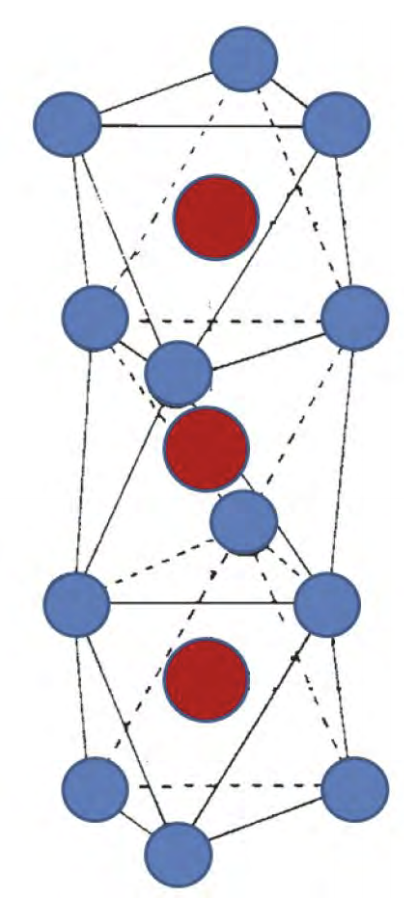
Face shared octahedra
Calculating valence electron wave functions for embedded clusters including all relevant interactions
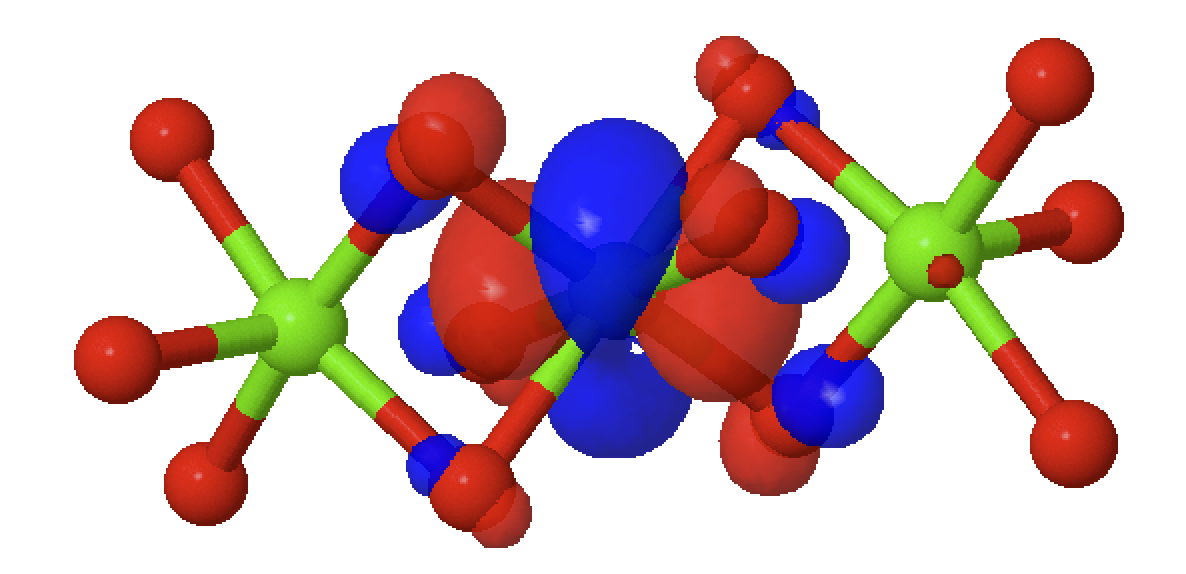
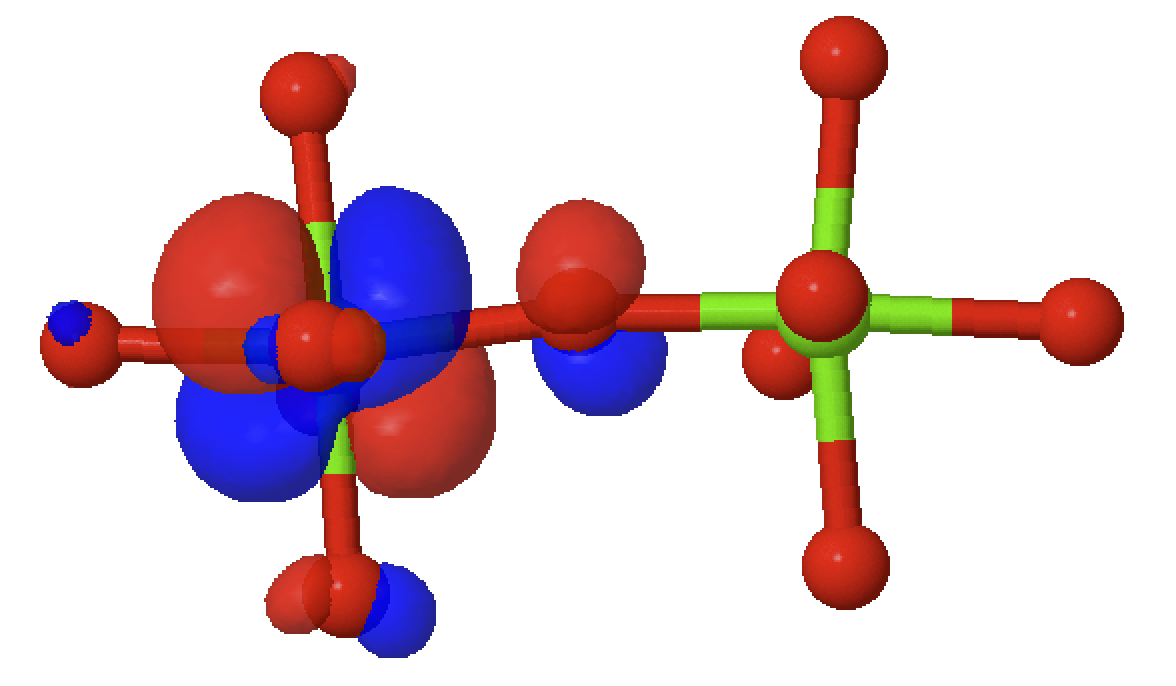
Low lying energy levels:
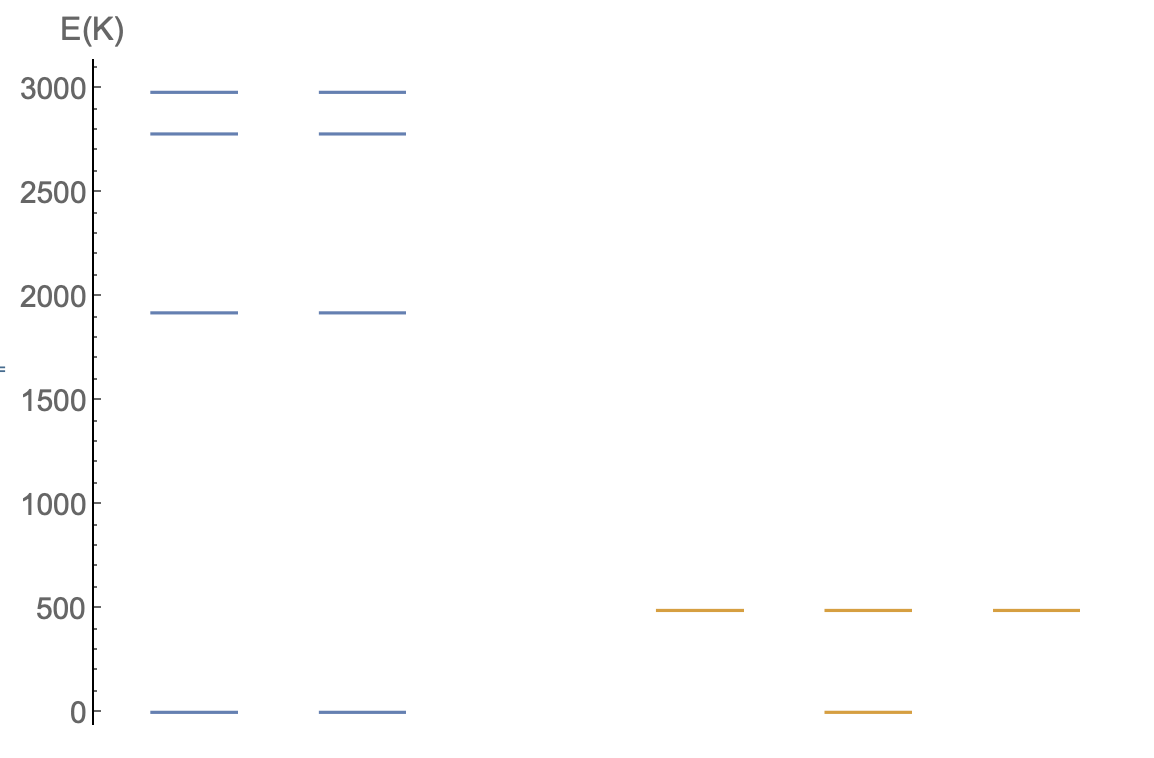
Face shared
Corner shared
Different descriptions
Electron model:
\(H = t_{ij}c_i^{\dagger}c_j +v_{ijkl}c_i^{\dagger}c_j^{\dagger}c_lc_k + \dots\)
Spin model:
\(H = J_{ij}\mathbf{S}_i.\mathbf{S}_j + J_{ijkl}(\mathbf{S}_i.\mathbf{S}_j)(\mathbf{S}_k.\mathbf{S}_l) + \dots \)
Parton theory:
\(H = t_{ij}f_i^{\dagger}A_{ij}f_j + \dots\)
Future directions
- Properties and excited states
- Importance sampling and constraints in AFQMC, hybrid MD-MC
- Variational CCSD, other wave functions like MPS, Jastrow in AFQMC
- Spin liquid states in iridates using VMC