Accurate trial wave functions in AFQMC
Motivation
Projection QMC methods:
Better \(|\psi\rangle\) approximates \(|\psi_0\rangle\), faster the convergence with \(\tau\)
Energy estimator:
Outline
- Sampling in AFQMC
- The sign problem in AFQMC and contour shift
- Reducing noise using selected CI wave functions and efficient local energy evaluation
- Benchmark results
review paper: Motta and Zhang, arXiv:1711.02242
Sampling in AFQMC
Exponentiating \(\hat{H}\): \([\hat{K}, \hat{V}] \neq 0\)
- Exponentiating \(\hat{K}\): orbital transformation
where \(|\phi\rangle\) and \(|\phi'\rangle\) are nonorthogonal determinants.
- Exponentiating \(\hat{V} = \frac{1}{2}\sum_{\gamma} \left(L^{\gamma}_{pr}\hat{a}_p^{\dagger}\hat{a}_r\right)^2\):
\(x_{\gamma}\): auxiliary field
Sample Gaussian auxiliary fields \(X\), propagate, and measure
CCSD as \(|\psi_r\rangle\): sampling Slater determinants from CCSD
commuting ph excitations \(\rightarrow\) no Trotter error


The sign problem

Contour shift:
In AFQMC:
Baer, Head-Gordon, Neuhauser (1998)


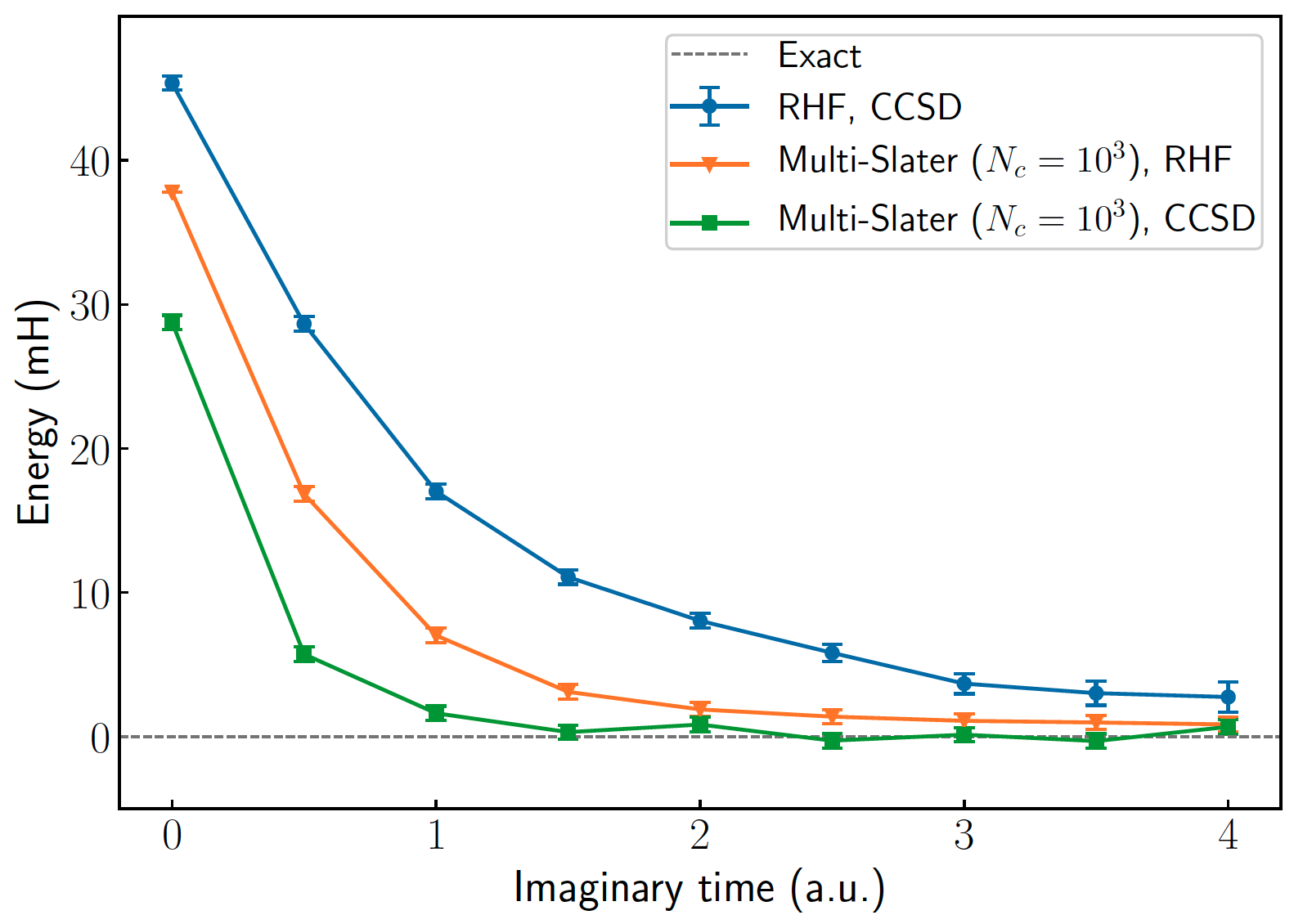
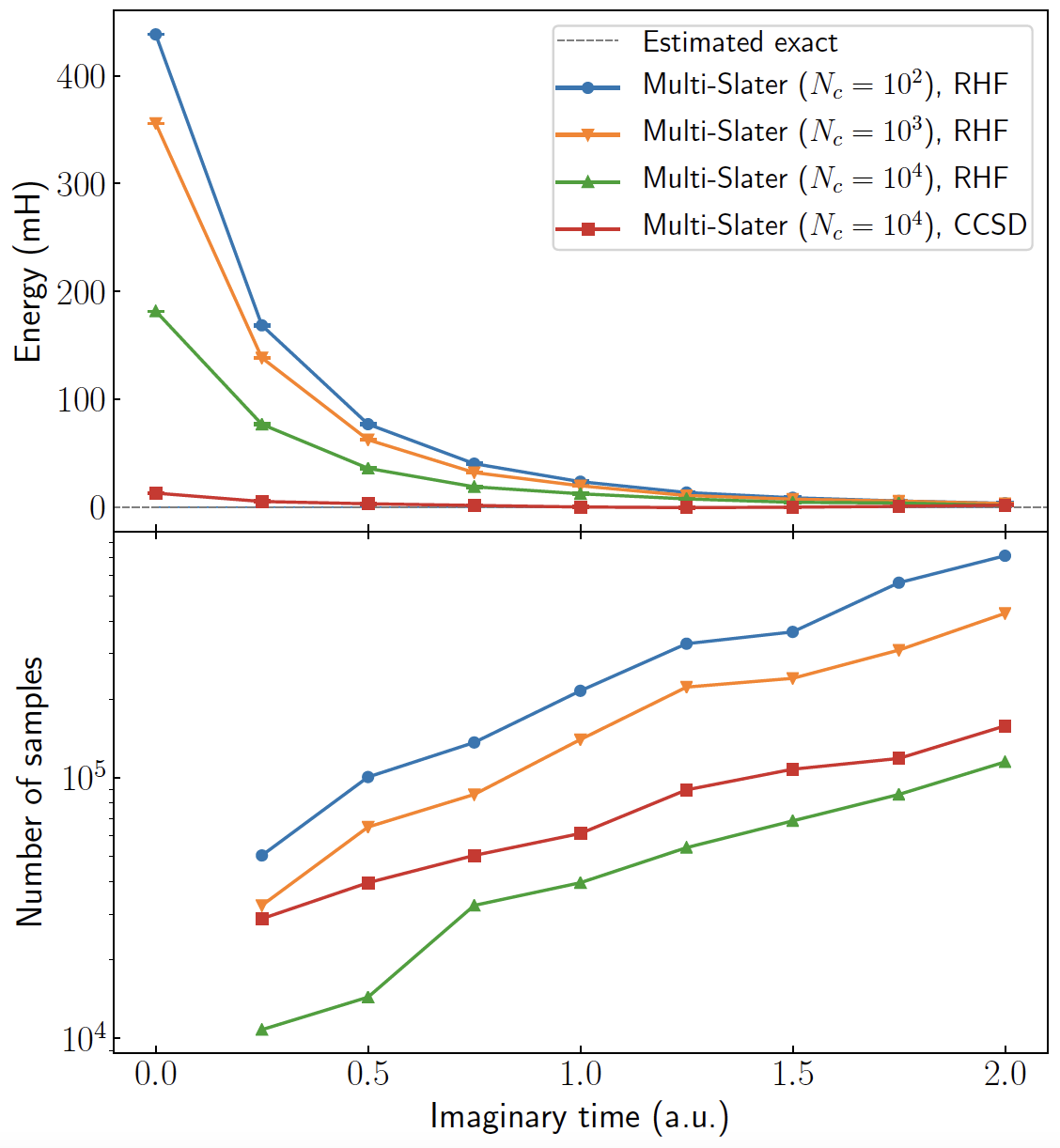
Selected CI trial state as \(|\psi_l\rangle\)
Zero variance principle: If \(|\psi_l\rangle\) is the exact ground state, then \(N\) and \(D\) are perfectly correlated, \(\langle\psi_0|\hat{H}|\phi_i\rangle = E_0 \langle\psi_0|\phi_i\rangle\), and the energy estimator has zero variance.
More accurate \(|\psi_l\rangle\ \rightarrow\ \) higher \(\text{Cov}(N, D)\)

Efficient local energy algorithm
If \(|\psi_l\rangle\) is a Slater determinant: \(|\psi_l\rangle = |\phi_0\rangle\)
If \(|\psi_l\rangle\) is a selected CI wave function: \(|\psi_l\rangle = \sum_i^{N_d} c_i |\phi_i\rangle\)
Naive way: calculating local energy of each Slater determinant as above costs \(O(N_dN^4)\)
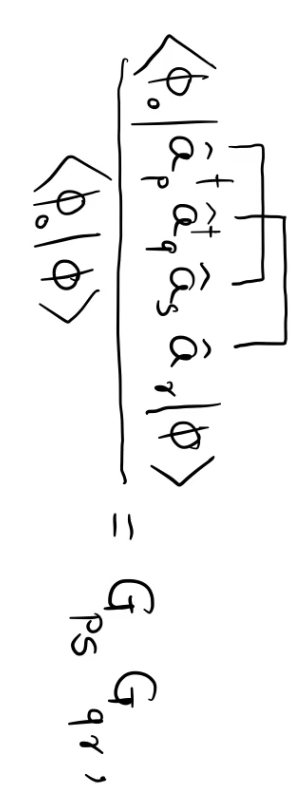
One of the terms:
Determinants in the CI expansion are related by ph excitations \(\ \rightarrow\ \) some repeated work
Consider doubly excited determinants: \(c_{jkil} \hat{a}_j^{\dagger} \hat{a}_k \hat{a}_i^{\dagger} \hat{a}_l |\phi_0\rangle\)

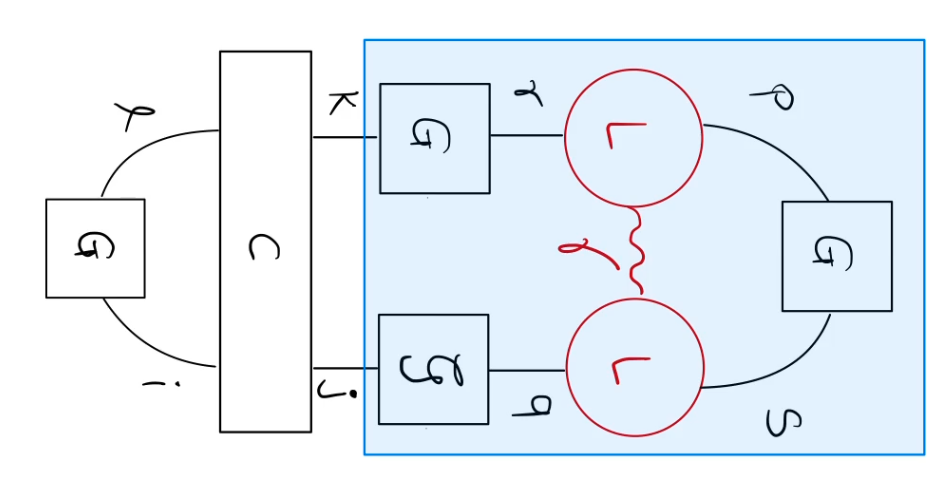
One of the terms:
store intermediate
Overall scaling: \(O(N^4 + N_dN)\)

Filippi, Assaraf, Moroni (2016)
Organic molecules
Benzene: ground state energy in Hartree
| Method | DZ (30e, 108o) | TZ (30e, 258o) |
|---|---|---|
| CCSD(T) | -231.5813 | -231.8058 |
| DMRG | -231.5846(7) | - |
| SHCI | -231.586(2) | - |
| AS-FCIQMC | -231.5855(3) | - |
| ph-AFQMC (RHF) | -231.5879(4) | -231.8122(4) |
| fp-AFQMC | -231.5851(7) | -231.809(1) |
Cyclobutadiene automerization barrier (kcal/mol)
| Method | DZ (20e, 72o) | TZ (20e, 172o) |
|---|---|---|
| CCSD(T) | 15.8 | 18.2 |
| CCSDT | 7.6 | 10.6 |
| TCCSD (12,12) | - | 9.2 |
| MRCI+Q | - | 9.2 |
| fp-AFQMC | 8.4(4) | 10.2(4) |
\([\text{Cu}_2\text{O}_2]^{2+}\) isomerization


kcal/mol

Future directions
- Properties and excited states
- Importance sampling and constraints
- Embedding approaches
- Relativistic Hamiltonians
- Variational CCSD using similarity transformed Hamiltonian, other wave functions like MPS