The Digital Loonie
Canadian Cash for the 21st Century
Authors:
Date:


Andreas Veneris, Andreas Park, Fan Long, Poonam Puri
February 10, 2021
Some background: Why are we talking about digital money?
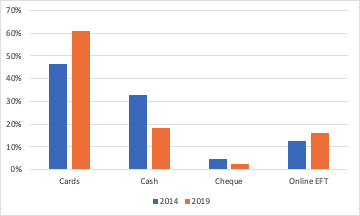
The usage of cash is declining
So what?
- 99% of adult Canadians have a bank account \(\to\) access to electronic payments
- cash is dirty \(\to\) COVID risk
- cash is risky for businesses and can be stolen
- cash requires a detour via an ATM
\(-38\%\)
But then \(\ldots\)
- If they have access to cards, why use cash?
- CBA: 70% pay off credit card each month \(\to\) 30% have an expensive balance
- Cash helps to curb spending.
- Cash helps to avoid fees.
- People live in remote communities.
- Cash allows you to do commerce without a third party.
- Cash is anonymous.
- Cash is universally available and accepted.
Canadians continue to have a preference for cash
What's on the horizon?
- Digitization of the economy
- Micro (sub-penny) payments?
- How can cash users participate?
- Tracking is everywhere
- How can users avoid retain privacy of how they pay for things?
- New types of money
- Displacement of the loonie?





The Internet of Things

There is a strong case to give Canadians the means to participate in the digital economy with cash-like privacy
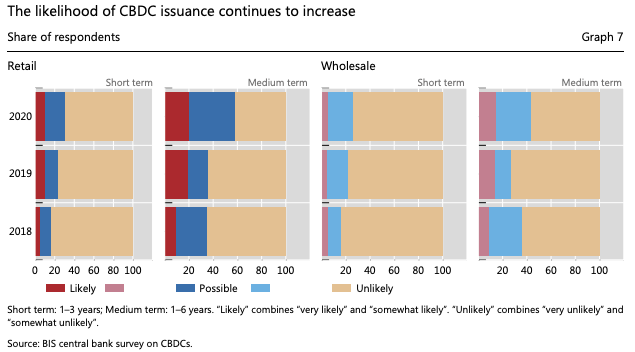
What's a CBDC?
What is a Central Bank-issued Digital Currency ?
not a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin!
"normal" liability on central banks balance sheets
Two types:
General Purpose/Retail
Wholesale/InterBank
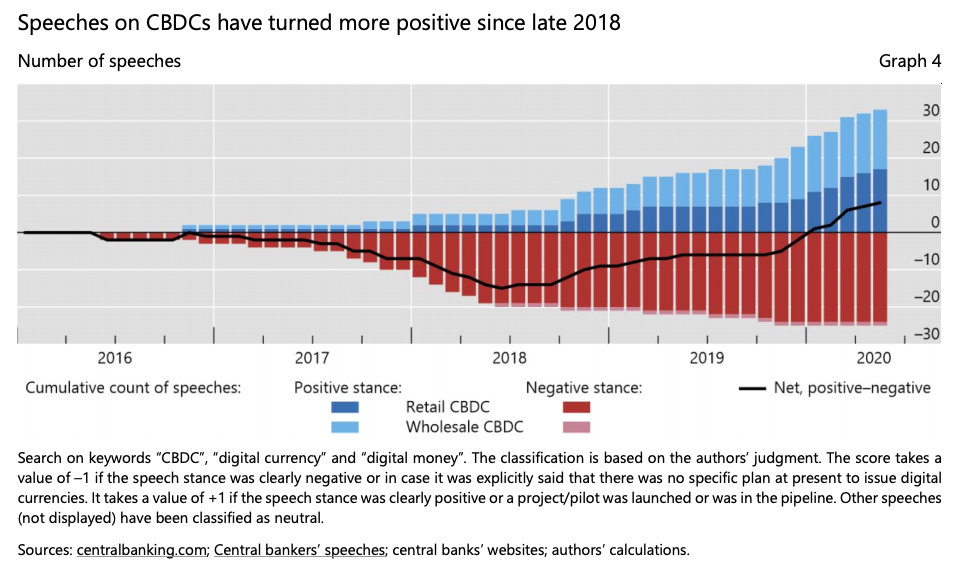
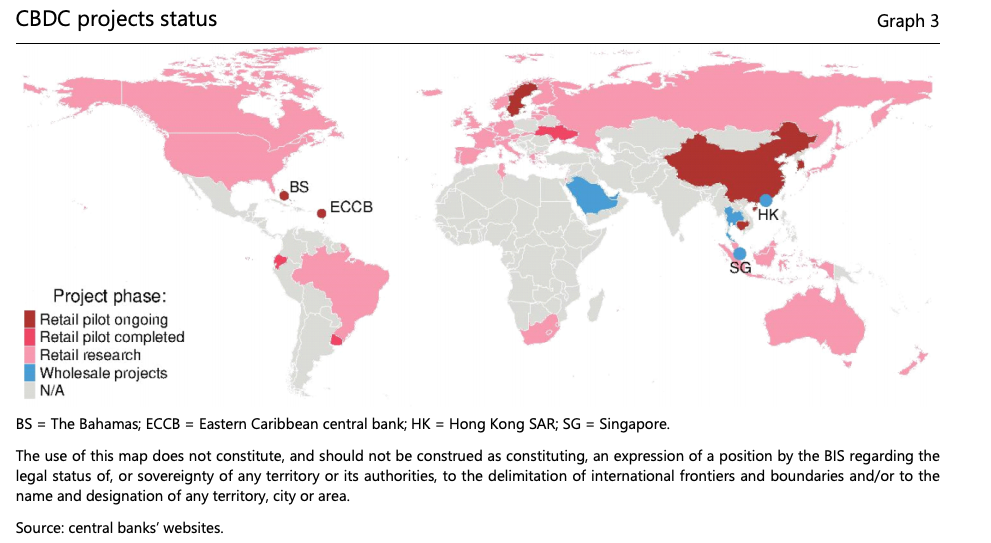
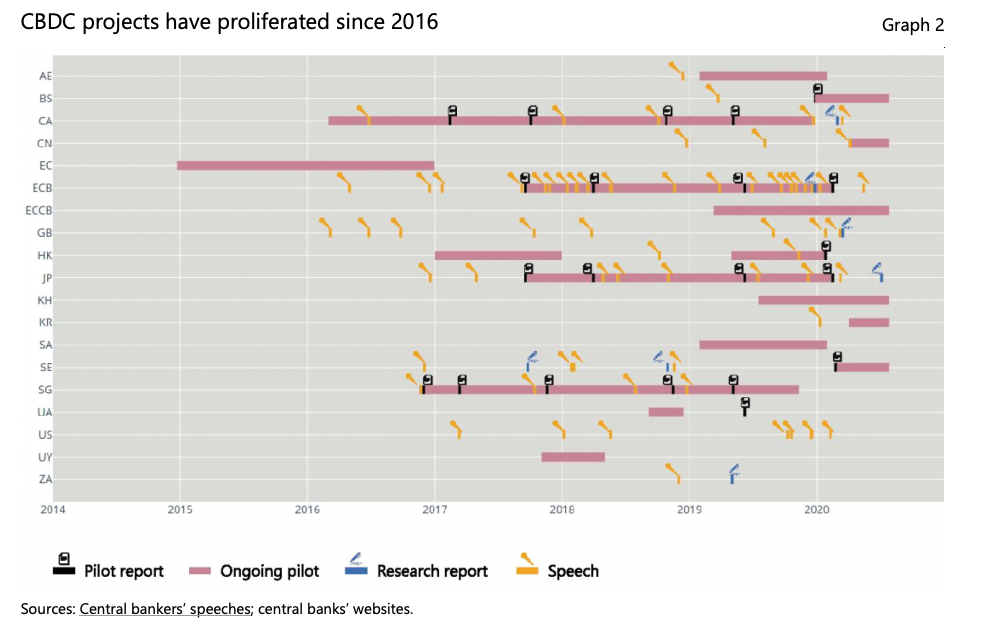
Source: BIS Working Papers No 880 "Rise of the central bank digital currencies: drivers, approaches and technologies" by Raphael Auer, Giulio Cornelli and Jon Frost
CBDC History
-
BIS Jan 2019: "Proceed with caution"
-
BIS Jan 2020: "Impeding Arrival"
-
BIS Jan 2021: "Ready-steady-go?"
Is it coming?
- the use of bank notes were to continue to decline to a point where Canadians no longer had the option of using them for a wide range of transactions; or
- one or more alternative digital currencies—likely issued by private sector entities—were to become widely used as an alternative to the Canadian dollar as a method of payment, store of value and unit of account.
The Bank of Canada has thought about this for years
Contingency Planning for a Central Bank Digital Currency February 2020
The BoC will consider issuing a CBDC if:
When \(\not=\) How!
Disclaimer: the Bank of Canada has no current plans to issue a CBDC
- The Bank has been doing research on general-purpose CBDCs for years.
- To dot the i's and cross the t's they sought external ideas from universities: the Model X Challenge/Competition.
- Three proposals were selected. This presentation is about ours.
The Bank of Canada Model X Challenge
Disclaimer: the Bank of Canada has no current plans to issue a CBDC
Our Proposal for a Digital Loonie
Our Proposal in a Nutshell Model X Challenge
Phase 1: centralized ledger
- e-KYC with public services and existing private sector solutions
- establishing a new entity process transaction: the "Narrow Bank" (NB)
- include offline token-based CBDL-cash cards
Phase 2: expand into blockchain
- public infrastructure to enable private sector innovation
- Phase 1 tech as backbone
- NB as "special power node" that can system can collapse to
key attributes
- efficient use of existing resources in e-KYC
- protects privacy yet AML/CFT compliant
- achieves objectives of universal access, privacy, competition



user obtains wallet












registers wallet address via e-KYC


- authenticator adds the public key to whitelist
- mapping person \(\leftrightarrow\) wallet stays with authenticator



NB processes transactions among whitelisted wallets quasi-anonymously
Step 1: e-Know-Your-Customer

issues transaction instructions









- signs transaction
- sends authentication request
- sends transaction instructions




checks
- signature
- whitelist
- balance












( )
( )

initiates wallet transfer



record keeping and AML/CFT processing



Step 2: Anatomy of CBDL Transfer




each offline card is linked to a KYC-ed user/e-wallet

NB transfers CBDL with serial numbers to the card




user pays offline








user pays offline
user pays offline
user pays offline
Step 2b: Anatomy of an Offline CBDL Transfer






user initiates transfer from card to e-wallet

user initiates transfer from e-wallet to card


LVTS/
Lynx




consumers can initiate EFTs from chequing account at commercial bank to CBDL wallet at NB
existing payments system facilitates transfers to CBDL system





NB has reserve account at BoC to link with commercial banks







NB handles all
CBDL payments
How our system fits with the legacy system
The Stage 2: DLT
overnight house- keeping







*
service example: internal payment-reward system


service example: small business bookkeeping









NB transitions into a validator node



a
b
c
d
e
f
g



blockchain network with validators and nodes






Summary
Central Bank-issued Digital Loonie as a common infrastructure
provide a public good that enables Canadians to participate in the digital economy without being subjected to third-party commercial interests
e-KYC using existing resources
two-stage process
Stage 1: do-it-alone to kickstart
Stage 2: enable private sector innovation