Crypto Trading:
Centralized Platforms
Instructor: Andreas Park





















Broker


Exchange
Internalizer
Wholeseller
Darkpool


Venue



Settlement
DeFi Overview
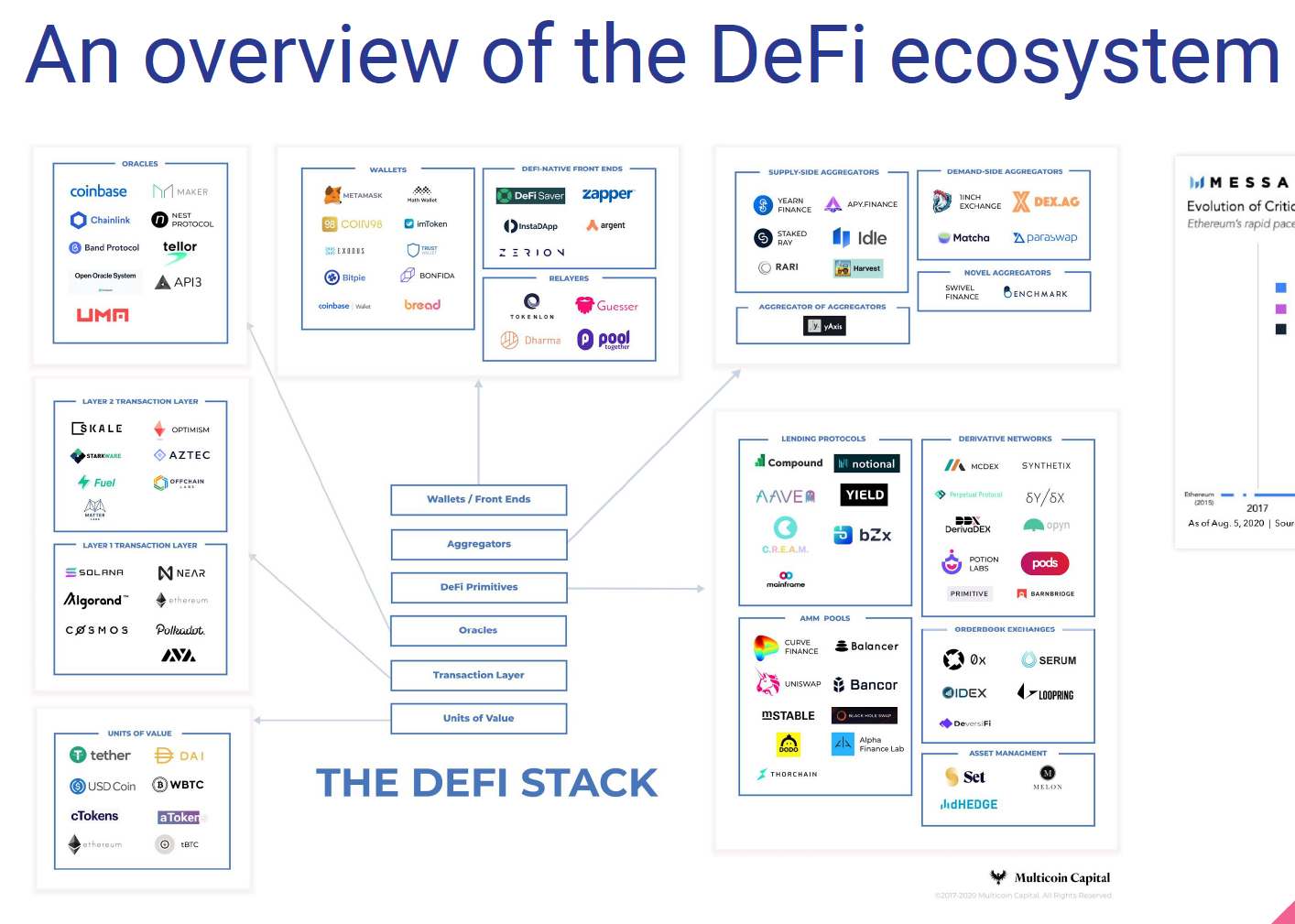



Overview of Traditional Trading
trading Infrastructure
payments network
Stock Exchange
Clearing House
custodian
custodian
beneficial ownership record
seller
buyer
Broker
Broker










Types of traders
Trading in Equity Markets today







Retail
Institutional
Pro-Traders
high volume securities
low volume securities
50%
50-60%
0%
30-40%
40-50%
10-20%
Summary of workflow


Exchange
Traditional


Internalizer
Wholeseller
Darkpool





Investor
Venue
Broker
Settlement





Exchanges
Wholesellers
Dark pools


Broker Internalizations



Where does trading occur?
Trading in Equity Markets today

Exchanges
Wholesellers
Dark pools
Broker Internalizations
How does trading work?
Trading in Equity Markets today

(
(

How to access the market?
Trading in Equity Markets today



Retail
Institutional
Pro-Traders


Retail: Canada
Trading in Equity Markets today





Rule: must send to exchange with best price
Retail: U.S.A.
Trading in Equity Markets today






Exchange
Wholeseller
market order
limit order
In Europe: no best price obligation
Institutions: U.S.A.
Trading in Equity Markets today





Exchange
Dark pools



Pro Traders
Trading in Equity Markets today

Type 2: "borrow" broker-dealer system


Type 1: licenced broker-dealer
risk control
Big Message
Trading in Equity Markets today



-
You commonly don't access the market directly.
-
Brokers take many decisions but they are bound by regulations.
-
Critical: markets are formally linked by best-price rules.
Crypto Trading Overview
Three Fallacies for Crypto Economics
crypto assets = traditional equities
crypto trading = traditional trading
crypto entities = traditional firms
Types of traders
Trading in Equity Markets today

Retail
Institutional
Pro-Traders
high volume securities
low volume securities
50%
50-60%
0%
30-40%
40-50%
10-20%
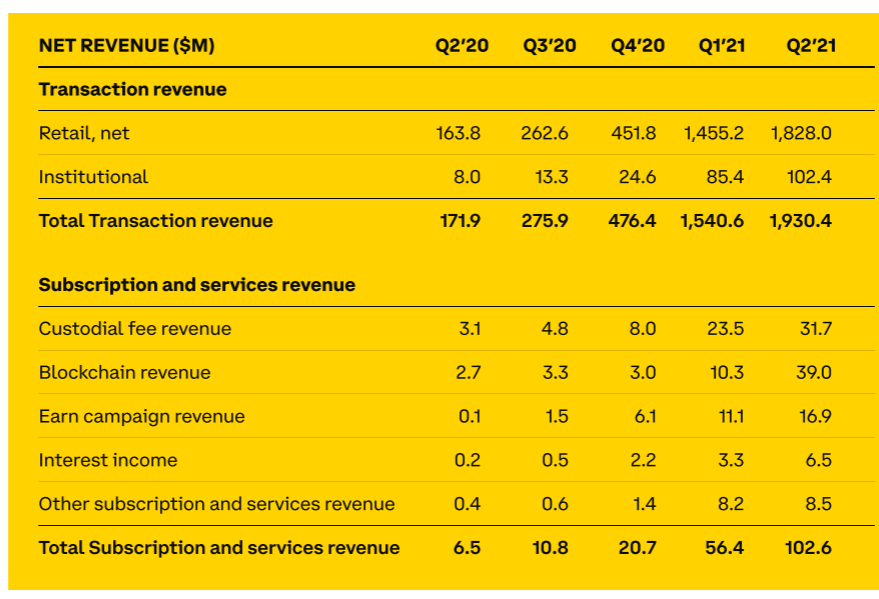
Coinbase's recent numbers
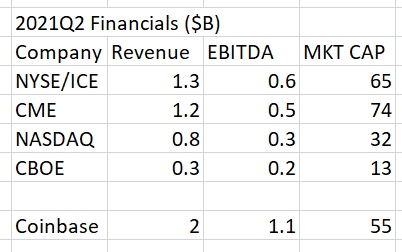
Coinbase's recent numbers
Some Stylized Facts on Crypto Trading
How many CEXes are there?

(307 CEX, rest DEX)


What are the differences?
What do they trade?
Link to traditional finance?
- spot trading
- derivatives
- crypto-only
- "fiat" linked
- regulation
- cryptos traded
- accessibility
- privacy
- credibility
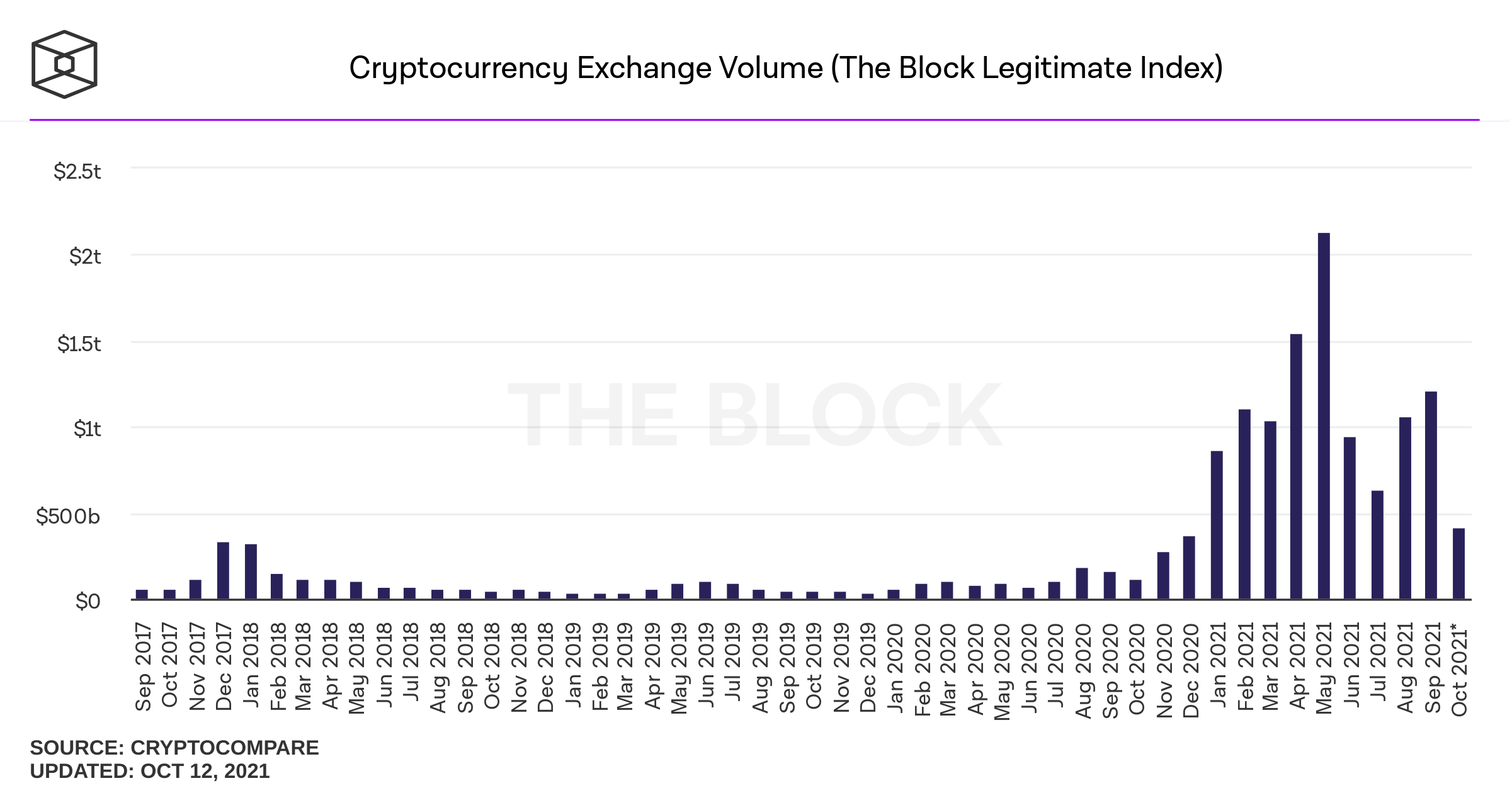
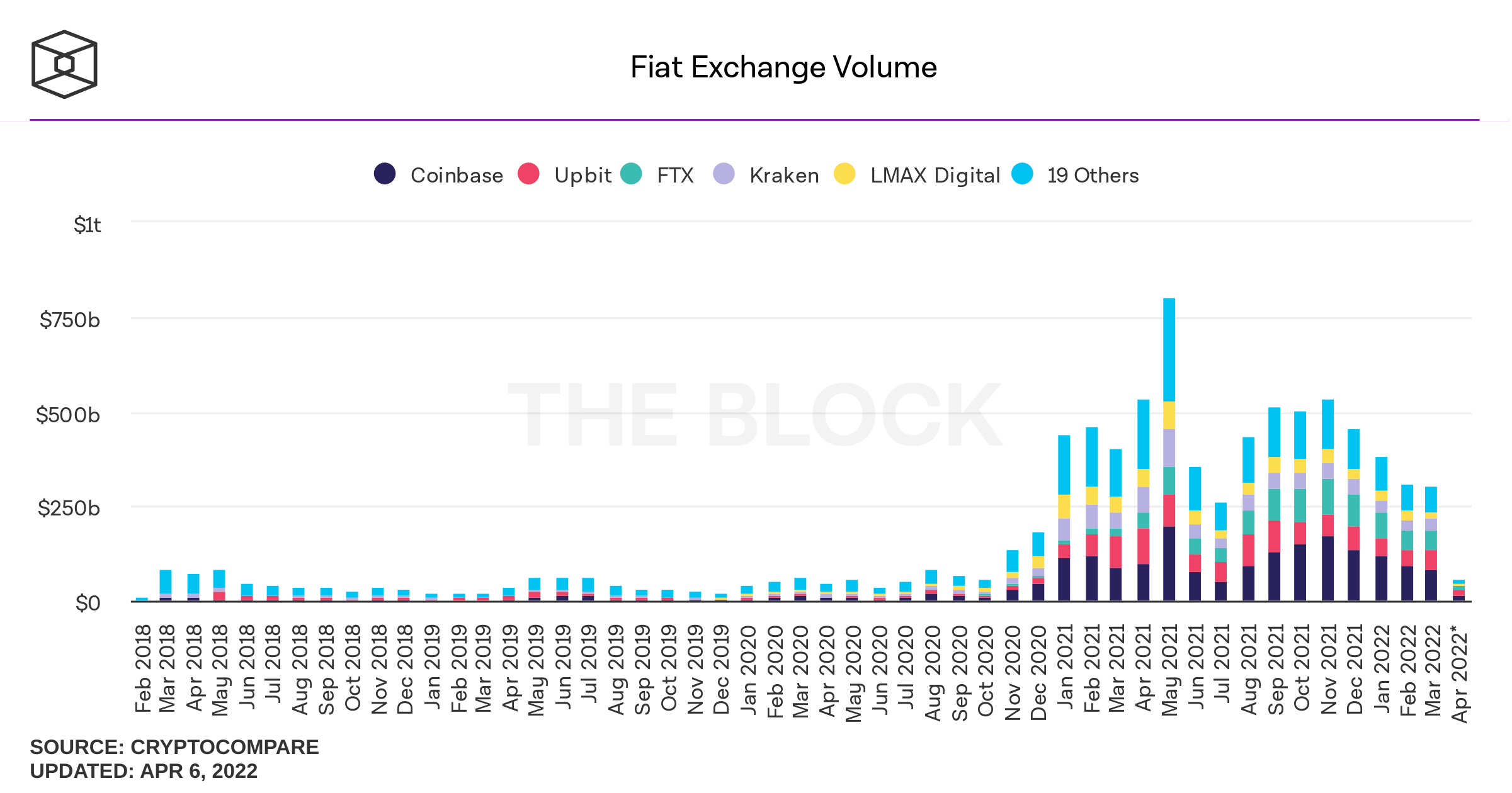
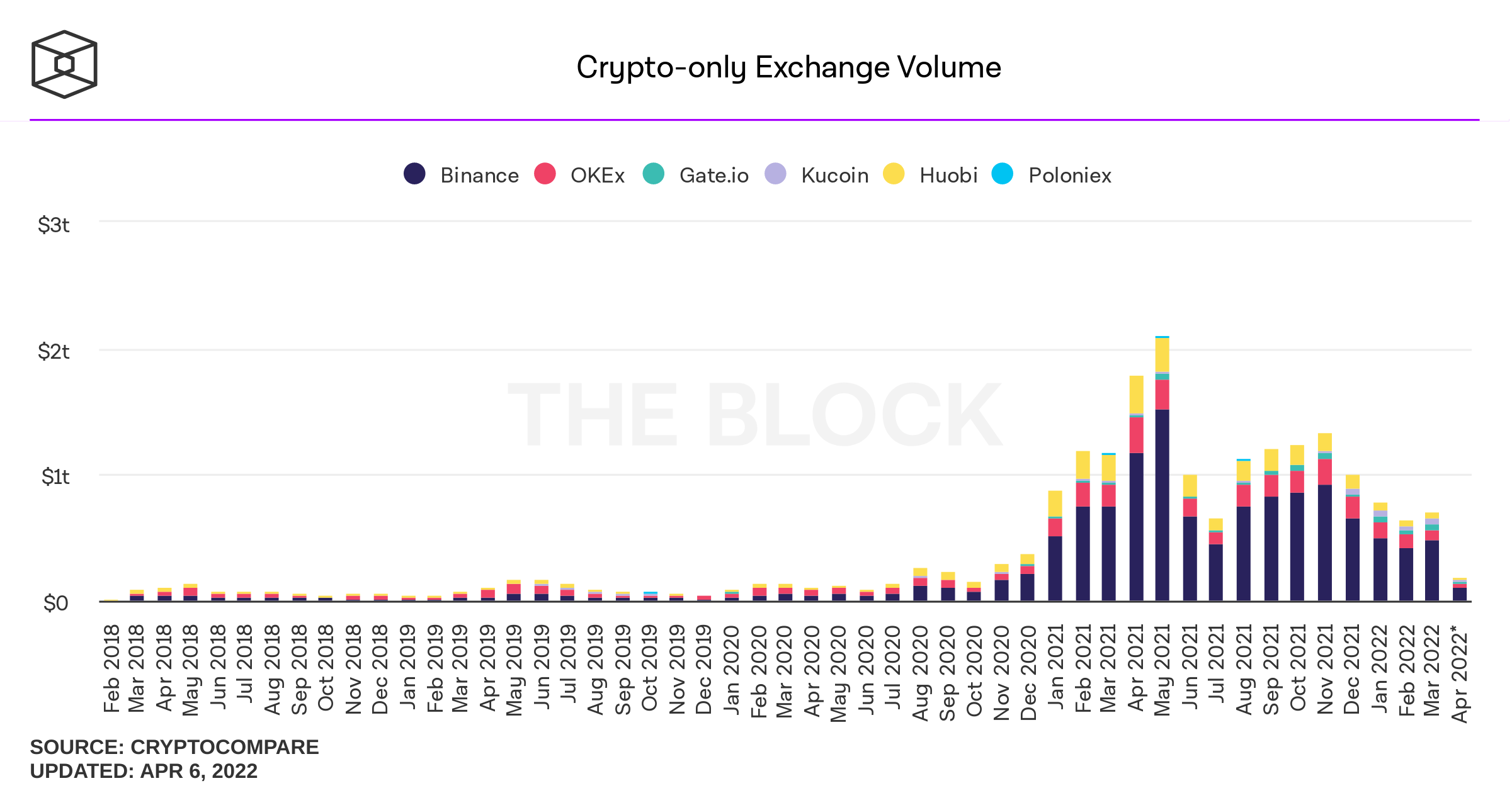
approx:
400B p.m.
approx:
700B p.m.
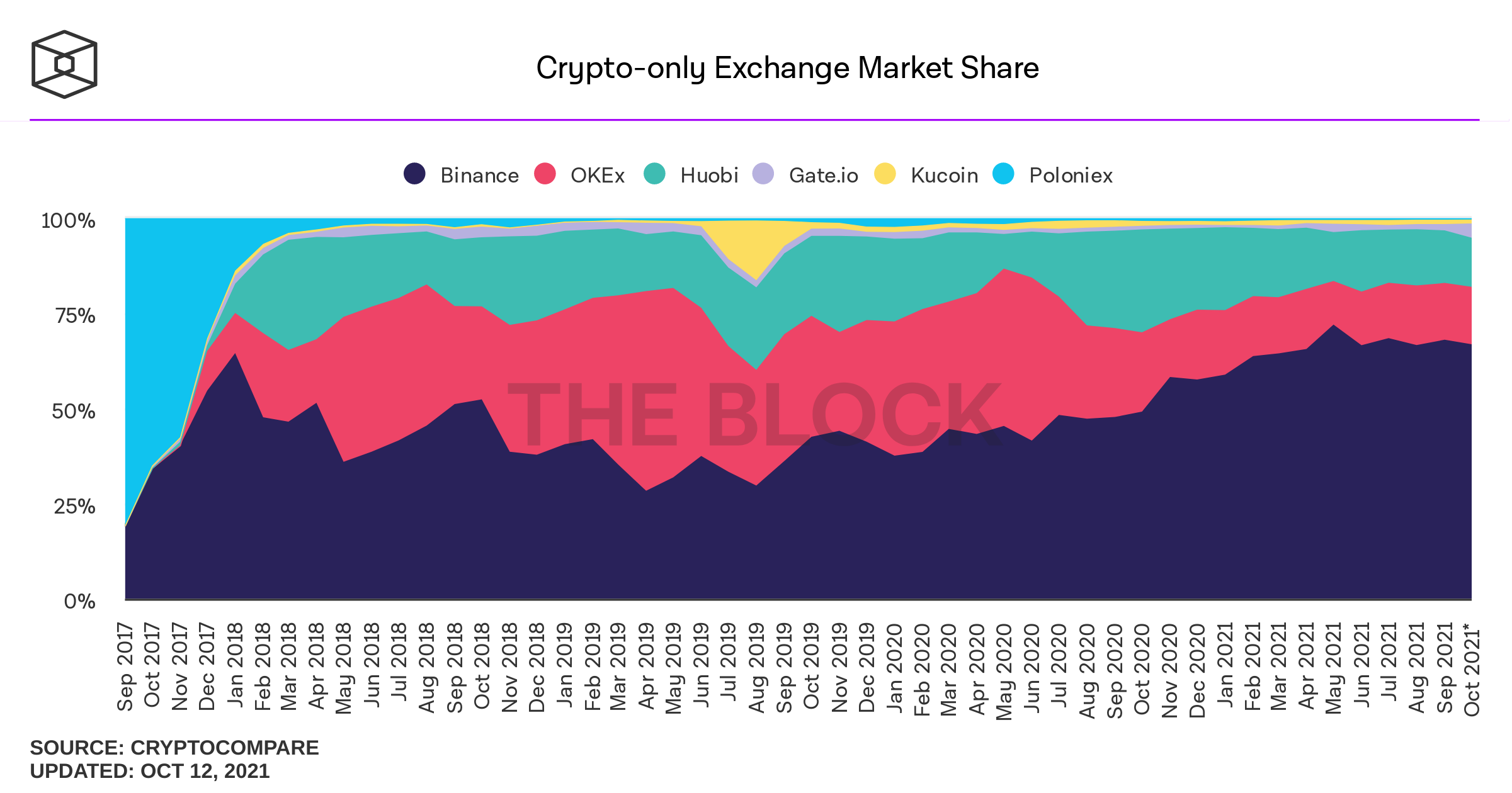
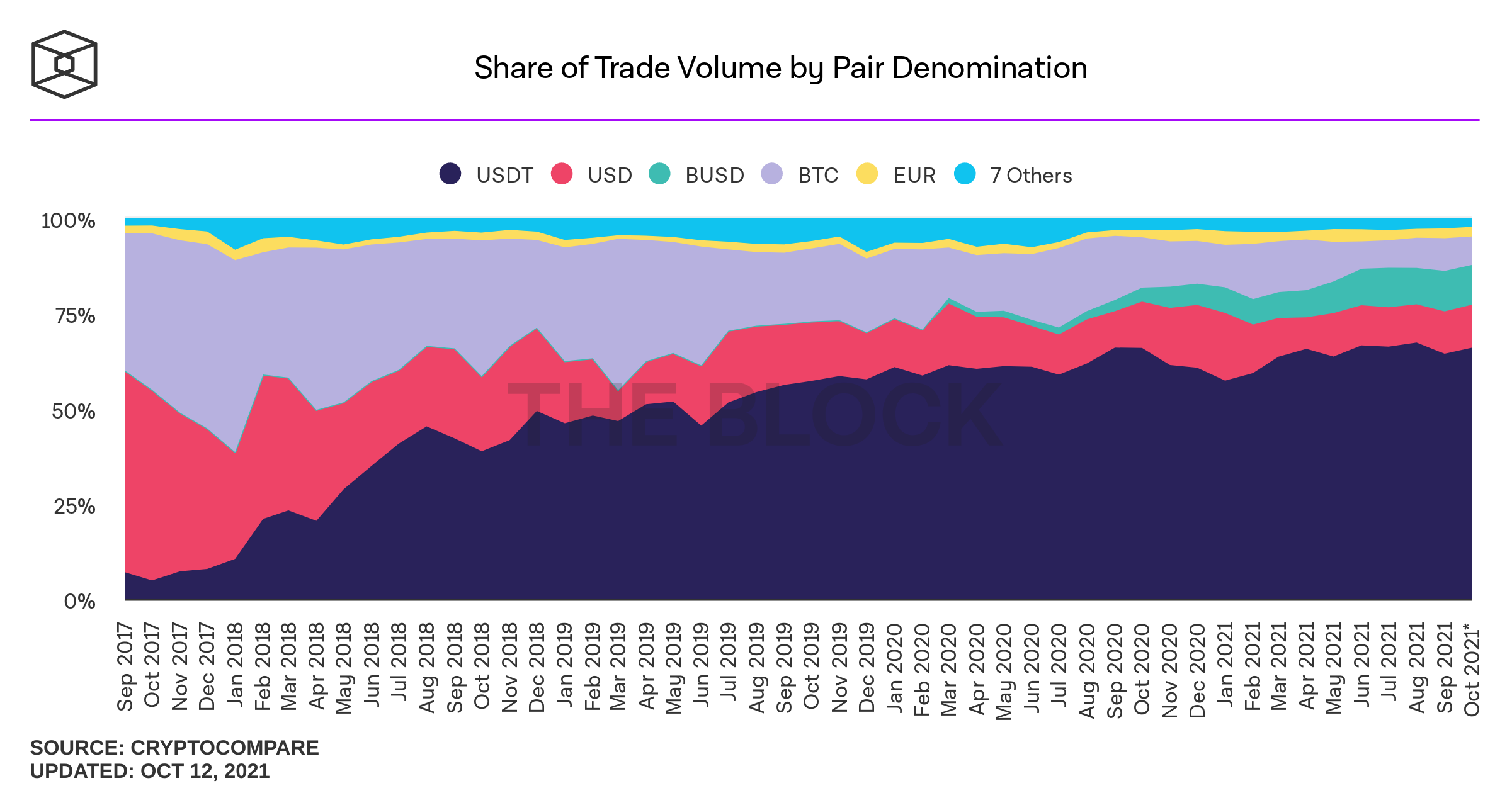
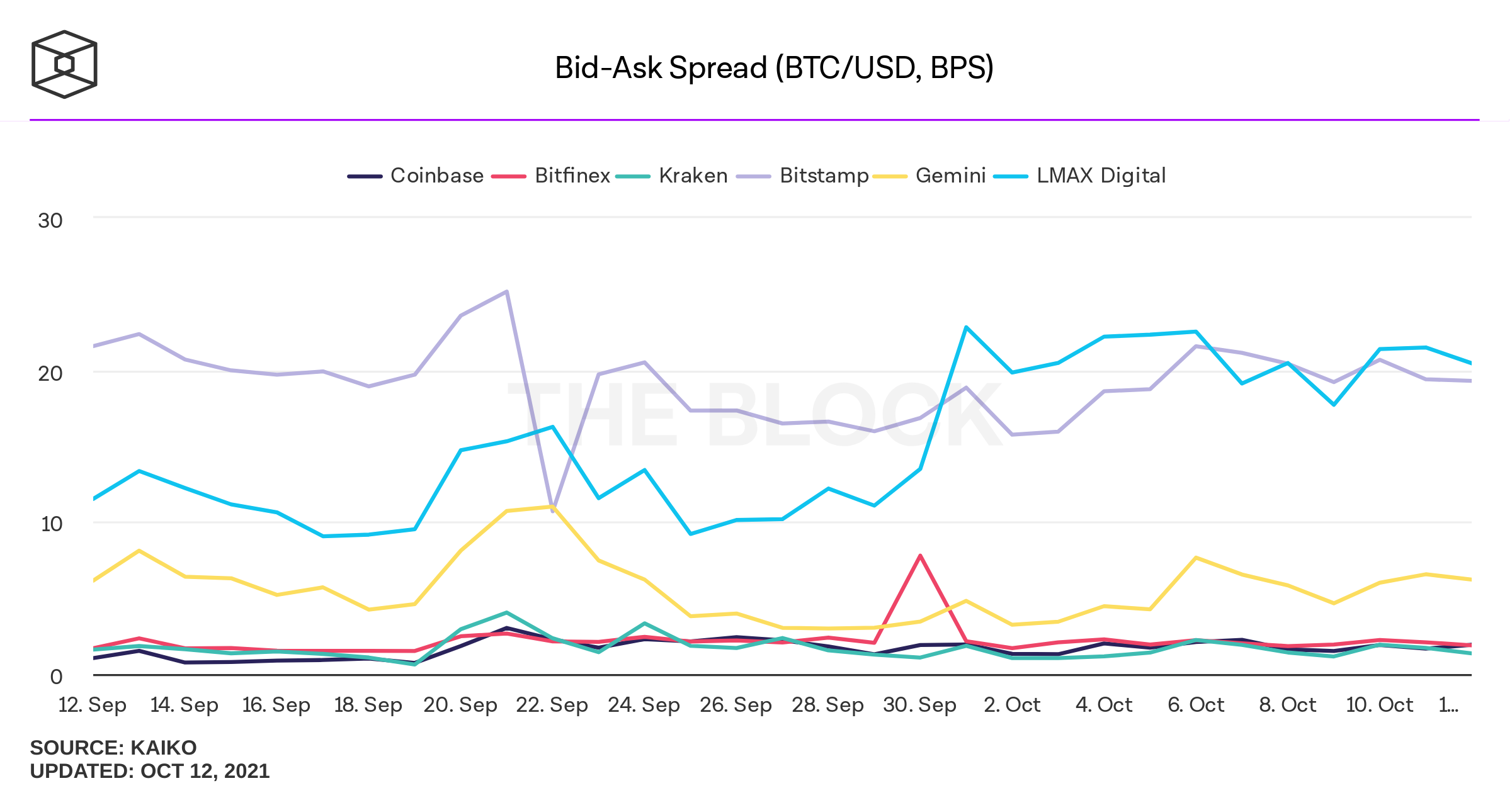
Concerns with CEX-Trading
CEX = Offramps for criminals
More broadly: cybercrime costs: in trillions!
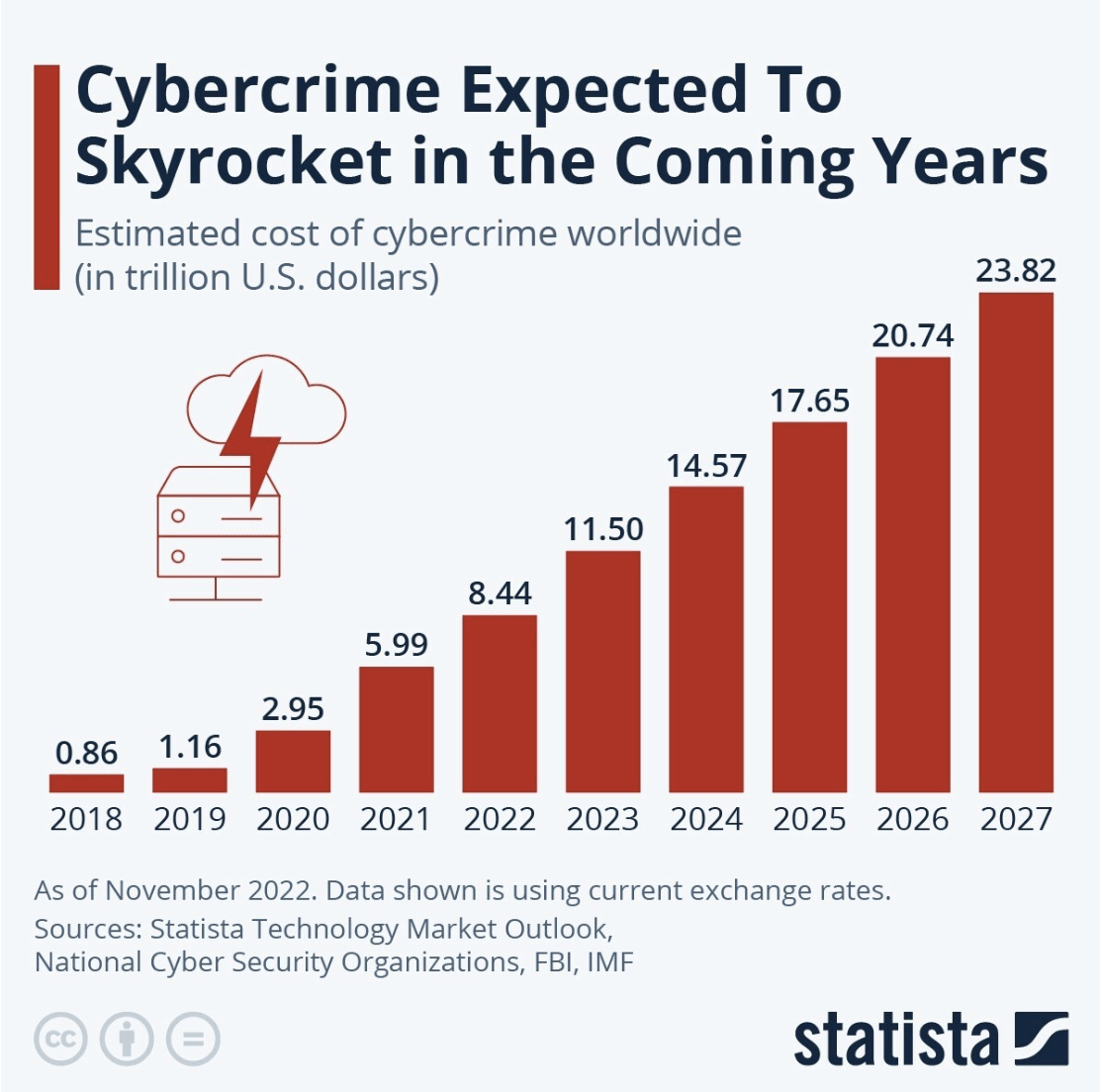
World Economic Forum:
- growing cyber inequity
- the highest barrier to cyber resilience is transforming legacy technology and processes.
Role for blockchain?
Costs vs benefits of decentralization?
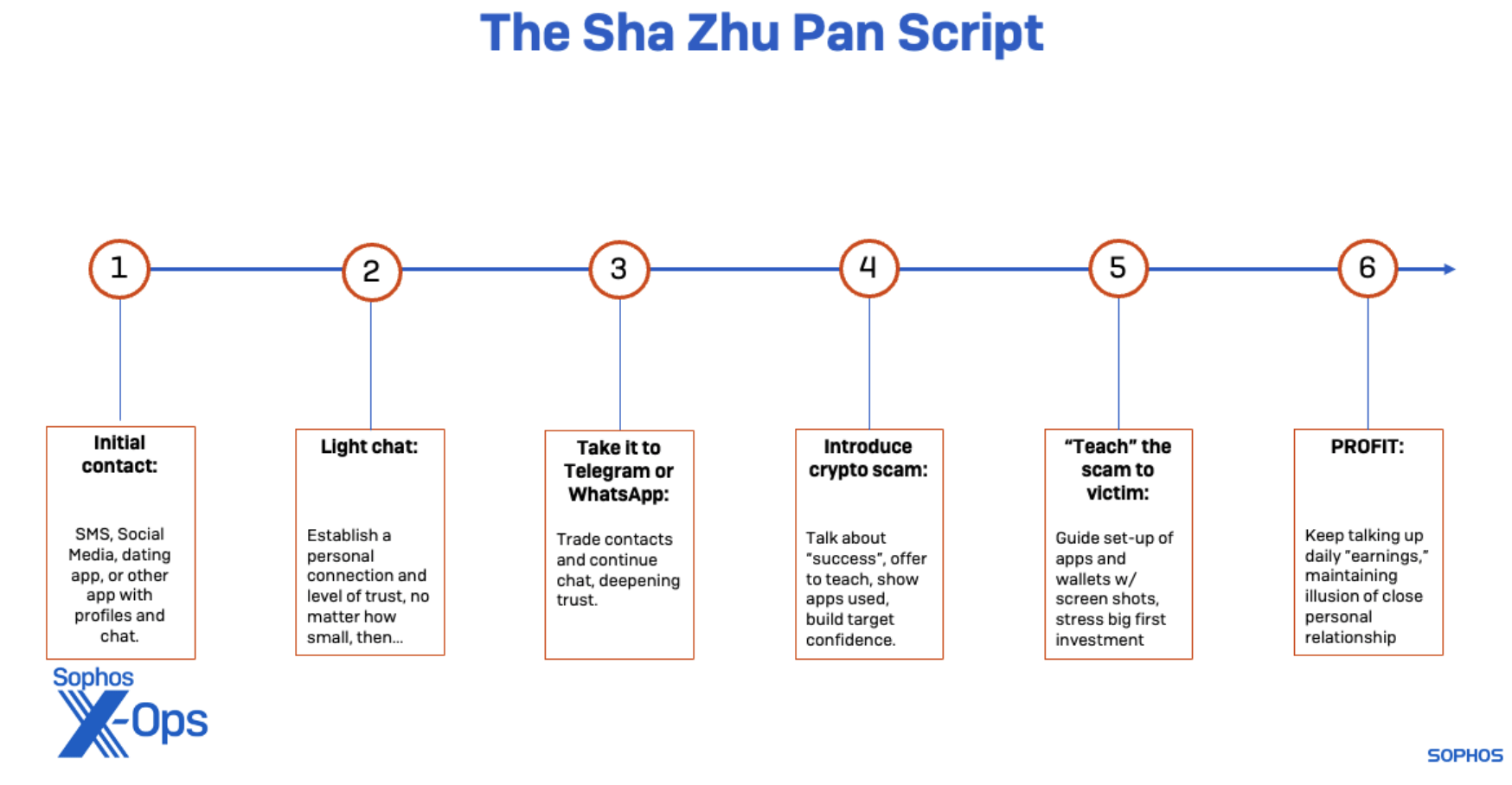
The Sha Zhu Pan (Pig Butchering) Script
UN REPORT 2023:
- \(\ge\) 120,000 people in Myanmar & \(\ge\) 100,000 in Cambodia
- “may be held in situations where they are forced to carry out online scams.”
- “may be held in situations where they are forced to carry out online scams.”
- scam industry in one (unnamed) Mekong nation alone “may be generating $7.5 to $12.5 billion”
What does it have to do with slavery?



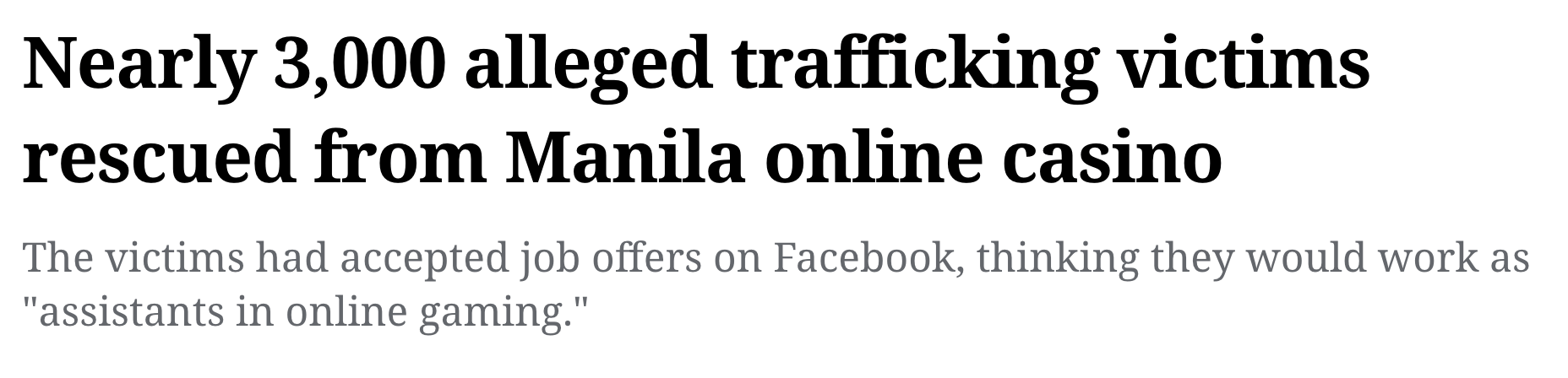
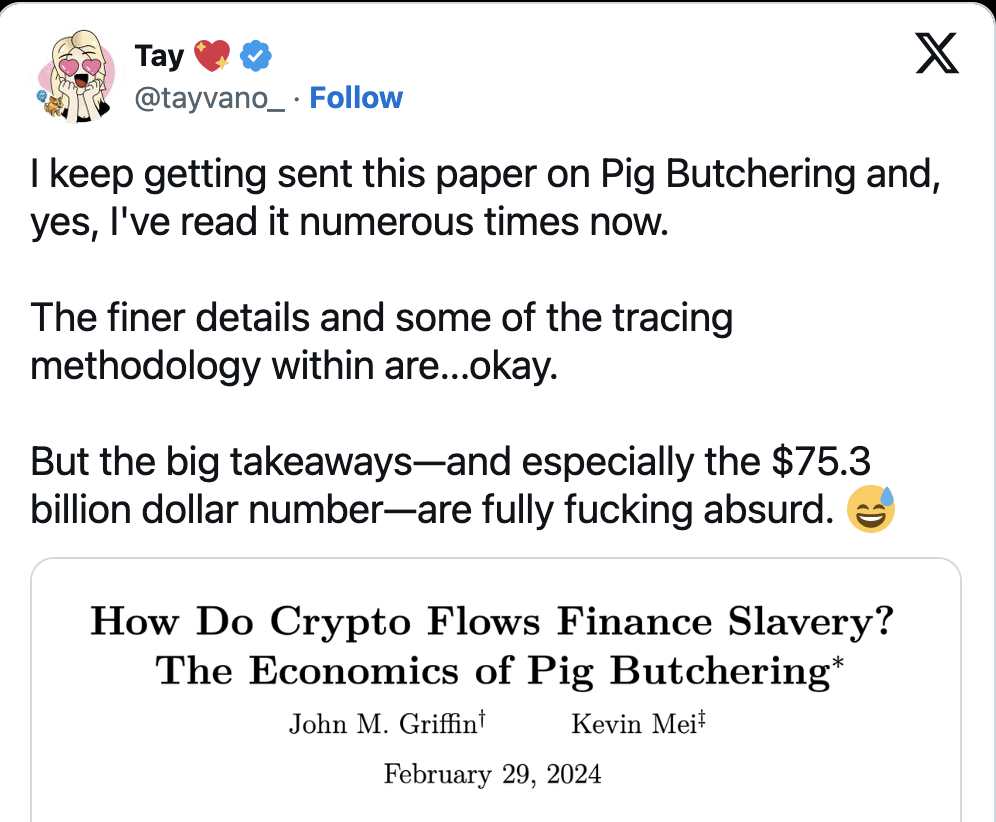
How Do Crypto Flows Finance Slavery? The Economics of Pig Butchering => $75B (!!) lost to pig-butchering scams







Text
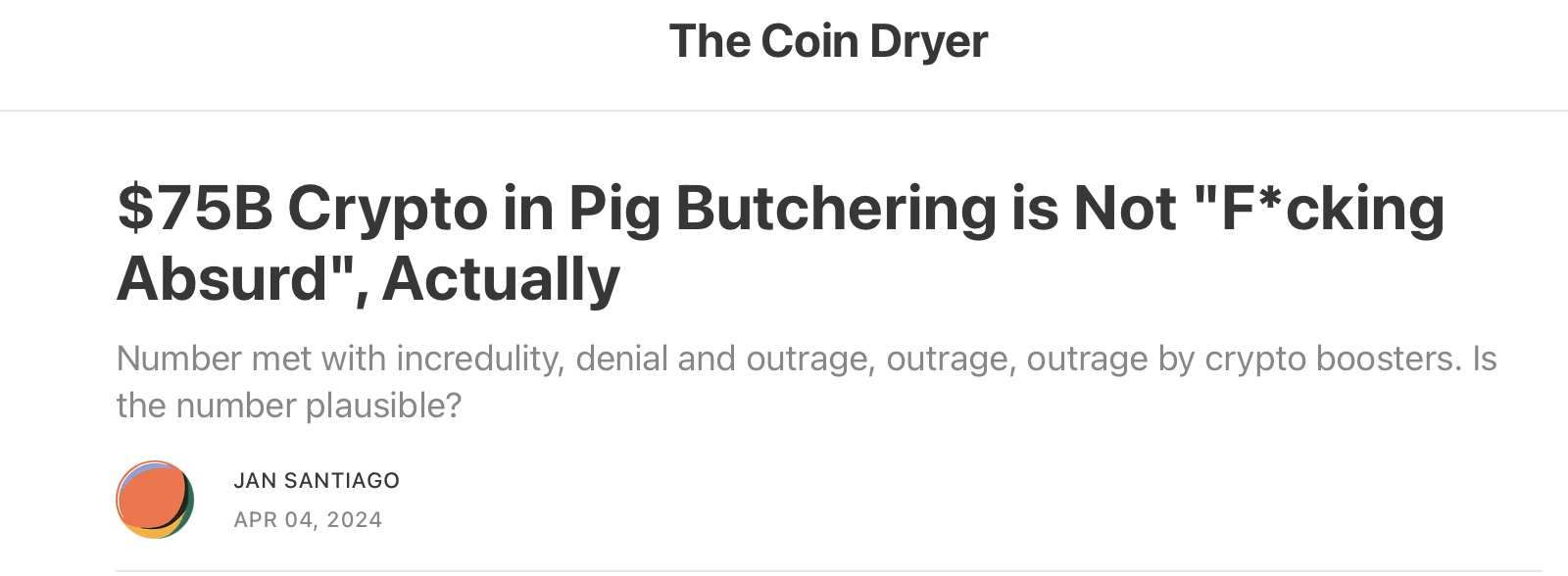
The $75.3 billion number
FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center Report (IC3)
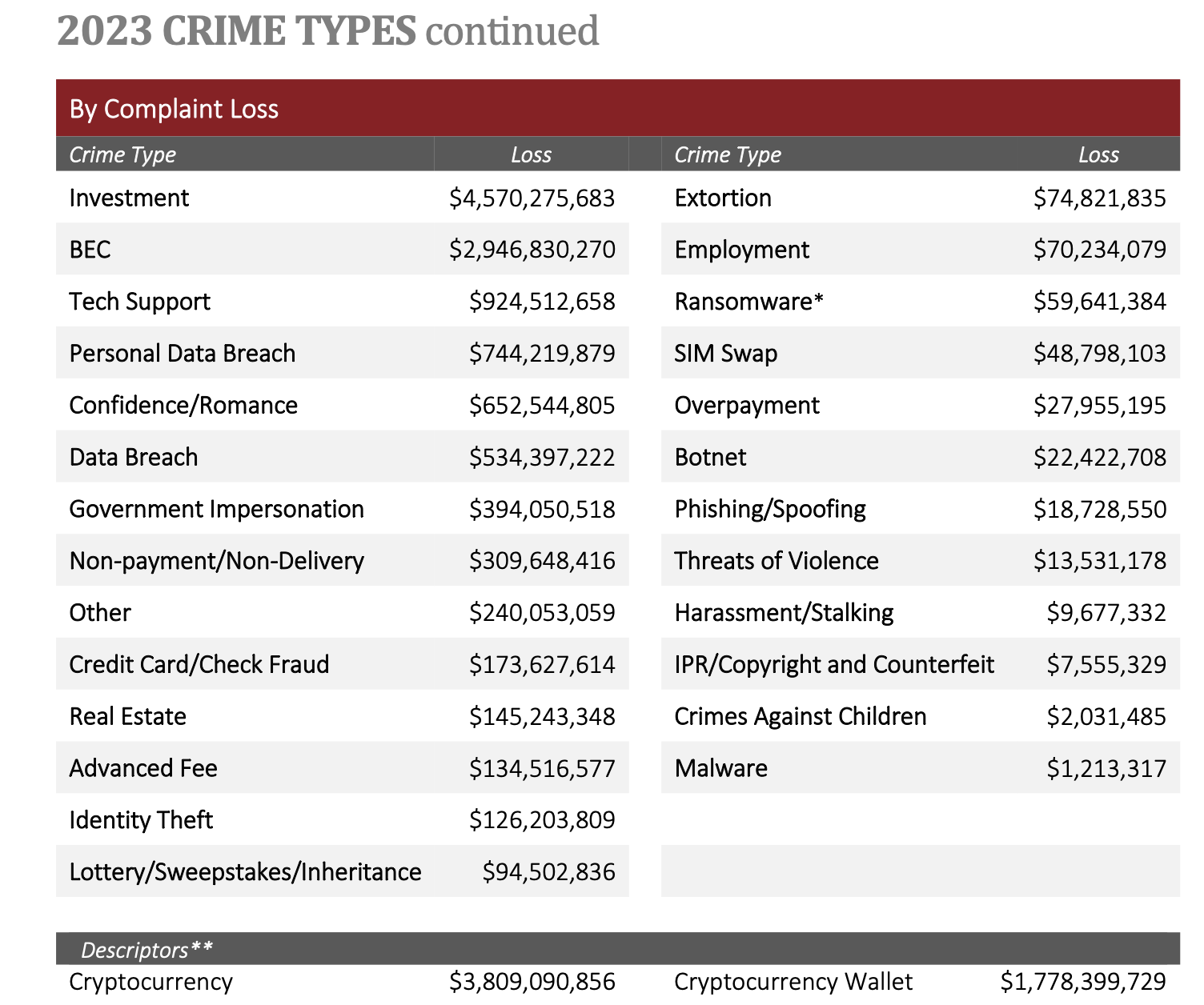
Investment: $4.57B
Business Email Compromise: $3B
...
Confidence/Romance: $0.65B
Crypto-related totals: $5.6B
The $75.3 billion number
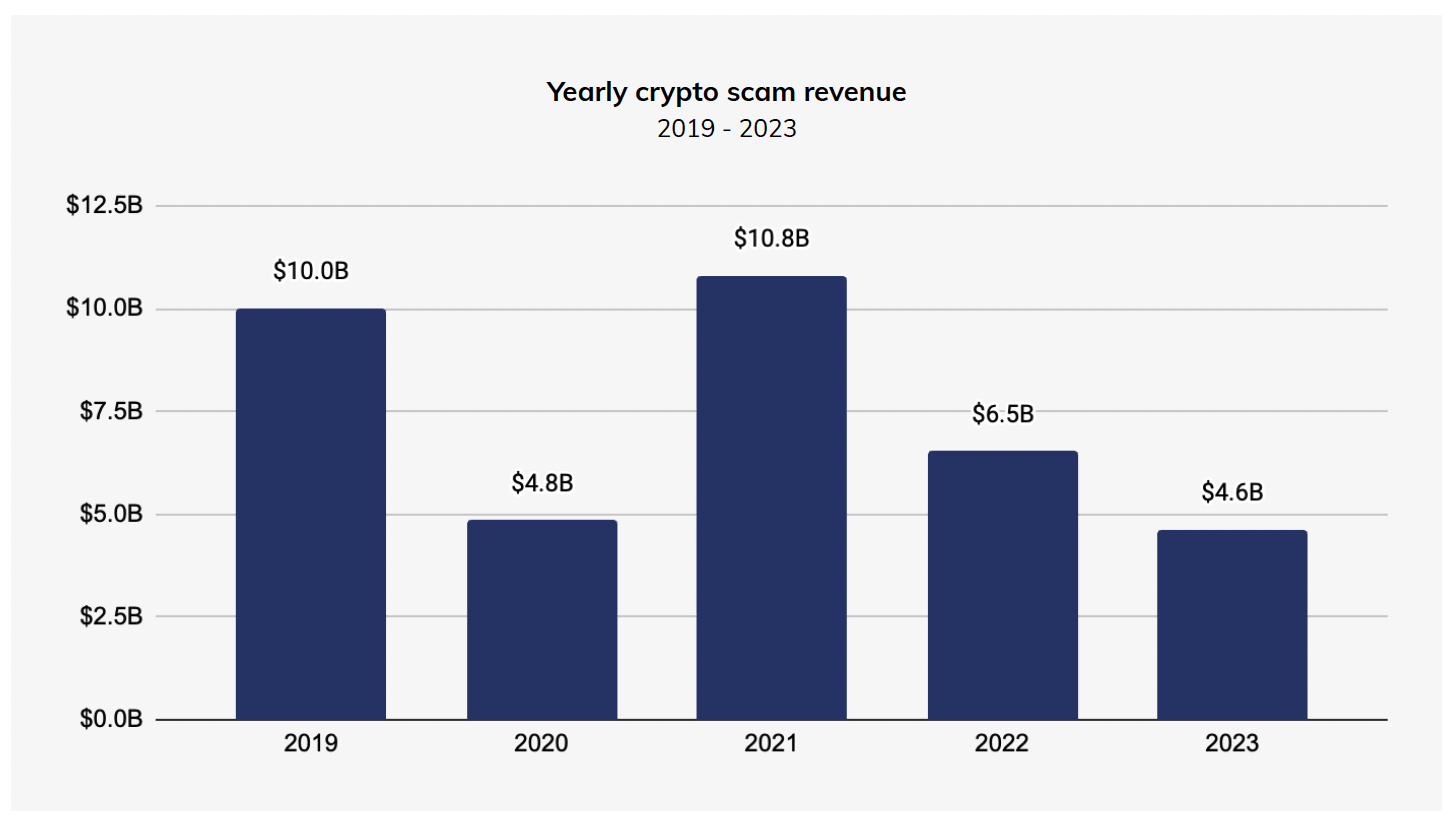

$26B Total Crypto Scam Revenue in 2020-2023
The $75.3 billion number: Tracing
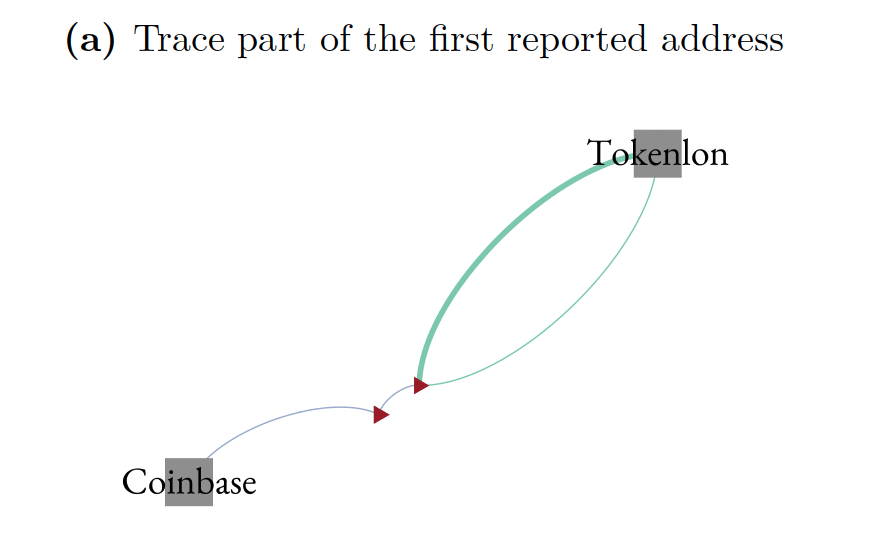
Reported Scammer Address
focus on Ethereum paths that start from exchange wallets sending funds
to scammer addresses and end at user deposit addresses
The $75.3 billion number
Reported Scammer Address
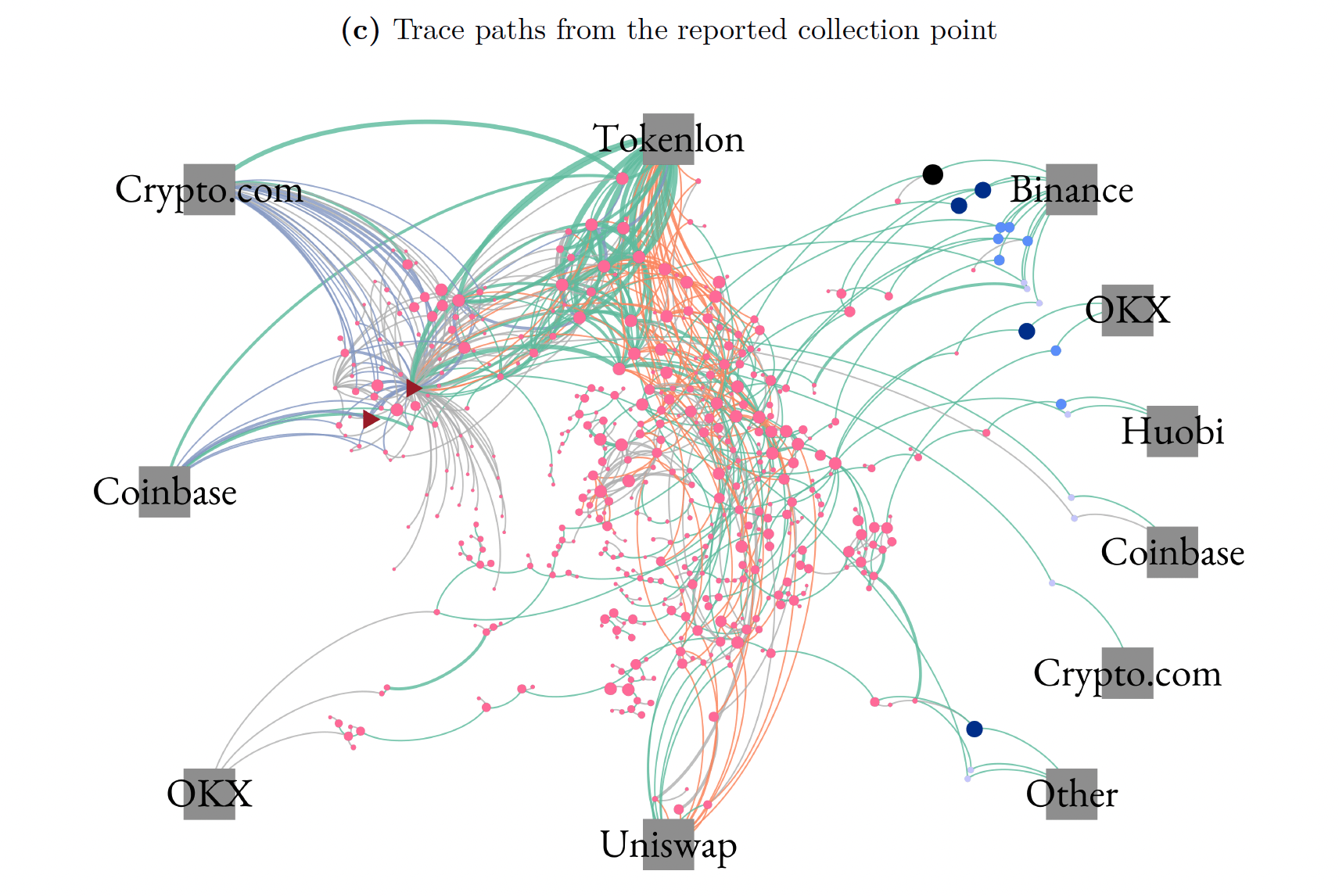
"Deposit Addresses"
at Exchanges
Concern 1: "tool includes proprietary
criteria to terminate a trace path if funds reach an address that is unlikely to be a scammer"
"Deposit Addresses"
at Exchanges
Deposit Addresses
at Exchanges
"sum all inflows to these addresses and find $75.3 billion"
Concern/Question 2: addresses may belong to entities that service other (illicit?) activities?
- Illegal gambling?
- Avoiding China Capital Controls?
Question 3: How much money EXIT the exchanges?
Comment/Concern 1B:
- collect 1,065 addresses
- the United States
Institute of Peace (USIP) shared a large set of additional addresses - "apply screens"
- \(\to\) 4,728 addresses
Comment/Question 4:
- The scam tactics have evolved
- No longer "send money to the [scammer] address"
Concerns
arbitrage is either not possible or requires large capital commitment => expensive
exchanges = brokers? => single point of failure
decentralized: totally anonymous => easy price manipulation (e.g. wash trades)
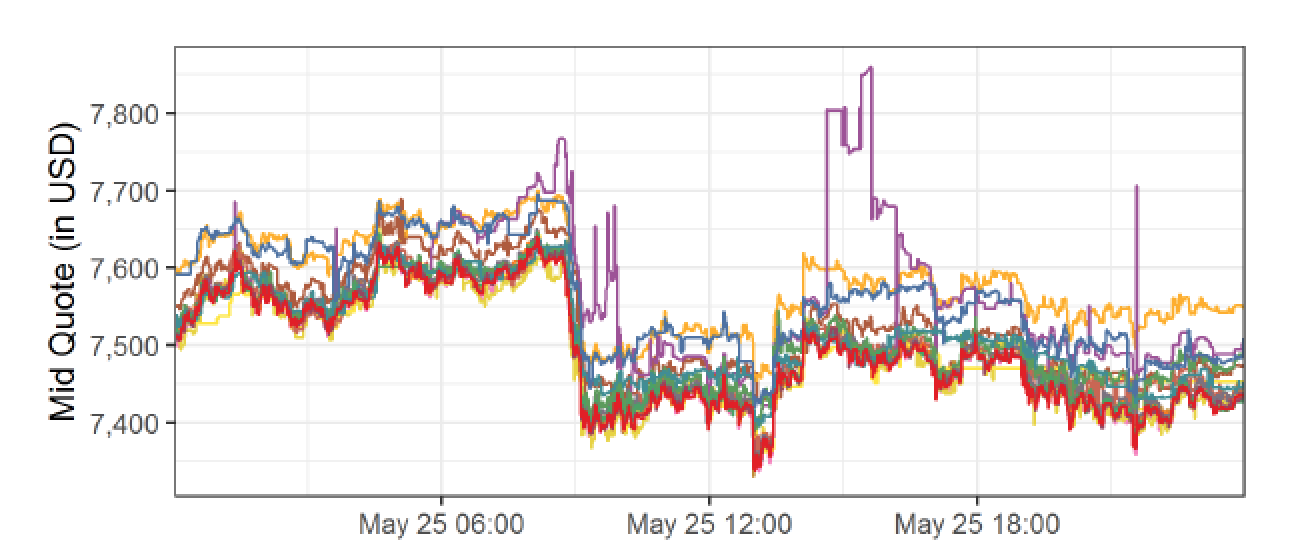
Bitcoin prices in USD, May 25 2018, 17 exchanges
Arbitrage?
Pre-req for Trading on a Crypto Exchange


trade


Settle on the blockchain for digital "assets"

Wire transfer for fiat
Arbitrage on a Crypto Exchange

BTC/USD
ask: 7,600
bid: 7,550
BTC/USD
ask: 7,500
bid: 7,450
buy low
sell high

Arbitrage on a Crypto Exchange

BTC/USD
ask: 7,600
bid: 7,550
BTC/USD
ask: 7,500
bid: 7,450

buy BTC
sell BTC
move BTC to Kraken



=> arbitrage = commit capital on multiple exchanges
Arbitrage on a Crypto Exchange




Wire: free*; 1-5 days
Credit card: 3.5%
trading fee: 10-25 bps
flat fee in BTC \(\approx\) $4-8
\(\approx\) 10-60 minutes
trading fee: 0-26 bps
35 USD + 0.125%
($5 if >$50,000)
1-3 business days;
possible other fees/delays
Some exchanges allow short selling

Crypto Wash Trading, Lin William Cong, Xi Li, Ke Tang, Yang Yang
- systematic tests:
- robust statistical and behavioral patterns in trading to detect fake transactions on 29 cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Regulated exchanges are OK
- unregulated exchanges: rampant manipulations
- wash trading on each unregulated exchange:
- on average over 70% of the reported volume
- improve exchange ranking
- temporarily distort prices
Volume Manipulation on Crypto Exchanges
Cryptocurrency Pump-and-Dump Schemes
Tao Li, Donghwa Shin, and Baolian Wang, 2020
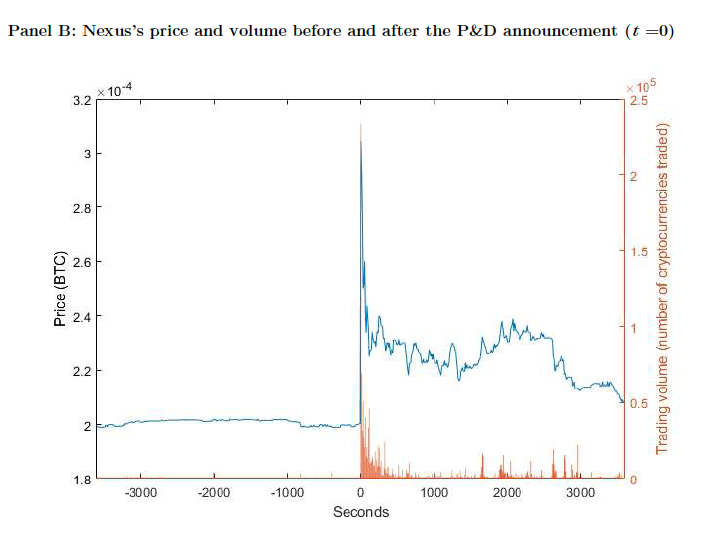

What is pump and dump?
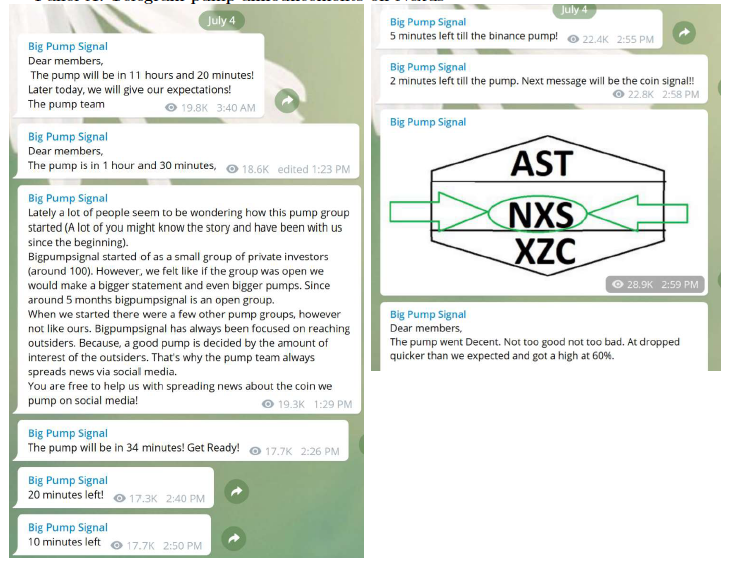
arranged via Telegram Channels
Price Manipulation on Crypto Exchanges

Still going strong -
this one is from Nov 25, 2023
- prices of pumped cryptocurrencies begin rising five minutes before a P&D starts.
- some pump group organizers offer premium memberships to allow certain investors to receive pump signals before others do (\(\to\) insiders)
- Average P&D insiders make one Bitcoin (about $10,000) in profit
- only investors who buy in the first 20 seconds after a P&D begins make a profit
Other Tidbits of Information
IS BITCOIN REALLY UN-TETHERED? JOHN M. GRIFFIN and AMIN SHAMS
Journal of Finance 2020
- basic idea: USDT is issued unbacked to trade Bitcoin and to inflate its price
- more on the next slides...
Price Manipulation on Crypto Exchanges
What's the result?
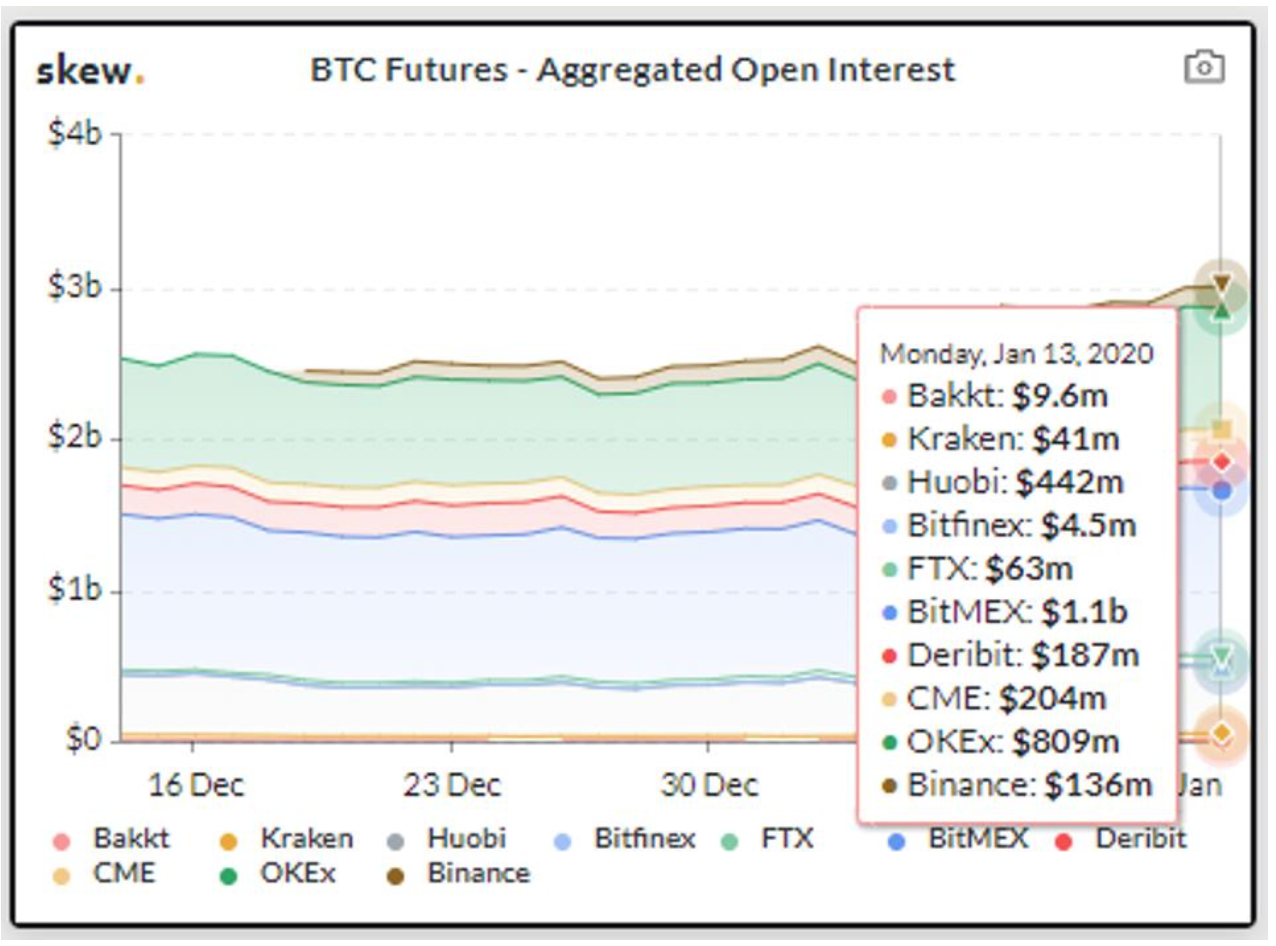
Regulated Exchanges
Derivatives trade mostly offshore! Unregulated(?!)
- on April 30, 2019: Tether does not have cash reserves equal to 100% of the outstanding Tethers.
- May 15, 2019 court hearing: Tether did invest in instruments beyond cash, including Bitcoin


Historically: “Tether Platform currencies are 100% backed by actual fiat currency
assets in our reserve account.”
Today: "The Tether Platform is fully reserved when the sum of all tethers in circulation is less than or equal to the value of our reserves."
IS BITCOIN REALLY UN-TETHERED?
JOHN M. GRIFFIN and AMIN SHAMS
Journal of Finance 2020
vs.
Why does that matter?
- Tether = ‘pushed’
- print an unbacked digital dollar to purchase Bitcoin.
- \(\to\) additional supply of Tether creates unwarranted inflation in Bitcoin price


Text
IS BITCOIN REALLY UN-TETHERED?
JOHN M. GRIFFIN and AMIN SHAMS
Journal of Finance 2020
vs.
- Tether = ‘pulled’
- driven by legitimate demand from investors who use Tether as a medium of exchange
- \(\to\) the price impact of Tether reflects natural market demand
Text
IS BITCOIN REALLY UN-TETHERED?
JOHN M. GRIFFIN and AMIN SHAMS
Journal of Finance 2020
Flow of events
- Tether is authorized
- moved to Bitfinex
- then slowly distributed to other Tether-based exchanges (Poloniex and Bittrex)
- \(\to\) almost no Tether returns to the Tether issuer to be redeemed
- Kraken (major exchange for Tether\(\to\) USD) accounts for only a small proportion of transactions
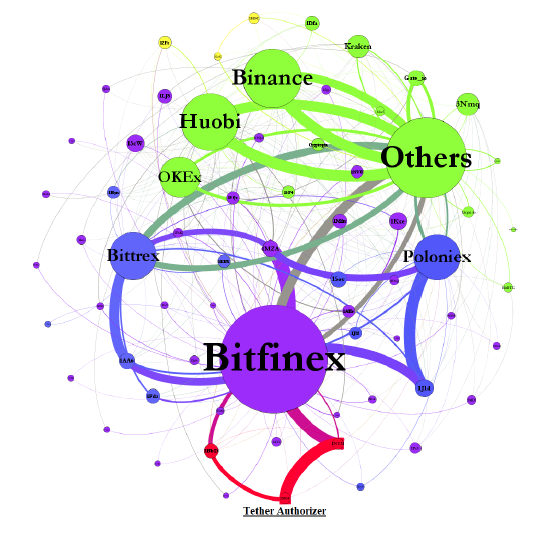
Figure 1. Aggregate Flow of Tether between Major Addresses
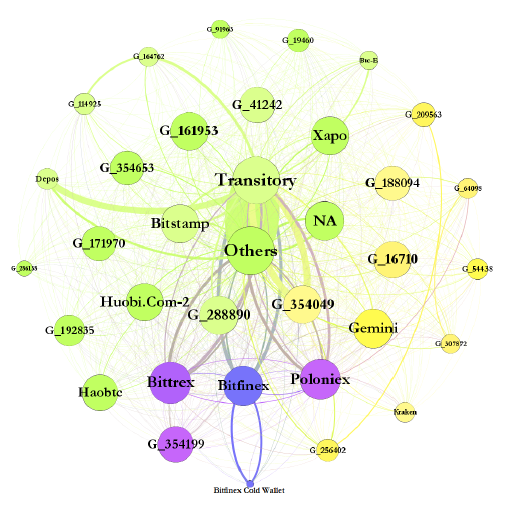
Figure 3. Aggregate Flow of Bitcoin between Major Addresses.
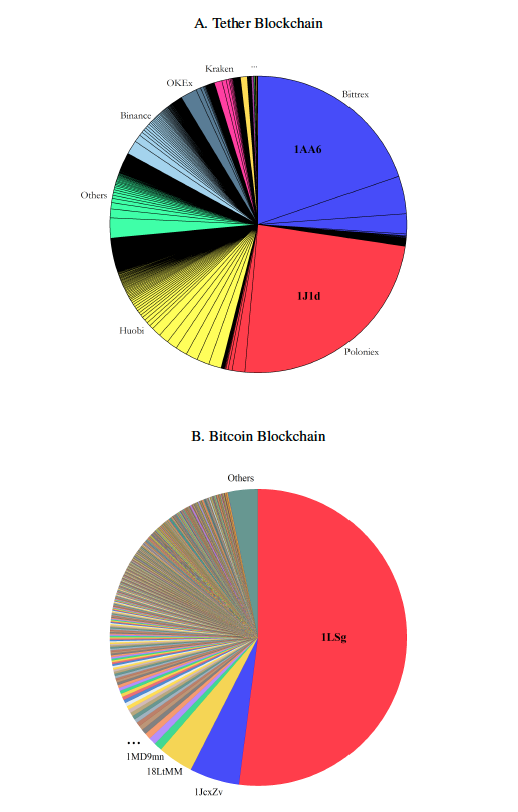
Top Accounts Associated with the Flow of Tether from and Bitcoin to Bitfinex
- three main Tether exchanges, Bitfinex, Poloniex, and Bittrex, have considerable cross-exchange Bitcoin flows
- cross-exchange Bitcoin flows on Bitcoin closely match Tether flows
- one large player has >50% of the exchange of Tether for
- Bitcoin at Bitfinex
- \(\to\) distribution of Tether into market from ONE large player and not many different investors
If Tether is printed independently
of demand and pushed onto the market then ...
- \(\nearrow\) money supply in crypto
- \(\nearrow\) cryptocurrency prices through artificial demand
- if traded strategically, Tether can further impact and manipulate Bitcoin prices
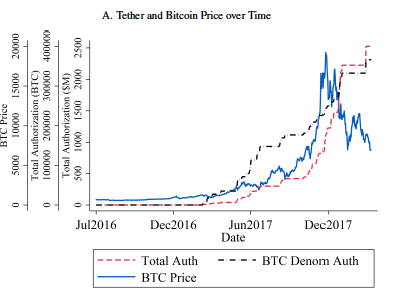
the 1% of hours with the strongest lagged Tether flow are associated with 58.8% of the Bitcoin buy-and-hold return over the period.
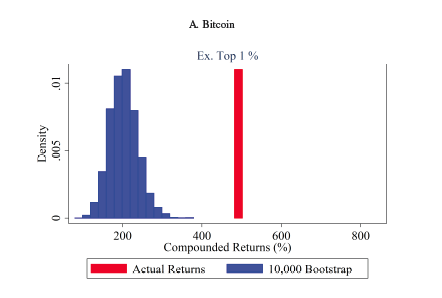
Is the Price Effect Economically Important?
the "normal-times" returns
Crypto exchanges are a security risk



August 2016




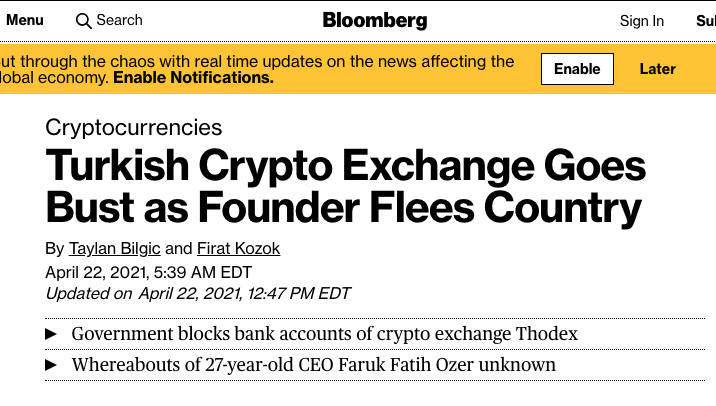
Crypto exchanges are a security risk

By yours truly, Dec 2017: "What really concerns me about the current craziness is the role of the cryptocurrency exchange platforms, such as Coinbase, Quadriga, or Bitfinex, which most people use to buy Bitcoins. These are like banks that hold deposits. For cryptocurrencies to succeed it is critical that these interfaces with the real world are financially robust. Are they? Do they have all the Bitcoins they sell? Can they always satisfy depositors’ demands?"
Crypto exchanges are a security risk


https://www.forbes.com/sites/jasonbrett/2019/12/19/congress-considers-federal-crypto-regulators-in-new-cryptocurrency-act-of-2020/#7ddcdfd65fcd
Crypto exchanges are a security risk

https://www.osc.ca/en/news-events/news/osc-working-ensure-crypto-asset-trading-platforms-comply-securities-law


SEC denies Bitcoin ETF
The FTX Collapse
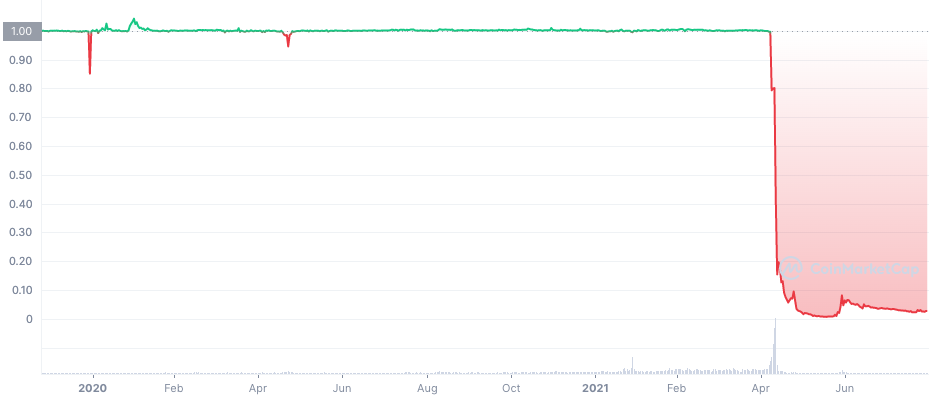
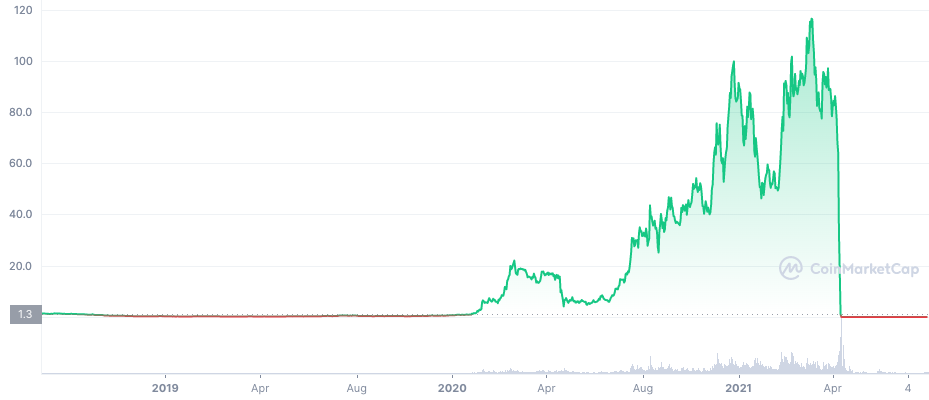
The Terra Implosion
UST Stablecoin
LUNA (cryptocurrency of the TERRA network)
A timeline
May 7: selling pressure on UST from Curve withdrawals
May 12: LUNA and UST at $0.01
June 27: Three Arrows Capital ordered to liquidate
June 12: Celsius Network suspends withdrawals
July 13: Celsius files for Chapter 11
July 6: Voyager Digital files for Chapter 11
July 4: Vault suspends withdrawals
Three Arrows Capital lost >60% of value and faces numerous margin calls that they did not react to
partially saved by \(\ldots\) FTX
The FTX Implosion
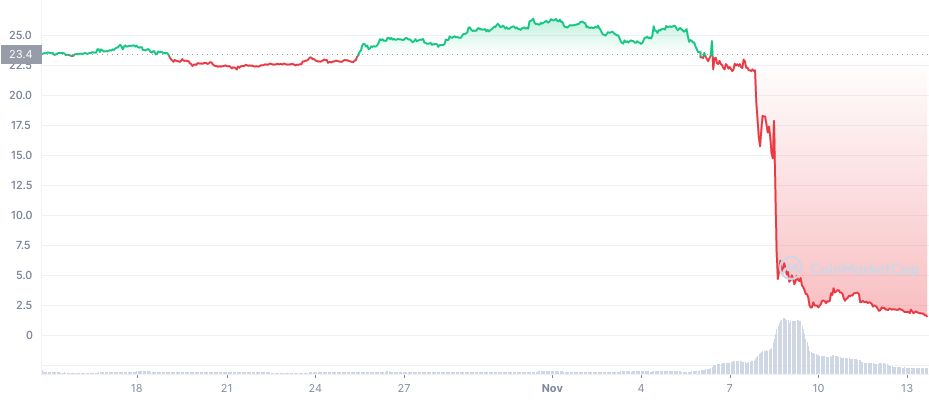
A timeline

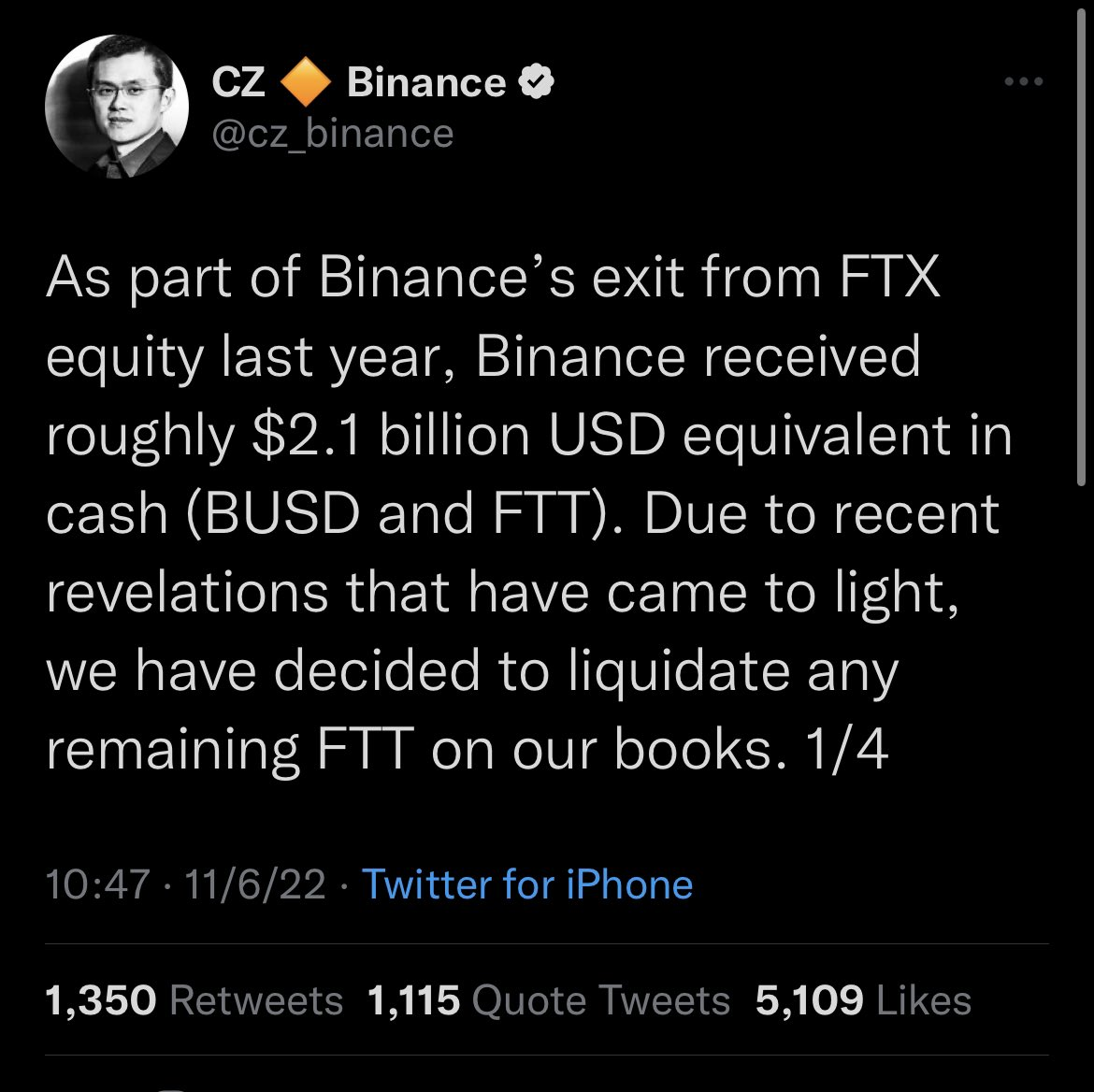

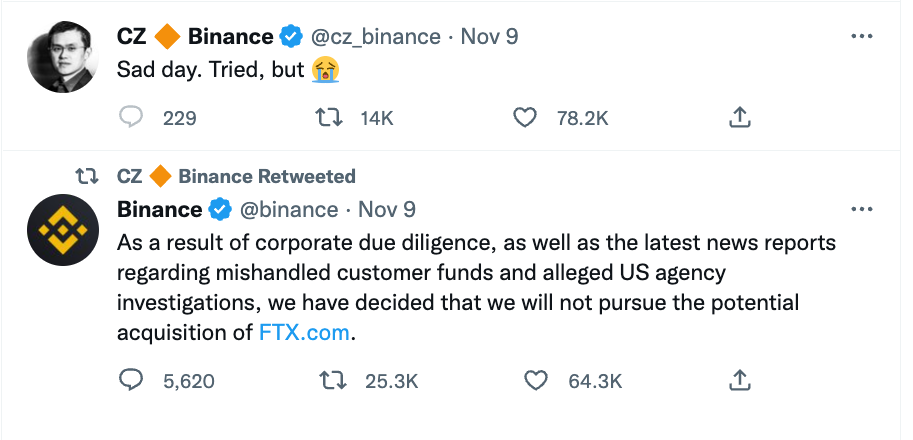
Nov 8

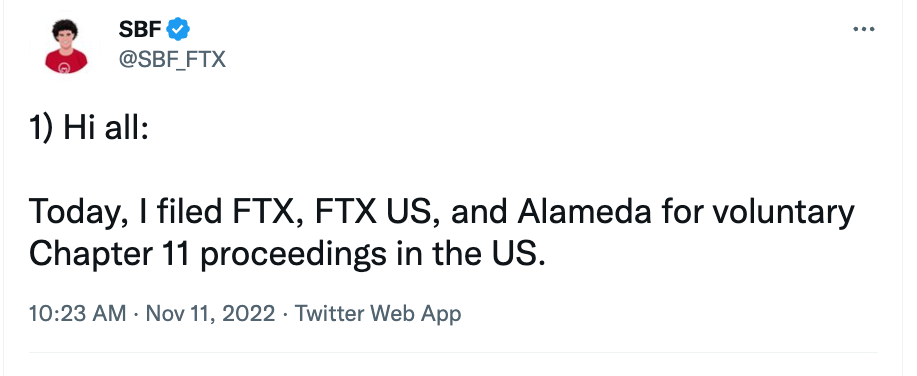
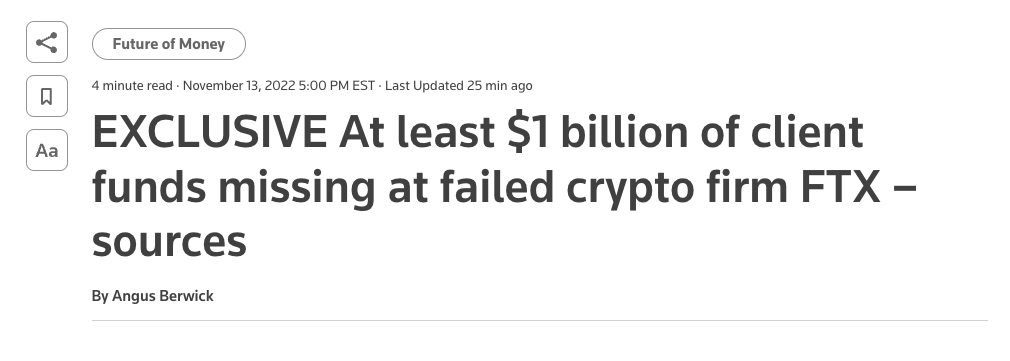

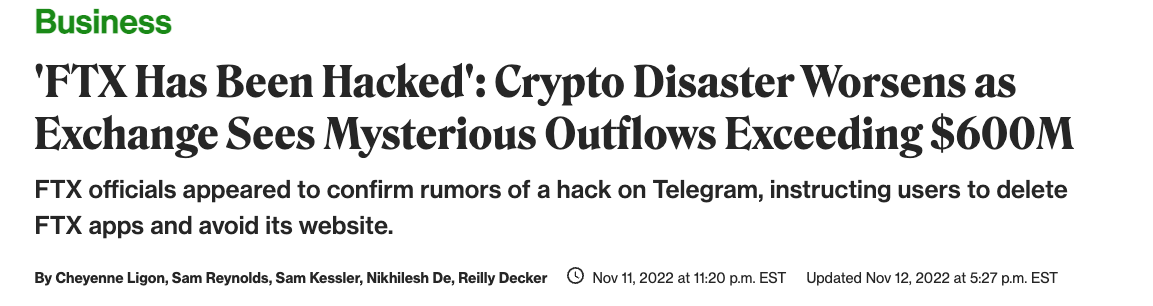
What's next?
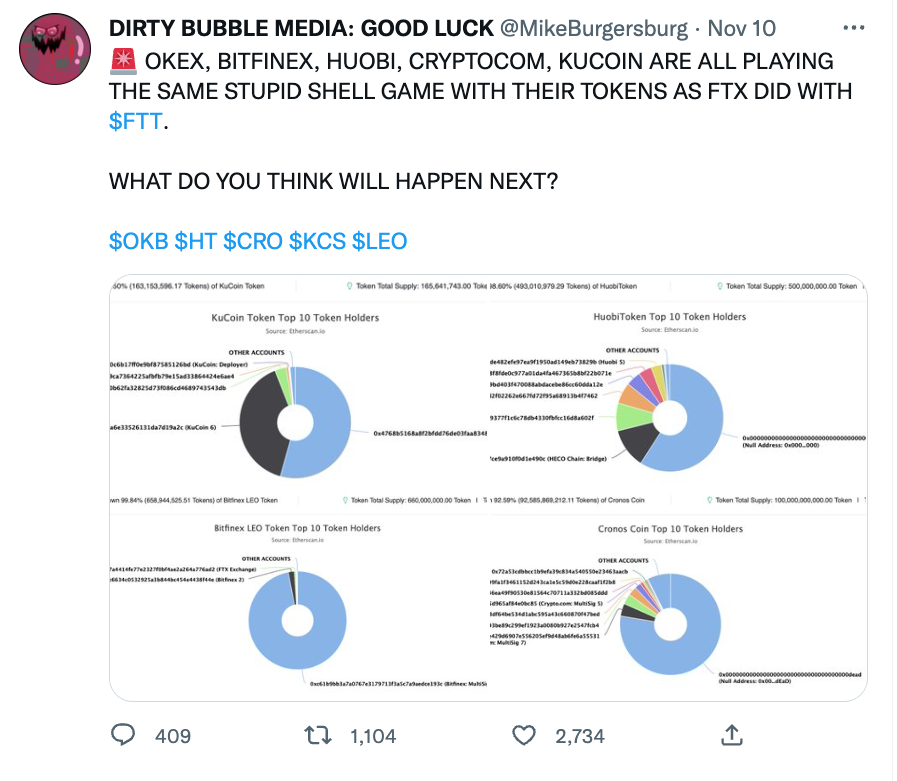
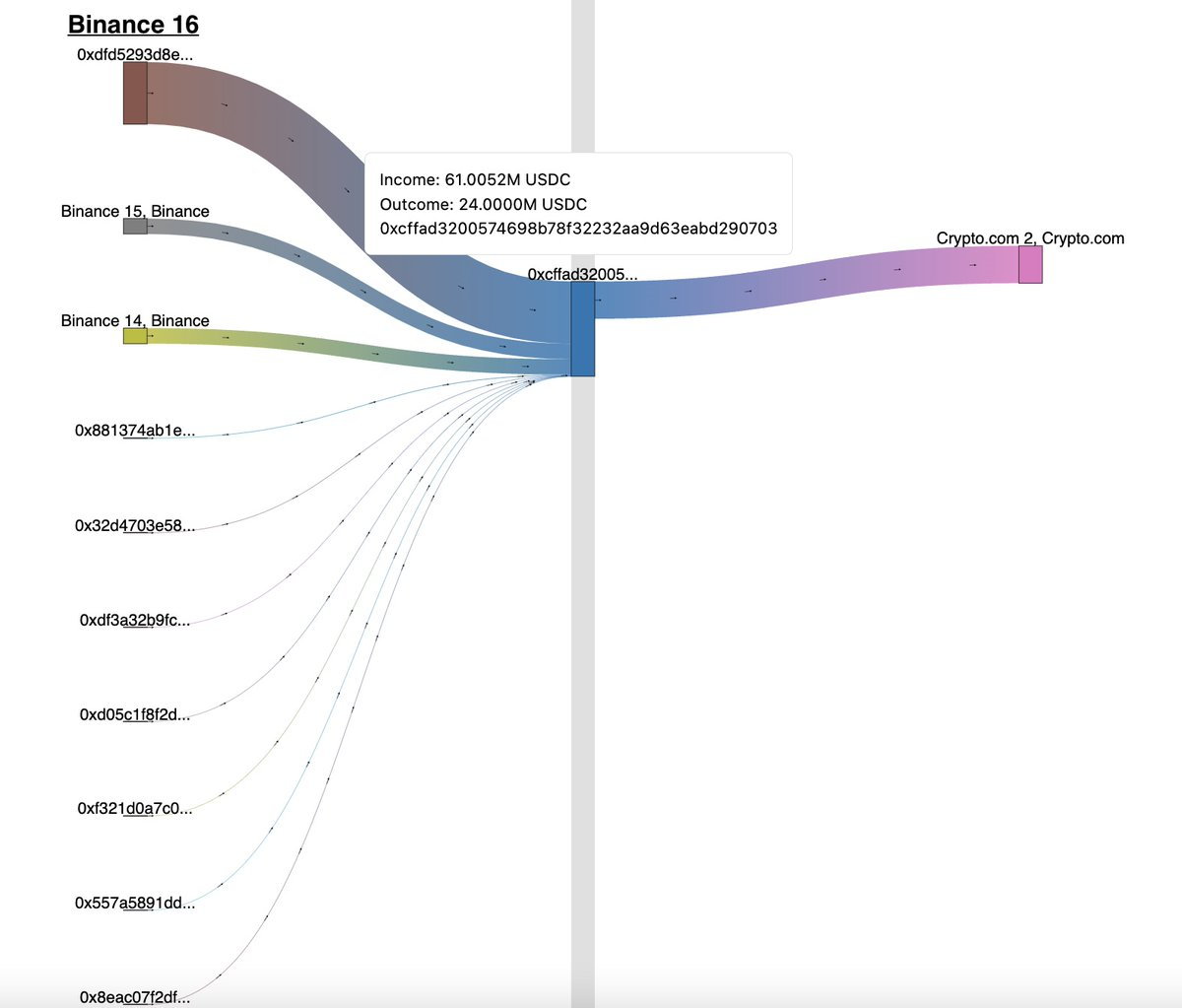

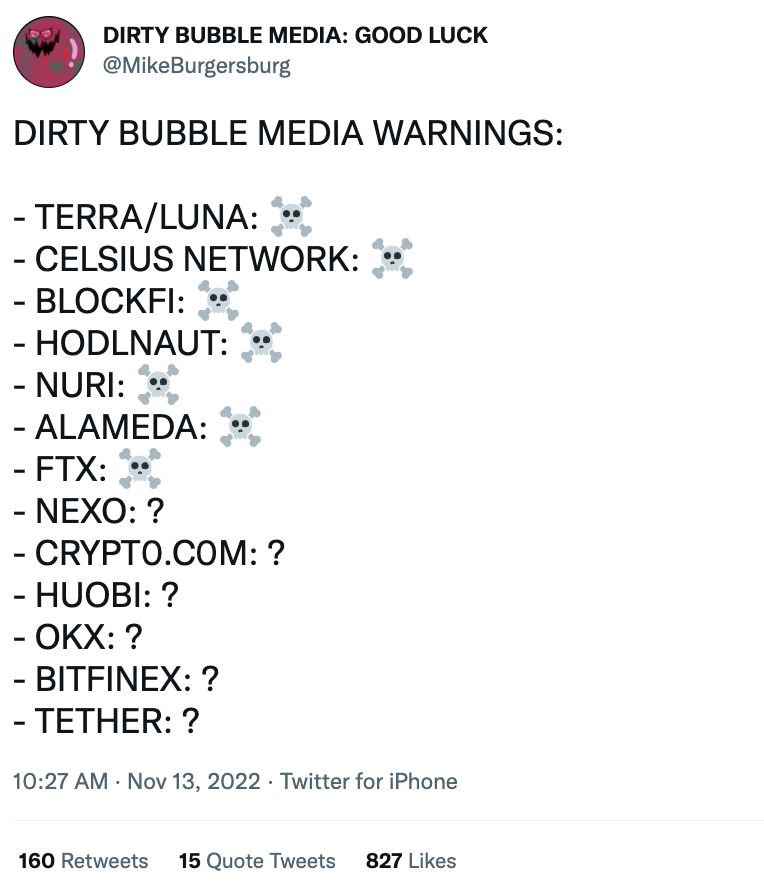
DEX vs CEX Tradeoffs
|
Option |
Exchange-side risk |
User-side risk |
|
Custodial exchange (eg.Coinbase today) |
User funds may be lost if there is a problem on the exchange side |
Exchange can help recover account |
|
Non-custodial exchange (e.g.Uniswap or dydx today) |
User can withdraw even if exchange acts maliciously |
User funds may be lost if userscrews up |
Source: https://vitalik.ca/general/2022/11/19/proof_of_solvency.html
Core problem with QuadrigaCX:
- Gerry Cotton sold people crypto he did not have.
Core problem FTX
- used customer funds to prop up their market maker Alameida
- => they gave Alameida customer assets
In finance terms
- call it unhedged "leverage"
- hedge means that you have an off-setting position
Possible solution
- prove your aggregate positions:
- prove your assets & liabilities
- if asset = liabilities \(\Rightarrow\) solvency
Source: https://vitalik.ca/general/2022/11/19/proof_of_solvency.html
Core Problems with CEXes
-
Assets: cash in bank accounts and crypto assets in exchange wallets
-
Liabilities: crypto and cash deposits made by customers
-
Proof of cash assets
-
requires an auditor report
-
-
Proof of crypto asset
-
publish all exchange wallets
-
problem: cold storage
-
proof of control: shift assets from one address to another at a pre-determined time
-
-
Proof of liabilities
-
public customer balances - customer can check
-
own holding
-
positive customer balances
-
sums to assets
-
-
-
Problem: privacy
-
Solutions:
-
hash of customer
-
Merkle tree-type organization
-
zero-knowledge proofs
-
-
Proof of assets & liabilities
Core Problems with CEXes
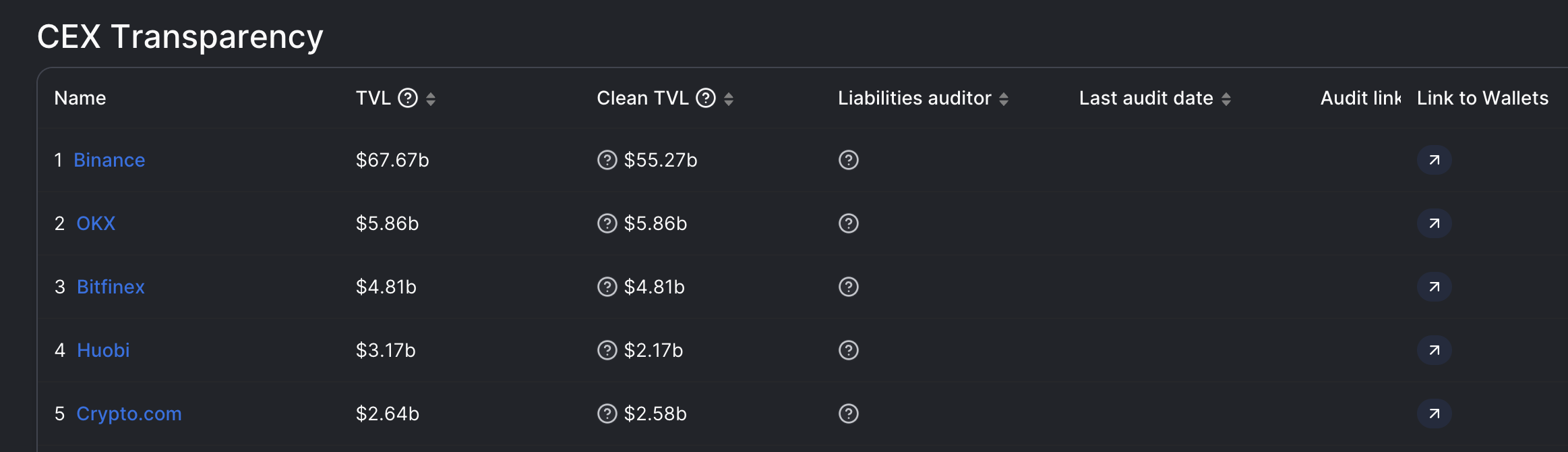
The Regulator's View
Canadian View
- Heavily influenced by QuadrigaCX debacle
- Custody questions paramount (how stored, how accessible, what risks)
- Custody = crypto trading platform (CTP) offers a security (irrespective of the underlying)
- Requirement on due diligence when listing
- Current $50K limit for new purchases
- CTP must register with IIROC (which has no process)
- Only BitBuy is compliant, some are in "Sandbox"
Summary
Main differences
Trading in Equity vs Crypto
- regulated environment
- firm trading rules
- listing requirements
- multi-step process
- complicated settlement
- many intermediaries
Equity Market
Crypto Market
- emerging regulatory environment
- 500+ CEXes worldwide
- use of intermediaries is a choice
- crypto exchange are closer to brokerages than equity exchanges
- settlement a choice and straightforward
- fully decentralized trading is possible and most exiting innovation
- much work remains to be done