{Typescript}
Supercharging Your JavaScript Development
{Hello!}
Javascript is free!
function countCharacter(value){
return value.length
}
var name = "Danger"
countCharacter(name) // 5
var name = 1
countCharacter(name) // ?
var name = false
countCharacter(name) // ?
// Previously: sayMyName(firstName, lastName) { ...
function sayMyName(fullName) {
console.log(`You acting kind of shady, ain't callin' me ${fullName}`);
}
sayMyName("Beyoncé", "Knowles");# var.camp 2.0
if(typeof name !== string) throw "Name should be string";
// find the error in this code
const obj = { width: 10, height: 15 };
const area = obj.width * obj.heigth;
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Ever written something like this?
<div>
{
data.products.map(item=><Card data={item}/>); // 😵 Cannot read the property map of undefined .. or blah blah
}
</div>// javascript has loose documentation
// what is the type of a and b
function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
const inputA = input()("Some async input for a!") // inputA could be anything
const inputB = input()("Some async input for b!") // inputB could be anything
add(inputA, inputB)# VAR.CAMP 2.0
TS provides documentation
Move potential errors from runtime to compile time
function add(a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b
}
add(3, "4")
// 😵 Argument of type 'string' is not assignable to parameter of type 'number'.Of course we can have something like JS Docs
/**
* Add two numbers
* @param {number} a
* @param {number} b
* @returns {number} total value
*/
function sum(a, b) { /* ... */ }- Nothing stops JSDoc descriptions from being wrong about code.
- Even if your JSDoc descriptions were previously correct, during code refactors it can be difficult to find all the now-invalid JSDoc comments related to your changes.
- Describing complex objects is unwieldy and verbose.
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
interface Address {
street: string;
city: string;
state: string;
zipCode: string;
}
interface User {
name: string;
email: string;
password: string;
address: Address;
}
function createUser(name: string, email: string, password: string, address: Address): User {
return {
name,
email,
password,
address : address
};
}
const address = {
street: "123 Main St",
city: "Anytown",
state: "CA",
zipCode: "12345",
};
const newUser = createUser("John Doe", "john@example.com", "secret", address);
Great documentation
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Stronger developer tooling
{Typescript}
Let's talk about Typescript !
Start with zero
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Types are opt-in

Created By Microsoft in early 2010 and open-sourced in 2012.
Typescript has four things
- Programming language
- Type checker
- Compiler
- Language server
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
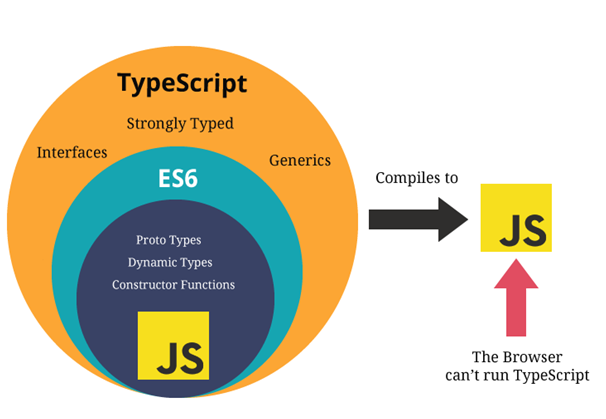
Notations!
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
function sayMyName(fullName) {
console.log(`Hello ${fullName}`);
}
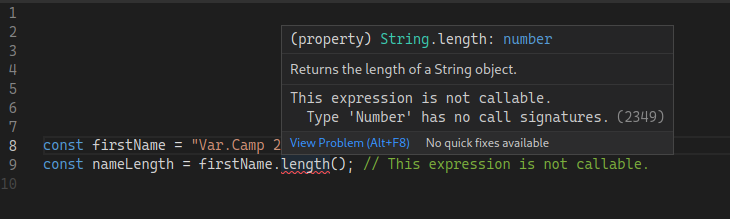
sayMyName("Beyoncé", "Knowles"); // 😵 Expected 1 argument, but got 2.const firstName = "Georgia";
const nameLength = firstName.length(); // 😵 This expression is not callable.
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Some of the basic primitives in Typescript
- number
- string
- boolean
- undefined
- null
let someNumber = 10;
let someString = "Hello String";
let isLive = true;
let someUndefined;
let somePossibleNull = Math.random() > 0.5 ? null : 10;
someNumber.toFixed(0.2)
someString.length // 11
somePossibleNull.toFixed() // 😵 possibly nullSome of the basic primitives in Typescript
- number
- string
- boolean
- undefined
- null
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Type system
Set of rules for a language to understand what types in a program contract may have.
Simply Typescript system works by
• Reading in your code and understanding all the types and values in existence
• For each value, seeing what type its initial declaration indicates it may contain
• For each value, seeing all the ways it’s used later on in the code
• Complaining to the user if a value’s usage doesn’t match its type
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Type of errors
Syntax error : Blocking Typescript from being converted to Javascript
let let wat;
//
~~~
// Error: ',' expected.Type error : Something mismatched has been detected by the type checker
let eventName : string = "Var.Camp 2.0";
eventName = "Var.Camp 2.0";
eventName = 20; // 😵 Type 'number' is not assignable to type 'string'.
eventName.toSomething(); // 😵 Type 'number' is not assignable to type 'string'. type possiblyNumberOrString = number | string;
let value : possiblyNumberOrString = Math.random() > 0.5 ? 12 : "Twelve";
let physicist = Math.random() > 0.5 ? "Marie Curie" : 84;
physicist.toString(); // Ok vaild for both type
physicist.toUpperCase(); // 😵 Error: Property 'toUpperCase' does not exist on type 'string | number'.
physicist.toFixed(); // 😵 Property 'toUpperCase' does not exist on type 'number'.
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Union Types
// Type of scientist: number | string
let scientist = Math.random() > 0.5 ? "Rosalind Franklin" : 51;
scientist.toUpperCase(); // 😵 Property 'toUpperCase' does not exist on type 'string | number'.
if (scientist === "Rosalind Franklin") {
scientist.toUpperCase(); // Ok
}
if (typeof scientist === "string") {
scientist.toUpperCase(); // Ok
}
typeof scientist === "string" ? scientist.toUpperCase() // Ok: string
: scientist.toFixed(); // Ok: number# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Narrowing
const poet = {
born: 1935,
name: "Mary Oliver",
};
poet['born']; // Type: number
poet.name; // Type: string
poet.end; // 😵 Error: Property 'end' does not exist on type '{ born: number; name: string; }'.
type Poet = {
born: number;
name: string;
};
let poetLater: Poet;
// Ok
poetLater = {
born: 1935,
name: "Sara Teasdale",
};
poetLater = "Emily Dickinson"; //😵 Error: Type 'string' is not assignable to 'Poet'.# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Object types
type WithFirstName = {
firstName: string;
};
type WithLastName = {
lastName: string;
};
const hasBoth = {
firstName: "Lucille",
lastName: "Clifton",
};
let withFirstName: WithFirstName = hasBoth; // Ok: `hasBoth` contains a `firstName` property of type `string`
let withLastName: WithLastName = hasBoth; // Ok: `hasBoth` contains a `lastName` property of type `string`# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Structural typing
type FirstAndLastNames = {
first: string;
last: string;
};
// Ok
const hasBoth: FirstAndLastNames = {
first: "Sarojini",
last: "Naidu",
};
const hasOnlyOne: FirstAndLastNames = {
first: "Sappho"
};
// 😵 Property 'last' is missing in type '{ first: string; }'
// 😵 but required in type 'FirstAndLastNames'.
const extraProperty: FirstAndLastNames = {
first: "Sarojini",
last: "Naidu",
age : 10
};
// 😵 'age' does not exist in type 'FirstAndLastNames'.# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Using Checking
type Book = {
author?: string; // optional author
pages: number;
};
// Ok
const ok: Book = {
author: "Rita Dove",
pages: 80,
};
const missing: Book = {
author: "Rita Dove",
};
// 😵 Error: Property 'pages' is missing in type
// '{ author: string; }' but required in type 'Book'.# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Optional properties
const poem = Math.random() > 0.5
? { name: "The Double Image", pages: 7 }
: { name: "Her Kind", rhymes: true };
/**
* {
* name : string;
* pages : number;
* }
* |
* {
* name : string;
* rythmes : boolean
* }
*
*/
poem.name; // string
poem.pages; // number | undefined
poem.rhymes; // booleans | undefined# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Inferred object union types
type Poet = {
born: number;
name: string;
};
interface Poet {
born: number;
name: string;
}
let valueLater: Poet;
// Ok
valueLater = {
born: 1935,
name: 'Sara Teasdale',
};
valueLater = "Emily Dickinson"; // 😵 Error: Type 'string' is not assignable to 'Poet'.
// 😵 Error: Type 'boolean' is not assignable to type 'number'.
valueLater = {
born: true,
name: 'Sappho'
};# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Interfaces
interface Animal {
name: string;
sound: string;
readonly legs: number;
run(speed: number): void;
}
interface Cat extends Animal {
meow(): void;
}
// OK !
const myCat: Cat = {
name: "Fluffy",
sound: "meow",
legs: 4,
run(speed: number) {
console.log(`I'm running at ${speed} mph!`);
},
meow() {
console.log("Meow!");
},
};# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Some differences
{ More }
// any
let anyValue: any;
anyValue = "Lucille Ball"; // Ok
anyValue = 123; // Ok
console.log(anyValue); // Ok
// unknown
function greetComedian(name: unknown) {
console.log(`Announcing ${name.toUpperCase()}!`); // 😵 Error: Object is of type 'unknown'.
}
// using narrowing
function greetComedianSafety(name: unknown) {
if (typeof name === "string") {
console.log(`Announcing ${name.toUpperCase()}!`); // Ok
} else {
console.log("Well, I'm off.");
}
}
greetComedianSafety("Var.Camp"); // "Announcing VAR.CAMP!"
greetComedianSafety({}); // "Well, I'm off." # VAR.CAMP 2.0
Top types
function isNumberOrString(value: unknown) {
return ['number', 'string'].includes(typeof value);
}
function logValueIfExists(value: number | string | null | undefined) {
if (isNumberOrString(value)) {
// 😳 ? Type of value: number | string
// 😵 'value' is possibly 'null' or 'undefined'
console.log(value.toString());
} else {
// Type of value: null | undefined
console.log("value does not exist:", value);
}
}
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Type predicates
function typePredicate(input: WideType): input is NarrowType;
function isNumberOrString(value: unknown) : value is number | string {
return ['number', 'string'].includes(typeof value);
}
function logValueIfExists(value: number | string | null | undefined) {
if (isNumberOrString(value)) {
// 😍 Type of value: number | string
console.log(value.toString());
} else {
// Type of value: null | undefined
console.log("value does not exist:", value);
}
}
logValueIfExists(null)# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Type predicates
interface Box<T> {
inside: T;
}
let stringyBox: Box<string> = {
inside: "abc",
};
let numberBox: Box<number> = {
inside: 123,
}
let incorrectBox: Box<number> = {
inside: false,
// 😵 Error: Type 'boolean' is not assignable to type 'number'.
}
function makeTuple<First, Second>(first: First, second: Second) {
return [first, second] as const;
}
makeTuple(true, "abc"); // OK Type of value: readonly [boolean, string]
makeTuple<string, number>("abc", 123); // OK ! Type: { key: string; value: number }
makeTuple<"abc", 123>("abc", 123); // Type: { key: "abc"; value: 123 }
makePair<string>("abc", 123); // 😵 Error: Expected 2 type arguments, but got 1.# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Generics
// Type: Promise<unknown>
const resolvesUnknown = new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve("Done!"), 1000);
});
// Type: Promise<string>
const resolvesString = new Promise<string>((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve("Done!"), 1000);
});
// // Type: (text: string) => Promise<number>
async function lengthAfterSecond(text: string) {
new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000))
return text.length;
}
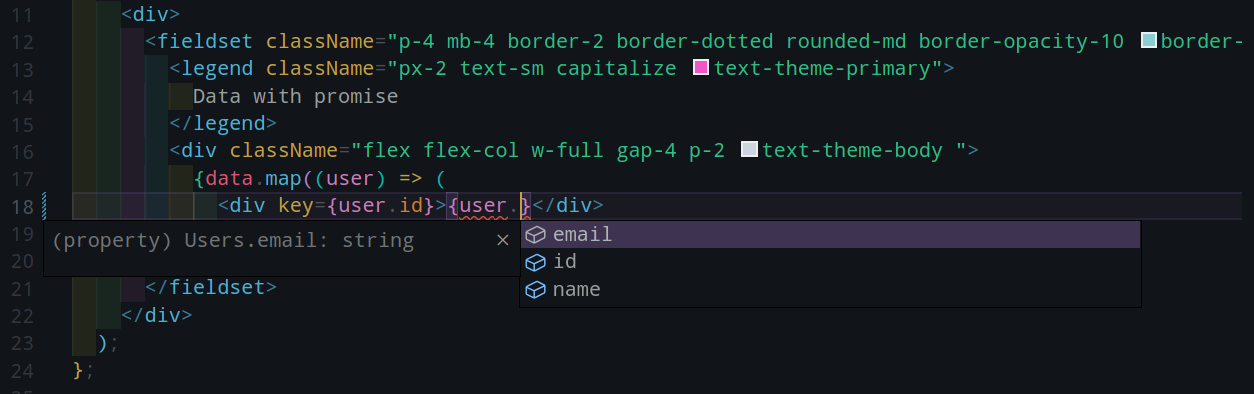
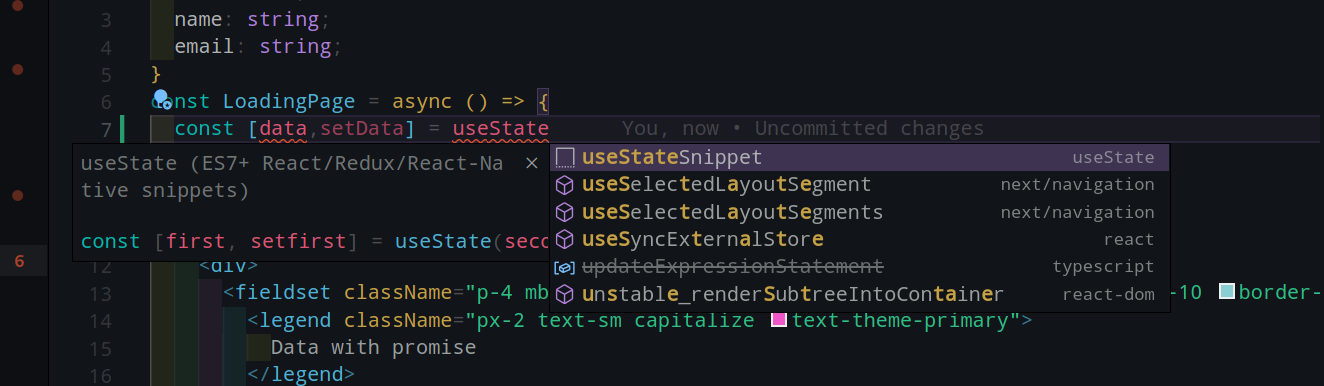
async function getData<T>(): Promise<T> {
const [data,setData] = useState<T>()
useEffect(()=>{
// set data
},[])
return data
}
interface Data {
name : string;
email : string;
}
const res = getData<Data>();# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Generics & Async
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Declaration files
// modules.d.ts
declare module "my-example-lib" {
export const value: string;
}
// index.ts
import { value } from "my-example-lib";
console.log(value); // Ok
// styles.d.ts
declare module "*.module.css" {
const styles: { [i: string]: string };
export default styles;
}
// component.ts
import styles from "./styles.module.css";
styles.anyClassName; // Type: string# VAR.CAMP 2.0
Example
// styles.d.ts
declare module "*.module.css" {
const styles: { [i: string]: string };
export default styles;
}
// component.ts
import styles from "./styles.module.css";
styles.anyClassName; // Type: string
// globals.d.ts
declare const version: string;
// version.ts
export function logVersion() {
console.log(`Version: ${version}`); // Ok
}{ Definately Typed }
- a giant community repo
- high-quality type definitions for popular libraries and modules
- Can install via npm and used in projects
- Make life easier for devs when dealing with libraries or modules
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
{
"dependencies": {
"react": "^18.1.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/react": "^18.0.9"
},
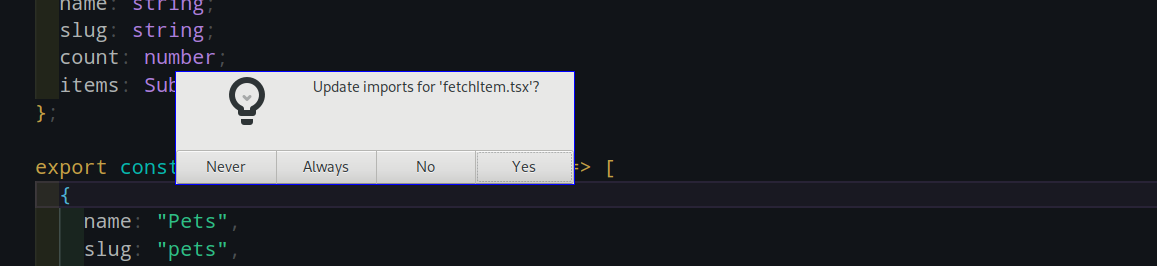
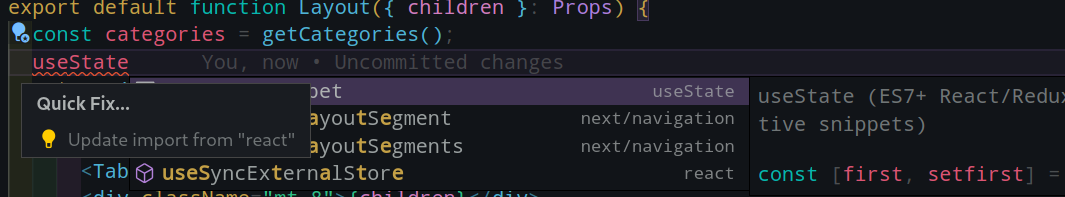
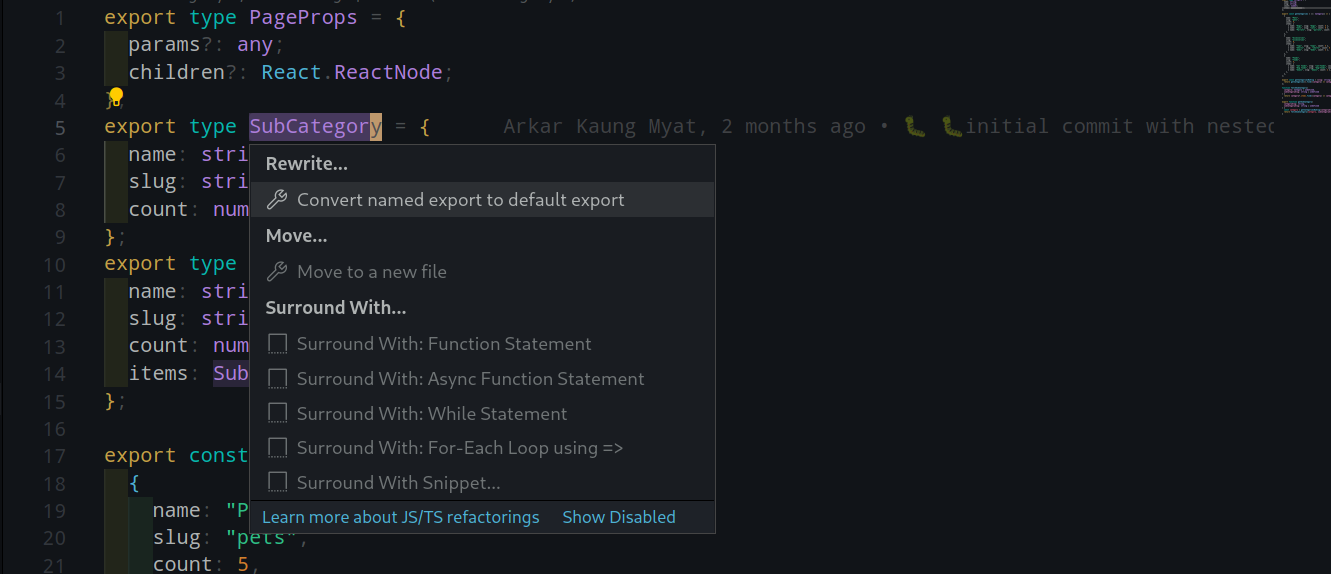
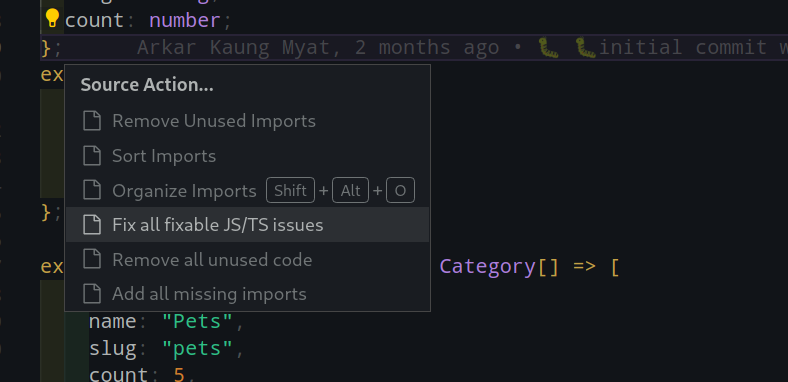
}{ USING IDE Features }
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
# VAR.CAMP 2.0
# VAR.CAMP 2.0