Data
Driven
Front-End
// Whoami
Alex Albu
Software Engineer @FlowX.ai

Trainer @JSLeague
// Why


// Inspiration
Back-end architecture

Micro-service architecture

Layered Architecture
// Inspiration
Software Design Techniques
reactive programming
low coupling
high cohesion
// Solution

The architecture is composed of layers each communicating only with its neighbours.
We are not going to care about stack, framework, libraries or specific implementation details.
Changes should only affect the layers above (children).
Data Handling
Responsibility to handle data from outside sources, transforming it and making it accessible to our app

// Solution
Business Logic
It holds the actual logic of how things work.
Rules, constraints, logical thinking goes into here.

// Solution
UI Components
These are reusable, generic, abstract, bits of UI that we can leverage to fast prototype the interface.

// Solution
Views
User interaction gets handled here but without the logic. Just handling events, triggers, rendering, ui actions. All logic gets delegated to the business logic.

// Solution
// Data Driven Front-end

// Data Driven Front-end

// Data Driven Front-end

// Data Driven Front-end

// Demo
Movies App
// Demo -- Data Sources
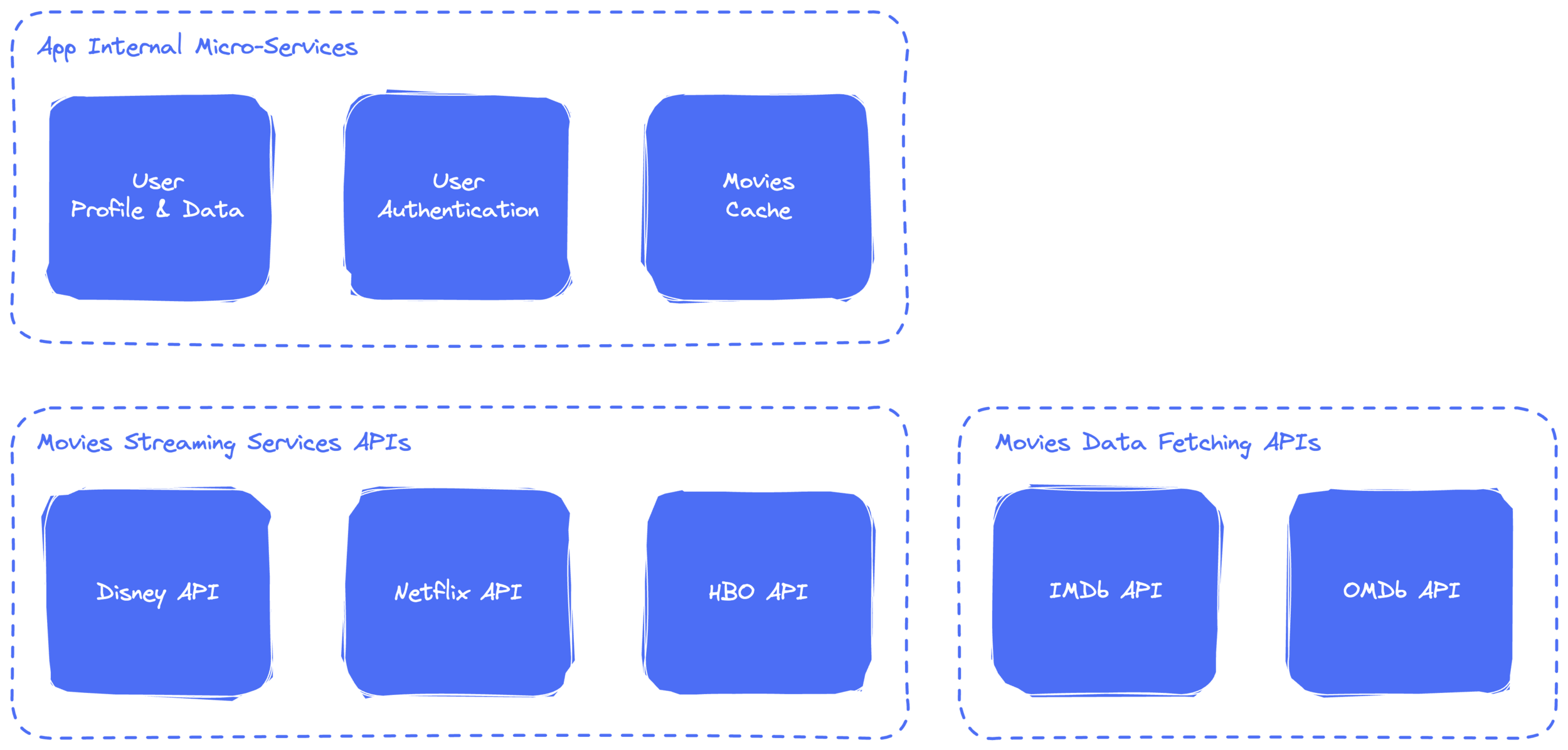
// Demo -- Models

// Demo -- Models
// rating.enum.ts
export enum Rating {
G,
PG,
PG13,
R,
M,
}
// genre.enum.ts
export enum Genre {
Comedy,
Romance
}// movie.entity.ts
import { Genre } from "@movieApp/entities";
import { Rating } from "@movieApp/entities";
export type Movie = {
title: string;
year: number;
plot: string;
posterUrl: string;
genre: Genre[];
rating: Rating;
};
// someplace.ts
import { Movie } from "@movieApp/entities";// Demo -- APIs

// Demo -- APIs
// movies.services.ts
export enum APIService {
OMDb = "https://omdb.example.com/api",
IMDB = "https://imdb.example.com/api",
Netflix = "https://netflix.example.com/api",
Disney = "https://disney.example.com/api"
}// movies.api.ts
import axios from "axios";
import { APIService } from "@movieApp/api/services";
import { Movie } from "@movieApp/entities";
type MovieDetailsFilters = {/* data model */};
type MovieDetailsRequest = {/* data model */};
type MovieDetailsResponse = {/* data model */};
export async function getMovieDetails(
movieId: Pick<Movie, "id">,
filters?: MovieDetailsFilters
): Promise<Movie> {
const omdbFilters: MovieDetailsRequest = filters
.map(/* map filters data to omdb model */);
return axios
.get(`${APIService.OMDb}/movies/${movieId}`, omdbFilters)
.then((data: MovieDetailsResponse) => {
/* map data here to movie model */
});
}
// someplace.ts
import * as MoviesAPI from "@movieApp/api/movies";
MoviesAPI.getMovieDetails(/* movieId */)// Demo -- Queries

// Demo -- Queries
// movies.queries.ts
import Store from "@moviesApp/queries/store";
import * as MoviesAPI from "@movieApp/api/movies";
import * as UsersAPI from "@movieApp/api/users";
import { Movie, StreamPlatform } from "@movieApp/entities";
type MovieSummary = Pick<Movie, "id" | "title" | "posterUrl" | "plot">;
type MovieDetails = Movie;
type MovieId = Pick<Movie, "id">;// Demo -- Queries
// movies.queries.ts
export async function getSummary(movieId: MovieId): Promise<MovieSummary> {
if (!Store.movies[movieId]) {
const movieData = await MoviesAPI.getSummary(movieId);
Store.movies[movieId] = movieData;
}
return Store.movies[movieId];
}
export async function getDetails(movieId: MovieId): Promise<MovieDetails> {
return MoviesAPI.getDetails(movieId);
}
export async function getNetflixStream(movieId: MovieId): Promise<string> {
return MoviesAPI.getStream(movieId, StreamPlatform.Netflix);
}// Demo -- Queries
// movies.queries.ts
export async function setLike(movieId: MovieId): Promise<boolean> {
return UsersAPI.likeMovie(movieId)
.then(() => {
Store.user["likes"].push(movieId);
})
.then(() => true)
.catch(() => false);
}
export async function setRating(movieId: MovieId): Promise<boolean> {
return UsersAPI.setRating(movieId)
.then((data) => {
Store.user["rantings"][movieId] = data;
})
.then(() => true)
.catch(() => false);
}
// Demo -- Big Picture

// Conclusions -- PROS
When dealing with codebase changes, it will reduce complexity and make it easier to test and catch bugs early.
It makes it easier to transition between libraries, frameworks or sharing between teams.
It allows to adapt with observables easily and move from a passive programming style to a more reactive one
// Conclusions -- CONS
Codebase ends up being larger and having more dependencies (each layer becomes a dependency)
Requires more engineering discipline and guidelines to keep consistency
Raises cognitive complexity
// Conclusions
Always take everything with a grain of salt, there is not silver bullet or magical wand that is going to make things perfect. Change is constant.