CARDIAC
MASS
Atul Jaidka | Clin Card Rounds
- Dr. Lynn Bergin
- Dr. Rami Abazid
- Dr. Stuart Smith
Acknowledgement
Outline
Case
| PMH | MEDS | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| 20F | Abilify | Chest pain |
| Bipolar | Lyrica | Palpitations |
| PTSD | Shortness of Breath | |
| Anxiety | Syncope (x2) |
- Vitals: 36.8, 121/81, HR 100, RR 16, SAT 99% on RA
- Gen: Alert and oriented x 3, no distress
- Resp: Clear to auscultation
- Cardiac:
- NS1, S2, no EHS. ? very quiet "plop"
- No pedal edema. JVP is flat
- Peripheral
- No stigmata of autoimmune disease or endocarditis
Physical Exam
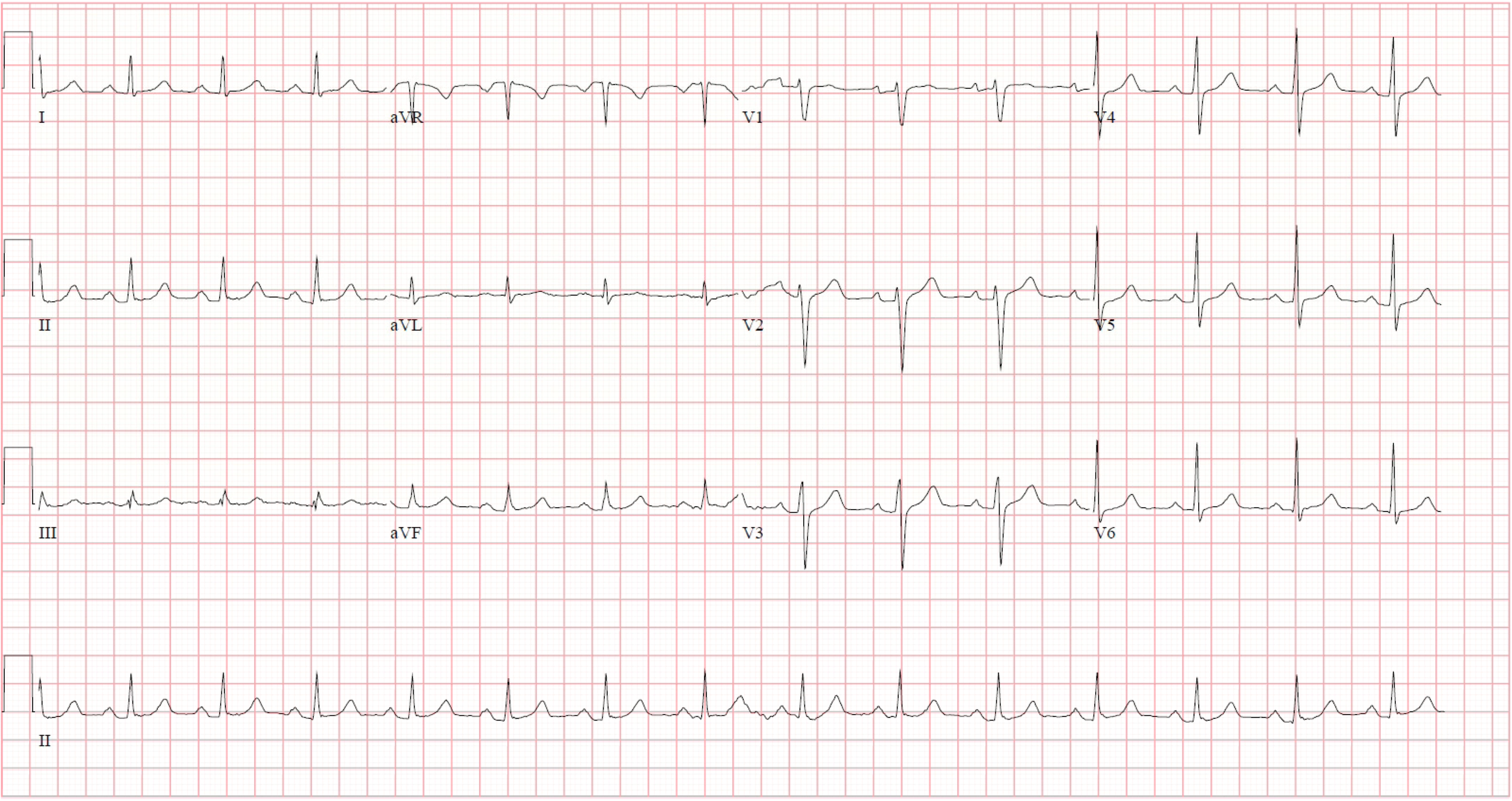
ECG
CXR
TTE
Ejection Fraction 65-70%
TTE
No significant inflow gradient
TTE
TTE
TTE
- Large ill defined ovoid mass noted in the right atrium measuring at least 22mm by 22mm.
- Normal LV and RV size and function
- No significant valvular disease
- No pericardial effusion
TTE
TTE
TTE
Differential
1.
2.
3.
Differential
Tumour /
Myxoma
1.
Blood Cyst / Vascular
2.
Artefact
3.
Differential
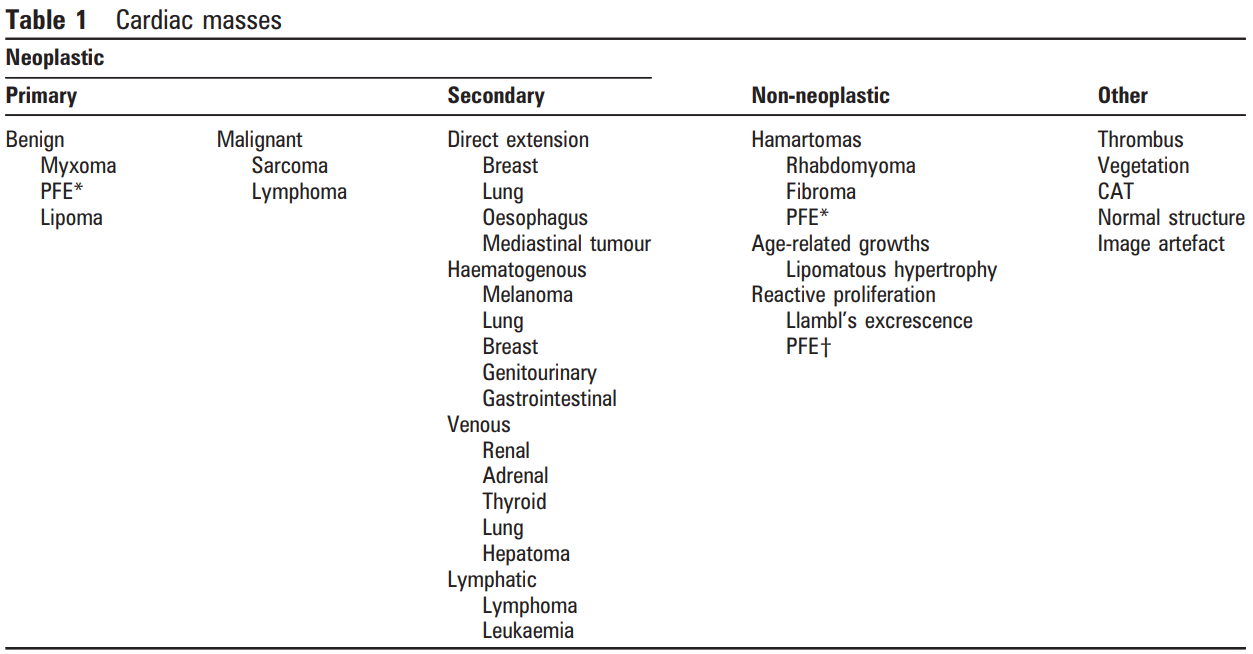
Differential

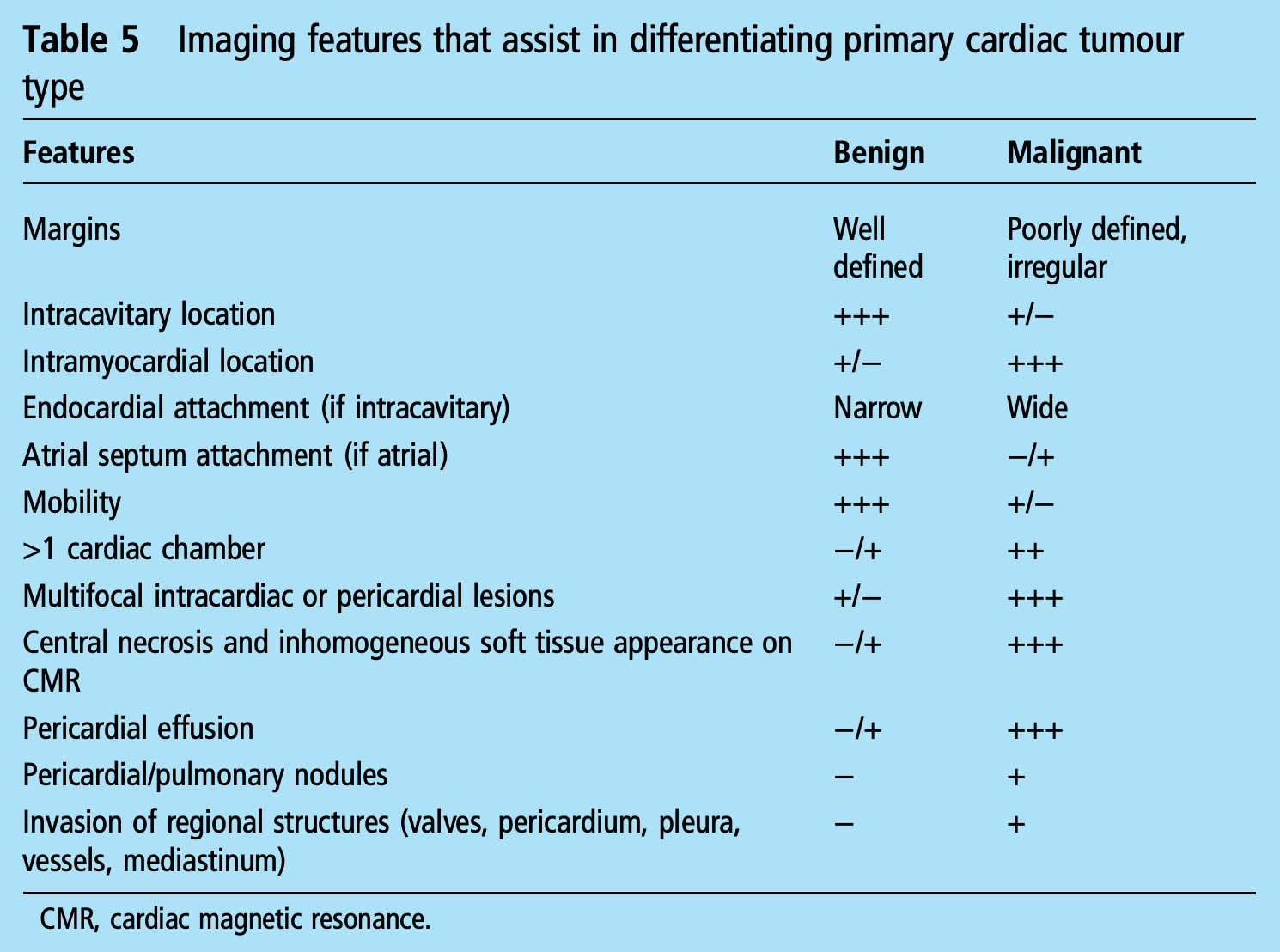
Differential
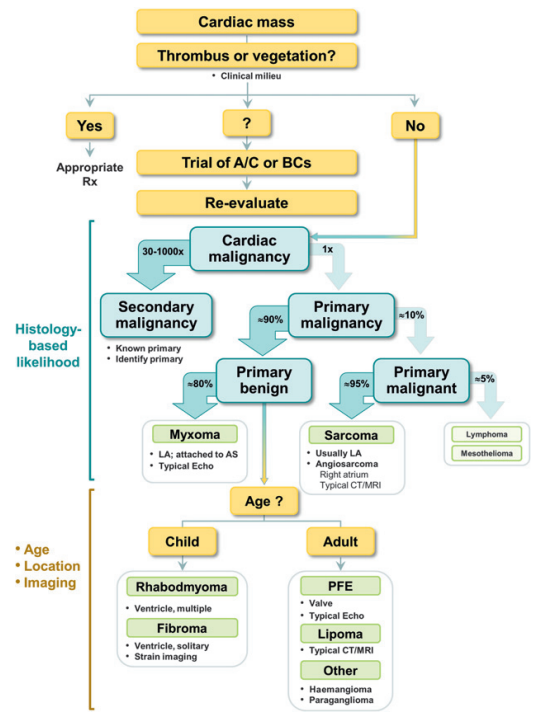
Next Steps?
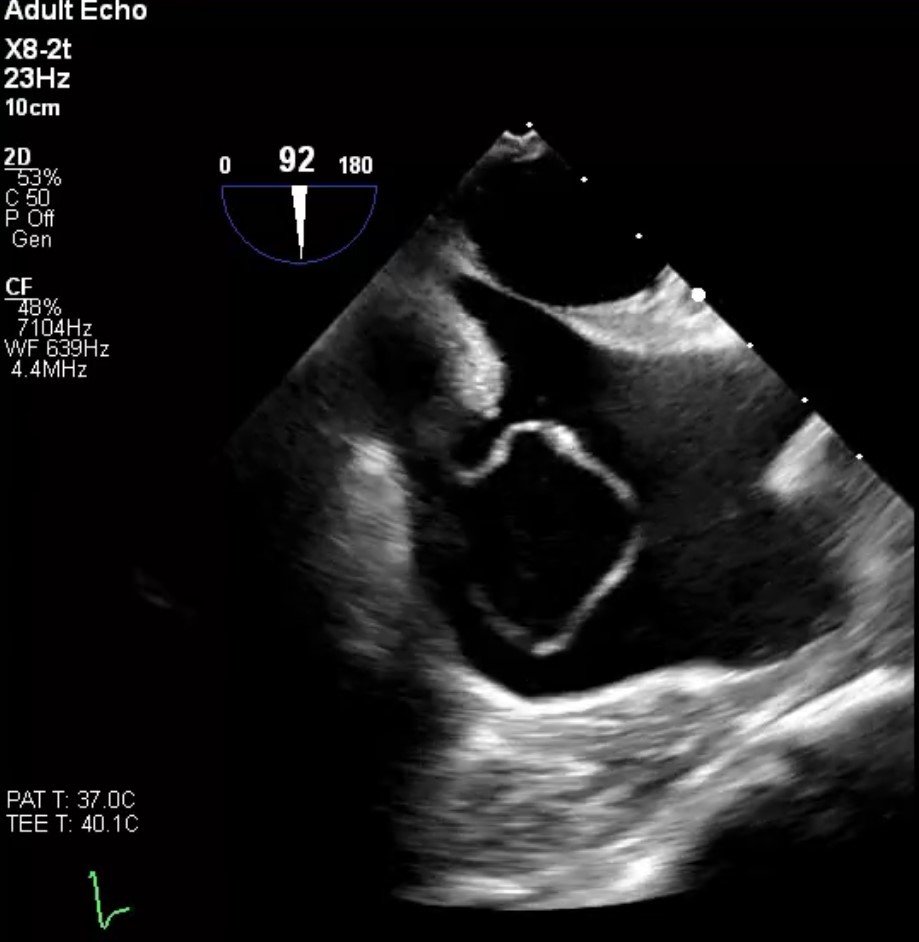
TEE
- Large circular shaped mass that measures approximately 3cm by 2cm that is seen in the right atrium. This mass is "sac -like" in shape.
- Flow is noted in both systole and diastole emptying into the right atrium from at least two distinct areas from this
mass.
TEE
Cath
CT Heart
- Coronary artery fistula with features of macrofistulous communication of the distal left circumflex artery with the coronary sinus and presumed exophytic varix extending into the right atrium
- Circumflex measuring up to 9mm proximally and 26mm distally
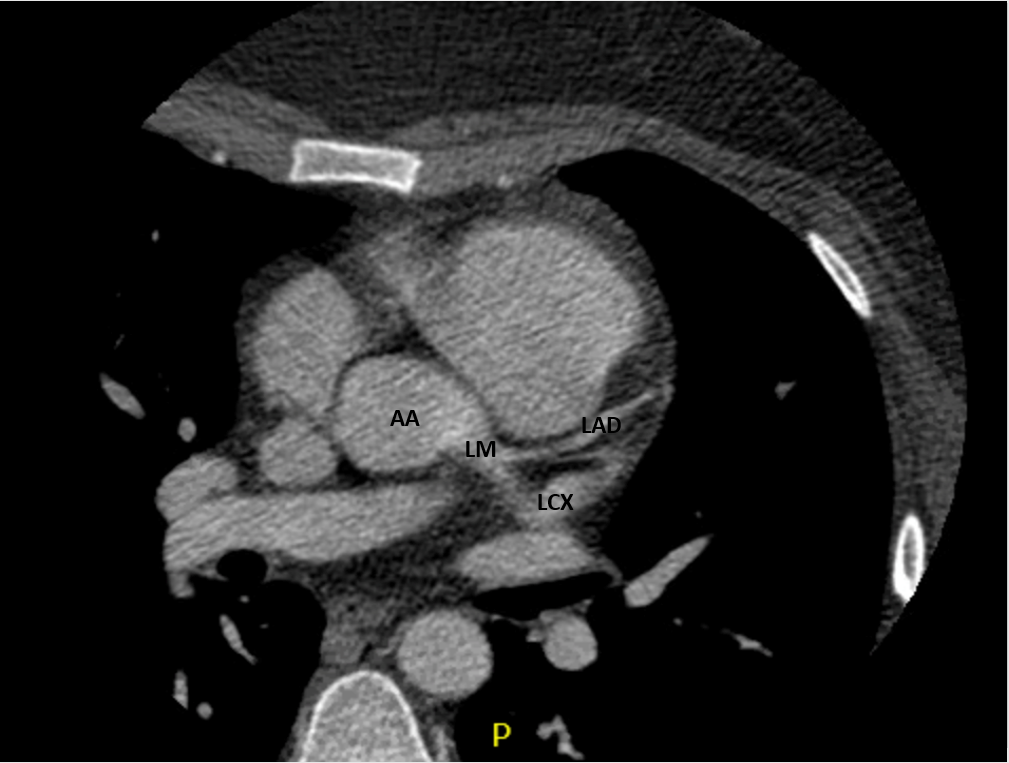
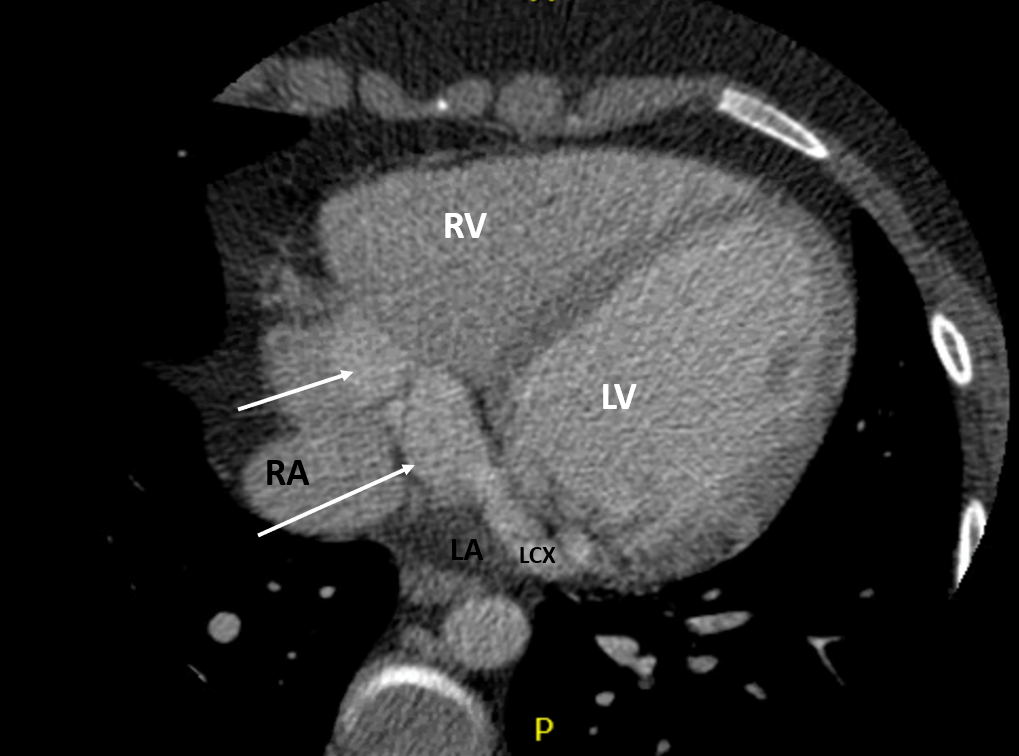
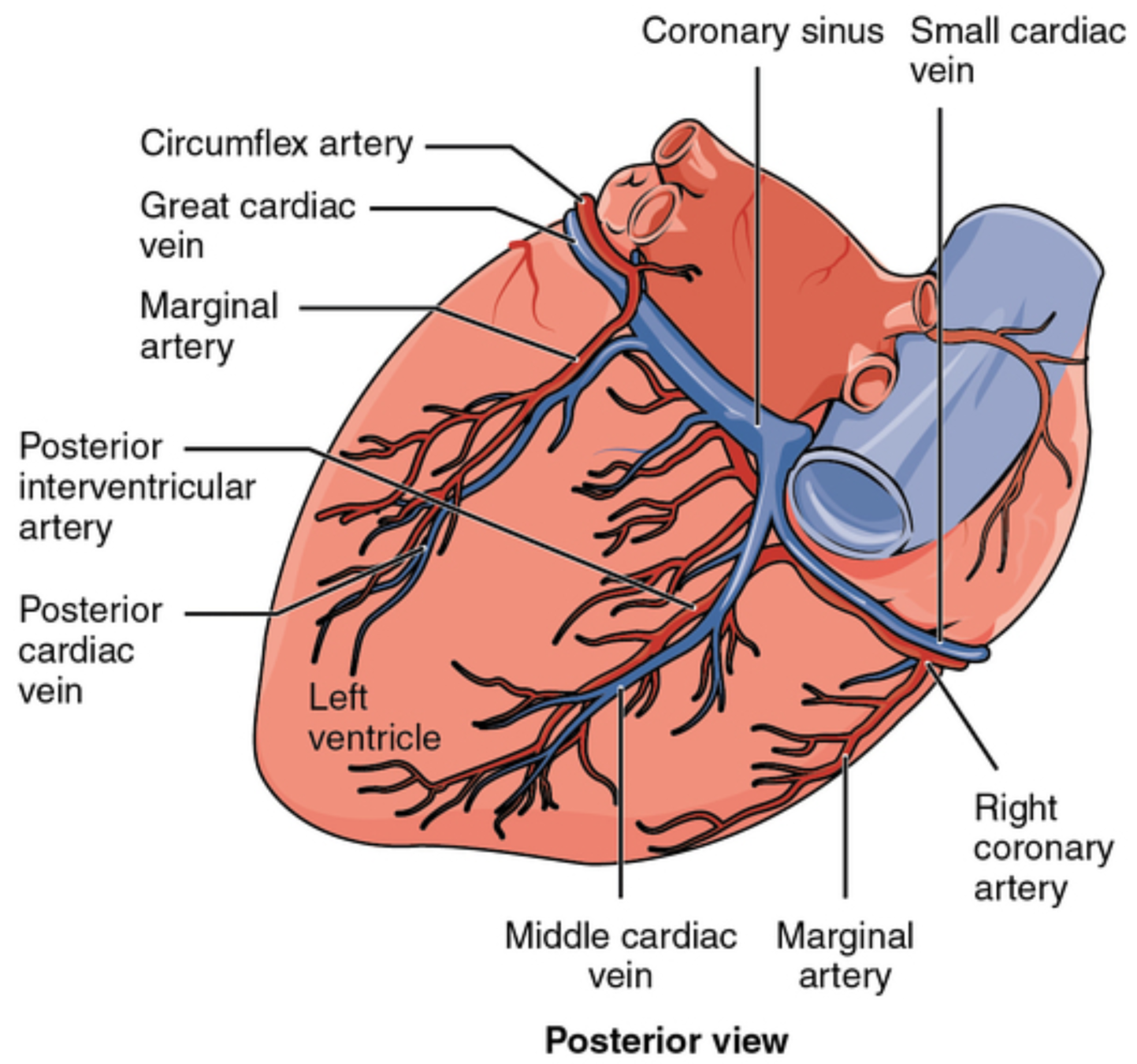
Anatomy
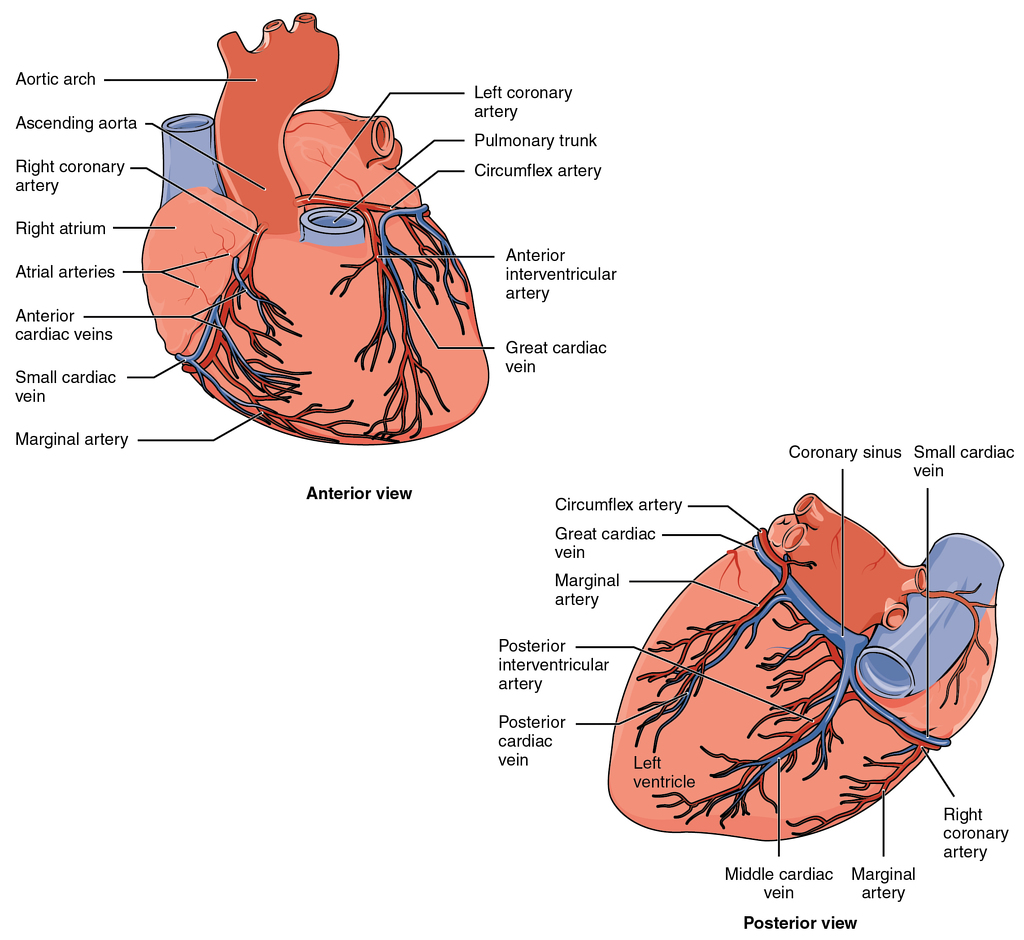
Text
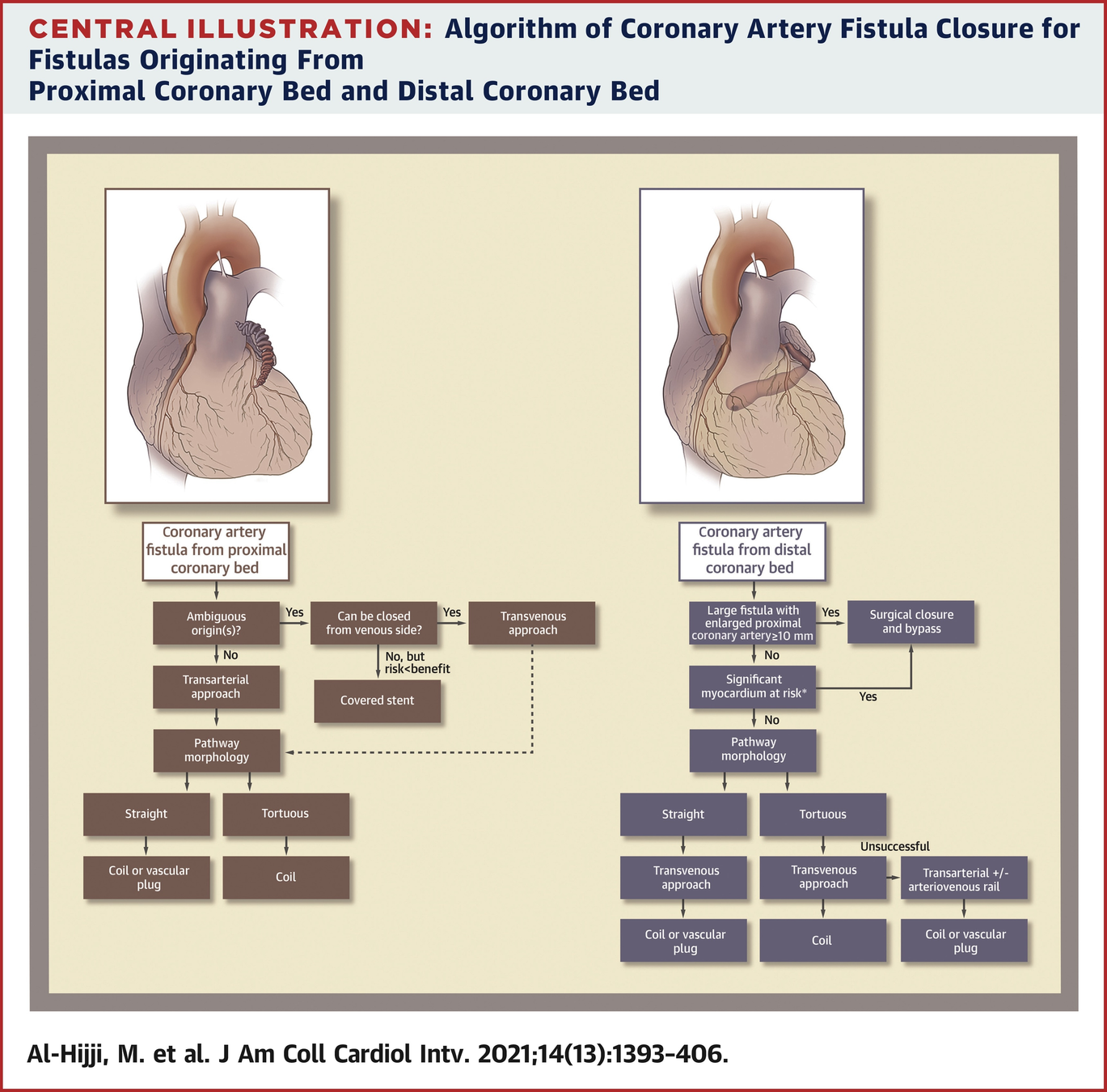
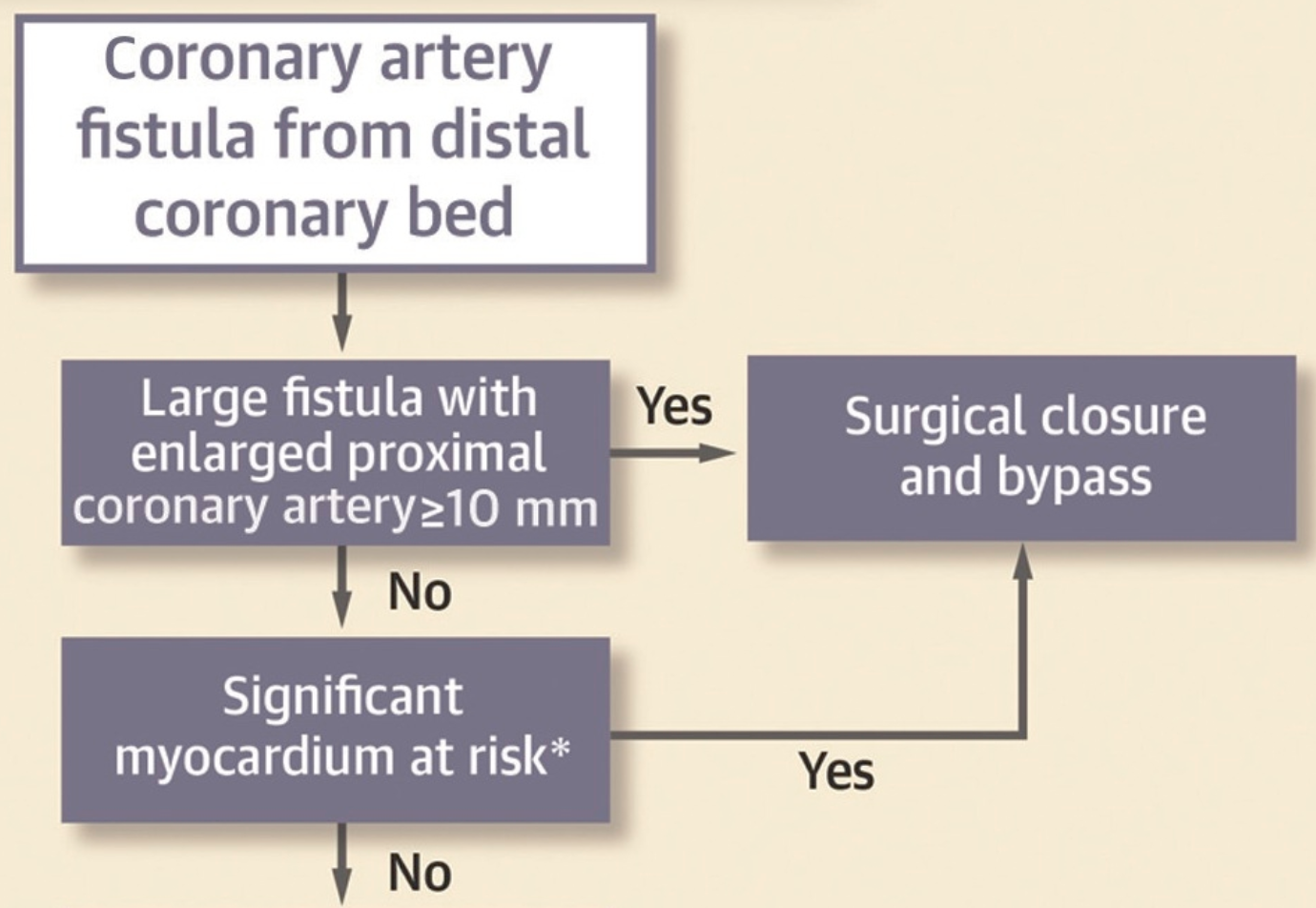
Intervention?
MPI
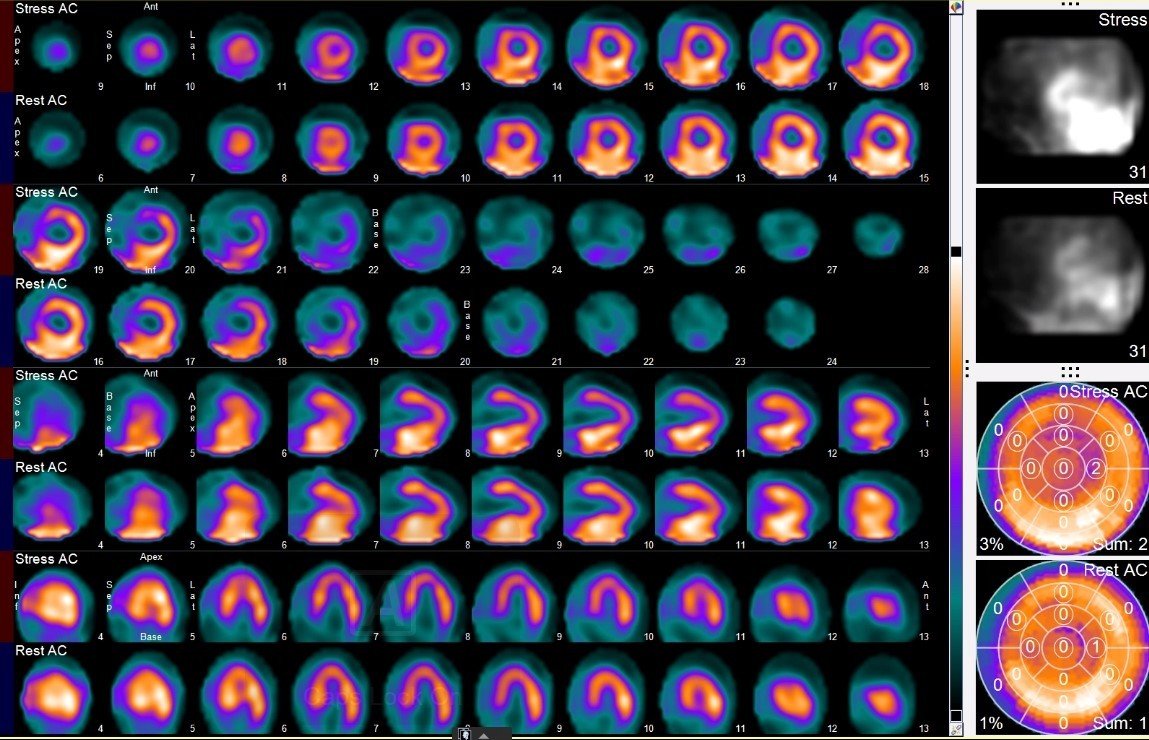
The myocardial perfusion is unremarkable with no evidence of prior infarct or significant ischemia. Note is made of decrease from rest EF of 60% to post-stress 52% of indeterminate significance.

MPI

The myocardial perfusion is unremarkable with no evidence of prior infarct or significant ischemia. Note is made of decrease from rest EF of 60% to post-stress 52% of indeterminate significance.
- Defined as dilated venous channel or cystic space
- Rare with incidence of 0.07-2.5% (most commonly found on autopsy)
- Right atrium and involving IAS most common location
- Often misdiagnosed as myxoma and other differential includes endocardial blood cyst
- Calcified rim or phlebolith has been described in one case
Cardiac Varix
Pichler Sekulic S, Glasgow A, Wasman J, Sabik JF, Fitzsimons B, Sekulic M. Cardiac varix: an example via a case report of a radiological mimicker of cardiac myxoma. Cardiovascular Pathology. 2020;45:107183.
- Coronary artery fistula rare with incidence of 0.1-0.2%
- Most commonly right coronary and most common drainage to RV, RA and PA (CS only 7% of cases)
- Coronary artery fistula can "steal" blood from coronary artery to low pressure cardiac chamber/vein
- Can lead to ischemia and progressive dilation of fistula (eventually possible aneurysm and thrombosis)
- High output congestive heart failure also possible
Cx to CS Fistula
Abdelmohsen G, Abd El Rahman MY, Dohain A, Latif SA, Attia W. Left circumflex coronary artery to coronary sinus fistula diagnosed in infancy. J Cardiol Cases. 2016;15(3):97-99. Published 2016 Dec 28.
Case Resolution
- Given significant size of fistula + coronary and symptoms, decision made to go ahead with surgery
Addendum!
Update
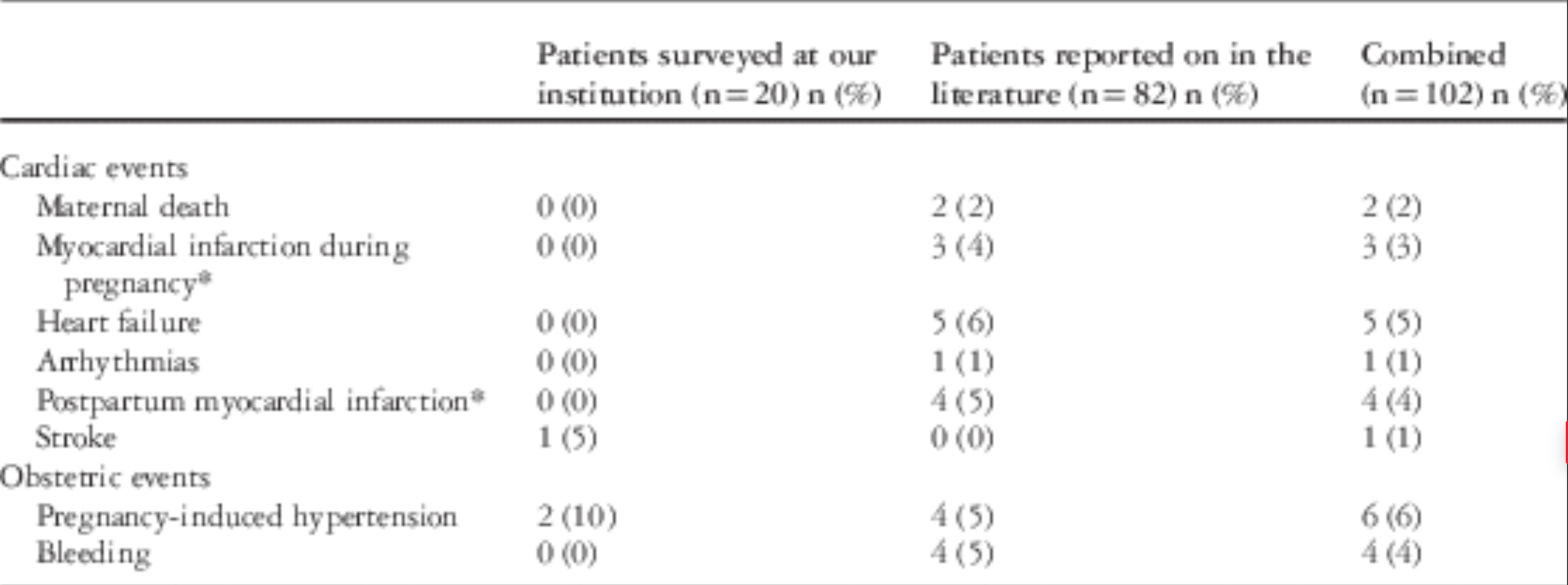
While waiting for surgery patient became pregnant


- Pregnancy causes a relative drop in hemoglobin and PVR
- Increased risk of clotting during pregnancy
- Above increases risk of adverse events in those with vulnerable coronaries
- Study found a 14% maternal cardiac event rate during pregnancy
- Recommend cardiology involvement and ASA