Lung Ultrasound
During Stress Echocardiography
Atul Jaidka | TGH Echo Rounds
Index
Background
Why
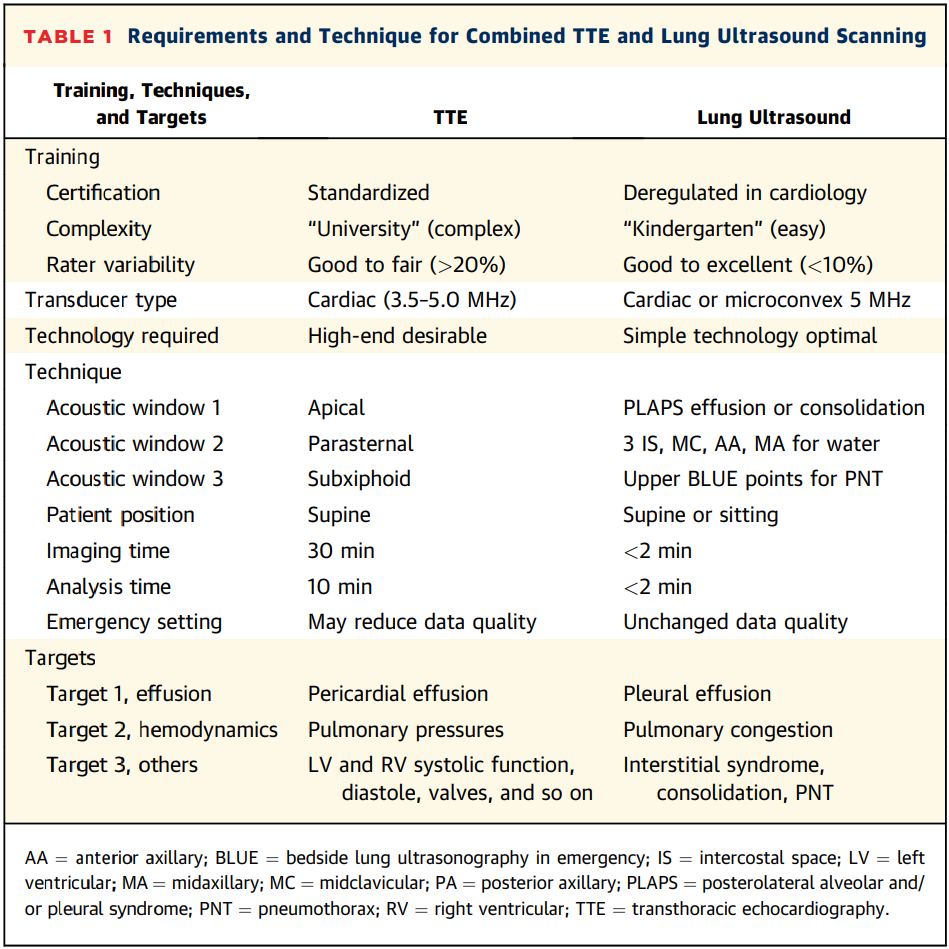
Lung US
Picano E, et al. (2018) Lung Ultrasound for the Cardiologist. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 11:1692-705.
- Simple, noninvasive, radiation-free and semi-quantitative tool
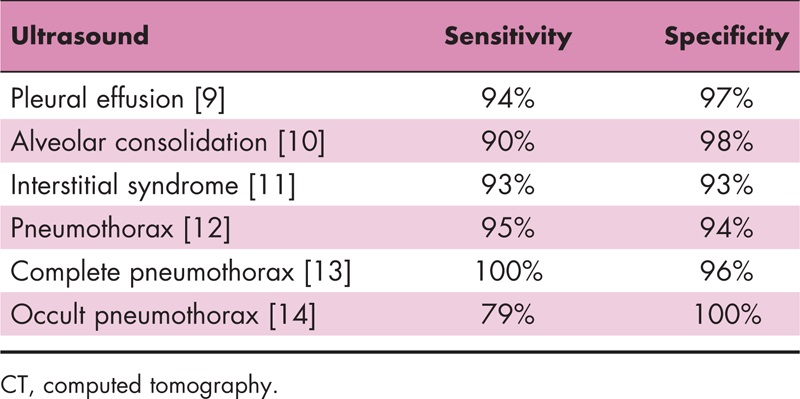
Why Lung Ultrasound
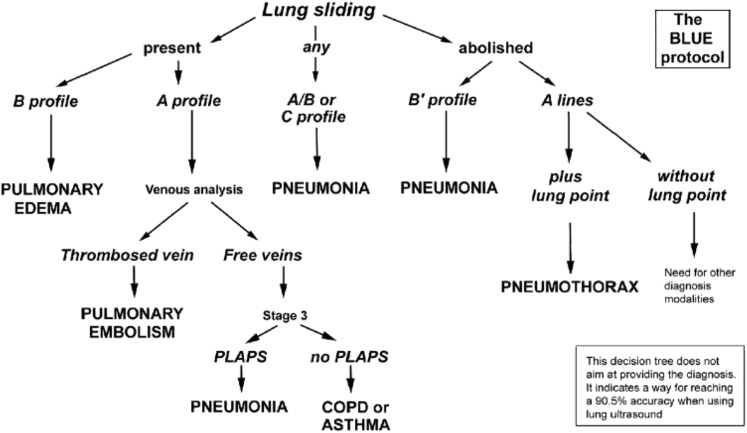
Lichtenstein DA; Mezière GA. (2008) Relevance of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute respiratory failure: the BLUE protocol. Chest 134:117-25.
Lichtenstein D. (2014) Lung ultrasound in the critically ill. Curr Opin Crit Care 20:315-22.
A lines:
- Horizontal repetitions of the pleural lines
Profiles
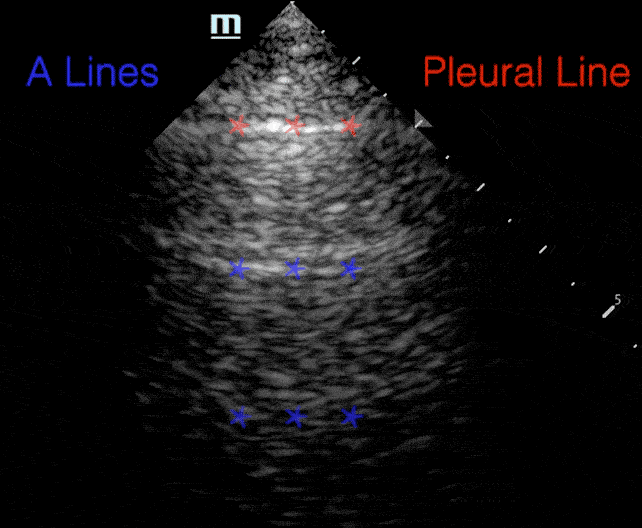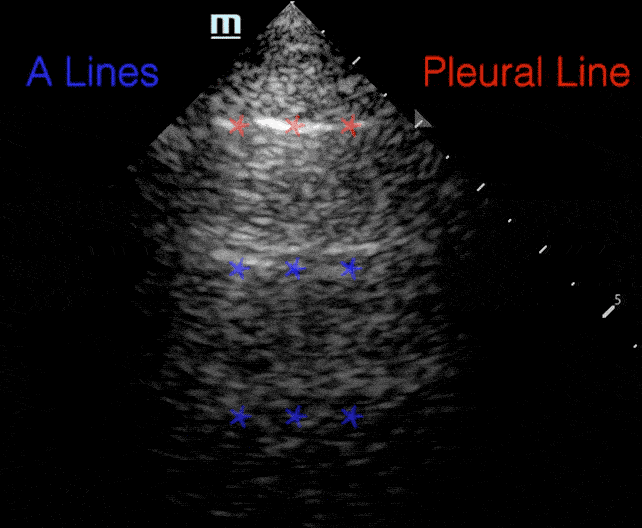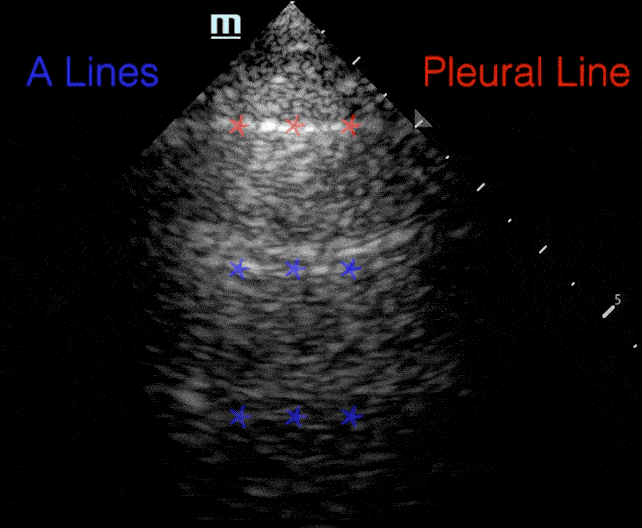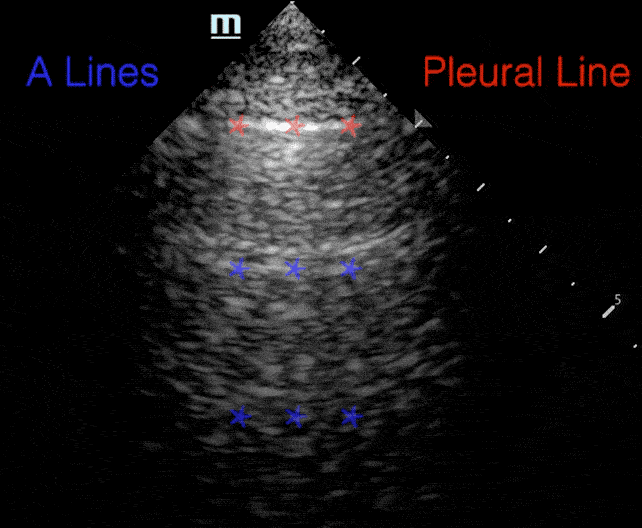
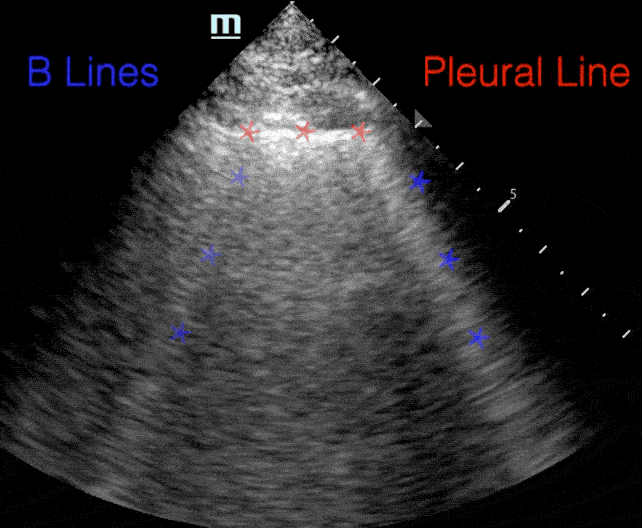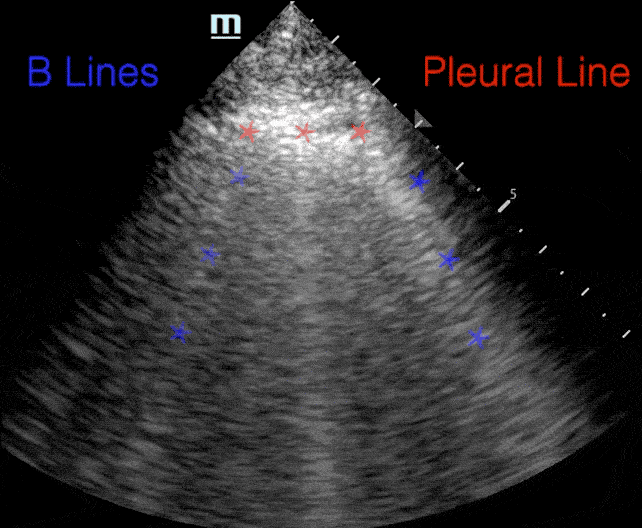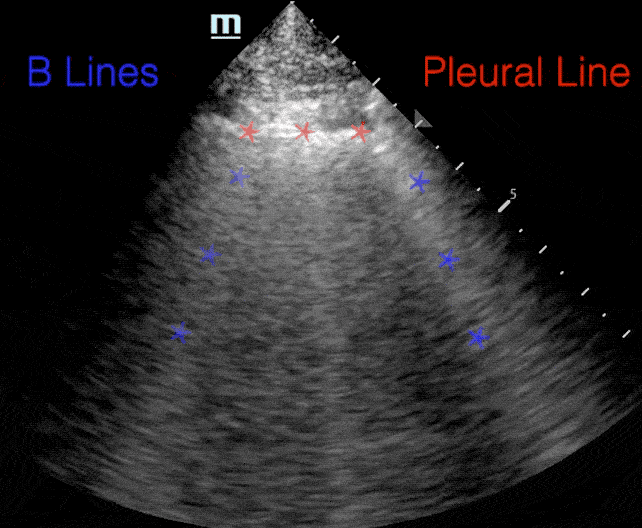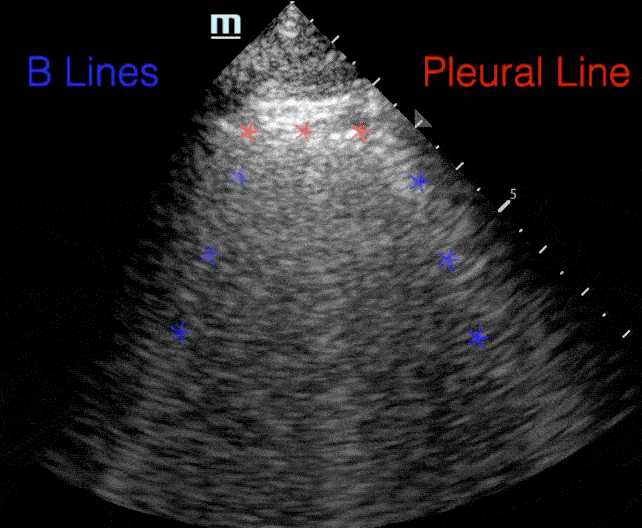
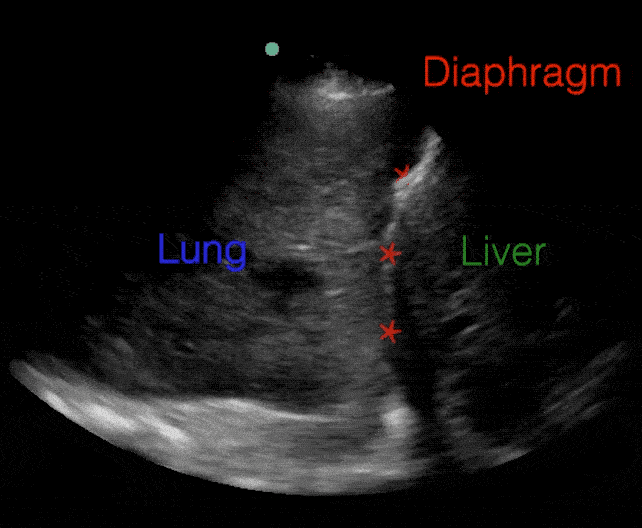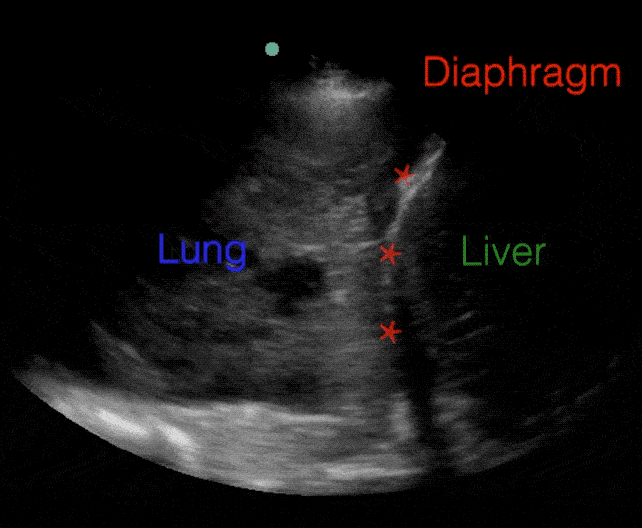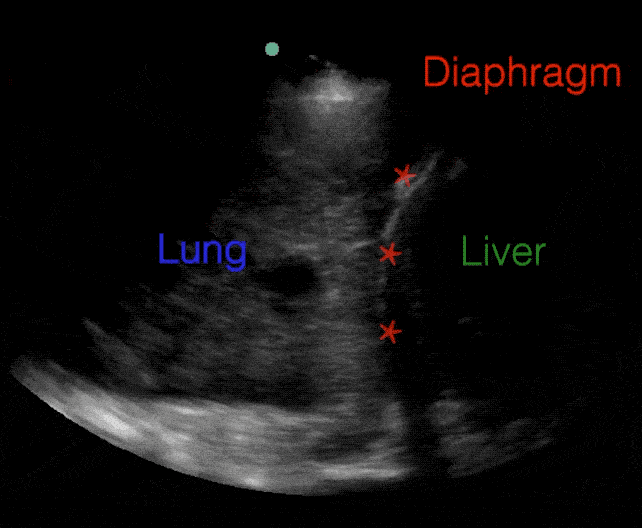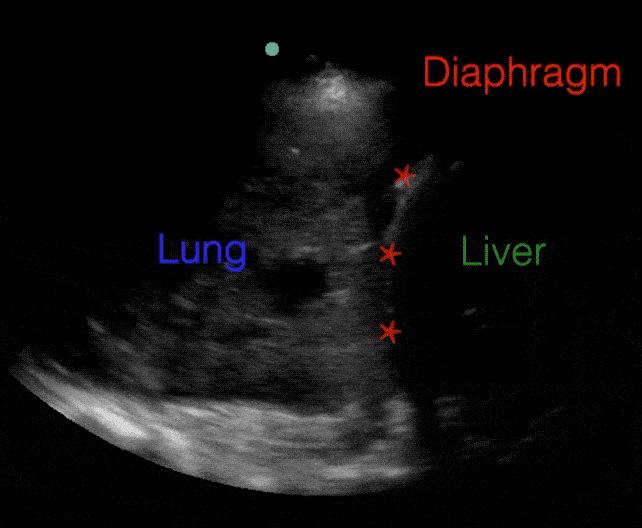
B lines:
- Comet tail artifact
- Arise from pleura
- Move with respirations
- Erase A-lines
C Profile (Consolidation):
- Non-aerated, fully consolidated lung has the appearance of liver
- "Hepatization"
Jaidka, AK. https://echoguide.ca/.
- Artifact generated in alveolar-interstitial syndromes
- Etiology depends on associated features and whether they are focal or bilateral
B-lines
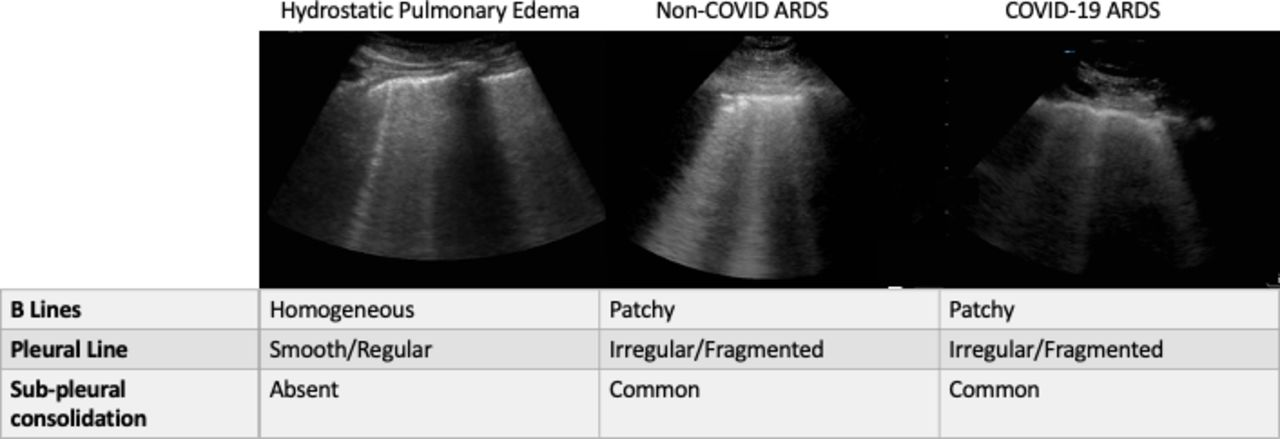
Arntfield R, et al. (2021). BMJ Open 11:e045120.
Kagami K, et al. (2023). Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 24:553-61.
- B-lines measured by LUS have been shown to correlate with NT-proBNP, PCWP, and MPAP
- B-lines have prognostic value in patients with HF
Pulmonary Congestion + B Lines
Szabó IA, et al. (2022) Prognostic Value of Lung Ultrasound in Aortic Stenosis. Front Physiol 13:838479.
Imanishi J, et al. (2023) Association between B-lines on lung ultrasound, invasive haemodynamics, and prognosis in acute heart failure patients. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care 12:115-23.
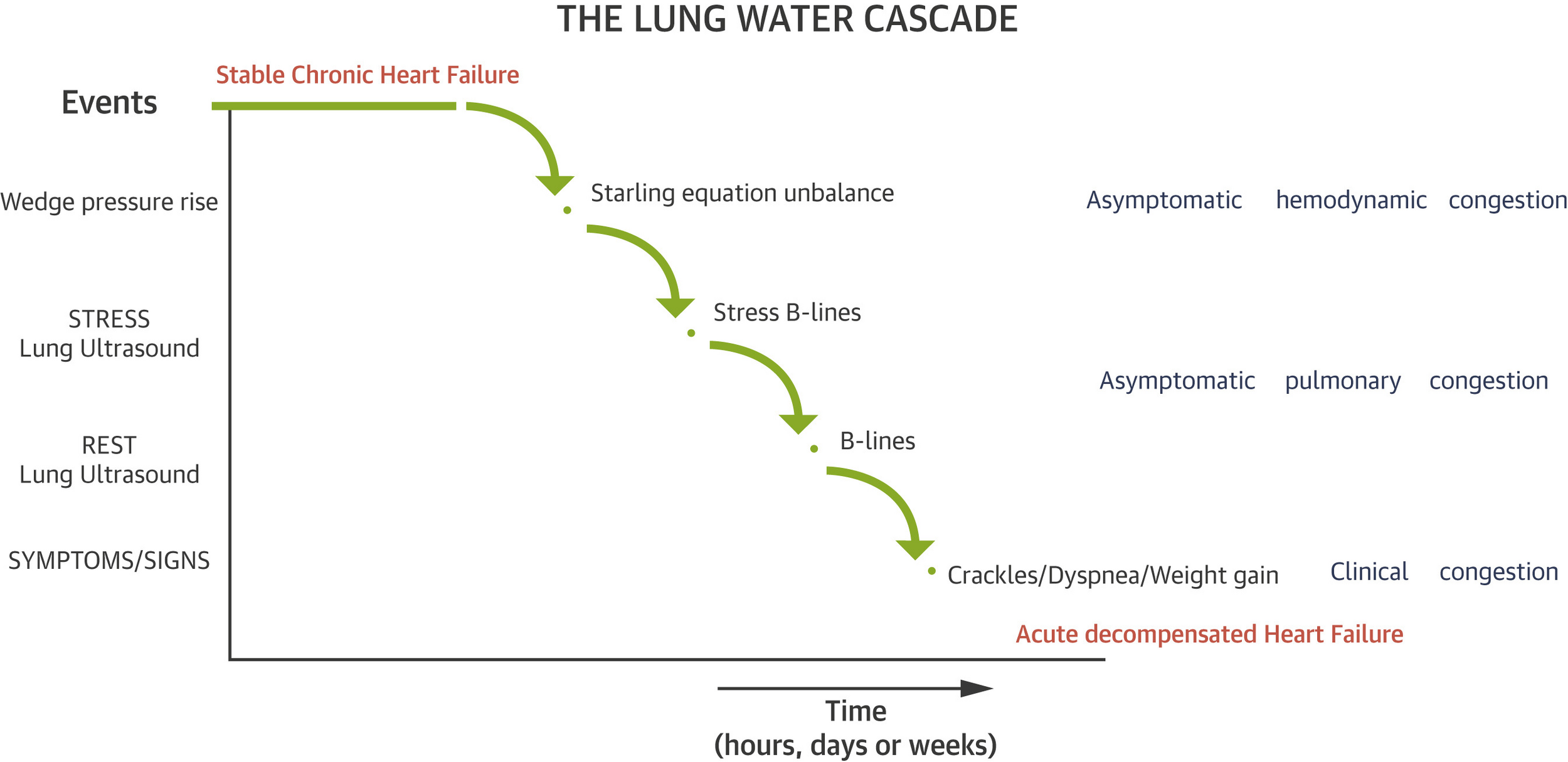
ASE/ESC Guideline:
- In both patients with preserved or reduced LVEF, the presence and the amount of B-lines (lung comets) likely correlate with the estimated LV filling pressure and the presence of pulmonary interstitial edema.
- The demonstration of B-lines during exercise SE seems a feasible way for demonstrating that exertional dyspnoea is related to pulmonary congestion.
Stress Echo + B Lines
Lancellotti P, et al. (2016) The clinical use of stress echocardiography in non-ischaemic heart disease: recommendations from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging and the American Society of Echocardiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 17:1191-229.
Stress Echo + B Lines
Lancellotti P, et al. (2016) The clinical use of stress echocardiography in non-ischaemic heart disease: recommendations from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging and the American Society of Echocardiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 17:1191-229.


Protocols
- No consistency in protocols, ranging from 4-28 points
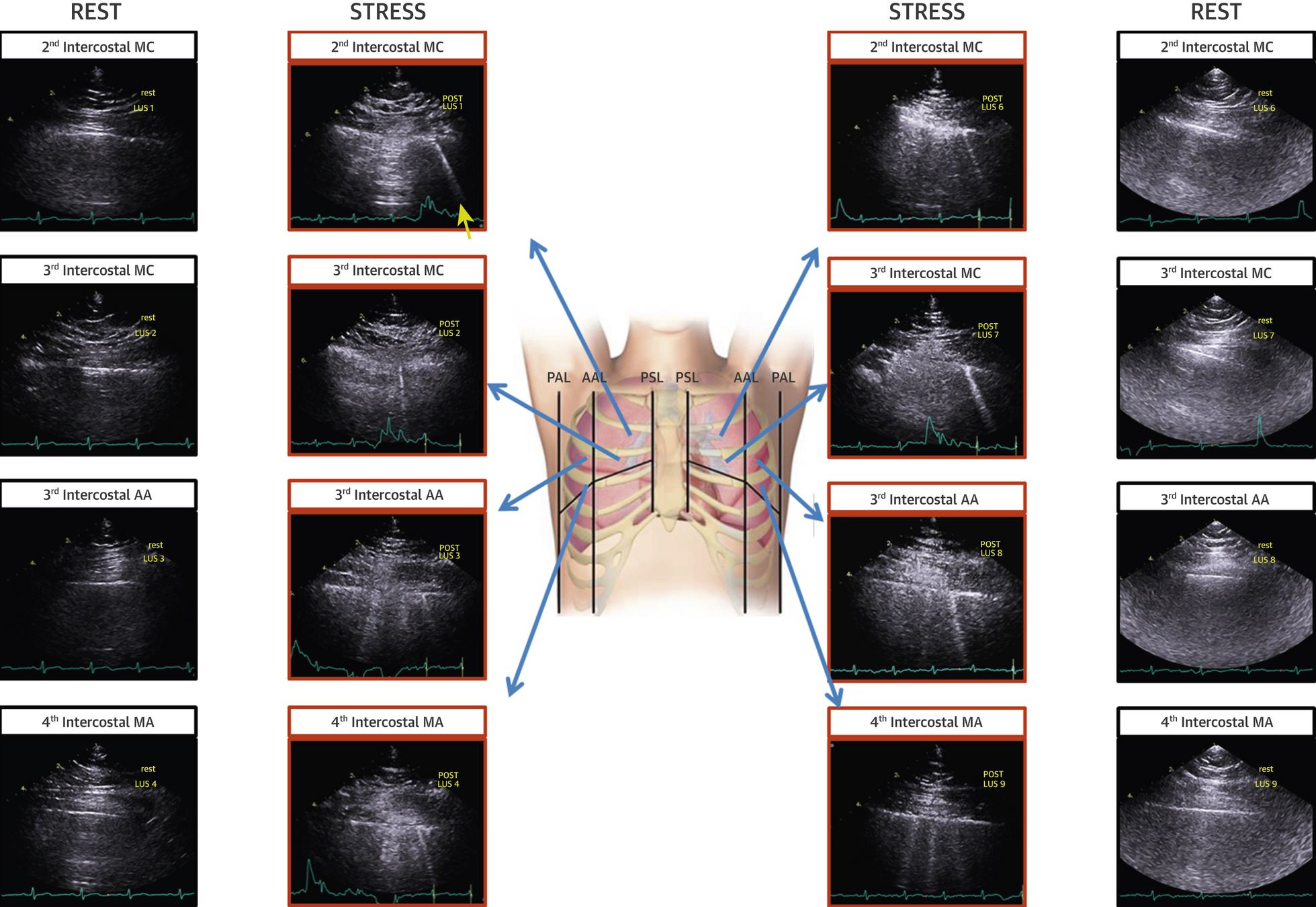
Non-Stress Protocols
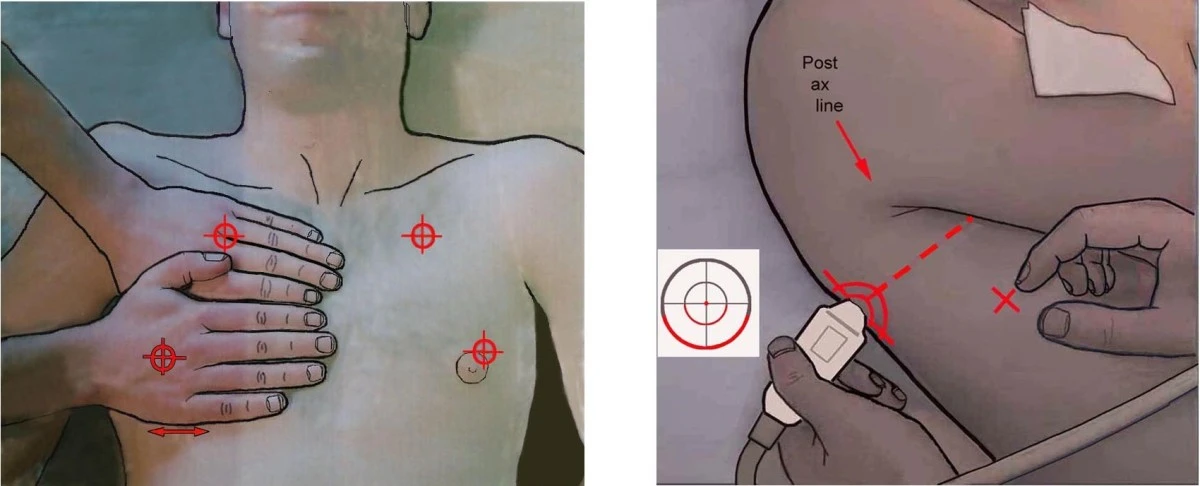
- 135 patients referred for CAD or HF
- Comparing different protocols
- Top 3 "wet" spots all 3rd IS
- Good agreement with 4-S and 28-S but reduced scan time from 140s to 20s
Stress Protocol
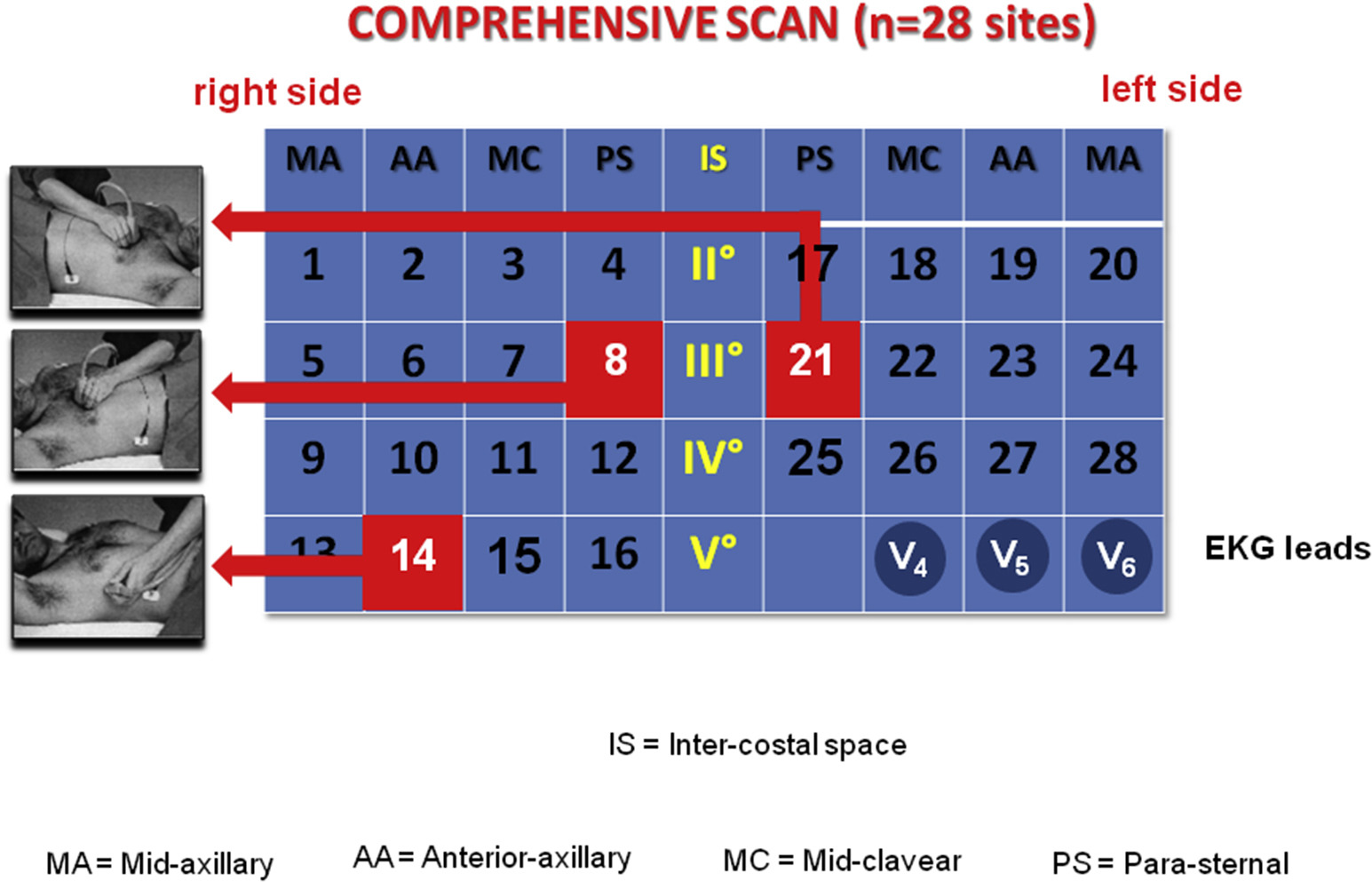
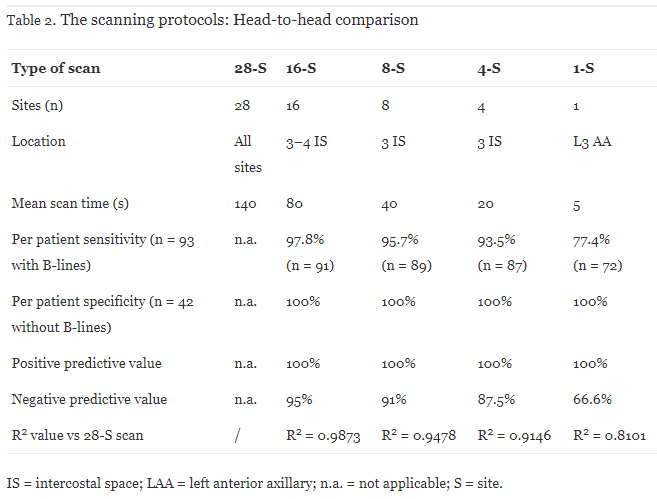
Scali MC, et al. (2020) Lung Ultrasound and Pulmonary Congestion During Stress Echocardiography. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 13:2085-95.
- Used in subsequent Stress Echo 2020/2030 studies
- Cardiac transducer
- Perpendicular to ribs
- 18cm depth
- 6s clips
Simplified Protocol
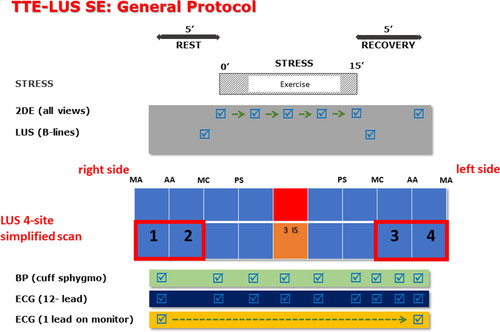
Scali MC, et al. (2020) Lung Ultrasound and Pulmonary Congestion During Stress Echocardiography. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 13:2085-95.
Acquisition
Example Acquisition
Jaidka A, Myslik J. POCUS Rapid Review: Lung Blue Protocol. Available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FS9FztSI460
Example Acquisition

Picano E, et al.. Stress lung Ultrasound stress echo2020.2019. Available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BwzgoG15E_A
Scoring Patients
Scali MC, et al. (2020) Lung Ultrasound and Pulmonary Congestion During Stress Echocardiography. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 13:2085-95.
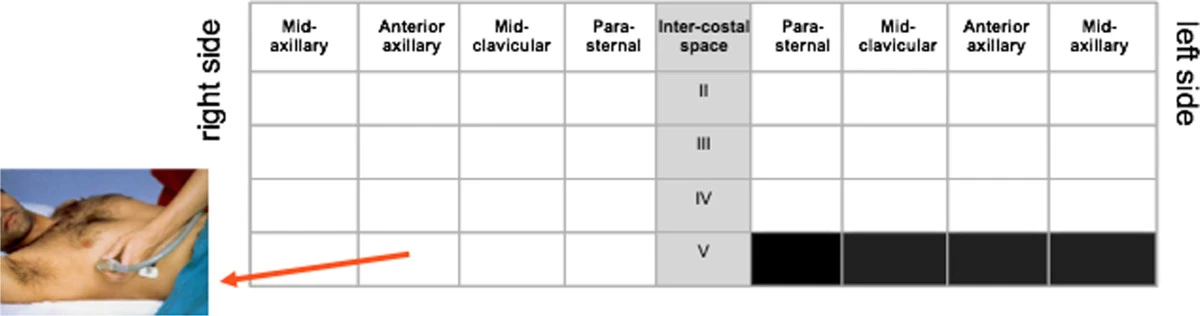
- 4 zone protocol
- Score each zone from 0-10 B-lines and sum 4 zones
- Report total at rest and stress and interval change
- Stress B-lines are categorized as:
- absent (score points 0 to 1), mild (2 to 4), moderate (5 to 9), and severe (≥10 points)
Case
Case
- RFR: dyspnea
- 58-year-old female
- PHT 141 ms, MVA 1.6 cm2
- Mild to moderate regurgitation
Wiley BM, et al. (2020) Lung Ultrasound During Stress Echocardiography Aids the Evaluation of Valvular Heart Disease Severity. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 13:866-72.
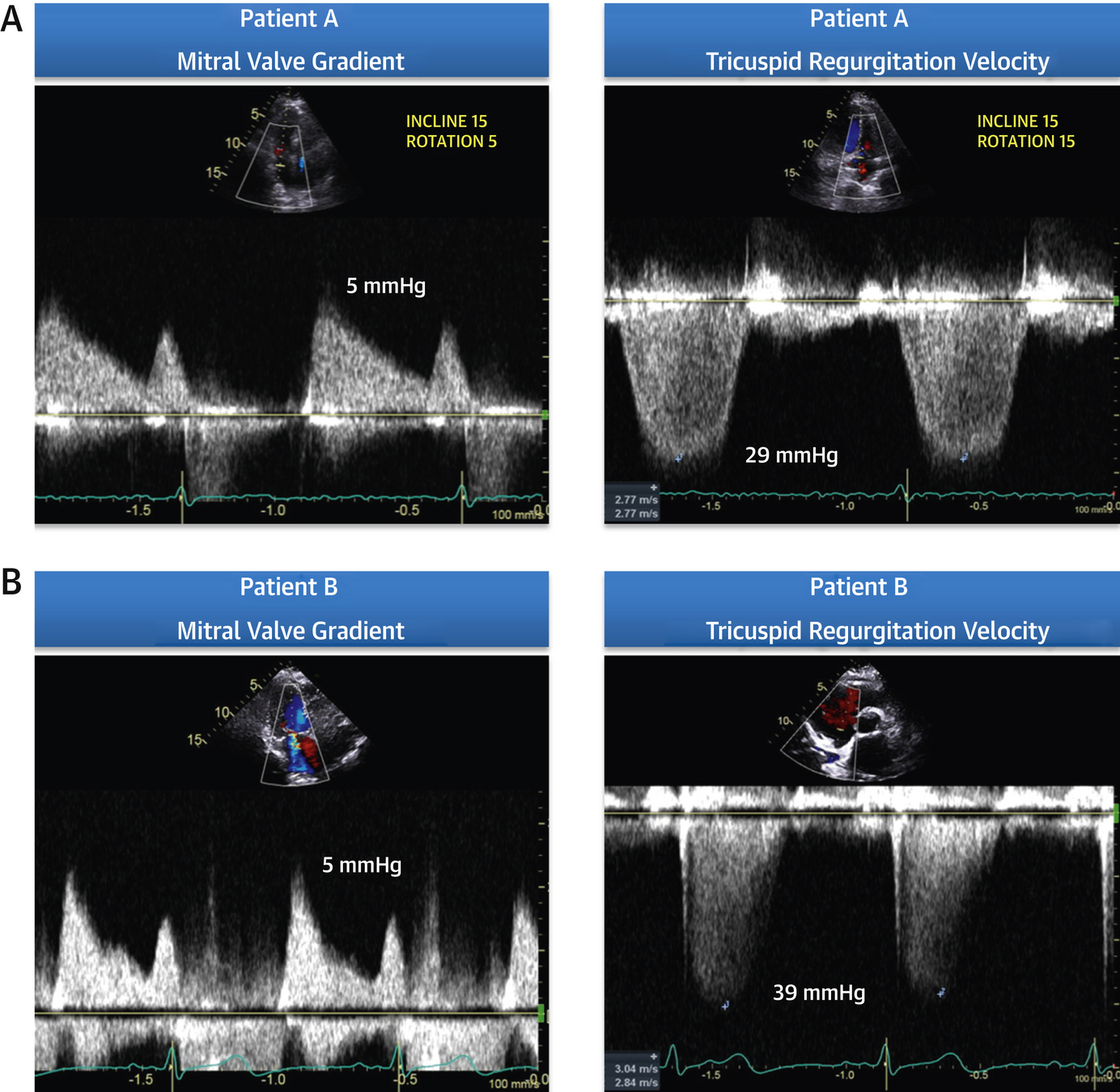
Case
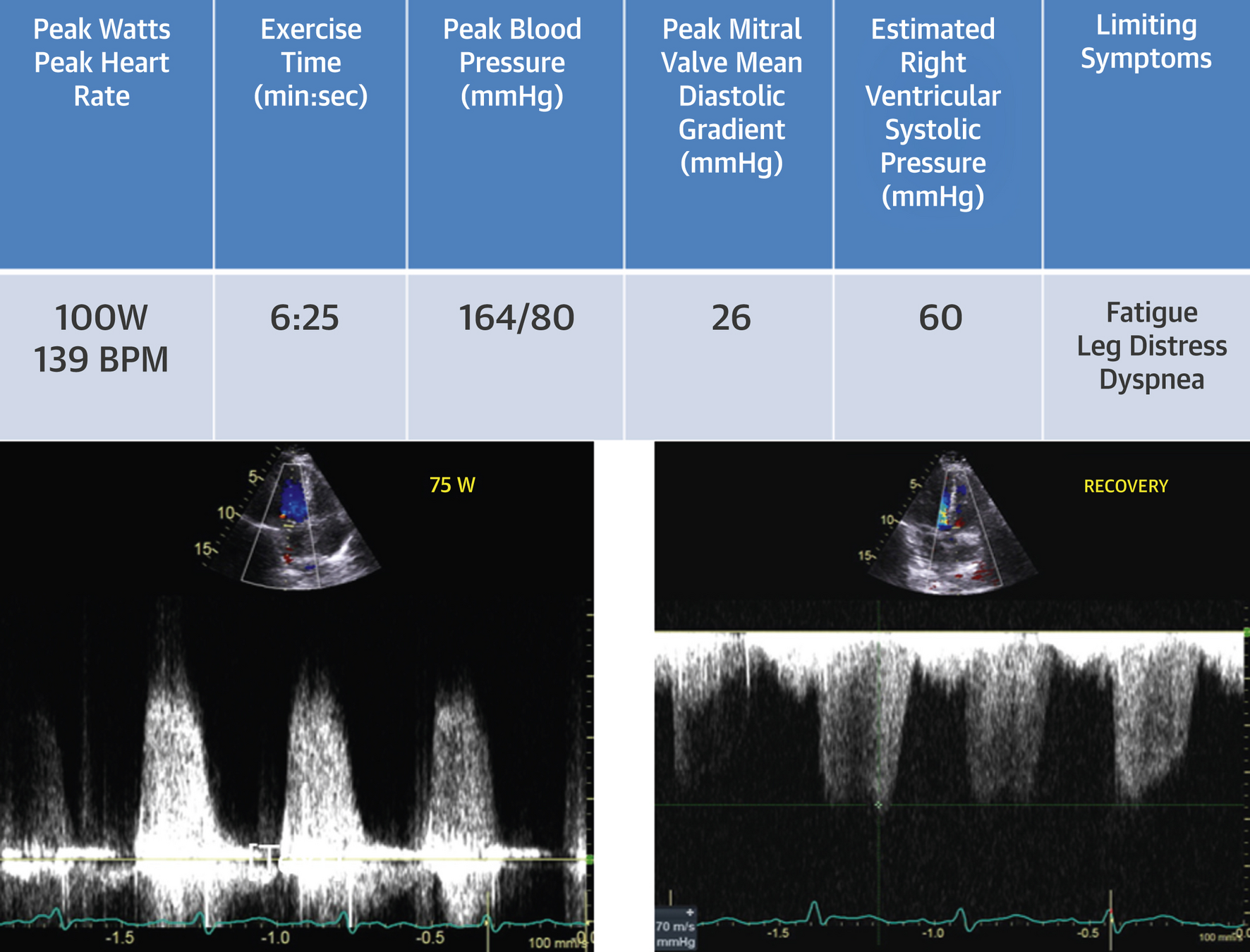
Wiley BM, et al. (2020) Lung Ultrasound During Stress Echocardiography Aids the Evaluation of Valvular Heart Disease Severity. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 13:866-72.
Case
Wiley BM, et al. (2020) Lung Ultrasound During Stress Echocardiography Aids the Evaluation of Valvular Heart Disease Severity. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 13:866-72.
Case
- B-lines are a result of dynamic elevation in LA pressure due to mixed MR/MS
- MV disease causing exercise induced pulmonary edema, in combination with increase in MG and RVSP, helps classify valve as hemodynamically severe
- Patient underwent MVR post stress test
Wiley BM, et al. (2020) Lung Ultrasound During Stress Echocardiography Aids the Evaluation of Valvular Heart Disease Severity. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 13:866-72.
Disease States
- Pulmonary congestion during Exercise stress Echocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- 128 patients with non-obstructive HCM
- B-lines present in 10% at rest and 30% at stress
- Patients with stress B-lines had higher rest/peak E/e', rest/peak SPAP, and increased increment in MR
- B-lines at rest and during stress in HCM may help to identify a pulmonary congestion phenotype
- Possibly direct diuretic usage
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Pálinkás ED, et al. (2022) Pulmonary congestion during Exercise stress Echocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 38:2593-604.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
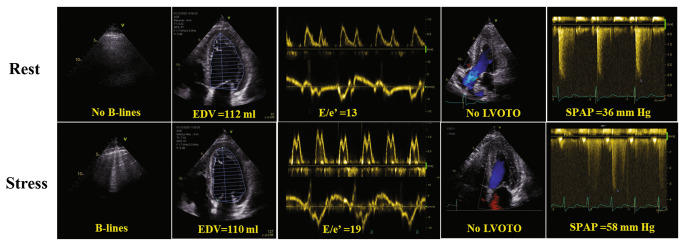
Pálinkás ED, et al. (2022) Pulmonary congestion during Exercise stress Echocardiography in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 38:2593-604.
- Prognostic Value of Lung Ultrasound in Aortic Stenosis
- 75 patients with mod-severe AS
- B-lines were significantly correlated with NYHA functional class, LV ejection fraction, and pulmonary artery systolic pressure
- Patients were followed for 13.4 ± 6 months and a higher number of B-lines was associated with HF-related adverse events and death
Valvular Disease
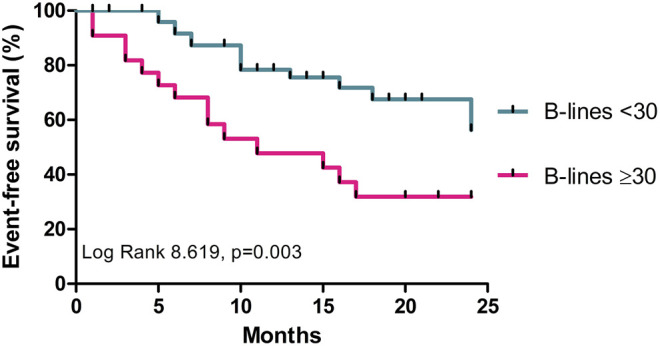
Szabó IA, et al. (2022) Prognostic Value of Lung Ultrasound in Aortic Stenosis. Front Physiol 13:838479.
- Incremental diagnostic value of post-exercise lung congestion in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- 134 patients with HFpEF and 121 controls
- Stress echo with B-line assessment at each stage
- B-lines were most prominent during early recovery
- This and other recent studies have shown improved diagnostic accuracy when B-lines are paired with HFpEF scores (H2FPEF and HFA-PEFF)
HFpEF
Coiro S, et al. (2023) Exercise-induced B-lines for the diagnosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a two-centre study. Clin Res Cardiol.
Kagami K, et al. (2023) Incremental diagnostic value of post-exercise lung congestion in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 24:553-61.
Wrap-up
- B-lines are not specific to pulmonary congestion
- ie. cannot use in patients with ILD
- No consensus on protocol or interpreting results
- No defined cutoff for abnormal LVEDP
Limitations
- Consider lung ultrasound when pulmonary congestion during stress is a consideration
- 4 zones - all in the 3 intercostal space
- Only adds 20 seconds
- Sum B-lines and stress B-lines >10 is likely significant
Take Home Points