Hyped about Hyperapp
Gleb Bahmutov, PhD
Monday, Nov 19, 2018 16:10

🔊 Dr Gleb Bahmutov PhD
C / C++ / C# / Java / CoffeeScript / JavaScript / Node / Angular / Vue / Cycle.js / functional
these slides

Cypress.io open source E2E test runner
One fine morning ...
<X> Bahmutov

Dad, make me a game
Clone of 2048
Vanilla JS
Game of GitHub
Vanilla JS
Vanilla JS is not going to scale

Goal: write an web application

Hard to pick
View + Data store
-
React + Redux
-
Angular + ng-
rx -
Vue + Vuex
-
X + ...x
Which JavaScript framework should I use next?
- Features
- Learning curve
- Size and speed
- Testability

Hyperapp
1 kB JavaScript framework for building web applications.
"Introducing Hyperapp 1.0 🎉"
- Minimal
- Pragmatic
- Standalone
Minimal
We have aggressively minimized the concepts you need to understand to be productive while remaining on par with what other frameworks can do.
github.com/hyperapp/hyperapp README
Pragmatic
Hyperapp holds firm on the functional programming front when managing your state, but takes a pragmatic approach to allowing for side effects, asynchronous actions, and DOM manipulations.
github.com/hyperapp/hyperapp README
Standalone
Do more with less. Hyperapp combines state management with a virtual DOM engine that supports keyed updates & lifecycle events — all with no dependencies.
github.com/hyperapp/hyperapp README
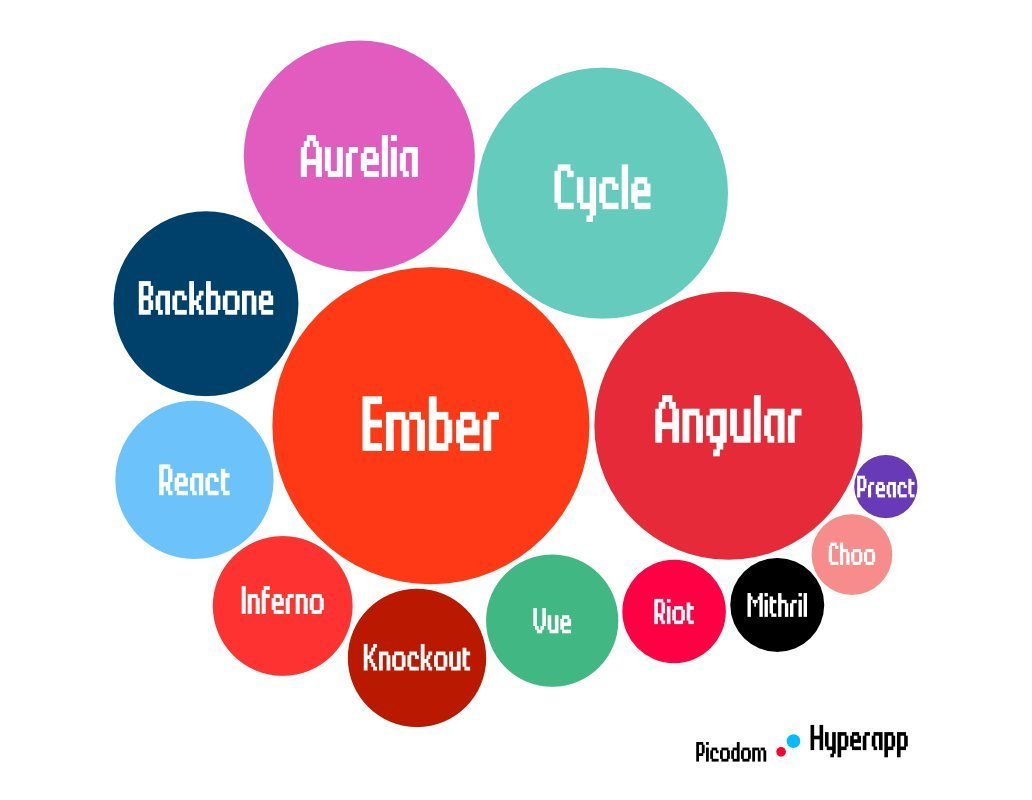
Entire Hyperapp script
Entire Hyperapp script

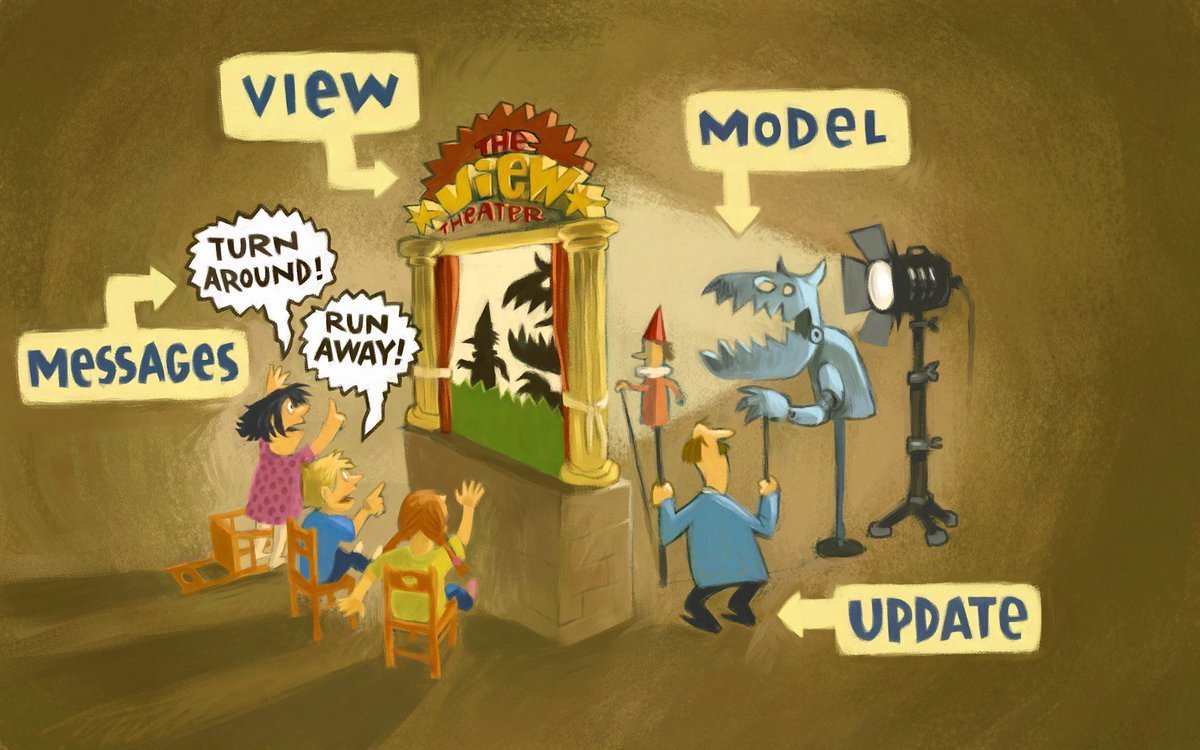
This is the most heartwarming picture of the Elm Architecture I've ever seen. 😍
Richard Feldman
actions
at the conference!
View
<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp

<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp

Single script
<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp
Virtual DOM helper

<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp
Application helper

<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp
View function

<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp
Element name "div"

<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp
Element attributes

<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp
Element contents

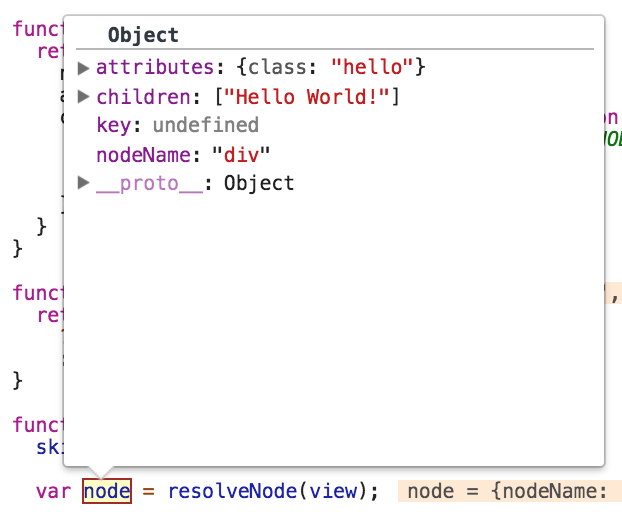
View function returns virtual node
<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp
Start application

<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp
Start application
View function

<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/hyperapp"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const view = () =>
h('div', {class: 'hello'}, 'Hello World!')
app(null, null, view, document.body)
</script>
</body>
"Hello World!" Hyperapp
Start application
Target DOM element

State
const state = {
message: 'Boston!'
}
const view = (state) =>
h('div',
{class: 'hello'},
`Hello ${state.message}`
)
app(state, null, view, document.body)"Hello <message>!" Hyperapp
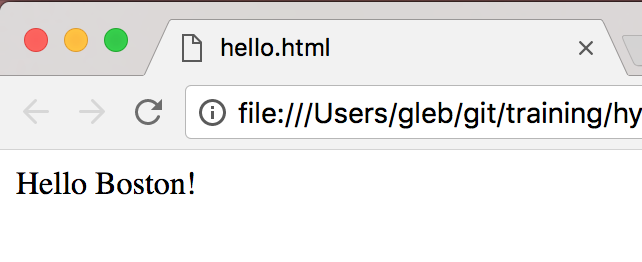
const state = {
message: 'Boston!'
}
const view = (state) =>
h('div',
{class: 'hello'},
`Hello ${state.message}`
)
app(state, null, view, document.body)"Hello <message>!" Hyperapp
Initial state

const state = {
message: 'Boston!'
}
const view = (state) =>
h('div',
{class: 'hello'},
`Hello ${state.message}`
)
app(state, null, view, document.body)"Hello <message>!" Hyperapp
Pass initial state

const state = {
message: 'Boston!'
}
const view = (state) =>
h('div',
{class: 'hello'},
`Hello ${state.message}`
)
app(state, null, view, document.body)"Hello <message>!" Hyperapp
Current state

Actions
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const state = {
message: ''
}
const actions = {
onchange: e => state =>
({message: e.target.value})
}"Hello <input>!" Hyperapp
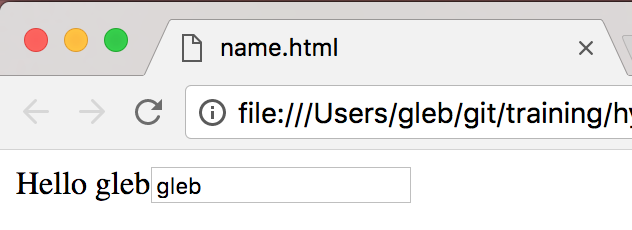
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const state = {
message: ''
}
const actions = {
onchange: e => state =>
({message: e.target.value})
}"Hello <input>!" Hyperapp

Object of actions
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const state = {
message: ''
}
const actions = {
onchange: e => state =>
({message: e.target.value})
}"Hello <input>!" Hyperapp

Action takes arguments
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const state = {
message: ''
}
const actions = {
onchange: e => state =>
({message: e.target.value})
}"Hello <input>!" Hyperapp

Then current state
const {h, app} = window.hyperapp
const state = {
message: ''
}
const actions = {
onchange: e => state =>
({message: e.target.value})
}"Hello <input>!" Hyperapp

and returns new state
const view = (state, actions) =>
h('div',
{class: 'hello'},
[`Hello ${state.message}`,
h('input', {
type: 'text',
placeholder: 'enter your name',
onchange: actions.onchange
})]
)
app(state, actions, view, document.body)"Hello <input>!" Hyperapp

Pass actions to view
const view = (state, actions) =>
h('div',
{class: 'hello'},
[`Hello ${state.message}`,
h('input', {
type: 'text',
placeholder: 'enter your name',
onchange: actions.onchange
})]
)
app(state, actions, view, document.body)"Hello <input>!" Hyperapp

Call action on event
const view = (state, actions) =>
h('div',
{class: 'hello'},
[`Hello ${state.message}`,
h('input', {
type: 'text',
placeholder: 'enter your name',
onchange: actions.onchange
})]
)
app(state, actions, view, document.body)"Hello <input>!" Hyperapp

Hyper app
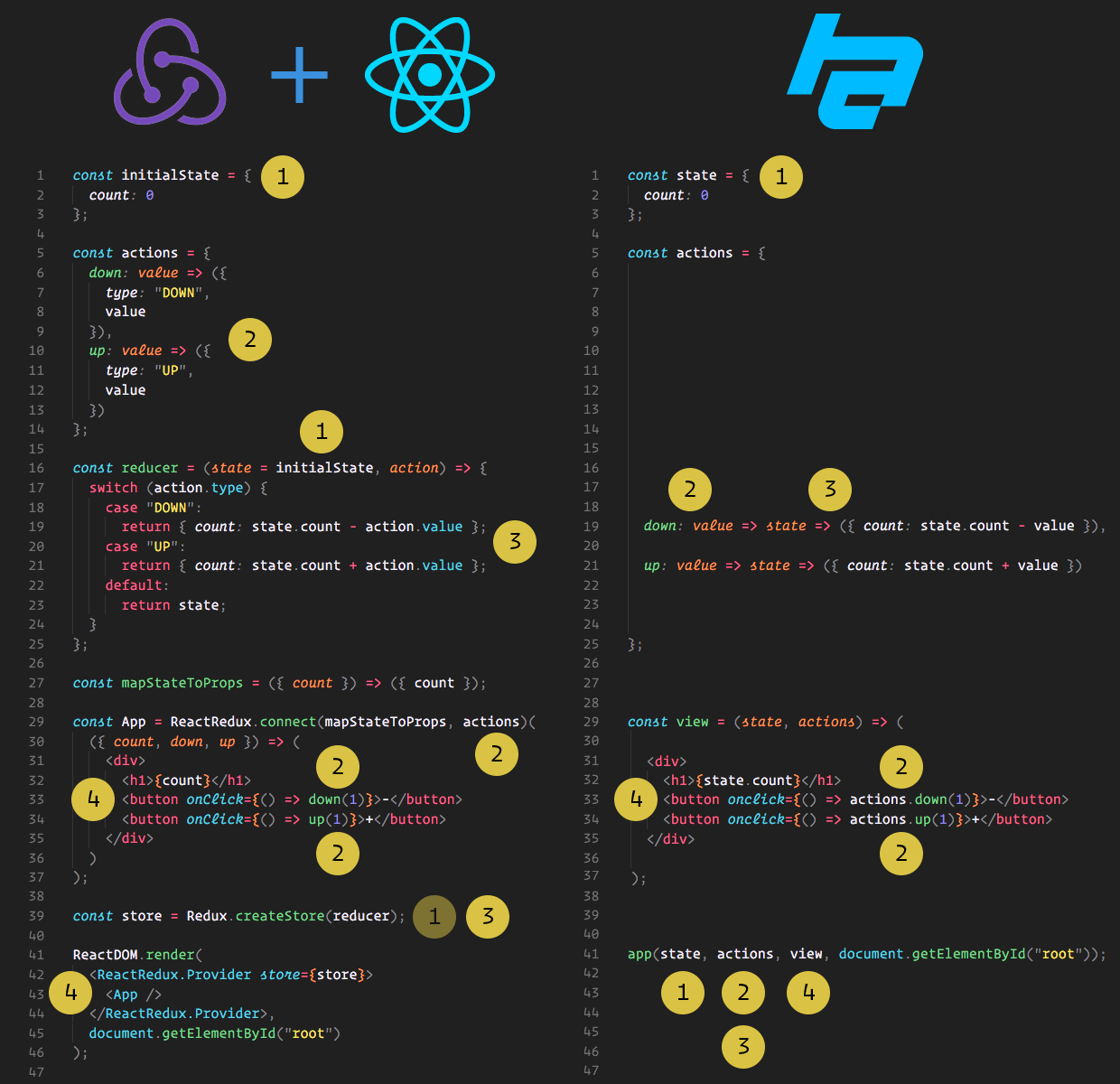
Why I ❤️ Hyperapp
View
State
Actions
Uses pure functions
const view = (state, actions) =>
h('div',
{class: 'hello'},
[`Hello ${state.message}`,
h('input', {
type: 'text',
placeholder: 'enter your name',
onchange: actions.onchange
})]
)View is a pure function, state and actions are arguments
const actions = {
onchange: e => (state, actions) =>
({message: e.target.value})
}Actions are pure functions with arguments, state, and other actions
-
Understand
-
Test
-
Extend
Pure functions are easy to:
Why I ❤️ Hyperapp
easy to handles view + state
<X> Bahmutov

Dad, make me a maze runner game
Ok, let's write "serious" app
🎁 organize code
✅ testing
import {state} from './state'
import {actions} from './actions'
import {view} from './view'
import {app} from 'hyperapp'
app(state, actions, view, document.body)app.js
<body>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</body>index.html
{
"scripts": {
"start": "parcel serve ./index.html"
},
"dependencies": { "hyperapp": "1.2.5" },
"devDependencies": {
"parcel-bundler": "1.7.0"
}
}package.json
Parcel 🎁 is awesomesauce
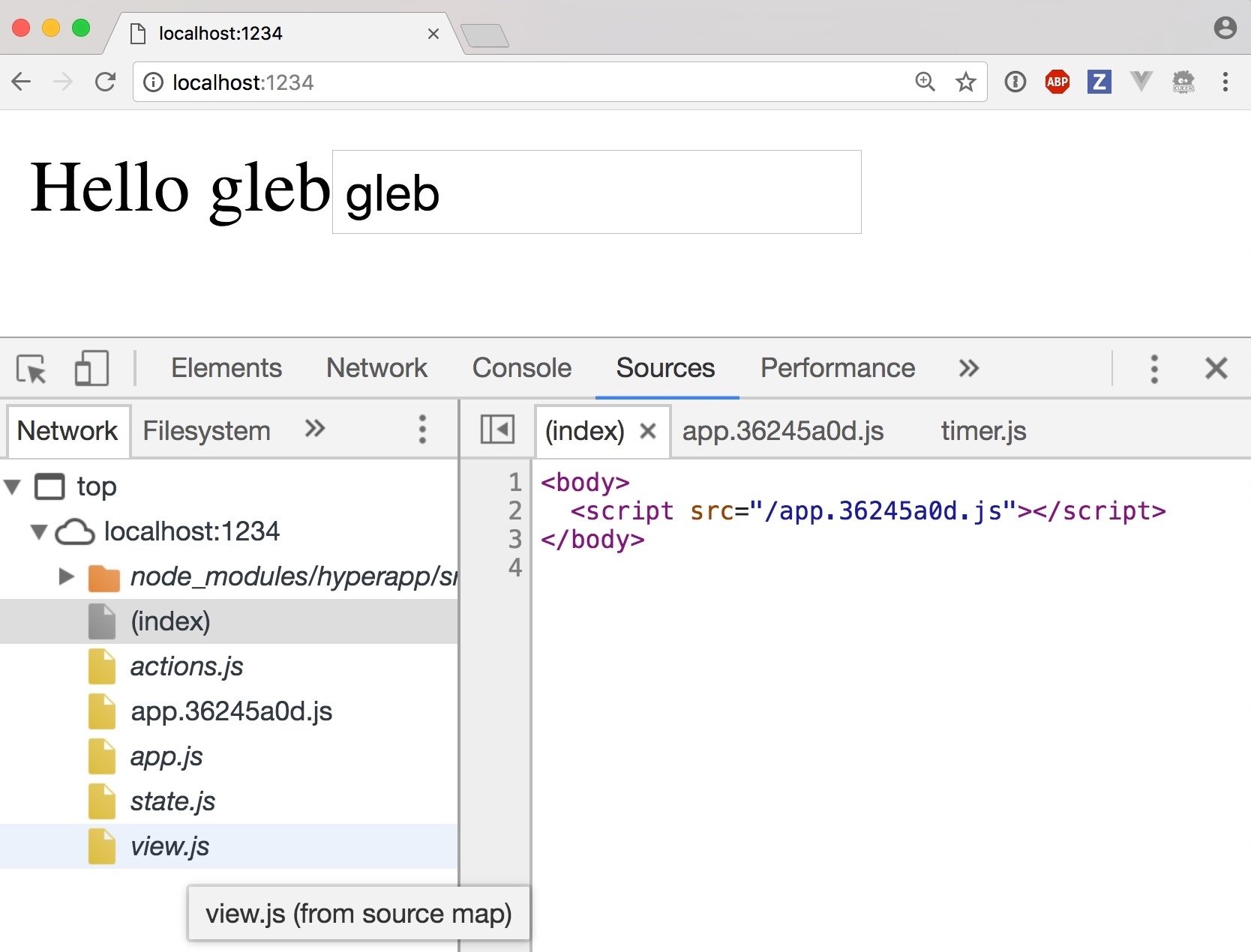
Parcel 🎁 is awesomesauce
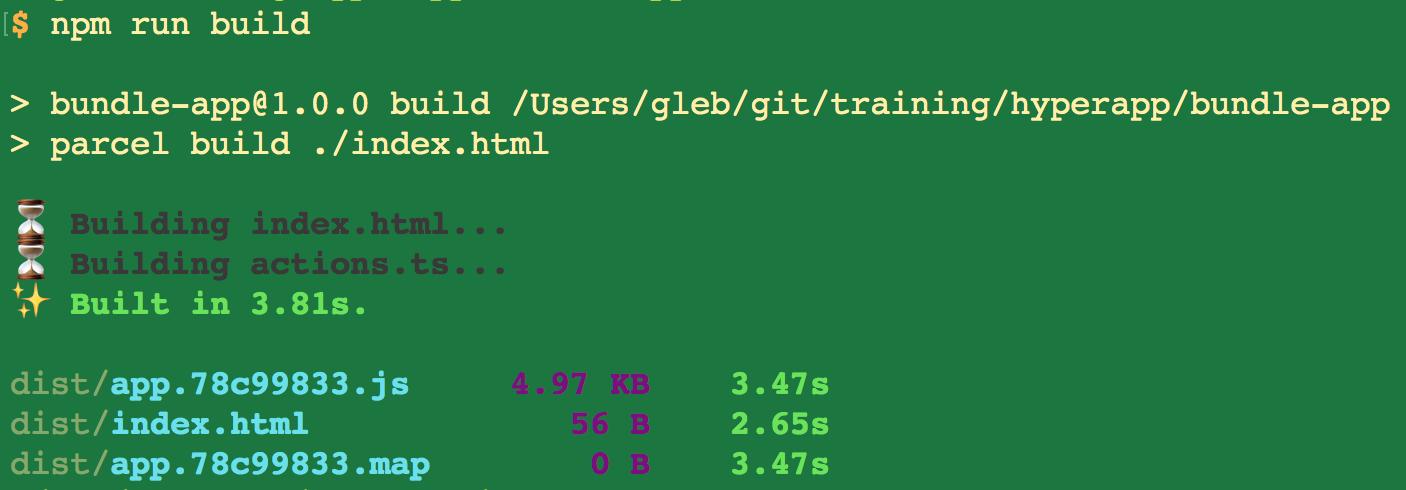
Parcel 🎁 is awesomesauce
import {h} from 'hyperapp'
export const view = (state, actions) => (
<div className="hello">
Hello {state.message}
<input type="text"
placeholder="enter your name"
onchange={actions.onchange} />
</div>)view.js
$ npm startUse JSX
if VSCode removes unused "h" see #49794
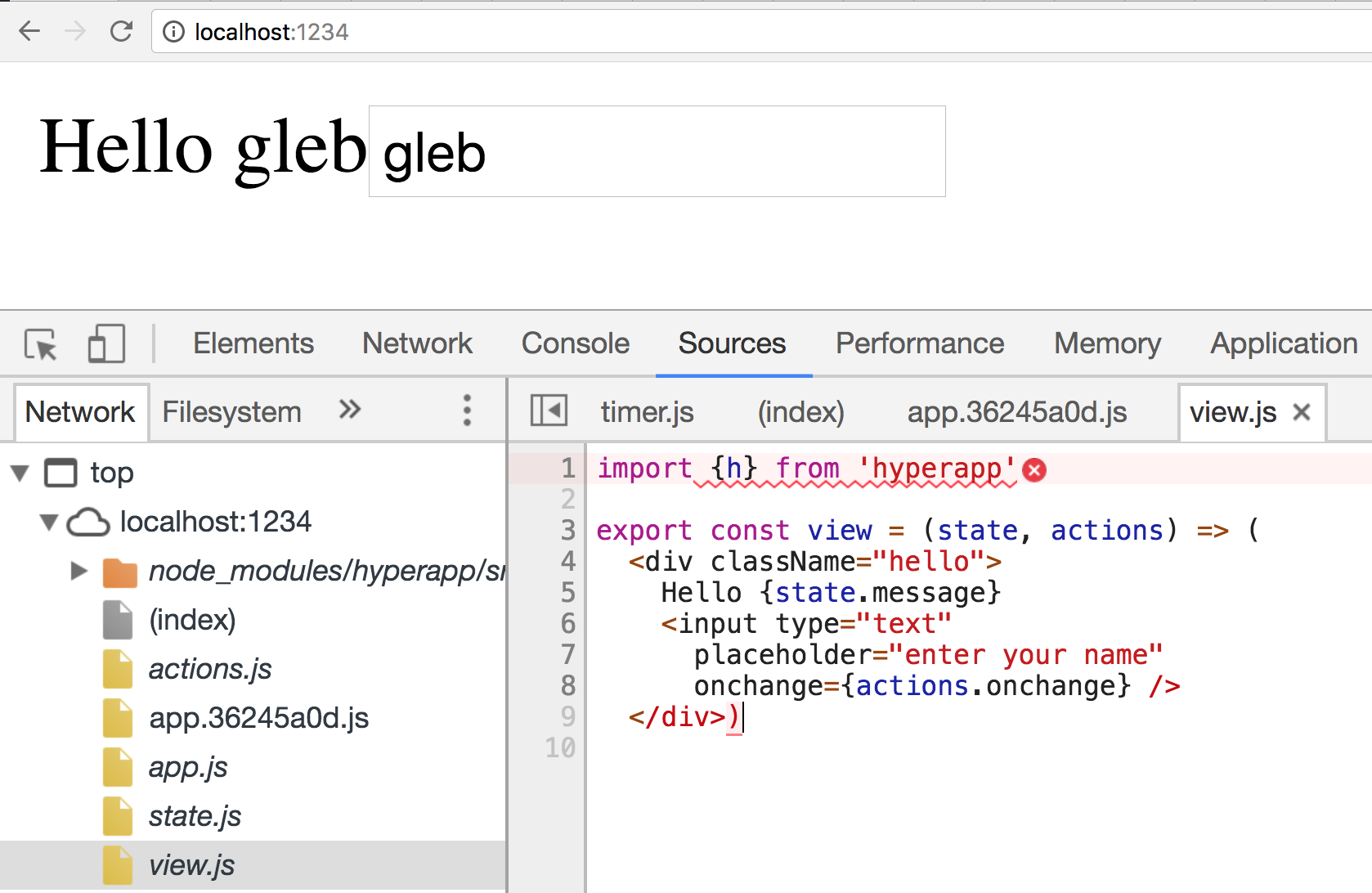
Parcel 🎁 is awesomesauce
export type State = {
message: string
}
export const state:State = {
message: ''
}state.ts
Use TypeScript
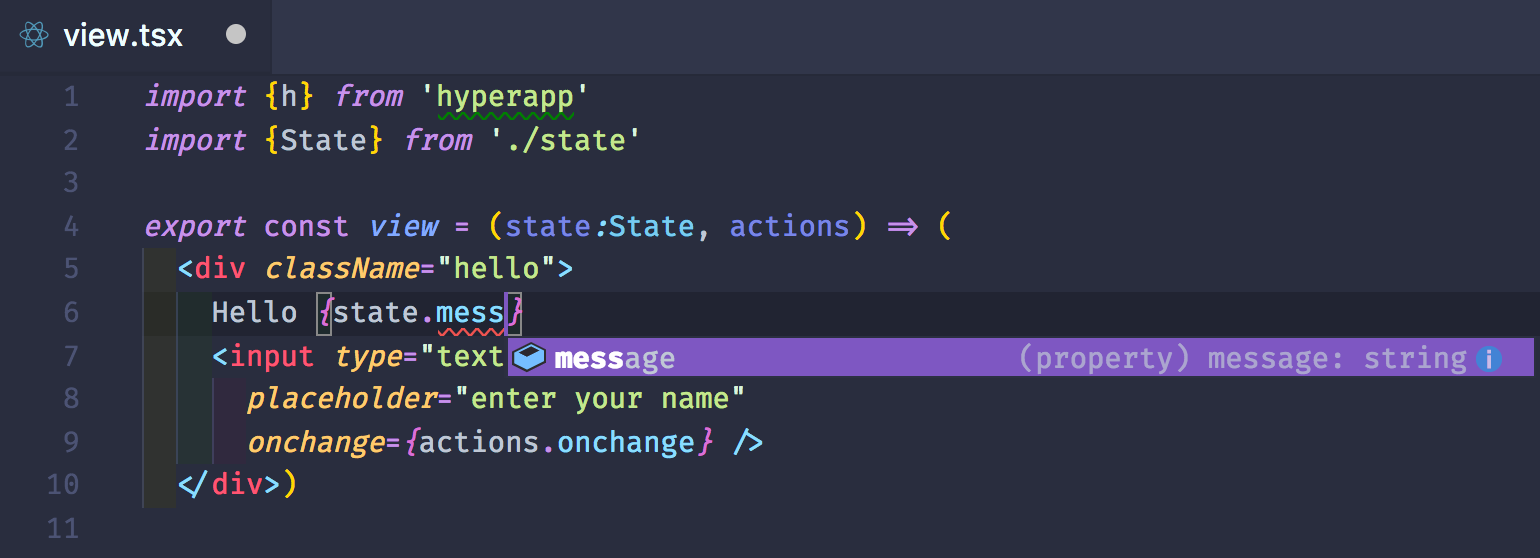
Hyperapp includes TypeScript definitions
Parcel handles TS pretty well with zero config
Pro tip: slice state and actions
const state = {
foo: { message: '' },
bar: { age: 21 }
}
const actions = {
foo: {
// slice = current state.foo
onchange: e => slice =>
({message: e.target.value})
},
bar: {},
print: () => state => console.log(state)
}Text
Text
Pro tip: call actions yourself
const actions = {
...
print: () => state => console.log(state)
}
window.__app = app(state, actions, view, document.body)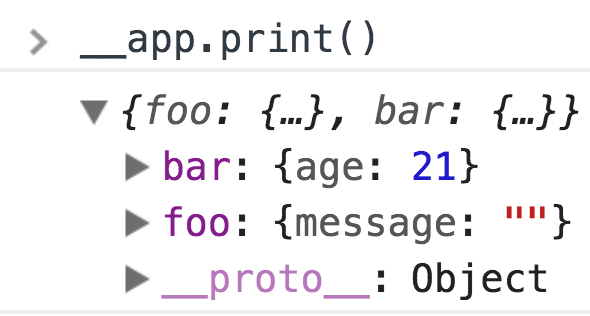
Pro tip: split view functions
// pure arguments => virtual node function
const HelloX = ({greeting, name}) =>
h('p', {}, `${greeting} ${name}`)
// call HelloX with arguments
const view = (state) =>
h('div',
{class: 'hello'},
[HelloX({
greeting: 'Hello',
name: state.message
})]
)Pro tip: actions can call other actions
const actions = {
set: todos => state => ({todos}),
click: () => (state, actions) => {
fetch()
.then(r => r.json())
.then(actions.set)
}
}Pragmatic approach to side effects
✅ Testing
End to end testing with Cypress.io
Unit testing using Cypress.io
E2E
unit
it('logs user in', () => {
cy.visit('page.com')
cy.get('#login').click()
})/// <reference types="cypress" />
beforeEach(() => {
cy.visit('http://localhost:1234')
})
it('greets', () => {
cy.get('input').type('tester{enter}')
cy.contains('.hello', 'Hello tester')
.should('be.visible')
})
$ npm i -D cypress start-server-and-test parcel-bundler{
"scripts": {
"start": "parcel serve ./index.html",
"test": "cypress run",
"ci": "server-test 1234"
}
}package.json
cypress/integration/e2e.js
$ npm run ciCan he do it? On 1 slide? No way!
Entire E2E test setup on 1 slide
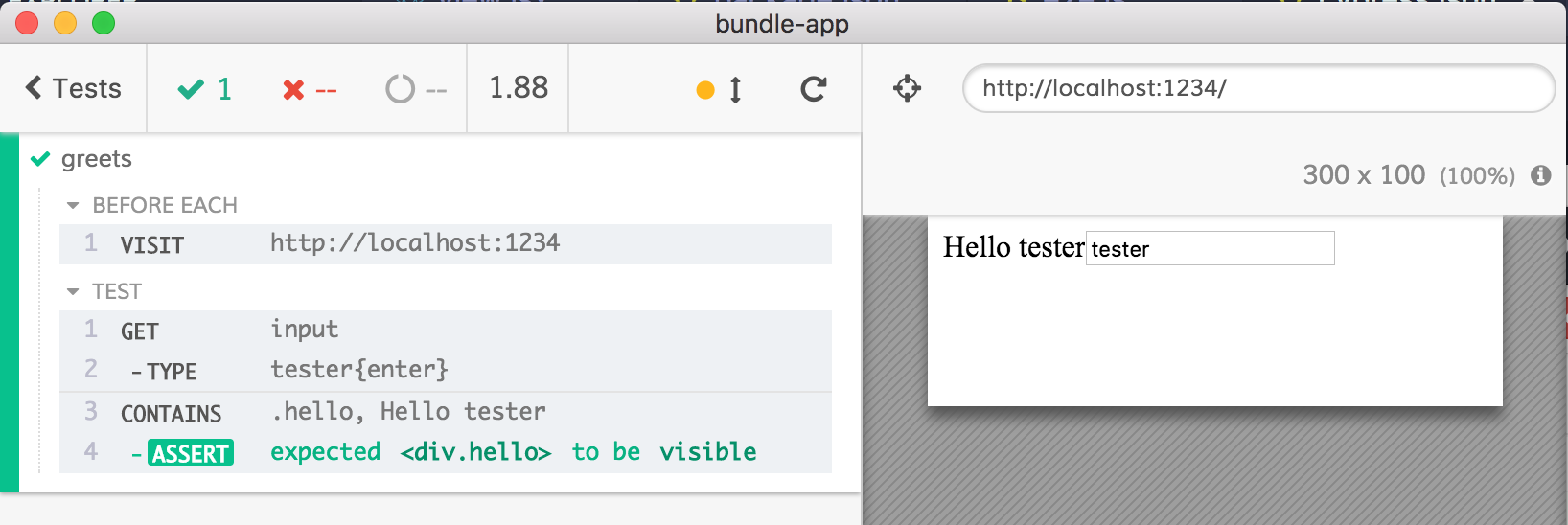
Cypress.io running end to end test
Cypress.io running count-app tests
E2E
unit
import {view} from '../src/view'
import {mount} from
'cypress-hyperapp-unit-test'
it('renders', () => {
mount(view)
cy.click(...)
})Unit testing using Cypress via an adaptor
Cypress ❤️ Hyperapp
📼 video of end to end testing
https://github.com/LearnHyperapp/hyperapp-cypress-demo
Hyperapp V2
December 2018?
Magic state (v1)
const state = {
message: '',
count: 0
}
const actions = {
onchange: e => state =>
({message: e.target.value}),
increment: e => state =>
({count: state.count + 1})
}just return a change
Explicit state (v2)
const state = {
message: '',
count: 0
}
const actions = {
onchange: (state, data, e) =>
({...state, message: e.target.value}),
increment: (state, data, e) =>
({...state, count: state.count + 1})
}return full state
Call actions (v1)
<button onclick={() => actions.increment(1)}>+</button>call action function
<button onClick={[IncrementBy, { number: 1 }]}+</button>list function and arguments
Declare actions (v2)
Side effects (v2)
import * as Http from "@hyperapp/http"
const SendHttp = state => [
{ ...state, error: null, fetching: true },
Http.fetch({
url: state.url,
action: SuccessResponse,
error: ErrorResponse
})
]action returns [new state, effect]
Hyperapp V2
=> Cycle.js
Ferp
Ferp is the easiest, functional-reactive, zero dependency javascript app framework for nodejs and modern browsers.
Inspired by Elm and Hyperapp v2 (declarative, state + effect actions)
Hyperapp is 💯
Easy to try
Easy to learn: state, actions, view
Easy to organize and test
Bonus
Parcel bundler + Hyperapp = ⚡️
Hyped about Hyperapp
