PHC7065 CRITICAL SKILLS IN DATA MANIPULATION FOR POPULATION SCIENCE

Access Web Data
Hui Hu Ph.D.
Department of Epidemiology
College of Public Health and Health Professions & College of Medicine
February 25, 2019
Web Scraping
API
Lab: Access Web Data
Web Scraping
Client-Network-Server

Internet
HTML, CSS, JavaScript, ...
PHP, MySQL, ...
HTTP, Request, Response, GET, POST, ...

Stack Connections
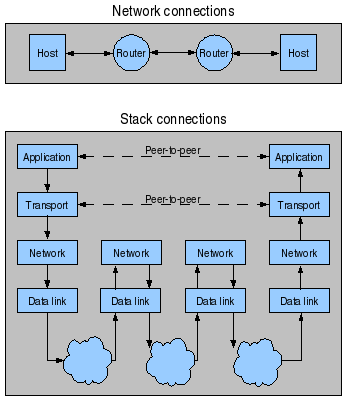
Transport Control Protocol (TCP):
- Built on top of IP (Internet Protocol)
- Assume IP may lose some data during transmission, and it will store and retransmit these data
- Provides a reliable pipe
Stream Sockets / TCP Connections
A stream socket is a type of interprocess communications socket or network socket which provides a connection-oriented, sequenced, and unique flow of data without record boundaries, with well-defined mechanisms for creating and destroying connections and for detecting errors.


Internet
Socket

TCP Port
-
A port is an application-specific or process specific software communications endpoint
- It allows multiple networked applications to coexist on the same server
- List of well-known TCP port numbers

www.ufl.edu
128.227.9.48
23
80
25
Login
Web Server


TCP Port (continued)
Sometimes, the port number is shown (if the server is running on a non-standard port)
Application Protocol
- What can we do with the TCP socket?
- Application protocols:
- a set of rules that all parties follow so that we can predict each other's behavior and not bump into each other
- Examples:
- mail
- World Wide Web

HTTP
- The set of rules that allow browsers to retrieve web documents from servers over the internet
- The dominant Application Protocol on the internet
- Invented for the web to retrieve HTML, images, documents, ...
- Extended to be data in addition to documents. E.g. RSS, web services, ...
- Basic flow:
- make a connection
- request a document
- retrieve the document
- close the connection
HTTP
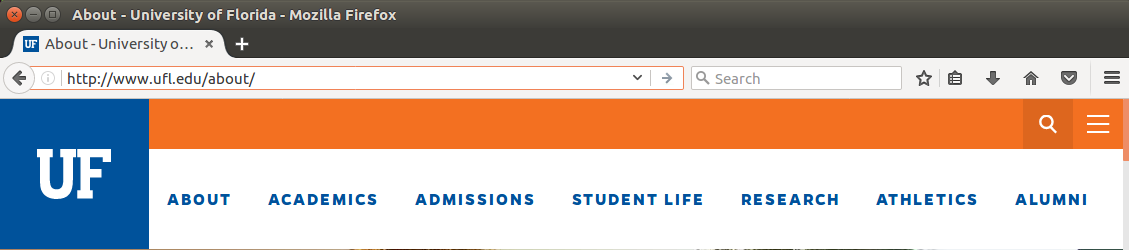
http://www.ufl.edu/about
protocol
host
document
Retrieving Data from the Server
- Each time the user opens a new page, the browser makes a connection to the server and issues a "GET" request - to retrieve the content of the page at the specified URL
- The server returns the HTML document to the browser, which formats and displays the HTML document to the user
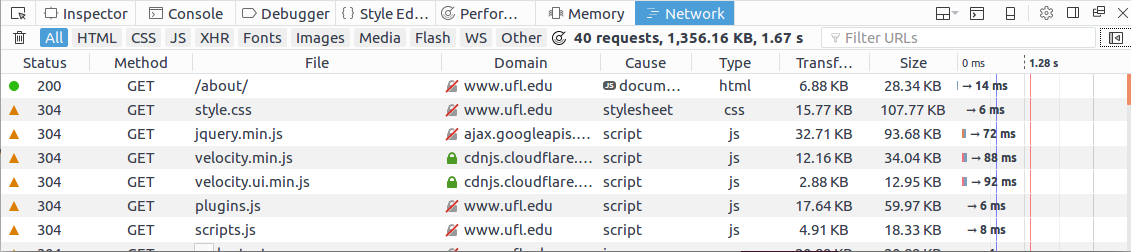
Making an HTTP Request
- Connect to the server, e.g. www.ufl.edu
- a "hand shake"
- Request a document
- GET http://www.ufl.edu/index.html
- Port 80 is the non-encrypted HTTP port
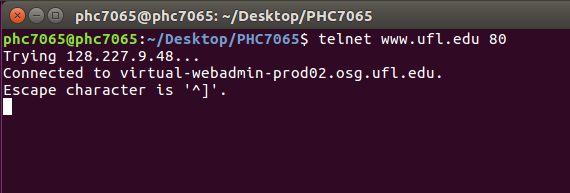
GET http://www.ufl.edu/index.html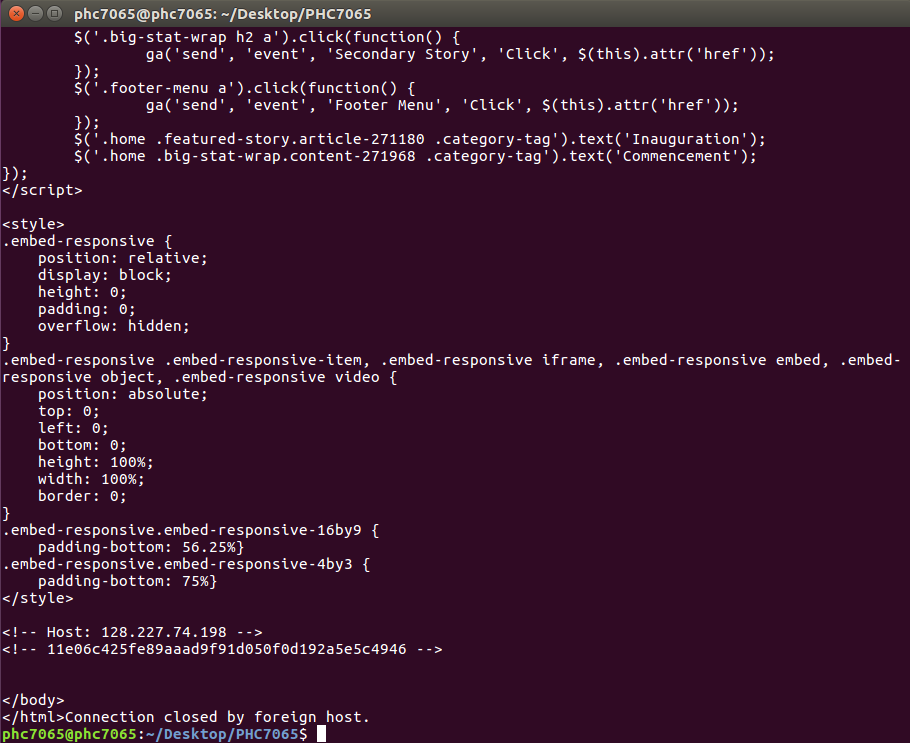
Send HTTP Requests in Python
Python has built-in support for TCP sockets through the socket library
import socket
mysocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
mysocket.connet( ('www.ufl.edu', 80) )
mysocket.send('GET http://www.ufl.edu/index.html \n\n')
while True:
data = mysocket.recv(512)
if ( len(data) < 1 ):
break
print data
mysocket.close()Send HTTP Requests in Python (continued)
We can also use the urllib library, which turns urls to files
import urllib
fhand = urllib.urlopen('http://www.ufl.edu/index.html')
for line in fhand:
print line.strip()Web Crawler
Web Scraping
Parsing HTML
- When a program or script pretends to be a browser to retrieve web pages and to extract information
- Search engines scrape web pages - "web crawling"

Server
Get
HTML
import urllib
fhand = urllib.urlopen('http://www.ufl.edu/index.html')
for line in fhand:
print line.strip()Get
HTML
Why Web Scraping?
- Get data:
- e.g. social network data
- Get your own data from some system that has no export capability
- Monitor a site for new information
- Crawl the web to make a search engine
Web Scraping with BeautifulSoup
import urllib
from bs4 import *
html = urllib.urlopen('http://www.ufl.edu/index.html').read()
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"html5lib")
tags = soup('a')
for tag in tags:
print tag.get('href',None)
API
Wire Protocol
- HTML is not really intended for consumption by an application which is interested in data
- We need an agreed way to represent data going between applications and across networks
- Wire Protocol
- Two common wire format: XML, JSON
Python Dictionary
Java HashMap
Wire Protocol
Serialize
De-Serialize
Web Services
- Most web applications use services
- use services from other applications: credit card charge, etc.
- Services publish the "rules" which must be followed by applications to make use of the service
Application Program Interface
-
Application programming interface (API) is a set of subroutine definitions, protocols, and tools for building application software
- In general terms, it's a set of clearly defined methods of communication between various software components
- Common web service technologies:
- SOAP - Simple Object Access Protocol
- REST - Representational State Transfer
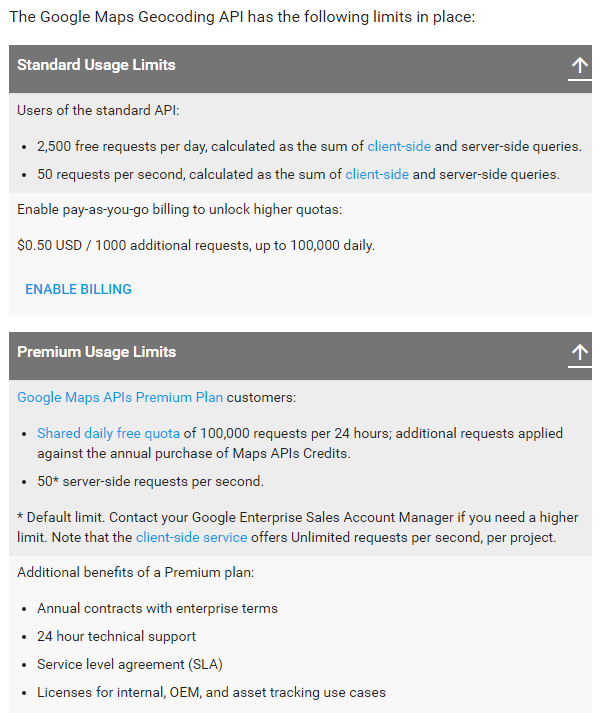
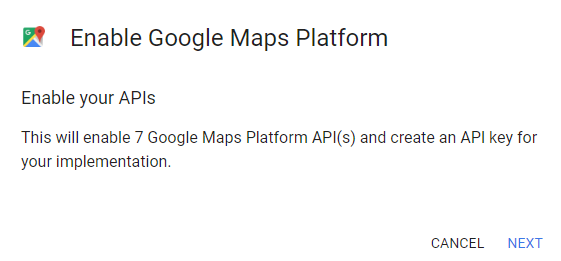
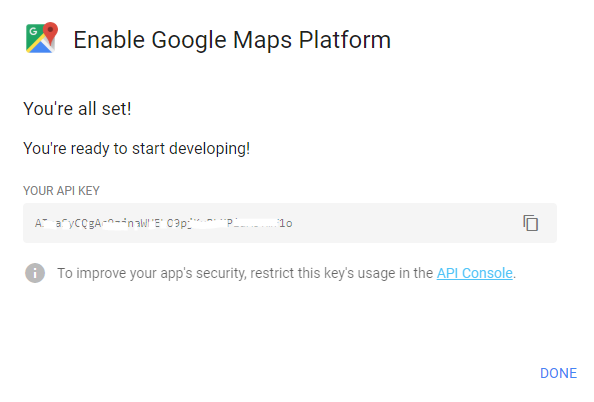
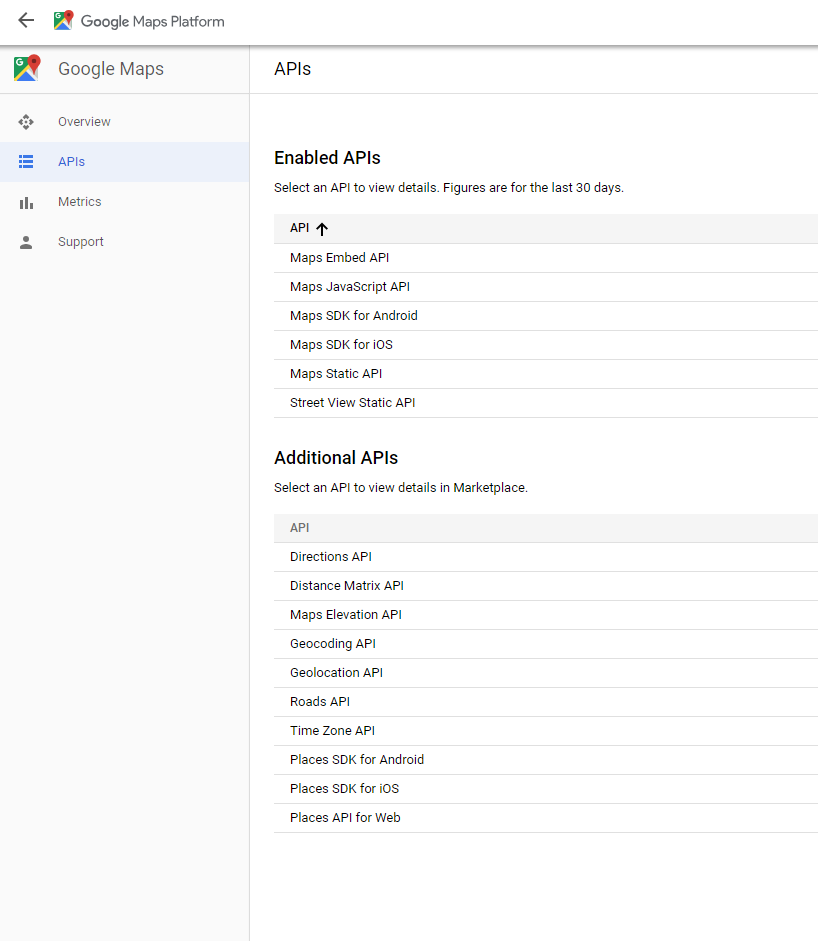
Google Geocoding API

Security and Rate Limiting
- The data provided by these APIs is usually valuable
- The data providers might
- limit the number of requests per day,
- or demand an API "key",
- or charge for usage

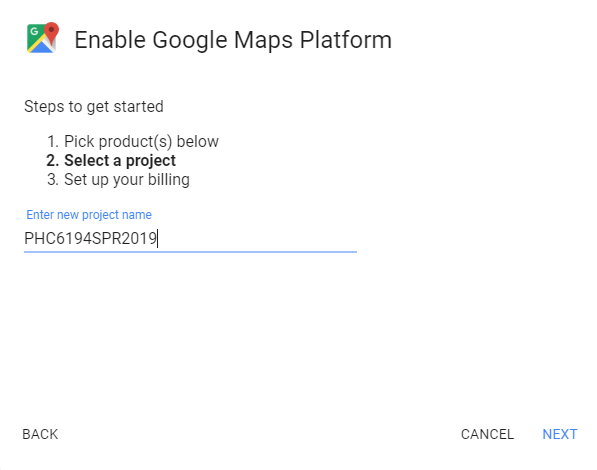
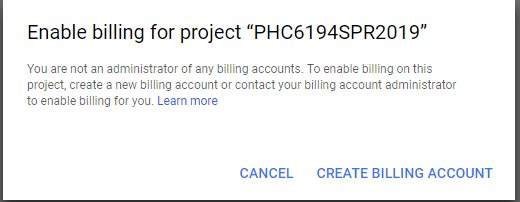
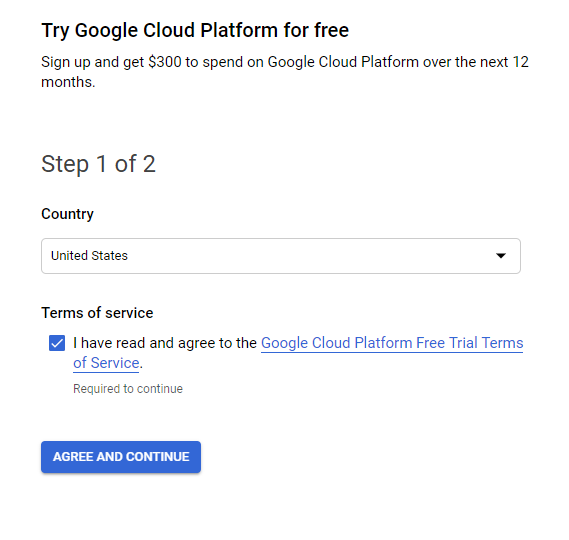
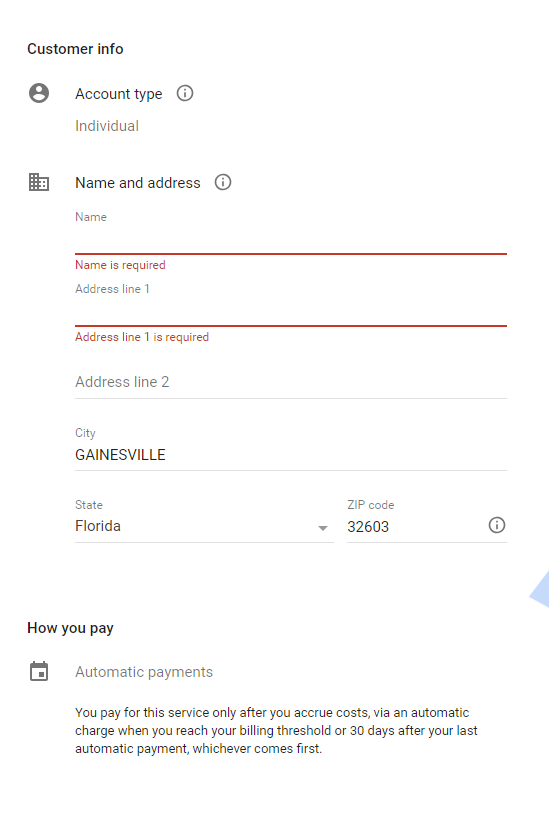
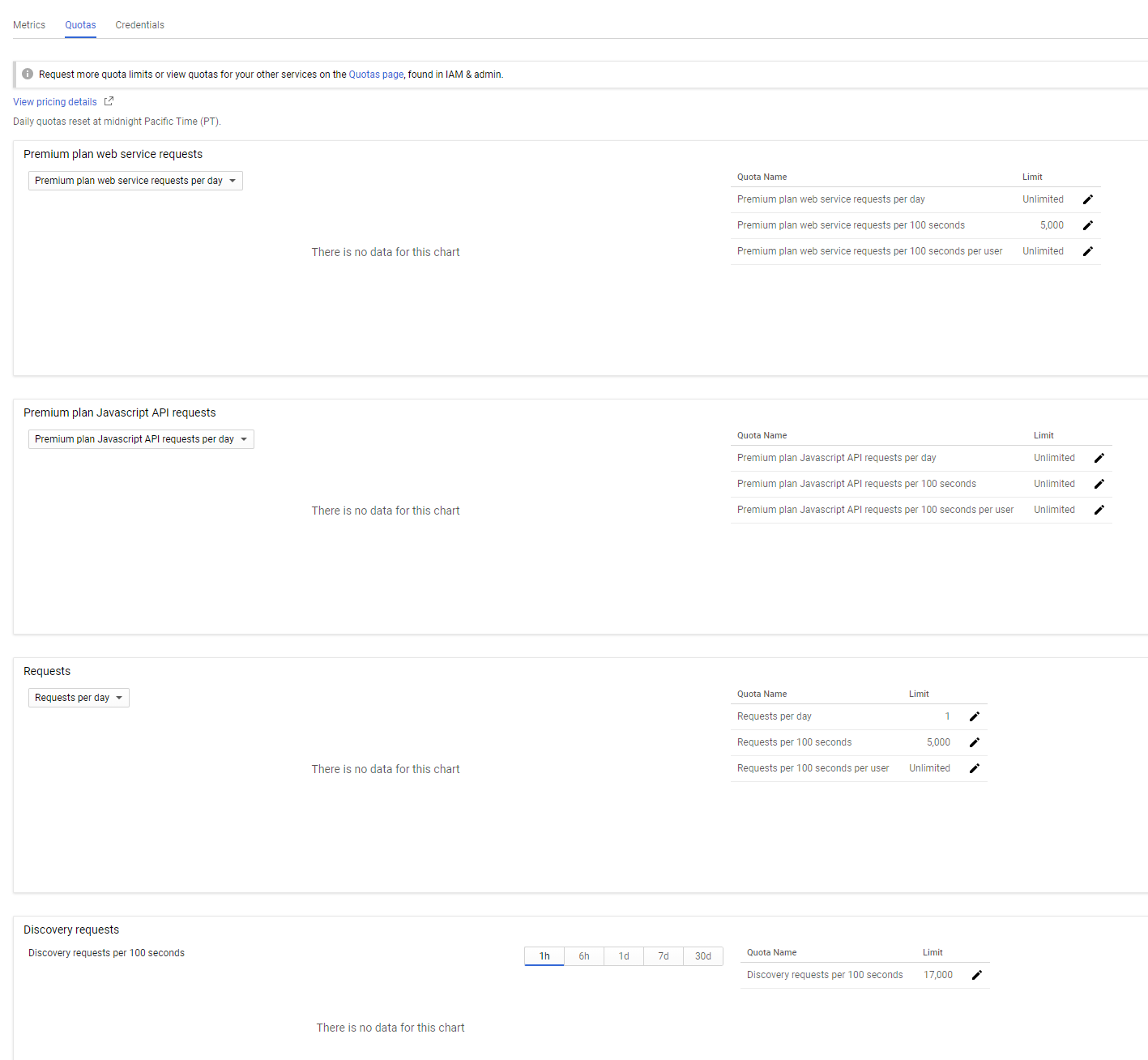
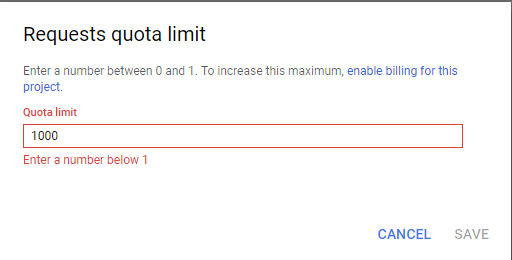
Increase the limit here: e.g. 1000
Twitter API
-
Documentation
- Twitter uses OAuth to verify authorized requests
- Steps to obtain an access token:
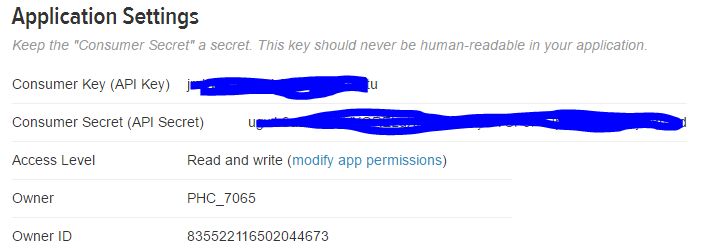
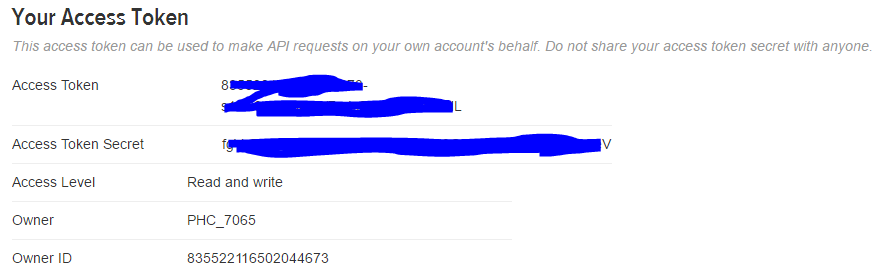
- create a new App (need to have a twitter account)
- go to "Keys and Access Tokens"
- "Create my Access Token"