Markup Basics
Markup is not New
- "Tick marks" for tallying totals
- Punctuation marks
- Mathematical operators
- Emojis
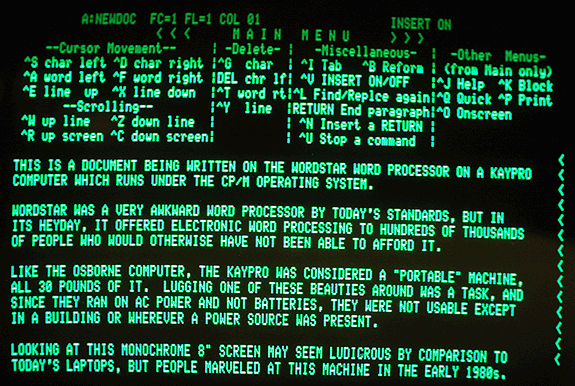
1st Generation Word Processors
...were "markup" systems, not the visual editors that we have today.
Markup symbols indicated which words would be bold, italicized, underlined, etc., but you had to print documents to see what they actually looked like
Content vs. Format
- How do you distinguish the text that is displayed, and the text that indicates how the text is displayed?
- The formatting text must not be presented in the display
- Ideally, interpreting the formatting text should not require propietary software
1990 - The World Wide Web is born
- HTTP: how computers and browser communicate
- HTML: how content is created and formatted in browsers
- URL: how browsers find the content to display
More functions, more features
1994 - <img> tag: add images
- 1995 - <table> tag: create table rows and column
- 1995 - <font> tag: [introduced by Netscape browser]
-
The problem: too many proprietary tags, or browsers that would not recognize certain tags
- The other problem: too many tags blurring the line between format and altering appearance
Format
- What page element is it: Header, paragraph, table header, list item, quote
- How the element is displayed: bold, italic, underlined, etc
Appearance
- Font: Arial, New Times Roman, Sans Serif, etc.
- Color
- Positioning
- Activity: visited link, hover over element
Cascading Style Sheets
- Cascading: multiple style sheets can be applied to the same page
- Style: Controls the aesthetic modification of page elements
- Sheets: Style directives (can be) stored in a separate file, further distinguishing controlling format from altering appearance



