Syntax[0]
algorithm[0] 22527 Brine
我是誰

22527 鄭竣陽
Brine
BrineTW#7355
- 隔壁社 學術長
- 這裡 學術
- 地科讀書會 正則人
- 資訊讀書會 講師
- 排版狂魔
- 只會語法
- 壓線大師
- 絕對會忘記你是誰
- 絕對不記得摯友有誰
- 絕對不會放棄你
索引(可以點)

注意!
今天和以後的演算法小社課都會以 C++ 來教學。
Brine 今天會講很多東西,你們可能沒有辦法一次聽懂。
上課的時候有問題就提出來,會有人幫你解決。
回家之後可以自己再看幾次簡報複習。
下次演算法小社課會複習一些部份,不用擔心。
Editor
要在哪裡寫程式
整合式開發環境 IDE
- 編輯編譯執行一次到位
- 好用方便功能多
- 直接用 IDE 可能不太好
- 專案開發常用
- Eclipse
- Dev-C++
- Code::Blocks



文字編輯器
- 給你打字的地方
- 要自己裝編譯器和其他外掛功能
- Visual Studio Code
- Vim
- Sublime Text



Compiler
編譯器
什麼是編譯器?
-
電腦程式
-
高階語言 \(\rightarrow\) 低階語言(執行檔)
-
直譯器
dian() -> 01000011 01001011 01000101 01000110 01000111 01001001 01010011 01000011如何下載編譯器
-
今天沒時間用,就先用其他的編輯器吧
-
先用 Code::Blocks 和 Dev-C++
簡單的 G++ 編譯指令
g++ fileName.cpp
./a
g++ fileName.cpp -o outputNameOnline Judges
線上評測系統
什麼是線上評測系統
- 測試你的程式是否能夠正常運作的網站
- 一問一答
- 有些系統會定期舉辦比賽
- 演算法競賽通常也會有個線上評測系統
一些好的 OJs
- Temporary INFOR Online Judge, TIOJ
- Code Submission Evaluation System, CSES
- Codeforces, CF
- AtCoder
- OJ 的啦, OJDL
- ZeroJudge, ZJ
- 建中資訊社學長和一些資訊奧林匹亞國手架的 OJ
- 有一些簡單的語法題和高水準的好題
- 沒有難度分類
- 有很多臺灣演算法競賽競賽考古題目
- 建中校內賽舉辦和題目
- 名言區
- 還有建中校內資訊培訓的講義
- 難度高
- 收穫多

- CSES problem set
- 300 題裸題
- 照解題方法分類
- 練技巧學技術
- 練完就會變超級強

- 世界最大 OJ
- 俄羅斯網站
- 可以選學校跟國籍
- 很多資源
- 每周多次線上競賽
- 積分
- division
- hack
- 作息破壞者

- 一樣有積分跟牌位
- 比賽時間比較正常
- 沒有 hack

- 建中資訊讀書會模擬競賽 OJ
- 有些好題目
- 非常好資訊讀書會
- 可以用很多語言
- 有 APCS 的考古
- 照競賽分類題目

Structure
C++ 程式的架構
一般人怎麼寫
- 有很多東西今天不會教,看過就好
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
bool check(string x) {
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) {
if (x[i] == '8') return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int main() {
string x;
while (cin >> x) {
if (check(x)) {
cout << "Yes\n";
} else {
cout << "No\n";
}
}
}Variables
變數
什麼是「變數」
- 儲存資料的東西
- 可以修改、查詢或類似的操作
- 文字、數字、圖像、位置
變數的宣告
- 奇怪的東西先當黑盒子,我們之後再來談
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number = 27;
string name = "Brine";
bool flag = true;
float decimalNumber;
decimalNumber = 3.14;
}
有關變數名稱
- 只能有英文字母、數字或底線
- 必須以英文字母開頭
- 大小寫很重要
- 不得使用保留字
基礎變數型態
- 還有更多,在 STL 的課程中會提到
| 中文 | 宣告時名稱 | 值域 |
|---|---|---|
| 整數 | int | |
| 浮動點 |
float | |
| 雙精度浮動點 |
double | |
| 字元 | char | |
| 字串 | string | |
| 布林值 | bool |
0\sim 255
-2^{31} \sim 2^{31}-1
0/1
0\sim 2^{63} - 1\ 個\ char(?)
\approx \pm (2 - 2^{-23}) \times 2^{\pm 2^7}
\approx \pm (2 - 2^{-52}) \times 2^{\pm 2^{10}}
不同長度的整數
- 以 int 為標準
| 名稱 | 效果 |
|---|---|
| short | 長度砍半 |
| long | 無 |
| long long | 長度加倍 |
簡單的修飾詞
- unsigned 只有整數可以用
| 名稱 | 效果 |
|---|---|
| unsigned | 沒有負數 |
| const | 不可修改 |
數字操作
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
bool brineIsWeak = true;
int a = 5;
int b;
b = a;
float c = 6.4;
double d;
unsigned long long e = 35;
const int M = 1000000007;
}
字串操作
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string name = "CKEFGISC27th";
string a = name;
string b = "name";
char c = 'x';
char d = '\n';
char e = name[5];
string student1, student2;
}
電腦如何存取文字
- ASCII code
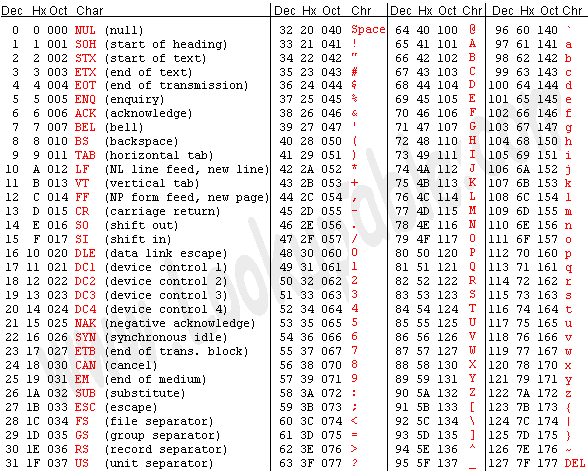
I/O
輸入/輸出
Hello World
- 最簡單的輸出
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello, world\n";
}
輸入
- 什麼型態都可以
- 可混合輸入
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a, b;
char c;
cin >> a;
cin >> b >> c;
}
打字時看起來像怎樣
- cin 吃到空白或換行為止
cin >> a >> b;cin >> a;
cin >> b;225 27225
27字串輸入
- 有空格怎麼辦?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string fullEnglishName;
cin >> fullEnglishName;
cout << "Hello, " << fullEnglishName << ".\n";
}
特殊輸入方法
- 一次取下一整行
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string fullName;
getline(cin, fullName);
cout << "Morning, " << fullName << ".\n";
}
I/O 加速
- 犧牲混用性和在線性,換來執行速度
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
// do something here
}
Operator
運算子
基礎指派
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a;
a = 0;
int b = 4;
int b = a;
a = 3;
cout << a << b;
}
五則運算
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 7;
int b = 3;
cout << a + b << '\n';
cout << a - b << '\n';
cout << a * b << '\n';
cout << a / b << '\n';
cout << b / a << '\n';
cout << a % b << '\n';
cout << b % a << '\n';
}
加加減減
- 先印再動 / 先動再印
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a, b, c, d;
a = b = c = d = 4;
cout << a++ << ' ' << a << '\n';
cout << ++b << ' ' << b << '\n';
cout << --c-- << ' ' << c << '\n';
cout << d-- << ' ' << --d << '\n';
}
相反數
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 15 * 15;
cout << -a << ' ' << a << '\n';
a = -a;
cout << -a << ' ' << a << '\n';
a = a * -1;
cout << a << '\n';
}
其他指派
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 18;
const int b = 5;
a += b;
cout << a << '\n';
a -= b;
cout << a << '\n';
a /= b;
cout << a << '\n';
a %= b;
cout << a << '\n';
a *= b;
cout << a << '\n';
}
比較運算
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 6;
int b = 9;
int c = 6;
cout << (a == b) << '\n';
cout << (a != b) << '\n';
cout << (a == c) << '\n';
cout << (a < b) << '\n';
cout << (a > b) << '\n';
cout << (a <= b) << '\n';
cout << (a >= b) << '\n';
}
邏輯運算
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << ( (6 == 9) && (4 > 2) ) << '\n';
cout << !true << '\n';
cout << !(6 > 9) << '\n';
cout << ( (6 > 9) || (6 <= 9) ) << '\n';
}
位元運算
- 一定要加括號
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
short a = 3; // 00000000 00000011
short b = 5; // 00000000 00000101
cout << (a & b) << '\n';
cout << (a | b) << '\n';
cout << (a ^ b) << '\n';
cout << ~a << '\n';
a = (a << 2);
cout << a << '\n';
a >>= 1;
cout << a << '\n';
}
If-Else
條件式
If only
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
bool asleep = 1;
if (asleep) {
cout << "This is just a dream.\n";
}
}
What else?
- if 失敗的時候要做不同事
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
unsigned int chineseFinal;
cin >> chineseFinal;
if (chineseFinal >= 60) {
cout << "You won!\n" << '\n';
} else {
cout << "You lost!\n" << '\n';
}
}
要很多層怎麼辦
- 暴力巢狀結構
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int grade;
cin >> grade;
if (grade <= 25) {
cout << "左轉國語實小\n";
} else {
if (grade >= 60) {
cout << "贏光光\n";
} else {
cout << "哭了\n";
}
}
}
唯一可以偷懶的特例
- 通常不要這樣比較好喔
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int possibility;
cin >> possibility;
if (possibility % 2 == 1) cout << "I like the odds.\n";
}
比較好的多重判斷
- 跟剛剛的一行 if 是不是有點像?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int chemGrade;
cin >> chemGrade;
if (chemGrade < 0) {
cout << "投胎 gogo!\n";
} else if (chemGrade < 60) {
cout << "非常好重補修!\n";
} else if (chemGrade > 90 && chemGrade < 95) {
cout << "化學 C 級免修!\n";
} else {
cout << "化學 B 級免修!\n";
}
}
Switch-Case
Loops
迴圈
While loops
- 裡面放的是「決定是否繼續一圈」的條件
- 含決定要不要跑第一圈
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n > 0) {
cout << n << '\n';
n--;
}
}
無限迴圈
- 裡面放的東西不會變成 false
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
while (true) {
cout << "學弟加建電,學妹加北資!\n"
}
}
Do-while loops
- 不管怎樣先跑一圈再說
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int counter = 0;
do {
cout << counter << '\n';
} while (counter > 0);
}
變數的存活領域
- 出了他被宣告的大擴號,他就不復存在!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
bool flag = 1;
while (flag) {
cout << "hello\n";
bool copyOfFlag = flag;
flag = 0;
}
cout << copyOfFlag << '\n';
// CE
}
For loops
- 初始化、繼續條件、常駐步驟三位一體
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 2; i < 5; i++) {
cout << i << '\n';
}
int i = 2;
while (i < 5) {
cout << i << '\n';
i++;
}
}
迴圈控制
- continue: 從當前位置直接跳到判斷條件
- break: 跳出該層迴圈
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i > 5) continue;
cout << i << '\n';
}
int counter = 0;
while (counter >= 0) {
if (counter > 10) break;
cout << ++counter << '\n';
}
}
多層迴圈
- 找一些數字的不是他自己的最大因數
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int l, int r;
cin >> l >> r;
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
for (int j = i - 1; j > 0; j--) {
if (i % j == 0) {
cout << j << '\n';
break;
}
}
}
}
輸入吃到飽
- 有時題目會提到「直到 EOF 為止」
- 什麼意思?要怎麼處理呢?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number;
while (cin >> number) {
cout << number * number << '\n';
}
}
輸入吃到飽,但不吃圓
- 有時題目會提到「直到輸出 0 結束」
- 什麼意思?要怎麼處理呢?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number;
while (cin >> number && number != 0) {
cout << number * number << '\n';
}
}
一行二分搜
- 看看就好
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int answer = 623;
bool check(int m);
int main() {
int maximum = 1000;
int l, m, r;
for (l = 0, r = maximum + 1; r - l > 1; (check(m) ? l : r) = m) m = l + r >> 1;
}
bool check(int m) {
return m <= answer;
}
Arrays(?)
陣列(其實不是)
簡單的陣列
- 需要 include "vector" 這個標頭檔喔
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int length;
cin >> length;
vector<int> arr(length);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
cin >> arr[i];
}
cout << arr[0] << '\n';
}
快速遍歷一個 vector
- 有些東西之後會講原理,先記著
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int length;
vector<string> name;
for (string& n: name) cin >> n;
}
Vector 的簡單功能
- 之後會跟你們講為什麼要這樣寫
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> v(3, 5); // v = {5, 5, 5};
cout << v.size() << '\n';
v.push_back(7); // v = {5, 5, 5, 7};
v.resize(6); // v = {5, 5, 5, 7, 0, 0};
v.resize(7, 1); // v = {5, 5, 5, 7, 0, 0, 1};
}
多維陣列
- 聽說 <> 裡面要放型別?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector< vector<int> > graph;
}
那要怎麼初始化
#include <iostream>
#incldue <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector< vector<int> > graph(4, vector<int>(20));
for (vector<int>& v: graph) {
for (int& n: v) {
cin >> n;
}
}
cout << graph[3][13] << '\n';
}
手痠了怎麼辦
- auto!
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector< vector<int> > graph(5, vector<int>(7));
for (auto& v: graph) {
for (auto& n: v) {
cin >> n;
}
}
}
Auto 的妙用
- 反正就是你不想寫或是你忘記他是什麼就讓電腦幫你
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector< vector<int> > graph(5, vector<int>(7));
auto copyOfGraph = graph;
}
真 ‧ 陣列
- 安全性不高
- 功能少
- 問題很多
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int length;
cin >> length;
int arr[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
cin >> arr[i];
}
}
Coding Style
排版和其他
我們為什麼要排版
- 增加程式可讀性
寫可悲 python
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "lmao\n" << '\n';
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main(){cout<<"lmao\n"<<'\n';}
好的 code 要有什麼
- 不毒瘤的縮排,通常 2 / 4 個空白
- 好的變數命名
- 有順序的定義函式和變數
- 正常的表達方式
- 分段
- 大括號不換行
- 小括號和大括號中間空格
- 函式名稱和小括號不空格
- 多層括號中間空格為佳
中文排版
- 中文文本也有排版的好壞
跟我傳訊息最好不要亂排欸- 參考資料
Problems
簡單的範例題
ZeroJudge
TIOJ
CSES
感謝聆聽
要繼續來聽喔

