Week 7
Please sit on the right half of the room
--->
Quiz
Malware Introduction
What is malware?
Malware (Malicious Software) is software specifically designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems.
- Common types of malware include:
- Viruses: Replicate themselves and infect files
- Worms: Spread through networks
- Trojans: Disguised as legitimate software to gain access to the device
- Ransomware: Encrypts files and demands payment for their release
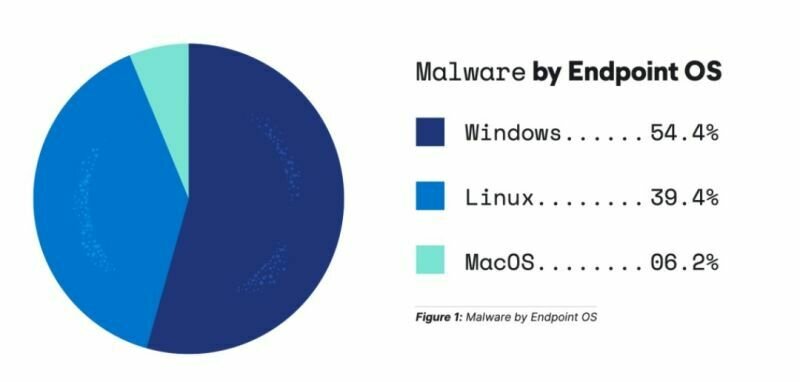
Most malware targets Windows
- We'll learn
- Portable executable format
- Windows reverse engineering
- Windows internals and API
- Common malware techniques
| Feature | PE (Portable Executable) | ELF (Executable and Linkable Format) |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows | Linux/UNIX |
| File Extensions | .exe, .dll | No specific extensions |
| Header | DOS/PE header | ELF header |
| Dynamic Linking | IAT | GOT and PLT |
| Metadata | Rich header, optional header | Program headers, section headers |
| Executable Entry Point | AddressOfEntryPoint field | e_entry field |
| Signature | MZ (at the start of the file) | 0x7F ELF at the start |
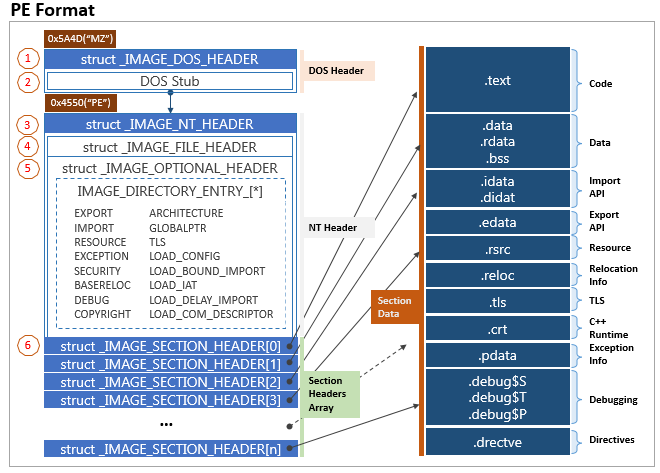
PE Layout
Calling Conventions
Windows has its own calling conventions, which differ from the x86_64 Linux ones in various ways
- A brief comparison:
-
Argument Passing: On Windows, args are passed in RCX, RDX, R8, R9, then the stack
- On Linux they're passed in RDI, RSI, RDX, RCX, R8, R9, then the stack
- Stack Cleanup: On Windows, the caller is responsible for cleaning up the stack
- Returns: Both platforms pass return values in the RAX register
-
Argument Passing: On Windows, args are passed in RCX, RDX, R8, R9, then the stack
- Ghidra will mostly handle this for you