Private data in
smart contracts on
blockchains
Chen-Mou Cheng
Osaka University & ATR
November 25, 2019
About myself
- 2007: PhD, Harvard University
- 2007—2016: National Taiwan University
- 2016—now: Osaka University (Miyaji Lab)
- 2020—?: Kanazawa University
- Recent research
- HW/SW implementation of
post-quantum cryptography - Privacy-preserving smart contracts
- HW/SW implementation of
Blockchain
- A decentralized trust machine
- Nakamoto consensus protocol
- Blockchain ≅ Merkle tree + digital signature
Merkle trees
The Bitcoin blockchain

Smart contracts
- Bitcoin Tx: Today Alice paid Bob 1 Bitcoin
- Ethereum Tx: y,s' = f(x,s)
- x: input, y: output
- s: current state, s': next state
- E.g., s = {who has how many Ethers}
- That's a smart contract!
Problems with Ethereum
- No privacy!
- Miners need to see everything to verify Tx's
- But many contracts depend on private data!
- A.k.a., "trade secrets"
- Two kinds of solutions
- Homomorphic encryption
- Secret sharing
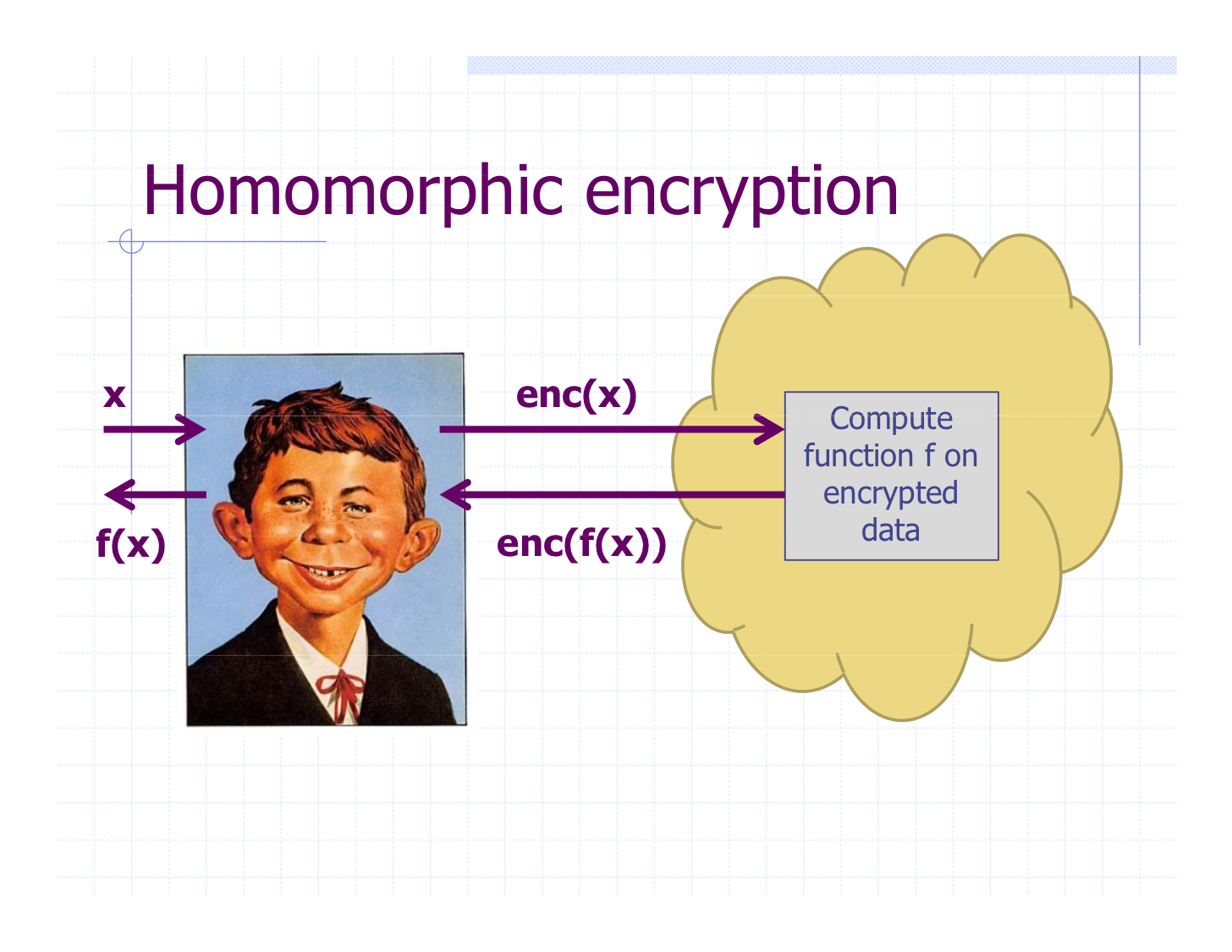
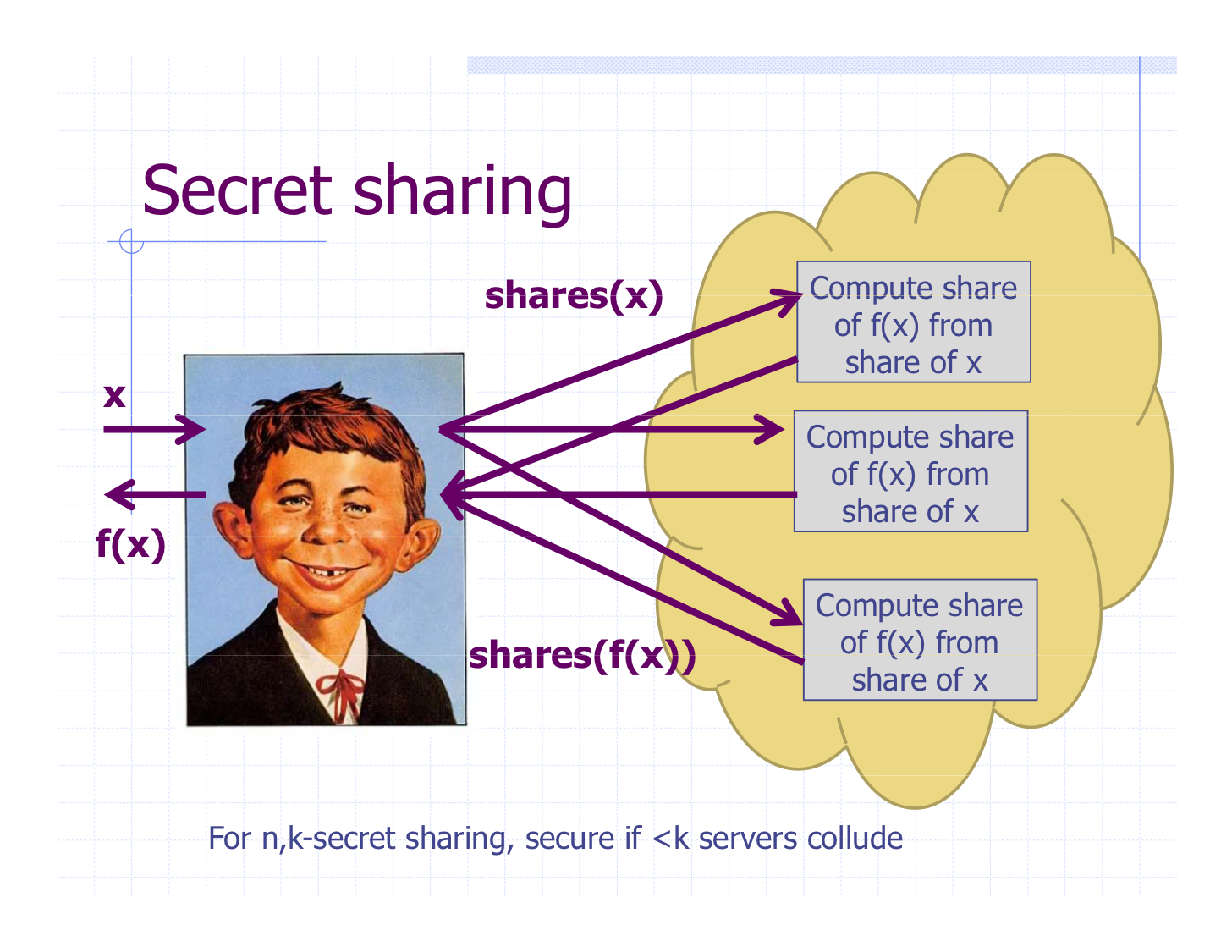
Solution: Disputeless Off-chain Computation (DOC)
- Idea
- Computation on private data done off-chain
- On-chain verification to prevent disputes
- Building blocks
- Cryptographic commitment schemes
- Domain-specific compilers
- Zero-knowledge proofs
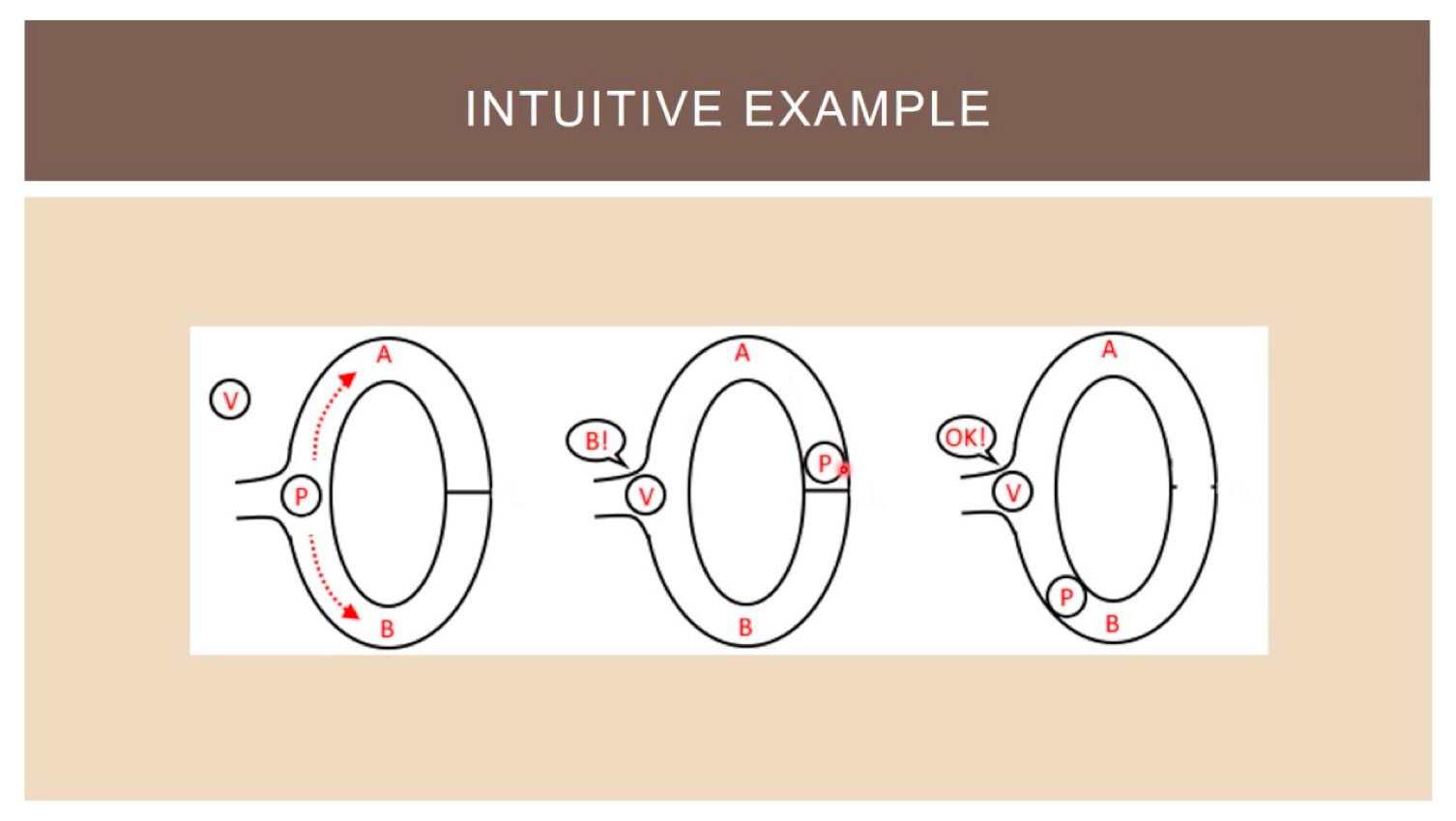
Zero-knowledge proofs
API design
- Data registration: (H(s),C) → ()
- Computer lookup: H(s) → [C]
- Function registration: f → (kprove,kverify)
- Evaluation request: (f,x,H(s),C) → ()
- Evaluation report: (f,x,H(s),f(x,s),π) → ()