Misuse Resistant Code
... a programming language designer should be responsible for the mistakes that are made by the programmers
- Tony Hoare
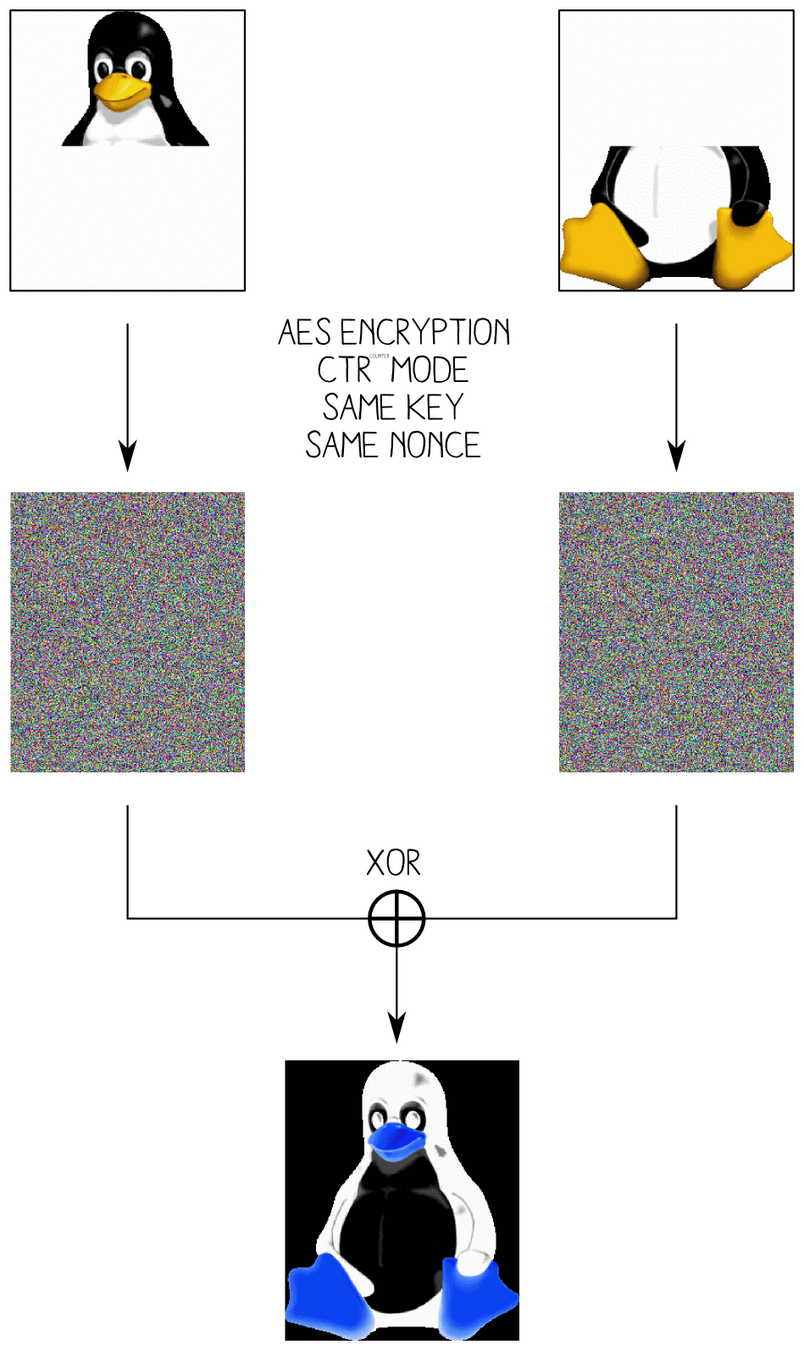
# Your crypto API
def encrypt(msg: bytes, key: bytes, nonce: bytes) -> bytes:
pass # impl
# Consumer code
def main() -> None:
nonce = make_nonce() # cryptographic nonce
key = get_key() # load up the key
encrypt(b"message A", key, nonce) # encrypt, hooray
encrypt(b"message B", key, nonce) # nonce reuse :(
class Nonce:
def __init__() -> None:
self.__nonce: Optional[bytes] = make_nonce()
def get_nonce() -> bytes:
if self.__nonce is None:
raise ValueError("Attepted to reuse nonce! This is a bug!")
nonce = self.__nonce
self.__nonce = Nonce
return nonce
def encrypt(msg: bytes, key: bytes, nonce: Nonce) -> bytes:
# in our crypto library we can ensure that
# we're very careful with the raw value
raw_nonce = nonce.get_nonce()
raise NotImplemented
def main() -> None:
nonce = Nonce() # cryptographic nonce
key = get_key() # load up the key
encrypt(b"message A", key, nonce) # encrypt, hooray
# Runtime error! Better than a crypto failure
encrypt(b"message B", key, nonce)
Affine Types (a little rust)
pub struct Nonce {
inner_nonce: Vec<u8>,
}
impl Nonce {
pub fn new() -> Self {
return Nonce { inner_nonce: unimplemented!() }
}
# private method - can't be accessed outside of our crypto module!
fn unchecked_get(self) -> Vec<u8> { return self.inner_nonce }
}
# Note that `nonce` is not passed in by value, it is *moved* into
# this function - it can't be accessed afterwards by the caller
pub fn encrypt(msg: &[u8], key: &[u8], nonce: Nonce) -> Vec<u8> {
let nonce = nonce.unchecked_get(); # Be careful with the raw value!
unimplemented!()
}
fn main() {
let nonce = Nonce::new();
let key = &b"very safe key!"[..];
encrypt(&b"Message A", &key, nonce); // Encrypts, yay
encrypt(&b"Message B", &key, nonce); // Compile time error!
}Refinement Types
# Implicit constraint: the user has a valid session
def disable_mfa(username: str) -> None:
pass
def handle_request(request: Request) -> Response:
# We forgot to check if the user is actually logged in
if request.path == "/disable_mfa":
disable_mfa(request.username)
Refinement Types
class User:
@staticmethod
def from_request(request: Request) -> User:
...
def as_logged_in_user(self) -> Optional[LoggedInUser]:
return LoggedInUser.try_from_user(self)
class LoggedInUser:
@staticmethod
def try_from_user(user: User) -> Optional[LoggedInUser]:
if !self.is_logged_in(): return None
... # construct
# Explicit constraint: the user has a valid session
def disable_mfa(user: LoggedInUser) -> None:
pass
def handle_request(request: Request) -> Response:
# We forgot to check if the user is actually logged in
if request.path == "/disable_mfa":
user = User.from_request(request)
if logged_in_user := user.as_logged_in_user():
disable_mfa(logged_in_user)
else:
return 403
Session Types: Affine + Refinement
+----------------------+
|connection established|
+----------------------+
||
\/
+--------------------------------------+
| server greeting |
+--------------------------------------+
|| (1) || (2) || (3)
\/ || ||
+-----------------+ || ||
|Not Authenticated| || ||
+-----------------+ || ||
|| (7) || (4) || ||
|| \/ \/ ||
|| +----------------+ ||
|| | Authenticated |<=++ ||
|| +----------------+ || ||
|| || (7) || (5) || (6) ||
|| || \/ || ||
|| || +--------+ || ||
|| || |Selected|==++ ||
|| || +--------+ ||
|| || || (7) ||
\/ \/ \/ \/
+--------------------------------------+
| Logout |
+--------------------------------------+
||
\/
+-------------------------------+
|both sides close the connection|
+-------------------------------+Session Types: Affine + Refinement
struct SomeState {}
struct NewState {}
impl SomeState { // ↱ Our successful or unsuccessful state transition
fn transition(self) -> Result<NewState, SomeState> { ... }
// ↳consumes self
}Session Types: Affine + Refinement
struct IMAPClient {}
impl IMAPClient {
fn new() -> Self {unimplemented!()}
fn connect(&mut self) -> Result<(), Error> {unimplemented!()}
fn login(&mut self) -> Result<(), Error> {unimplemented!()}
fn select(&mut self) -> Result<(), Error> {unimplemented!()}
fn authenticate(&mut self) -> Result<(), Error> {unimplemented!()}
fn logout(&mut self) -> Result<(), Error> {unimplemented!()}
}
fn main() {
let mut client = IMAPClient::new();
client.select(); // this makes no sense - we aren't authenticated!
}Session Types: Affine + Refinement
struct IMAPClient {}
struct Initial {
connection: IMAPClient
}
struct UnAuthenticated {
connection: IMAPClient
}
struct Authenticated {
connection: IMAPClient
}
struct Selected {
connection: IMAPClient
}
struct LoggedOut {
connection: IMAPClient
}
Session Types: Affine + Refinement
impl Initial {
fn connect(self) -> Result<UnAuthenticated, (Initial, Error)> {
unimplemented!()
}
}
impl UnAuthenticated {
fn login(self) -> Result<Authenticated, (UnAuthenticated, Error)> {
unimplemented!()
}
fn logout(self) -> Result<Logout, (UnAuthenticated, Error)> {
unimplemented!()
}
}
Session Types: Affine + Refinement
use imap::{Initial};
fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let client = Initial::init();
let client = match client.connect() {
Ok(client) => client,
Err((_client, error)) => {
panic!("failed to connect with {:#?}", error);
}
};
let client = match client.login() {
Ok(client) => client,
Err((_client, error)) => {
panic!("failed to login with {:#?}", error);
}
};
// etc
Ok(())
}Dependent Types
class Matrix:
def __init__(self, x, y) -> None:
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.values = [0] * x * y
def multiply(self, other: Matrix) -> Matrix:
if self.x != other.y:
raise ValueException("Matrix multiplication invariant violated")
...
def main():
matrix_a = Matrix(2, 4)
matrix_b = Matrix(3, 7)
matrix_c = matrix_a.multiple(matrix_b) # runtime errorDependent Types
class Matrix[X: int, Y: int]:
def __init__(self, x, y) -> None:
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.values = [0] * x * y
def multiply[N: int](self, other: Matrix[Y, N]) -> Matrix[X, N]:
...
def main():
matrix_a = Matrix(2, 4)
matrix_b = Matrix(4, 7)
# Compile time checks that the matrices can be multiplied
matrix_d: Matrix[2, 7] = matrix_a.multiple(matrix_b)
Dependent Types
class Matrix[X: int, Y: int]:
def __init__(self, x, y) -> None:
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.values = [0] * x * y
def append_rows[N: int](self, other: Matrix[N, Y]) -> Matrix[X + N, Y]:
...
def main():
matrix_a = Matrix(2, 5)
matrix_b = Matrix(4, 5)
matrix_d: Matrix[6, 5] = matrix_a.append_rows(matrix_b)
Dependent Types + Type Narrowing
class Matrix[X: int, Y: int]:
def __init__(self, x, y) -> None:
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.values = [0] * x * y
def append_rows[N: int](self, other: Matrix[N, Y]) -> Matrix[X + N, Y]:
...
def check_for_append[A: int, B: int](self, other: Matrix[A, B]) -> Optional[Matrix[A, Y]]:
if self.y == other.y:
return other
else:
return None
def main():
matrix_a = Matrix(2, 5)
matrix_b: Matrix[_, _] = load_matrix_from_disk()
if matrix_c := matrix_a.check_for_append(matrix_b):
matrix_c: Matrix[_, 5]; # We know this type checks now
matrix_d: Matrix[_ + 6, 5] = matrix_a.append_rows(matrix_b)
Dependent Types + Flow Typing
class Matrix[X: int, Y: int]:
def __init__(self, x, y) -> None:
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.values = [0] * x * y
def append_rows[N: int](self, other: Matrix[N, Y]) -> Matrix[X + N, Y]:
...
def main():
matrix_a = Matrix(2, 5)
matrix_b: Matrix[_, _] = load_matrix_from_disk()
if matrix_b.y == matrix_a.y: # Flow Typing
matrix_d: Matrix[_ + 6, 5] = matrix_a.append_rows(matrix_b)