Advanced Data Analysis in Excel


Advanced SUM and COUNT Functions

Learning Outcome
6
Use SUBTOTAL to perform calculations on filtered data
5
Use COUNTIFS to count records based on multiple conditions
4
Use COUNTIF to count records based on a single condition
3
Use SUMIFS to sum values based on multiple conditions
2
Use SUMIF to sum values based on a single condition
1
Differentiate between basic and advanced SUM/COUNT functions

What You Already Know
SUM & COUNT Functions
Logical operators
Clean, tabular datasets
IF statements and logical thinking
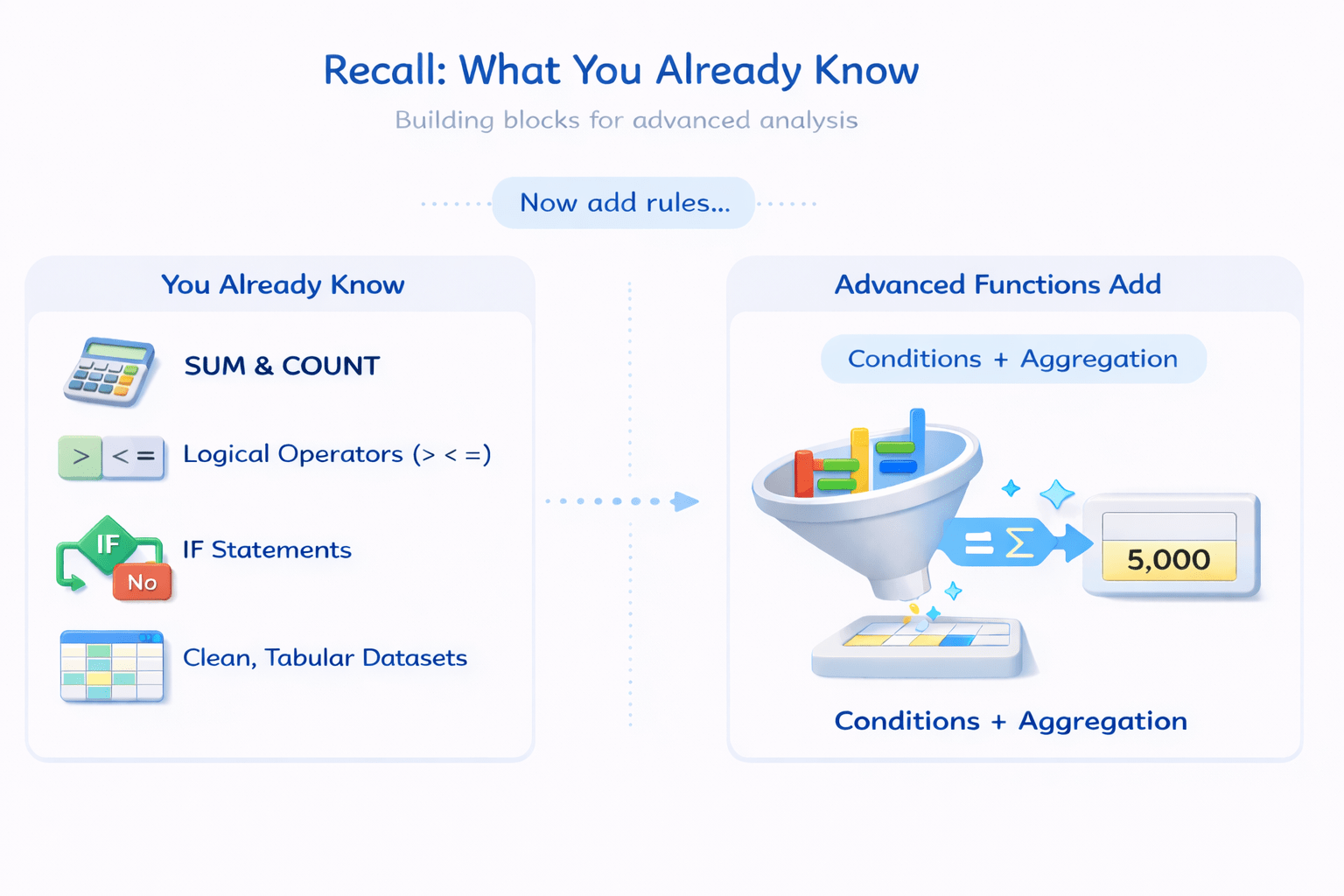



Advanced functions extend this by adding:
+
Conditions
Aggregation

Imagine you are managing a busy supermarket.
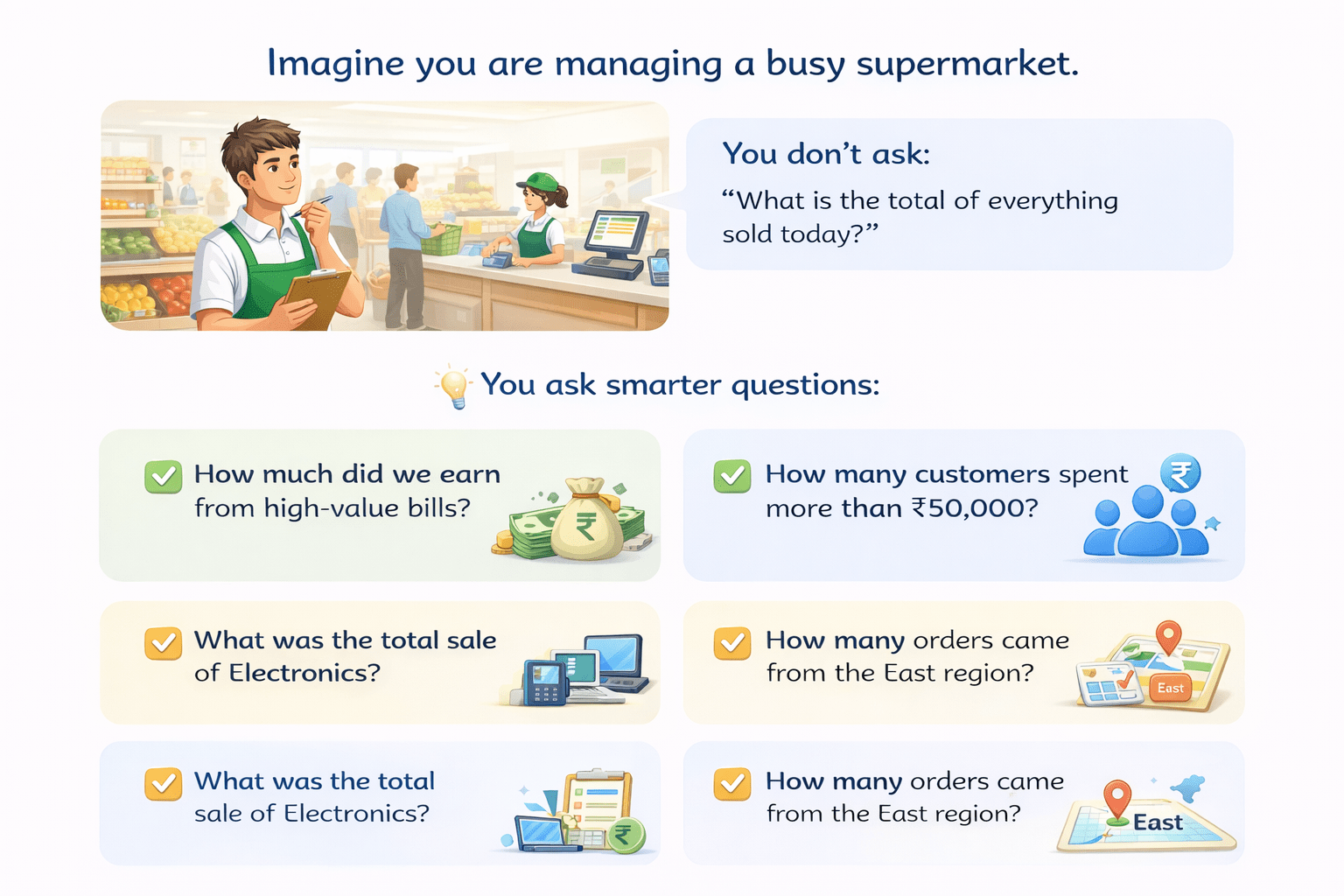
You don’t ask:
“What is the total of everything sold today?”

You ask smarter questions:
“How much did we earn from high-value bills?”
“How many customers spent more than ₹50,000?”
“What was the total sale of Electronics?"
“How many orders came from the East region?"


Manually adding and counting is slow and error-prone.


What you really need is a calculator that listens:
“Add only what matches my rule.”

Transition from Analogy to Technical Concept(Slide 5)

Core Concepts (Slide 6)

Core Concepts (Slide 7)

Core Concepts (.....Slide N-3)

Summary
5
These functions enable targeted analysis
4
SUBTOTAL ignores hidden rows
3
SUMIFS and COUNTIFS handle multiple criteria
2
SUMIF and COUNTIF handle single criteria
1
Advanced SUM and COUNT functions apply conditions

Quiz
Which platform is mainly used for professional networking and B2B marketing ?
A. Facebook
B. Instagram
C. LinkedIn
D. Snapchat


Quiz-Answer
Which platform is mainly used for professional networking and B2B marketing ?
A. Facebook
B. Instagram
C. LinkedIn
D. Snapchat
