DOM Navigation


Finding elements and Handling Event
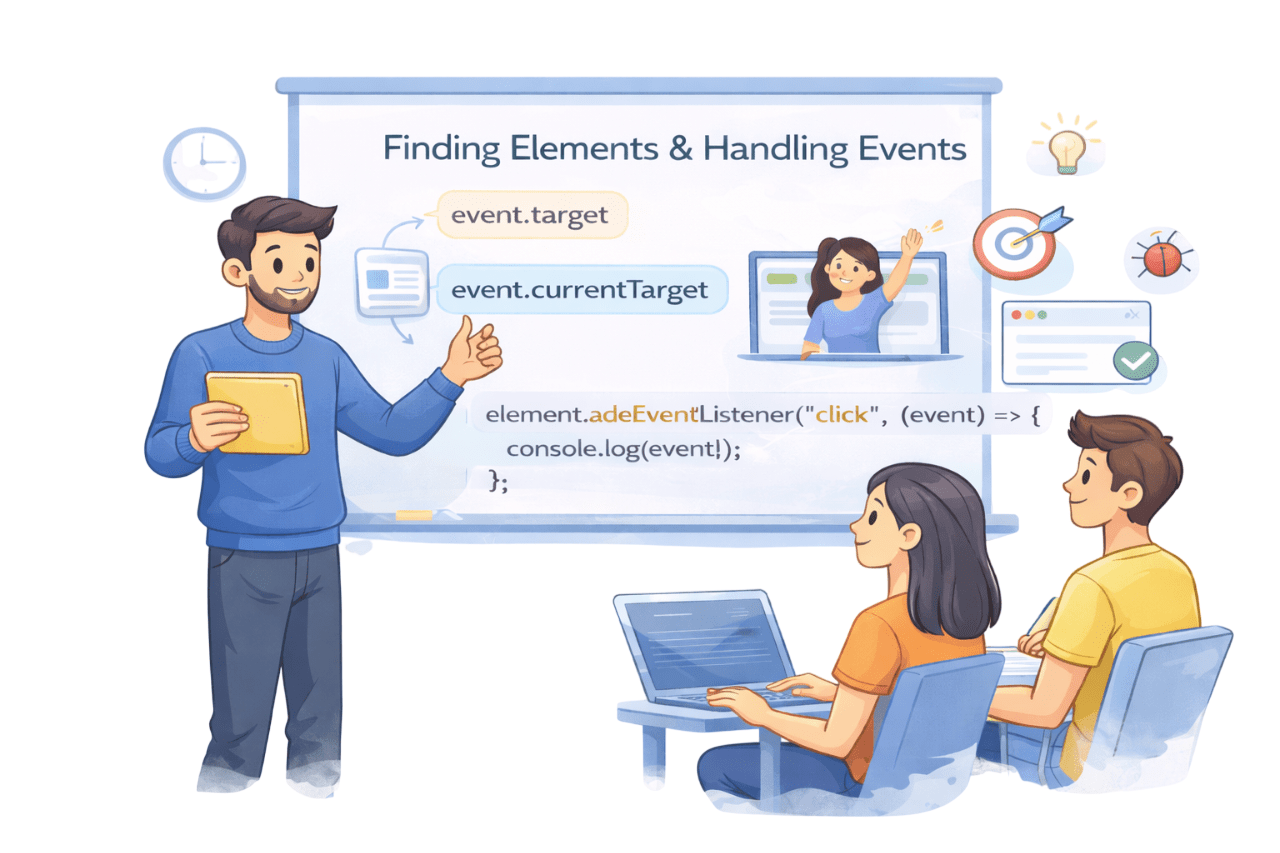

Learning Outcome
6
Control default browser behavior using preventDefault()
5
Identify and use common mouse, keyboard, form, and window events
4
Explain why addEventListener is preferred over onclick()
3
Use addEventListener() and removeEventListener() correctly
2
Connect user actions to JavaScript using event listeners
1
Explain what browser events are and why they exist

Analogy: Doorbell in a Smart Home
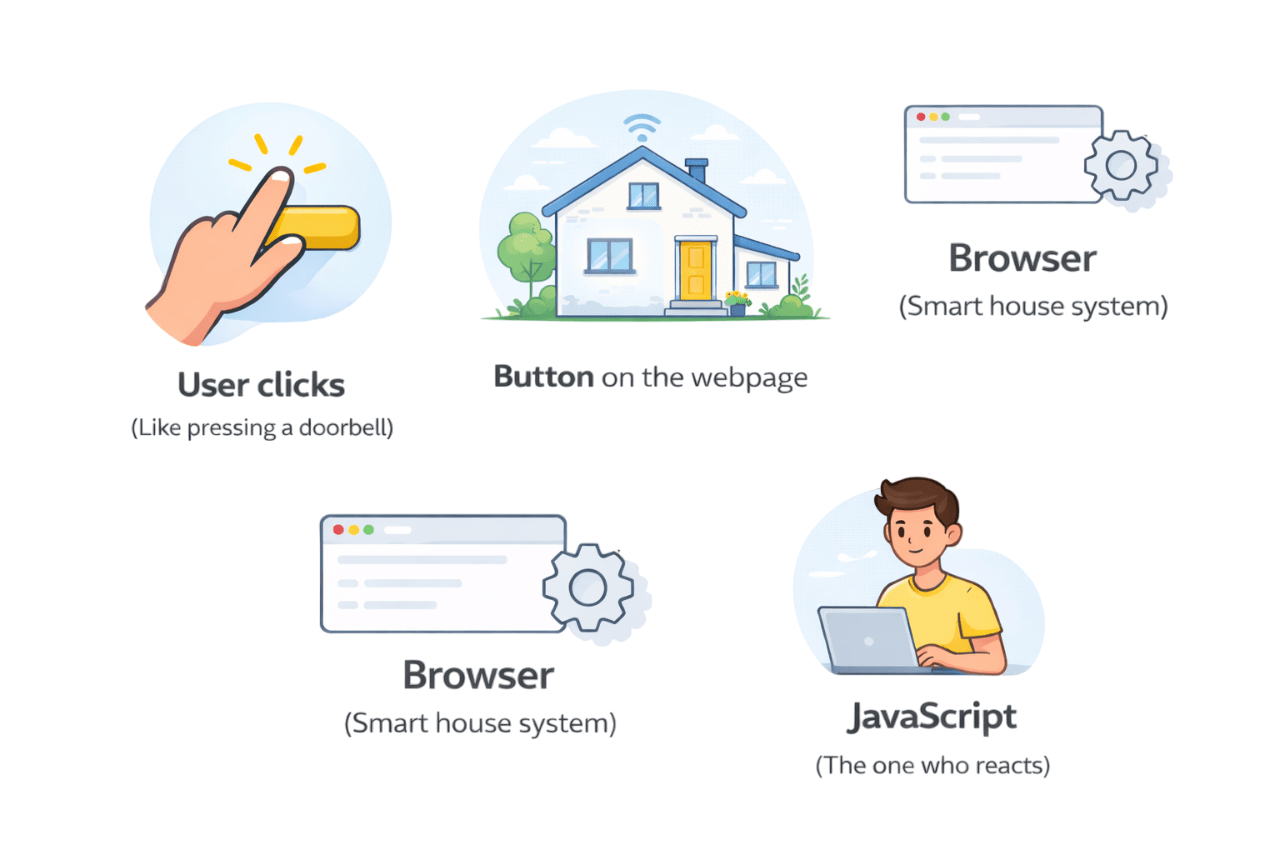
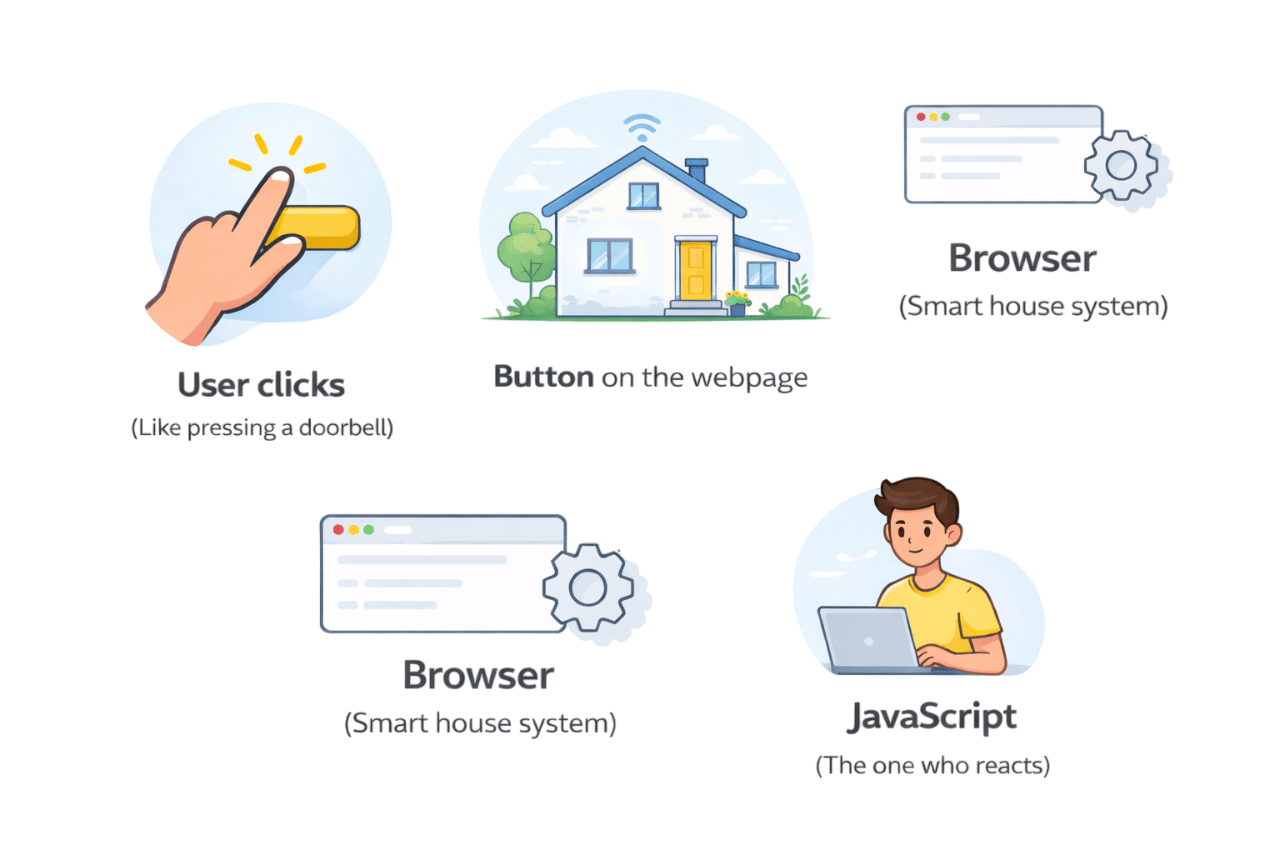
How does the browser know what code to run when a user clicks,types, or scrolls?
Events and Event Listener


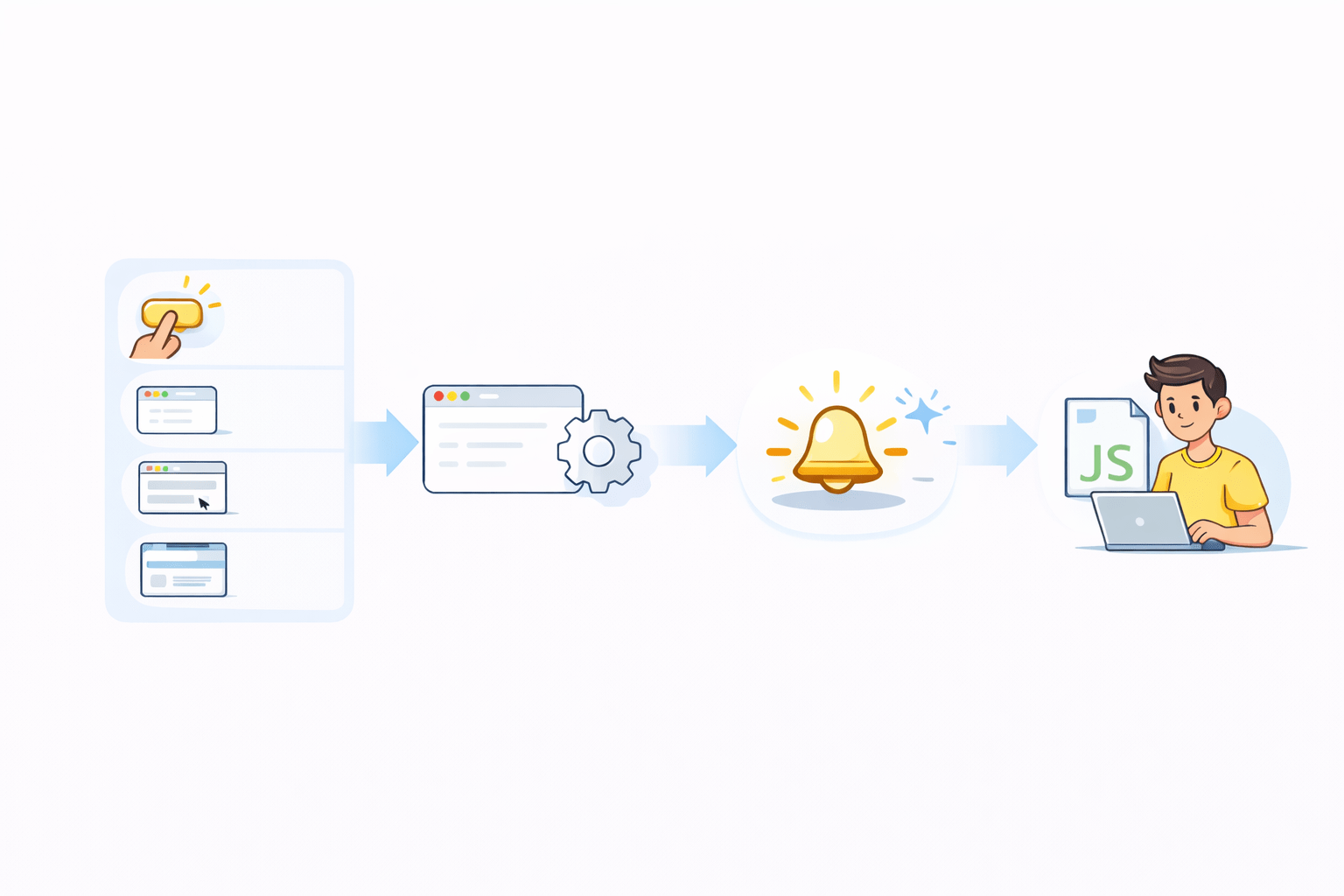
From User Actions to Code Execution
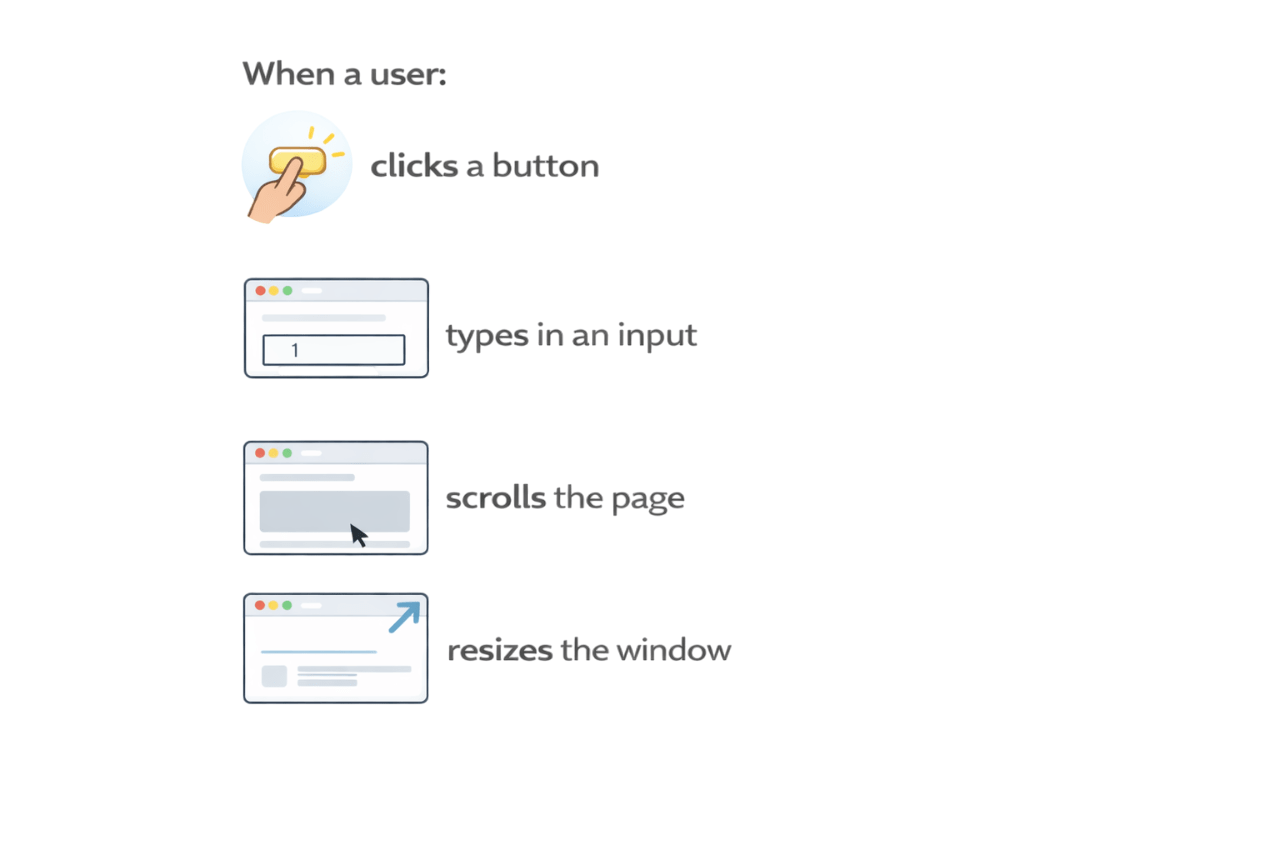
Click a button
types in an input
Scrolls the page
resizes the window
Detects the action
Creates an event
Notifies Javascript
Listening is done using Event Listeners








What is an Event?
An event is a signal sent by the browser to indicate that something happened
Who creates events ?
The browser,not Javascript
User actions
(click,type,scroll)
Browser actions
(page,load,resize)
System actions
(network finished,image loaded)




What is an EventListener?
Event
Notification
Listener
Waiting function
Handler
Code that runs
An Event listener is:
A function
Registered on a DOM element
Executed when a specific event occurs



Without a listener:
The event still happens
But Javascript never reacts






addEventListener(): Syntax & Meaning
General Syntax
element.addEventListener("eventType",handlerFunction);
Example
button.addEventListener("click", () => {
console.log("Button was clicked");
});
What each part means
element -> the DOM element to monitor
"eventType" -> what action to watch for
handlerFunction -> what action to watch for




Why addEventListener() Is a best choice
Key Advantages
keeps Javascript separate from HTML
Supports multiple event handlers
Works with modern frameworks
Allows removal of listeners later




addeventListener respects this separation

<html>
{css}
<script>
<button>..
</button>
button {
color: blue;
}
button.add
eventListener();
<html>
Structure
<CSS>
Style
<script>
behavior
Design Principle

Why removeEventListener(): Why and How
Why Remove a Listener?
To stop unnecessary actions
To avoid memory leaks
To clean up dynamic elements



Example
function handleClick() {
console.log("Clicked");
}
button.addEventListener("click", handleClick);
button.removeEventListener("click", handleClick);
You must pass the same function reference.
Anonymous functions cannot be removed


Why removeEventListener(): Why and How
Why Remove a Listener?
To stop unnecessary actions
To avoid memory leaks
To clean up dynamic elements



Example
function handleClick() {
console.log("Clicked");
}
button.addEventListener("click", handleClick);
button.removeEventListener("click", handleClick);
You must pass the same function reference.
Anonymous functions cannot be removed



onclick vs addEventListener
Inline Event(Old Style)
<button onclick="alert('Hi')">Click</button>
Modern Appoarch
button.addEventListener("click", sayHi);
Problems
Mixes HTML and Javascript
Allows only one handler
Difficult to scale



Why Modern Wins
Cleaner code
Multiple handler
Better Maintainability




Industry standarad

Multiple Event Listeners on One Element
Example
button.addEventListener("click", () => console.log("Log"));
button.addEventListener("click", () => console.log("Track"));
What Happens
Both handlers executes
Inorder they were added
Why This Matters
Logging
Analytics
UI updates
Accessibility handling







Event Categories
Events are grouped based on user interaction type
Mouse Events
Pointer Interactions
Keyboard Events
Key presses
input and submission
Form Events
Window/Document Events
browser lifecycle
Each category solves a different interactions problem




Mouse Events
click - Single click
dblclick - Double click
mousedown - Button Pressed
mouseup - Button Released
mousleave - Pointer leaves element
mousemove - Pointer Moves
mousleave - pointer leaves element
Mouse Event Types
Mouse Event Types
UseCases
Buttons
Menus
Hover effects
Drag and drop




Keyboard Events
keydown - Key Pressed Down
keyup - key released
keypress - character legacy
keyboard Event Types
UseCases
shortcuts( Ctrl + S)
Form Validation
Games




Event Object: What is it?
When an event occurs:
The browser creates an event object
Passes it automatically to the handler
contains details about the event


element.addEventListener("click", (event) => {
console.log(event);
});
- "click" -> User clicked the element
- (event) -> This is the event object

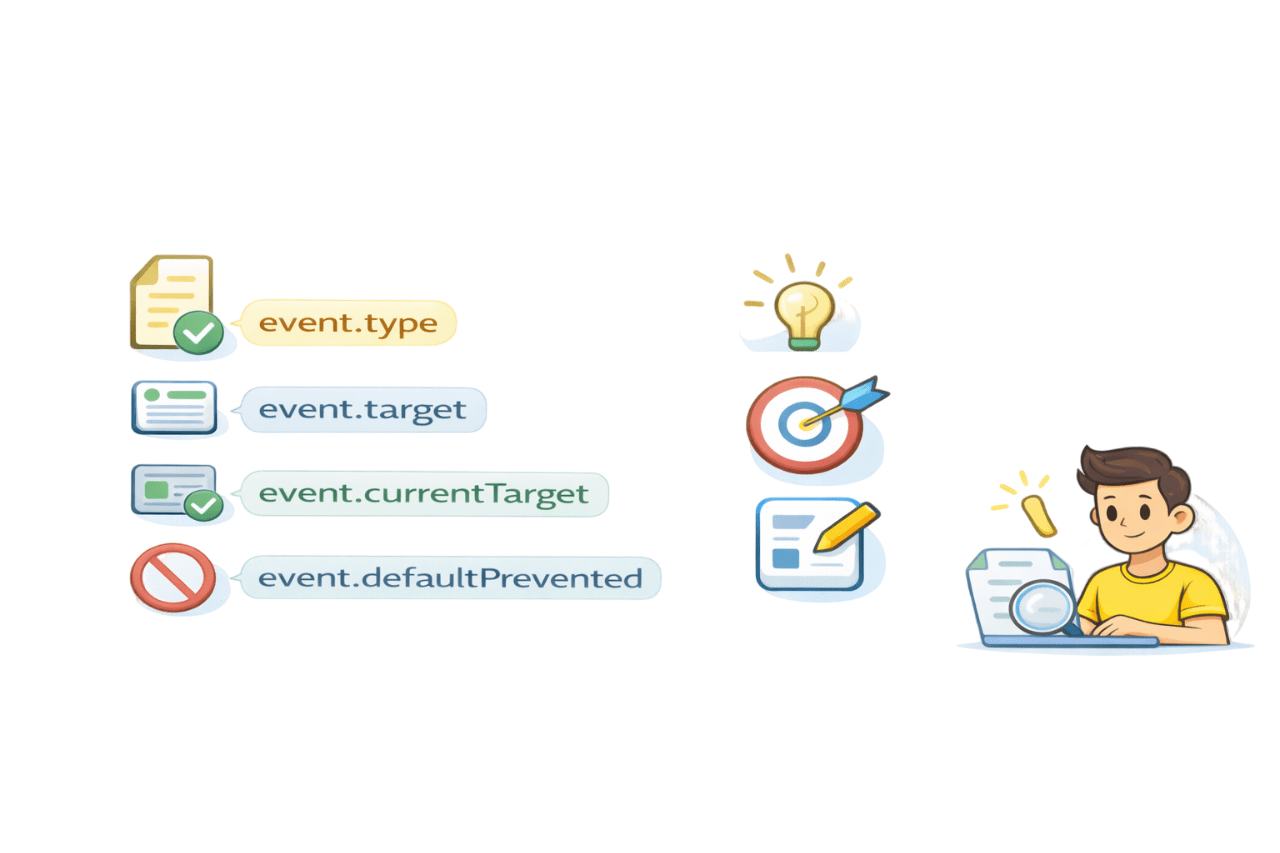
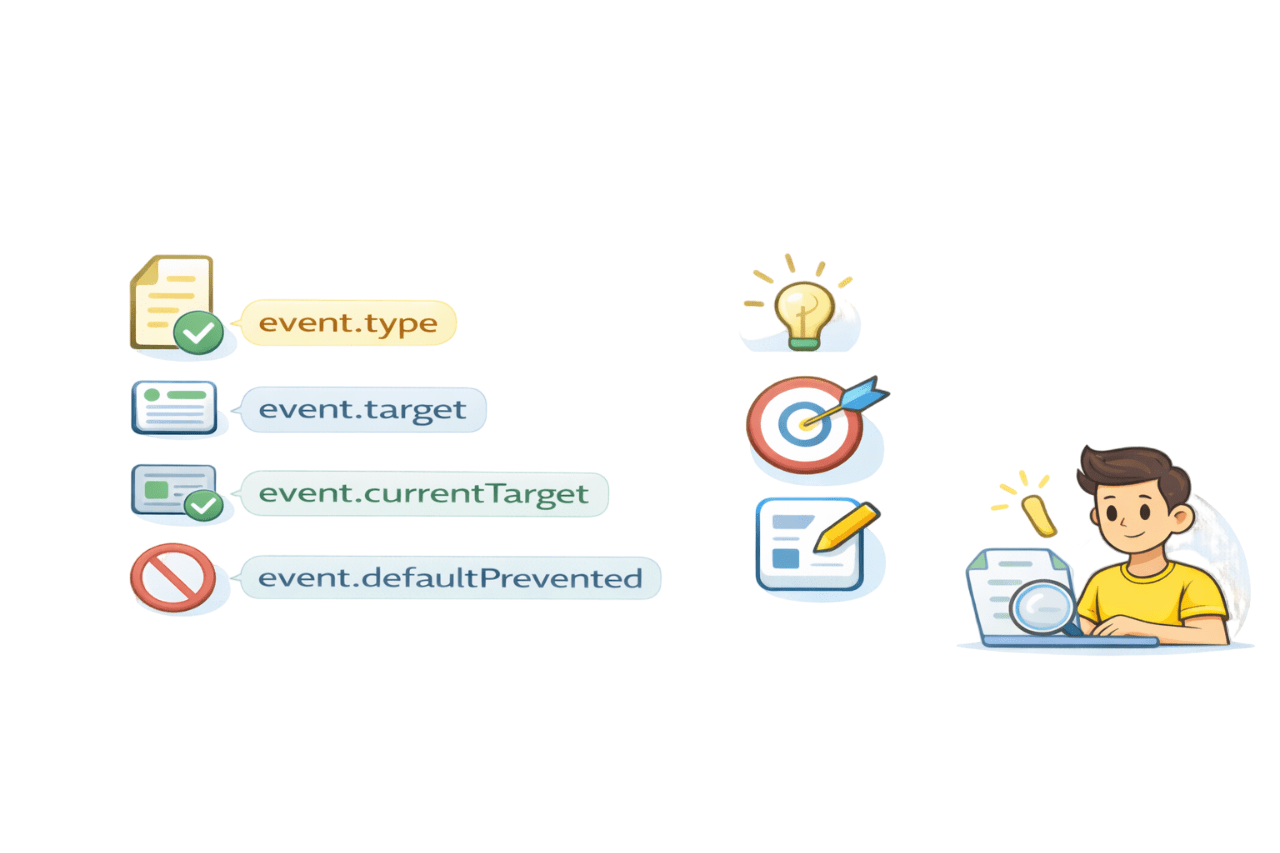
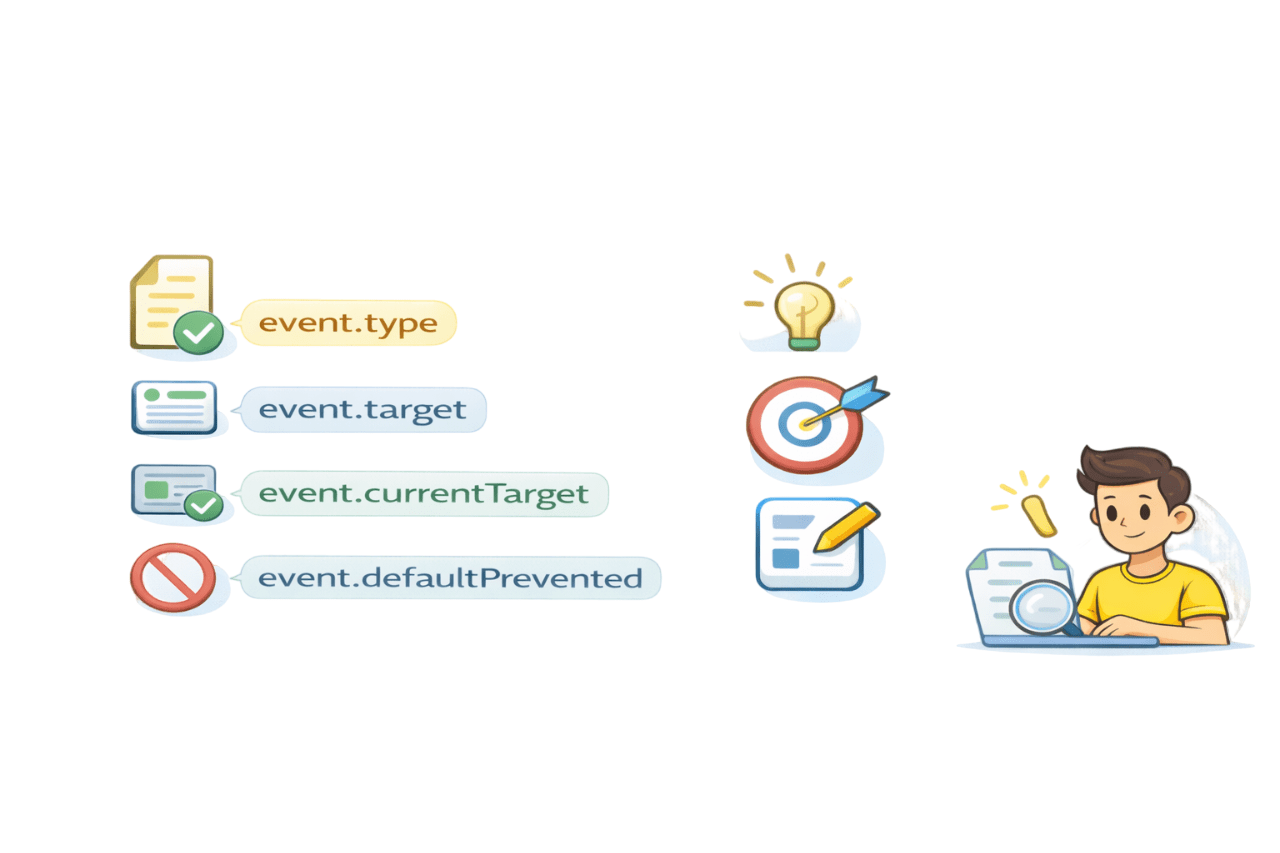
Important Properties of the Event Object
event.type - event name
event.target - element that triggered event
event.currentTarget - element with listener
event.defaultPrevented - Whether default action stopped
Identify clicked element
Handle dynamic content
Debug interactions

Why Useful

Window and Document Events
load - everything loaded
resize - window resized
scroll - scrolling detected
Window-Level Events
Document-Level Events
DOMContentLoaded - DOM ready
Key Difference
DOMContentLoaded does NOT wait for images
load waits for everything



PreventDefault() : Controlling Behaviour
Form submission reloads page
Anchor tag navigates
Right-click shows menu
Default Browser Actions
Stopping Default Action
event.preventDefault();
Use Case
Single-page applications
Client-side Validation



Summary
5
Event object provides context and control
4
Events are categorized by interaction type
3
addEventListener is the modern standard
2
Event listeners connect events to code
1
Events represent user or browser actions

Quiz
Which method allows multiple handlers on one element?
A. onclick
B. addEvent
C. attachEventListener
D. onClick


Quiz
Which method allows multiple handlers on one element?
A. onclick
B. addEvent
C. attachEventListener
D. onClick


Quiz
Which method allows multiple handlers on one element?
A. onclick
B. addEvent
C. addEventListener
D. onClick


Quiz-Answer
Which method allows multiple handlers on one element?
A. onclick
B. addEvent
C. addEventListener
D. onClick
