Java Basics

Data Types, Variables

Learning Outcome
5
Use methods to print data
4
Apply correct variable naming rules
3
Declare, initialize, and assign variables
2
Differentiate primitive and non-primitive types
1
Understand purpose of Java data types


Have you ever tried storing rice in a net
Pouring milk into a paper envelope?
OR



No matter how careful you are, it just doesn’t work properly.”
Why does this happen?
Not because the rice or milk is wrong…
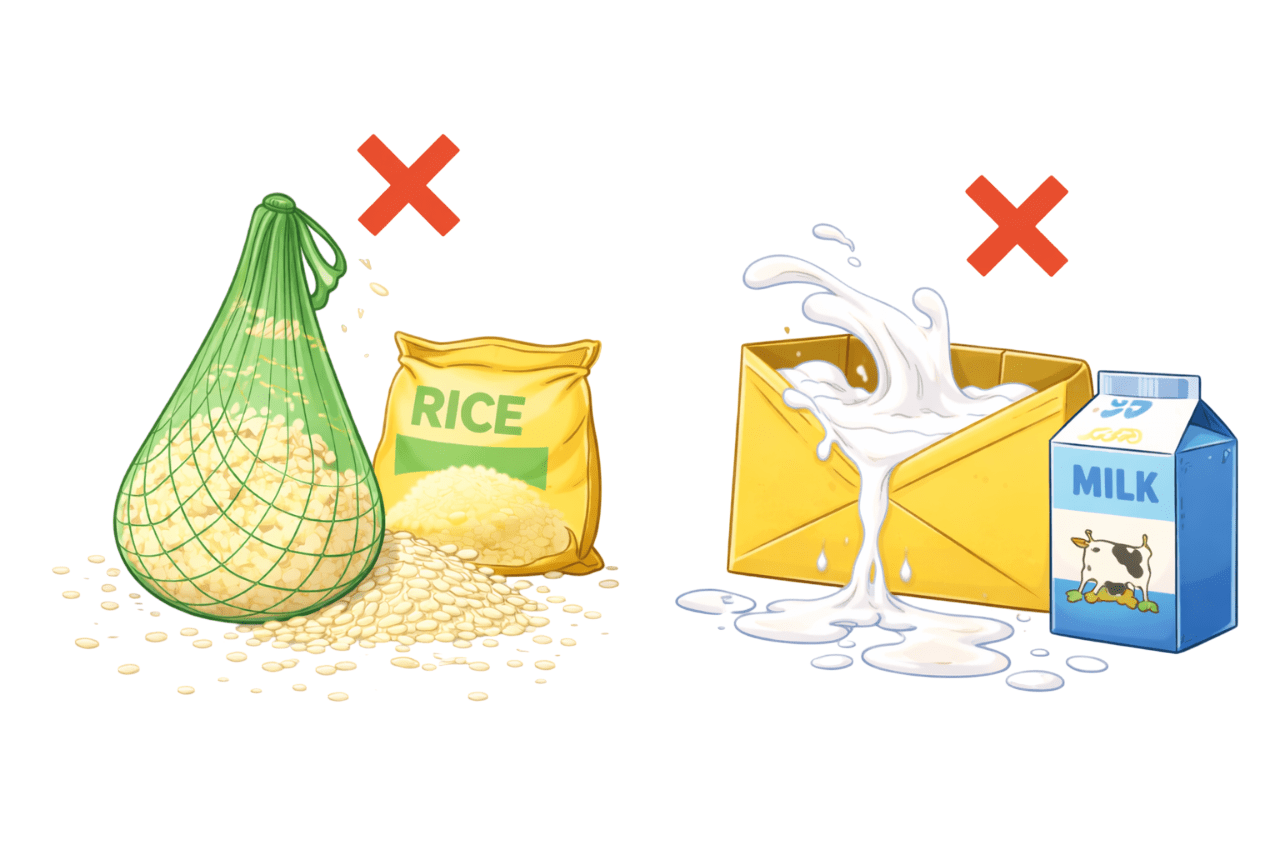
But because the container isn’t meant for what we’re putting inside.”

Now imagine facing this problem every single time you want to store something important.
Java faces the same problem when storing data in memory.


And that’s exactly where data types come in.
Before Java stores any value, it must decide what kind of container to use.”



Data types in Java
Data types in Java tell the program what kind of data a variable can store and how much memory to reserve for it.
Types of Data Types
Primitive
A primitive data type specifies the type of a variable and the kind of values it can hold.

Data types in Java
Data types in Java tell the program what kind of data a variable can store and how much memory to reserve for it.
Types of Data Types
Primitive
Non-primitive
Non-primitive data types in Java store references to objects, not actual values.

Primitive Data Types
byte
|
Stores whole numbers from -128 to 127 |
short
Stores whole numbers from -32,768 to 32,767
|
int |
Stores numbers from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
long
|
Stores numbers from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |

float
|
|
Stores fractional numbers. Sufficient for storing 6 to 7 decimal digits |
|
boolean |
|
Stores true or false values |
|
double |
Stores fractional numbers. Sufficient for storing 15 to 16 decimal digits |
char
|
|
Stores a single character/letter or ASCII values |

Non-Primitive DataTypes
-
String
-
Stores a sequence of characters
-
Example: String name = "Alice";
-

-
Array
-
Stores multiple values of the same data type
-
Example: int[] marks = {90, 85, 80};
-
-
Class
-
Acts as a blueprint for creating objects
-
Defines variables and methods
-



Variables in Java
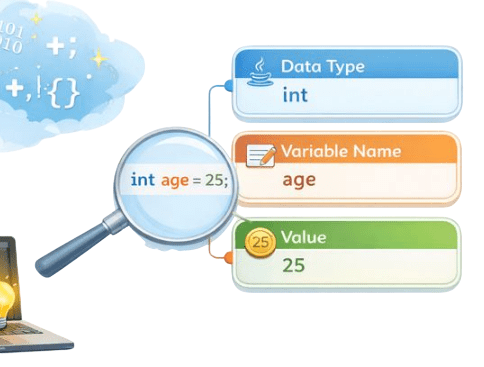

What is a Variable?
In Java, variables are containers used to store data in memory. Variables define how data is stored, accessed, and manipulated.
A variable in Java has three components,
-
Data Type
-
Variable Name
-
Value

Variable Declaration and Initialization
Initialization means giving the variable its first value.
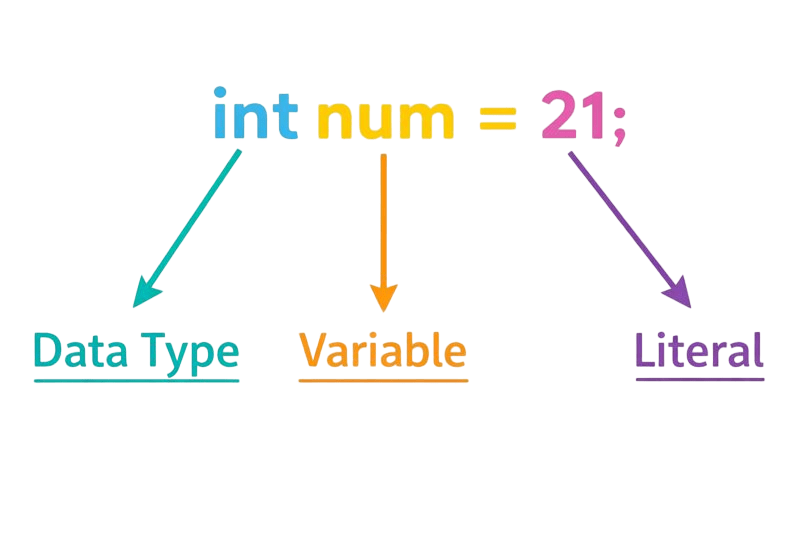
Example : int count = 10;
Declaration means telling the program:
-
what type of data the variable will store
-
what name it will have.
For example : int count;
1.Declaration
2.Initialization
3.Assignment
Assignment means changing or giving a value to an already declared variable.
Example: count = 20;

Rules to Name Java Variables
Start with the right character
A variable name should begin with a letter, an underscore
( _ ), or a dollar sign ($). It cannot start with a number.
Don’t use Java keywords
Words that Java already uses, like int, class, or if, are reserved and cannot be variable names.
Java is case-sensitive
Java treats age and Age as two different variables, so capitalization matters.
RULES




Methods of Printing Variables and Data
Hello World
Age is 20

print()
System.out.print("Hello ");
System.out.println("World");
Prints the value without a new line
OUTPUT:

printf()
Allows for formatted printing using variables
System.out.printf("Age is %d", age);
OUTPUT:
println()
Hello
World

Prints the value with a newline at the end
System.out.println("Hello");
System.out.println("World");
OUTPUT:
Hello
World
println()

Literals in Java
-
Literals in Java are fixed values assigned to variables.
-
They can be numbers, characters, strings, or constants.
-
Literals initialize variables or define constants in code.
Types of Literals
Integer Literals
Floating point
Character
Java String
Boolean
Null

Integer

Represent whole numbers
Character

single character enclosed in single quotes.
Example: int a = 10;
Example:float x = 3.14f;
Float

Represent numbers with decimal points
-
In Java, decimal numbers are double by default.
-
Adding f tells Java the value is a float, not a double.
Example: char ch1 = 'A';

Java String

sequence of characters enclosed in “double quotes”.
Boolean
Represent true or false values
Null

Represents the absence of a value.
Example: boolean isJavaFun = true;
boolean isRaining = false;
Example: String name = null;
Example: String s1 = "Hello";

Summary
5
Literals represent fixed constant values
4
Printing displays variable values
3
Variables store and manage data
2
Java has primitive and non-primitive types
1
Data types define storage and memory

Quiz
Which of the following is a non-primitive data type?
A. int
B. char
C. boolean
D. String


Quiz-Answer
Which of the following is a non-primitive data type?
A. int
B. char
C. boolean
D. String
