Exception Handling Unveild


Types, Hierarchy, and Advantages

Learning Outcome
3
Apply try–catch blocks to handle exceptions in Java programs.
2
Explain the purpose and benefits of Exception Handling.
1
Understand exceptions and their types

OOP (Inheritance): Exceptions are classes; understanding parent–child relationships helps in catching parent exceptions for multiple child errors.
The Call Stack: Errors propagate backward through method calls until they are caught.

Before Starting ,Lets Recall


Imagine you go to an ATM to withdraw money


You insert your card


Enter the PIN
Type the amount.
But suddenly, something goes wrong

Everything seems fine.....

After reading the message, you understand that there is a server problem with the ATM,
So You cancel the transaction, walk out, and visit another ATM.”



The ATM displays an error message:
‘Server Not Responding’.

Now think for a moment:
If the ATM simply crashed or shut down, you would feel confused and frustrated because: You don’t know what actually went wrong
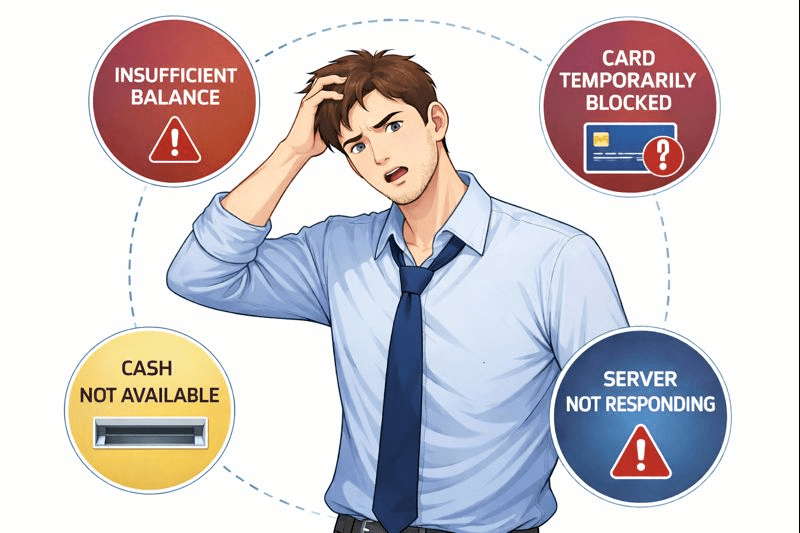

Instead, the ATM displays clear error messages, such as:
“Insufficient Balance”
“Server Not Responding”
“Cash Not Available”



Because of these messages, you understand what went wrong and can decide what to do next—try another ATM, wait, or check your balance.


So just like an ATM needs a system to handle problems gracefully,
Java provides try, catch, and finally blocks to handle errors properly.
That system is called: Exception Handling in Java.

What is an Exception in Java?
An exception is an event that occurs during program execution and causes the program to behave abnormally.
Defination

Common Examples

Transition from Analogy to Technical Concept(Slide 5)

Transition from Analogy to Technical Concept(Slide 5)

Transition from Analogy to Technical Concept(Slide 5)

Transition from Analogy to Technical Concept(Slide 5)

Transition from Analogy to Technical Concept(Slide 5)

Core Concepts (Slide 6)

Core Concepts (Slide 7)

Core Concepts (.....Slide N-3)

Summary
4
Compile-time = syntax errors, Run-time = logic/data errors.
3
Types: Checked, Unchecked , and Errors
2
Exception Handling prevents crashes and maintains program flow.
1
An Exception is an error during program execution

Quiz
Which of the following is a checked
exception in Java?
A. ArithmeticException
B. NullPointerException
C. IOExceptio
D. ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException


Which of the following is a checked
exception in Java?
A. ArithmeticException
B. NullPointerException
C. IOExceptio
D. ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException

Quiz-Answer