

React Context & Reducers
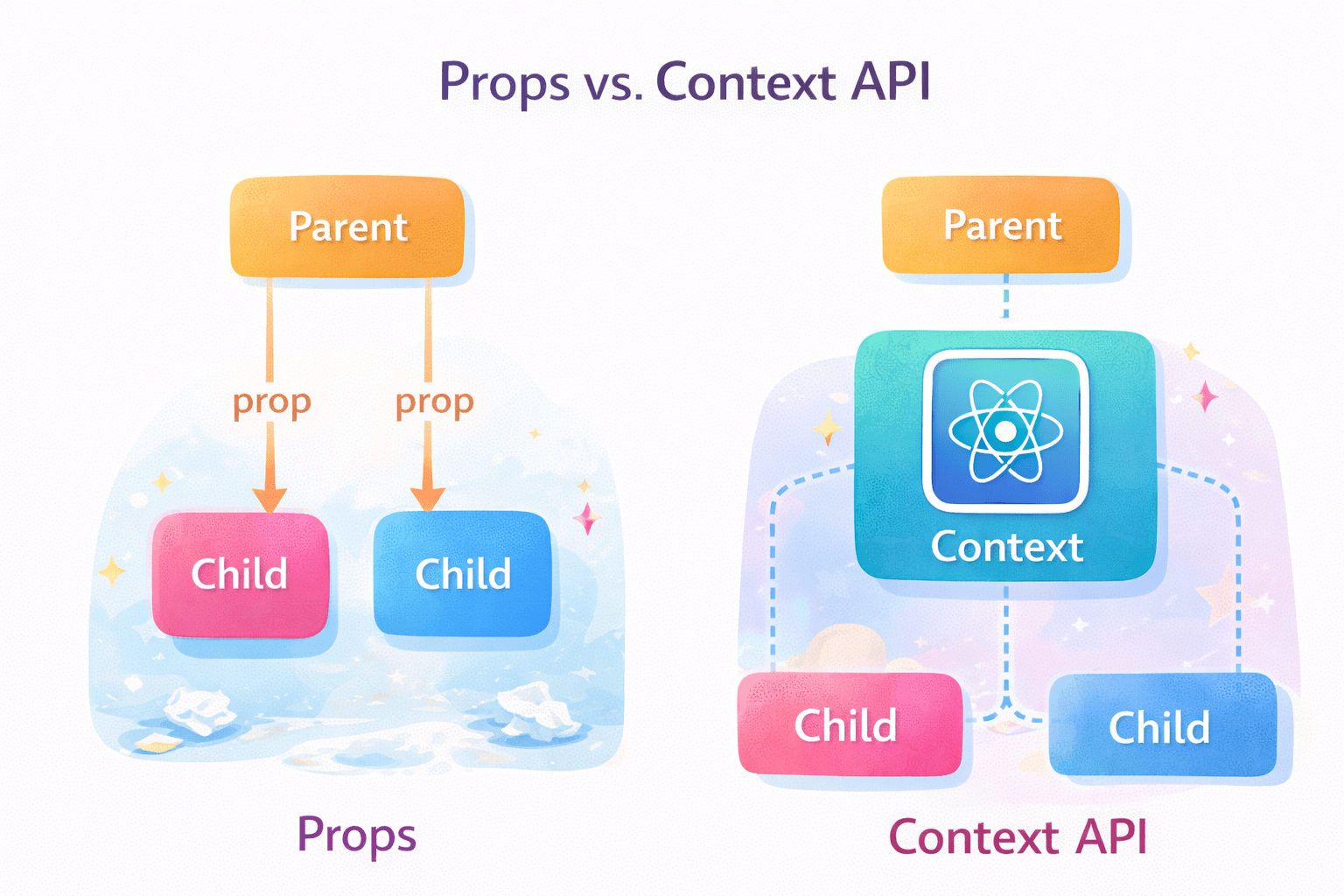
Props vs. Context API

What you’ll learn in this session
4
Using Context API with useContext
3
Introduction to Context API
2
Problems with Props Drilling
1
What is Props Drilling

Before learning Context API, let’s quickly recall Props
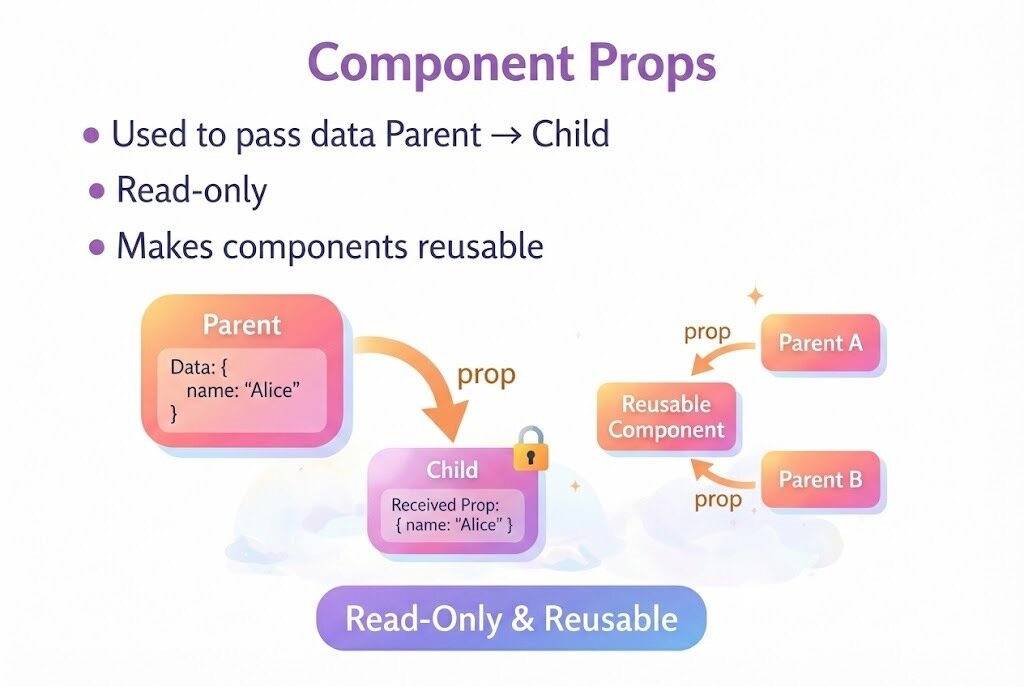
Props
Used to pass data Parent → Child
Read-only
Makes components reusable
function Child({ name }) {
return <h3>{name}</h3>;
}
<Child name="React" />



Water Tank System Analogy

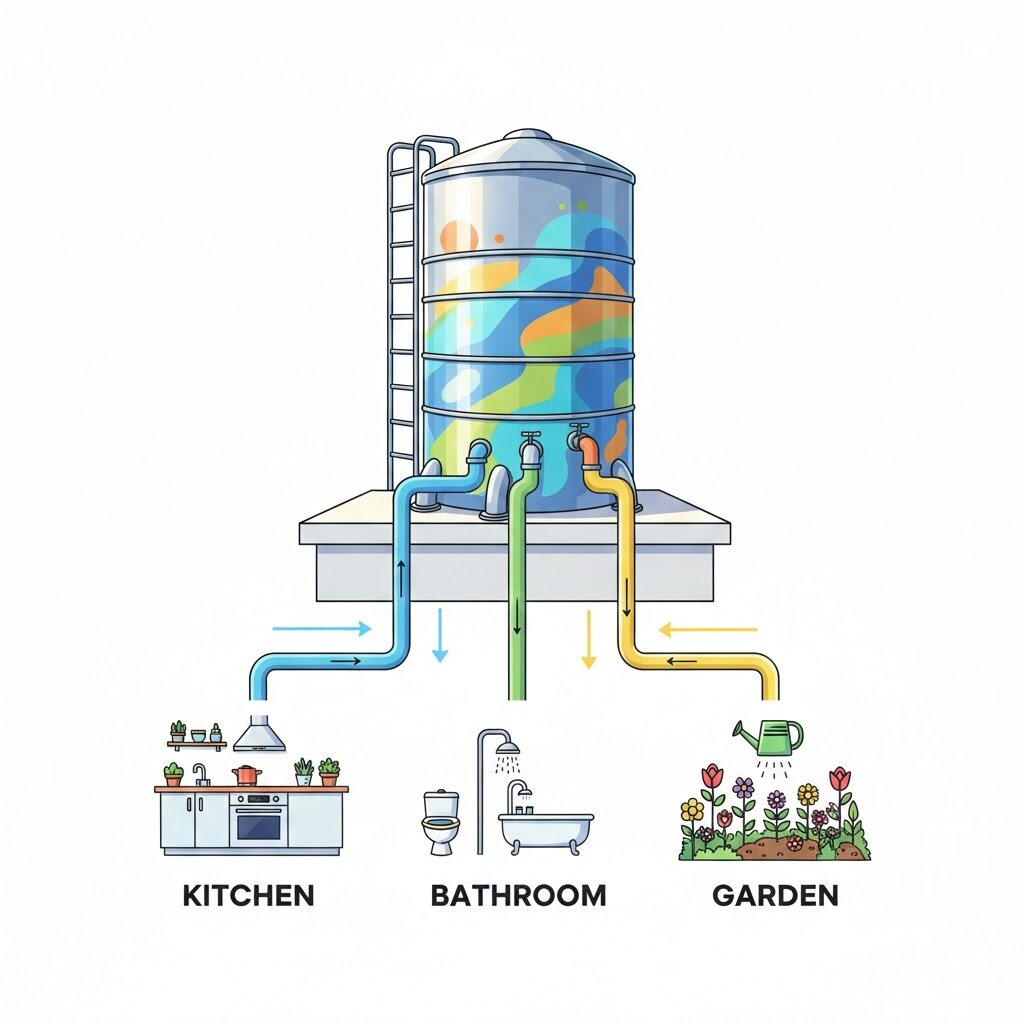
One tank supplies water to:
Imagine a water tank on the roof

Water Tank System Analogy
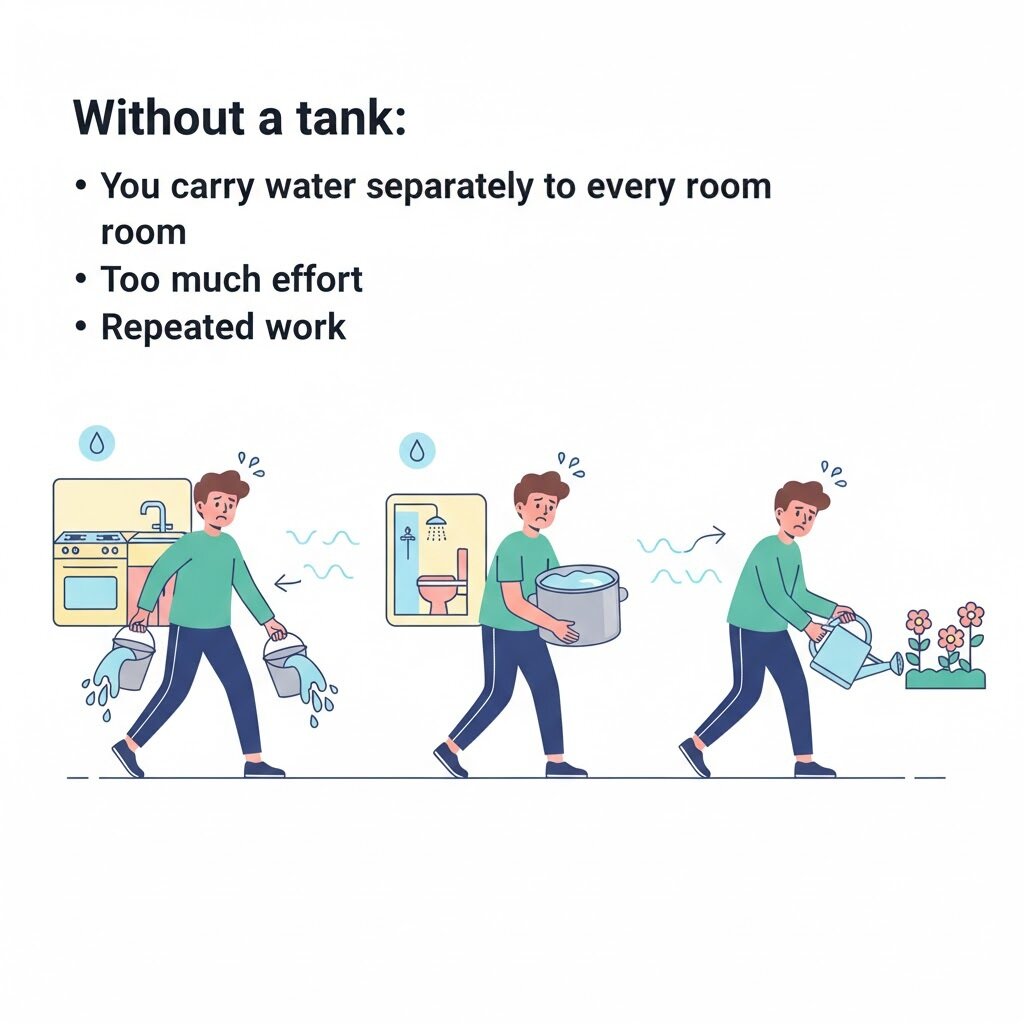
Without a tank:
You carry water separately to every room
Too much effort
Repeated work
In React:
Context = water tank
Components = rooms
Data flows directly where needed

WHY not just use props and state?
With Props:
This problem is called Props Drilling
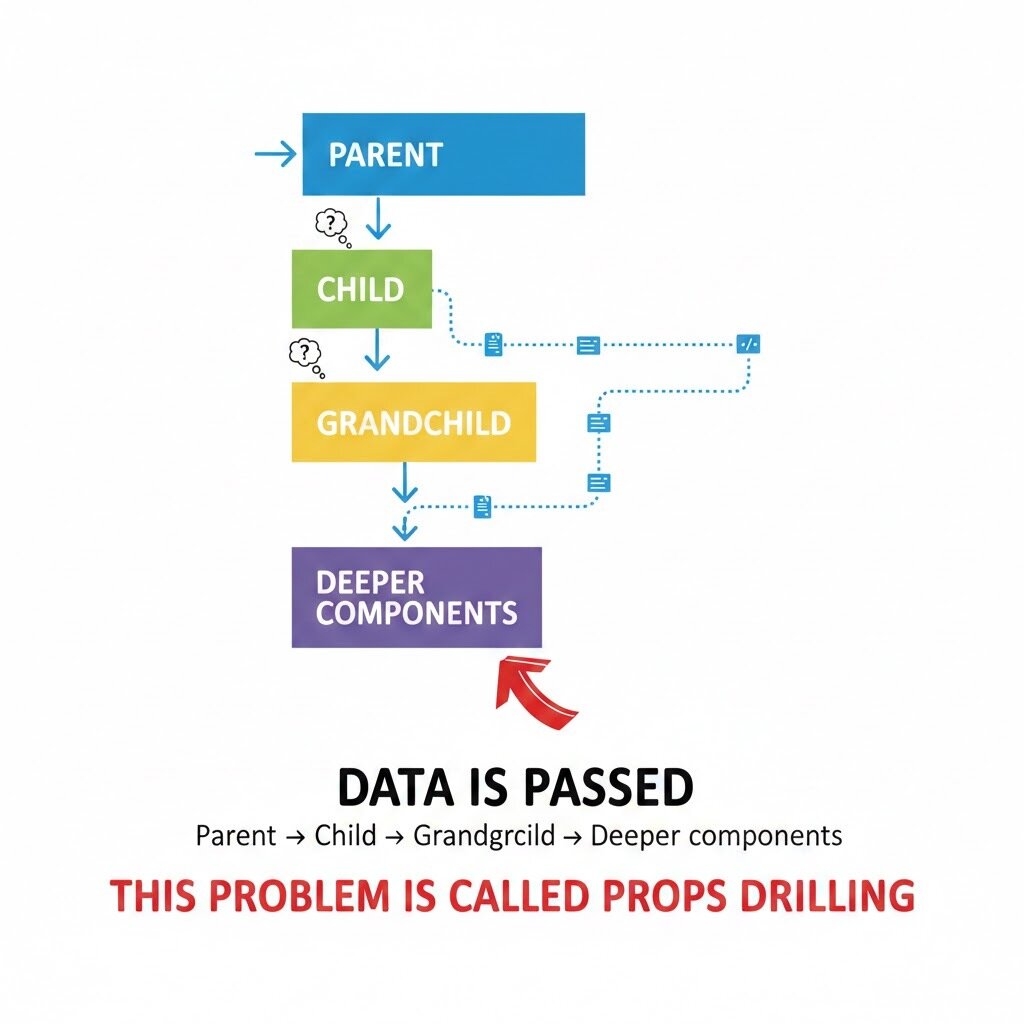
Data is passed
Even when middle components don’t need the data

WHY not just use props and state?
Just Like Without a Water Tank

You carry water manually
Roof → Floor → Room → Bathroom
Too much effort and repeated work
React solves this using :
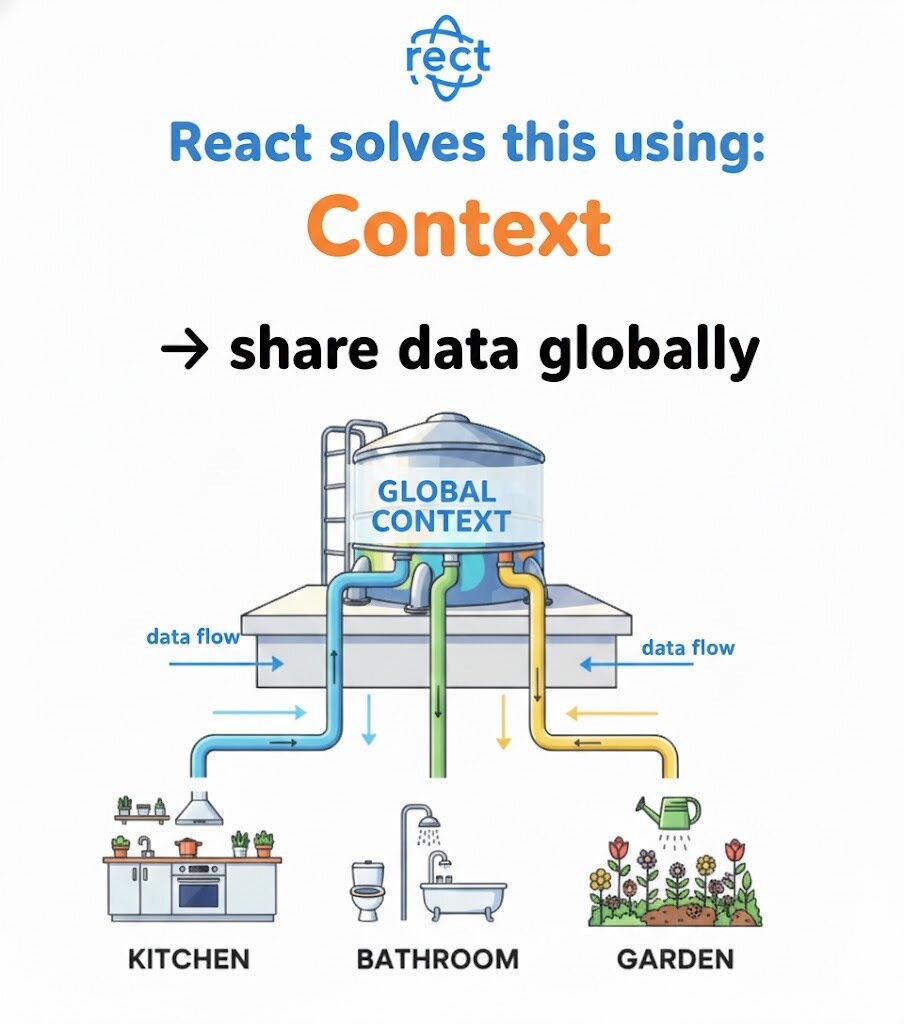
Context API → share data globally
Every level must pass the water forward
Even rooms that don’t need water must carry it

What is Context API?
The Context API is a feature in React that lets you share data across components without passing props down manually at every level
Think of it as a global data channel for your React app

Component A
Component B
Component C

Creating Context & Provider
Steps:
Create context

import { createContext } from "react";
export const AppContext = createContext();
function AppProvider({ children }) {
const user = "Rohit";
return (
<AppContext.Provider value={user}>
{children}
</AppContext.Provider>
);
}Wrap app with Provider

<AppProvider>
<App />
</AppProvider>Purpose:
Makes data available to child components

Accessing Context Values
Ways to access
useContext() hook
Syntax :
import { useContext } from "react";
import { AppContext } from "./AppContext";
function Profile() {
const user = useContext(AppContext);
return <h3>{user}</h3>;
}Why useContext?
-
Clean
-
Easy
-
No wrapper components
Any child can directly consume shared data.


Summary
4
Improves code readability and maintainability
3
useContext simplifies data usage
2
Context API enables global data access
1
Props drilling complicates state sharing

Quiz
Which hook is used to access context?
A. useEffect
B. useState
C. useContext
D. useMem


Quiz-Answer
Which hook is used to access context?
A. useEffect
B. useState
C. useContext
D. useMem
