Topic Name

Subtopic Name



Learning Outcome
3
Explain defect flow from detection to closure
2
Identify different defect states
1
Understand what Defect Life Cycle

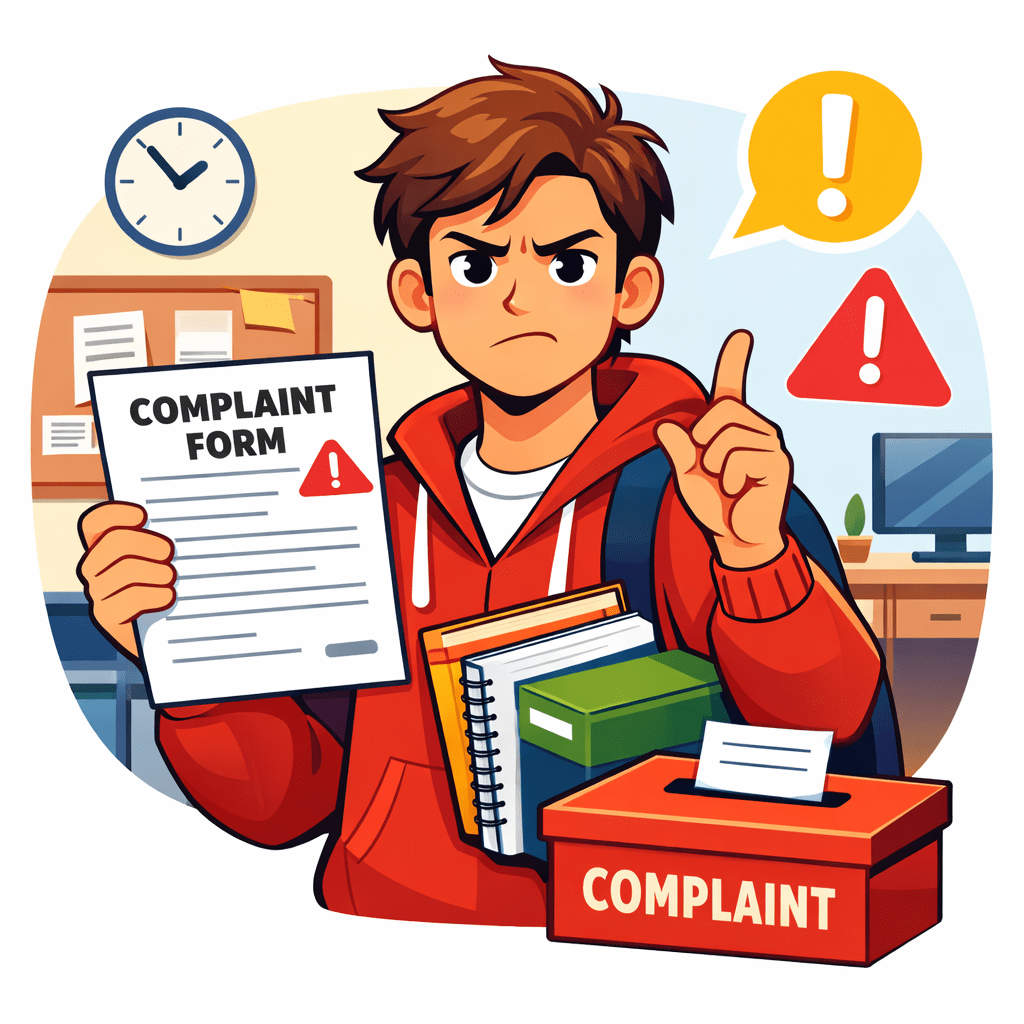
Imagine a student raises a complaint to college administration
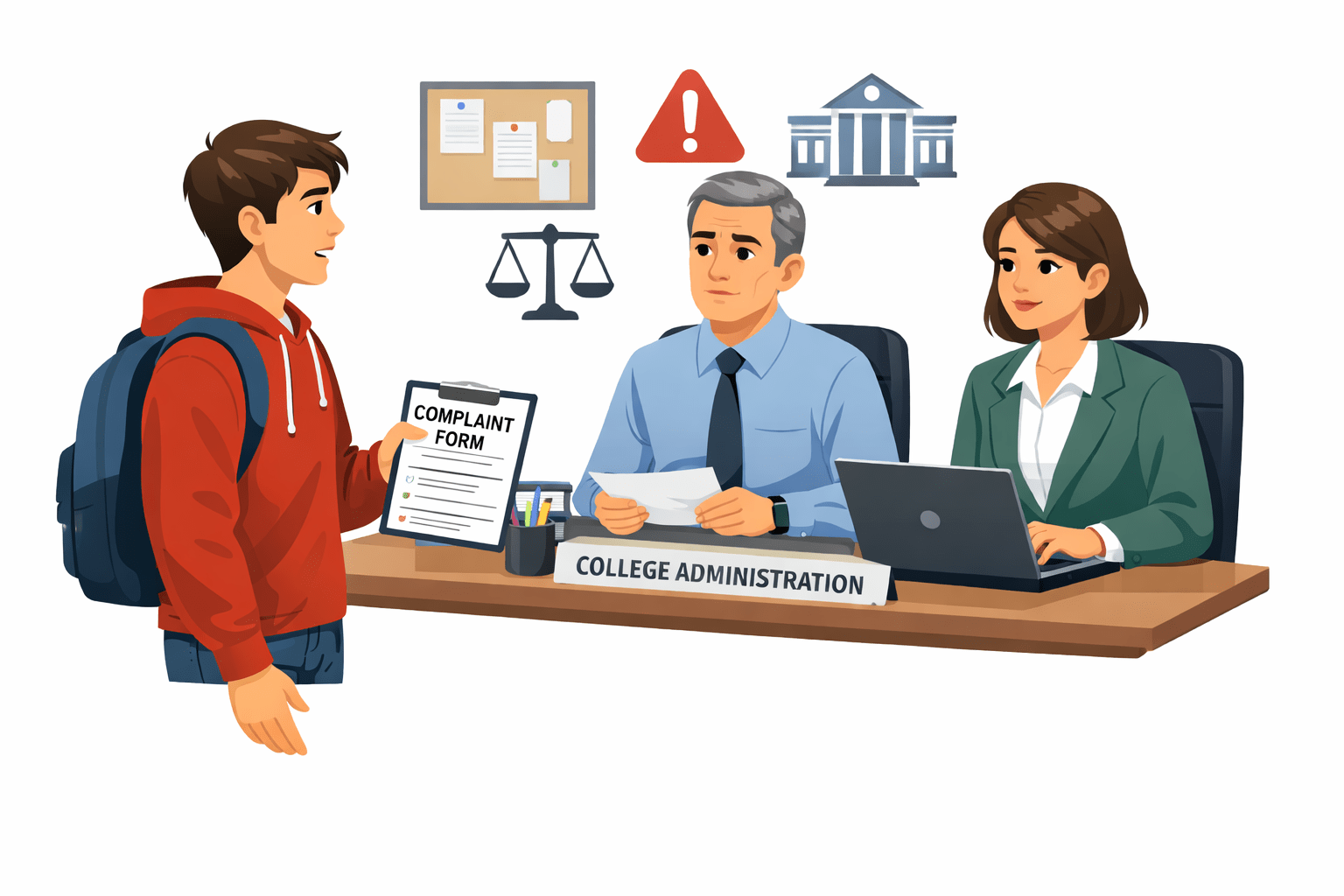

Transition from Analogy to Technical Concept(Slide 5)
Complaint raised
Complaint reviewed
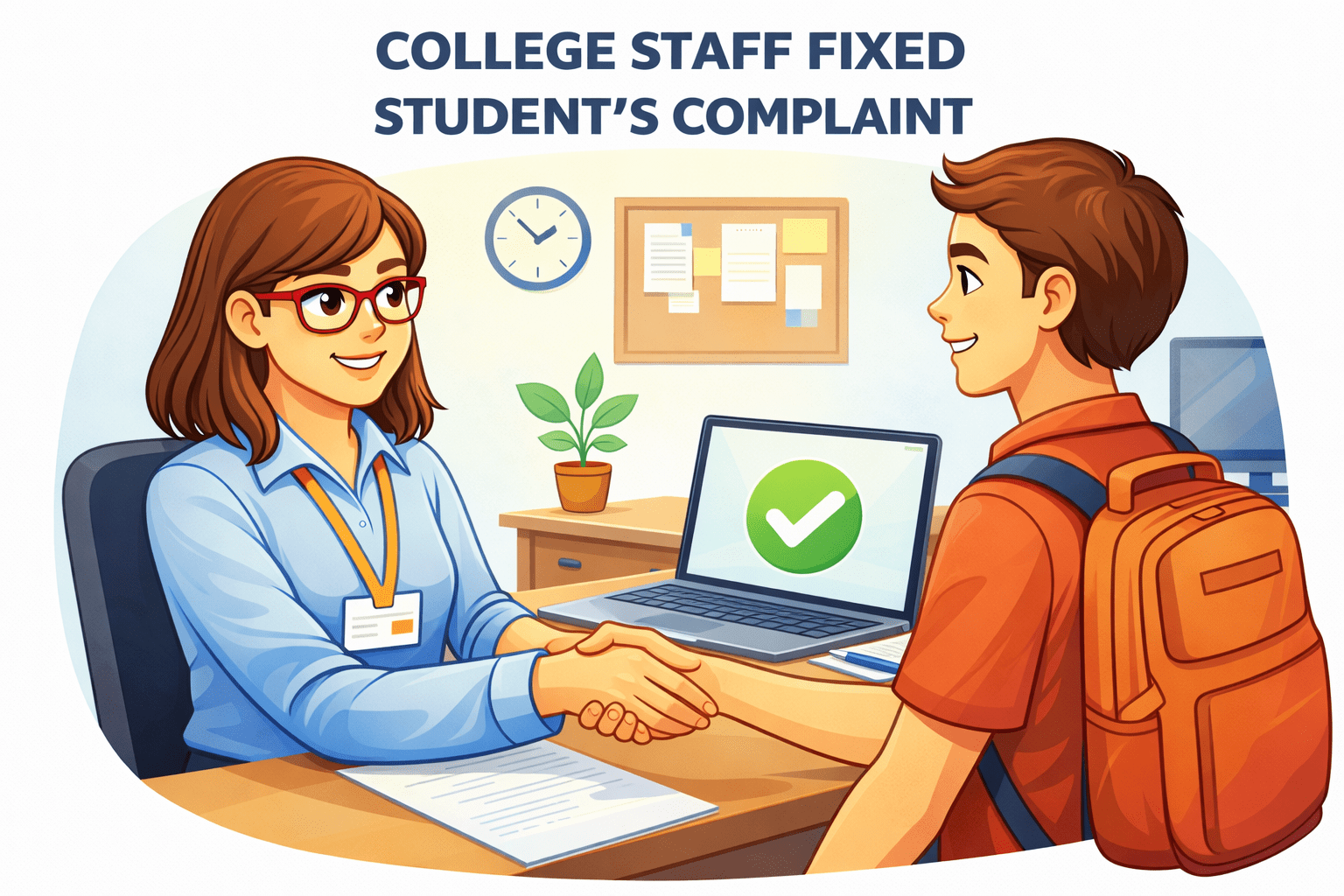
Complaint fixed
Verification done




Before we start....

What is a defect / bug?

What is a defect / bug?
Why do we report defects?


Who fixes defects

What are the causes of defects?

Why do we need a Defect Life Cycle?


To track defect status clearly
To avoid missing or duplicate bugs
To improve communication between tester & developer
To ensure quality software delivery

Bug Lifecycle









New
Open
Duplicate rejected deffered not a bug
ReOpen
Fixed
Pending Retest
Retest
Closed
Verified
Assigned

Defect Life Cycle (Main Flow)
1. New
- Tester finds a defect during testing
- Defect is logged in the defect tracking tool
- Initial status of every bug
Bug is identified but not yet reviewed
2. Assigned
-
Test lead or manager assigns the defect to a developer
- Responsibility is given to fix the defect
Bug ownership is decided
3. Open
-
Developer accepts the defect
-
Developer analyzes the issue and starts working on it
Bug is under investigation
4. Duplicate / Rejected / Deferred / Not a Bug
After analysis, developer may mark the bug as:
- Not a Bug – Working as per requirement
-
Duplicate – Bug already exists in system
-
Rejected – Bug is invalid
-
Deferred – Fix postponed to future release
Bug will not move forward in the cycle

5. Pending Retest
-
Defect is sent back to tester
-
Tester prepares test environment for retesting
Waiting for tester action
-
Developer fixes the defect
-
Code changes are completed
-
Bug status updated to Fixed
4. Fixed
Fix is done, but not yet verified

-
Tester retests the defect
-
Checks whether the issue is resolved
7. Retest
Verification of fix is in progress

8. Reopened
- If issue is not fixed properly, tester reopens the defect
- Defect goes back to Open state
Bug re-enters the life cycle

-
Tester confirms that the defect is fixed successfully
-
No issue found during retesting.
9. Verified
Fix is approved by tester
10. Closed
-
Defect is finally closed
-
No further action required
Bug life cycle ends


Roles & Responsibilities
Find & log defects
Retest defects
Developer
Tester
Close defects
Fix defects
Analyze defects
Update defect status





Tester retests → Closed
Tester reports → New
Developer fixes → Fixed
Manager assigns → Assigned
Defect Life Cycle – Example
Login Button Not Working

Summary
3
Defect Life Cycle ensures controlled defect management
2
Tester and developer both are involved
1
Defect goes through multiple states

Quiz
In which stage does the developer start working on the defect?
A. Assigned
B. Open
C. Retest
D. Verified


Quiz
In which stage does the developer start working on the defect?
A. Assigned
B. Open
C. Retest
D. Verified
