String Mastery


Class Hierarchy, Buffer, Builder, and Methods

Learning Outcome
4
Use StringBuilder/StringBuffer methods for editing strings.
3
Apply common String methods.
2
Learn the difference between StringBuilder and StringBuffer.
1
Understand String, StringBuilder, and StringBuffer hierarchy.

Hierarchy of String Class
java.lang.object
String
String
Buffer
String
Builder
The String class is a core component of the java.lang package.
Extends Object
String directly inherits from Object
Implements CharSequence for character handling
Implements Interfaces
Sibling Relationship
String, StringBuffer, and StringBuilder are siblings




What is StringBuffer?
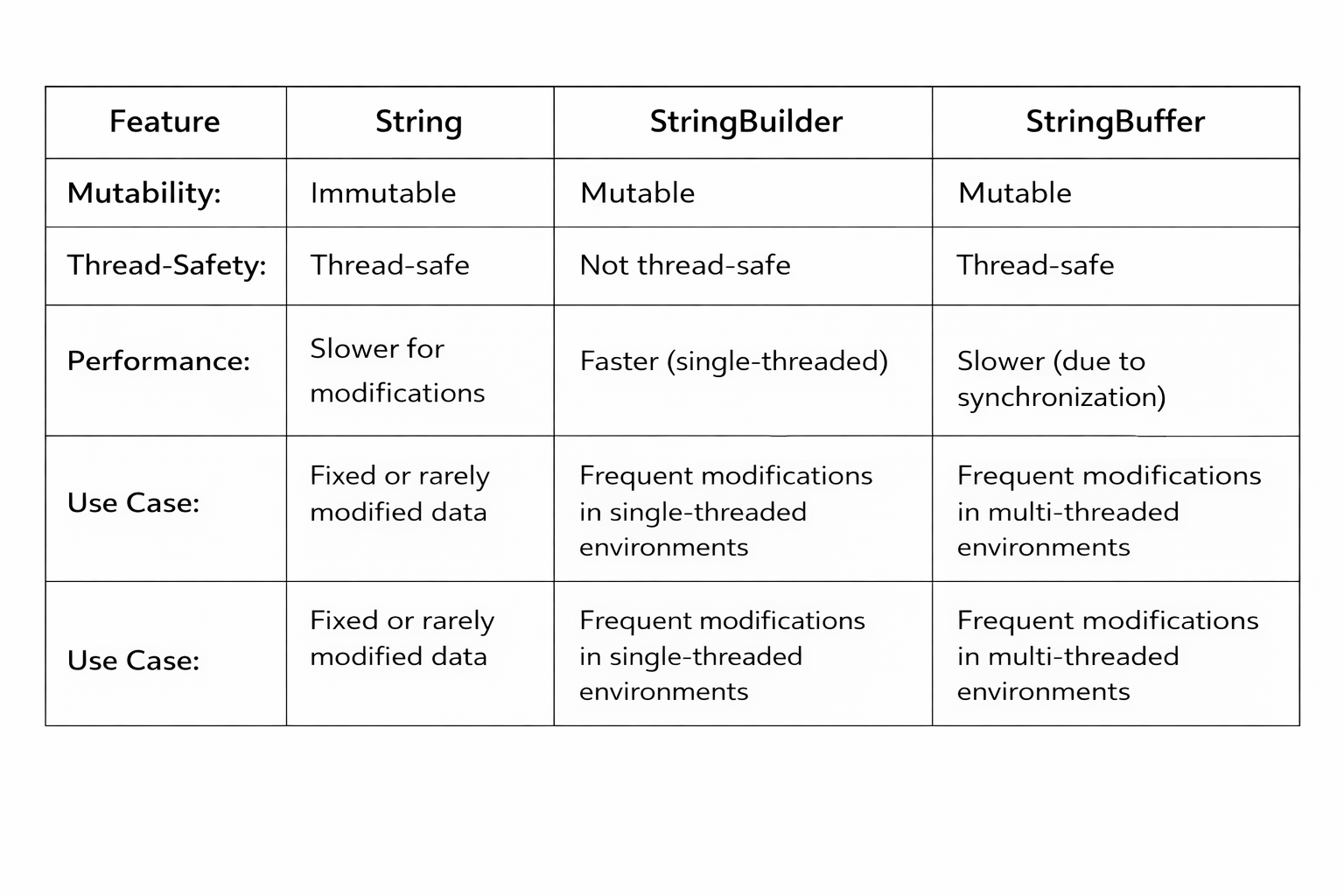
StringBuffer is a mutable sequence of characters. Unlike String, it can be modified. It provides thread-safety through synchronized methods.
Key Features
Thread-Safe (Synchronized)
All methods are synchronized, making it suitable for multi-threaded applications.

Performance Trade-off
Synchronization introduces a slight performance overhead compared to StringBuilder.


public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a StringBuilder object
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
// Modifying content without new object
sb.append(" Programming");
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
StringBuffer Example

What is StringBuilder?
StringBuilder is a mutable sequence of characters. Unlike StringBuffer, it is not synchronized, making it faster & efficient for single-threaded operations.
Key Features
Mutability
Methods like append(), insert(), or delete() modify the object in-place.
Not Thread-Safe
StringBuilder does not synchronize its methods, making it unsuitable for multi-threaded environments.



StringBuilder Example
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a StringBuilder object
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Java");
// Modifying content without new object
sb.append(" Programming");
System.out.println(sb);
}
}


String
StringBuilder

StringBuffer

String Builder/Buffer Methods

append(String)



insert(int, String)
replace(int, int, String)
delete(int, int)




reverse()
capacity()
ensureCapacity(int)
setLength()
Note: "The length(), charAt(), substring(), and indexOf() String methods are also used by StringBuffer and StringBuilder.”


public class StringBuilderDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder("Hello");
sb.append("World");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.insert(5," ");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.replace(0,5,"Hi");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.reverse();
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
Example

Summary
3
Mutable and thread-safe, best for multi-threaded environments.
2
StringBuilder: Mutable, fast, but not thread-safe
1
String: Immutable, thread-safe, best for fixed or changed data.

Quiz
Which method is used to add text at the end of a StringBuilder object?
A. add()
B. append()
C. insert()
D. concat()


Which method is used to add text at the end of a StringBuilder object?
A. add()
B. append()
C. insert()
D. concat()
Quiz-Answer
