SQL LaunchPad


Juggling Data Types

Learning Outcome
4
Ensure data integrity and consistency using correct datatypes.
3
Choose the appropriate datatype for different kinds of data.
2
Identify different MySQL datatypes and their categories.
1
Understand datatypes and why they are needed in databases.

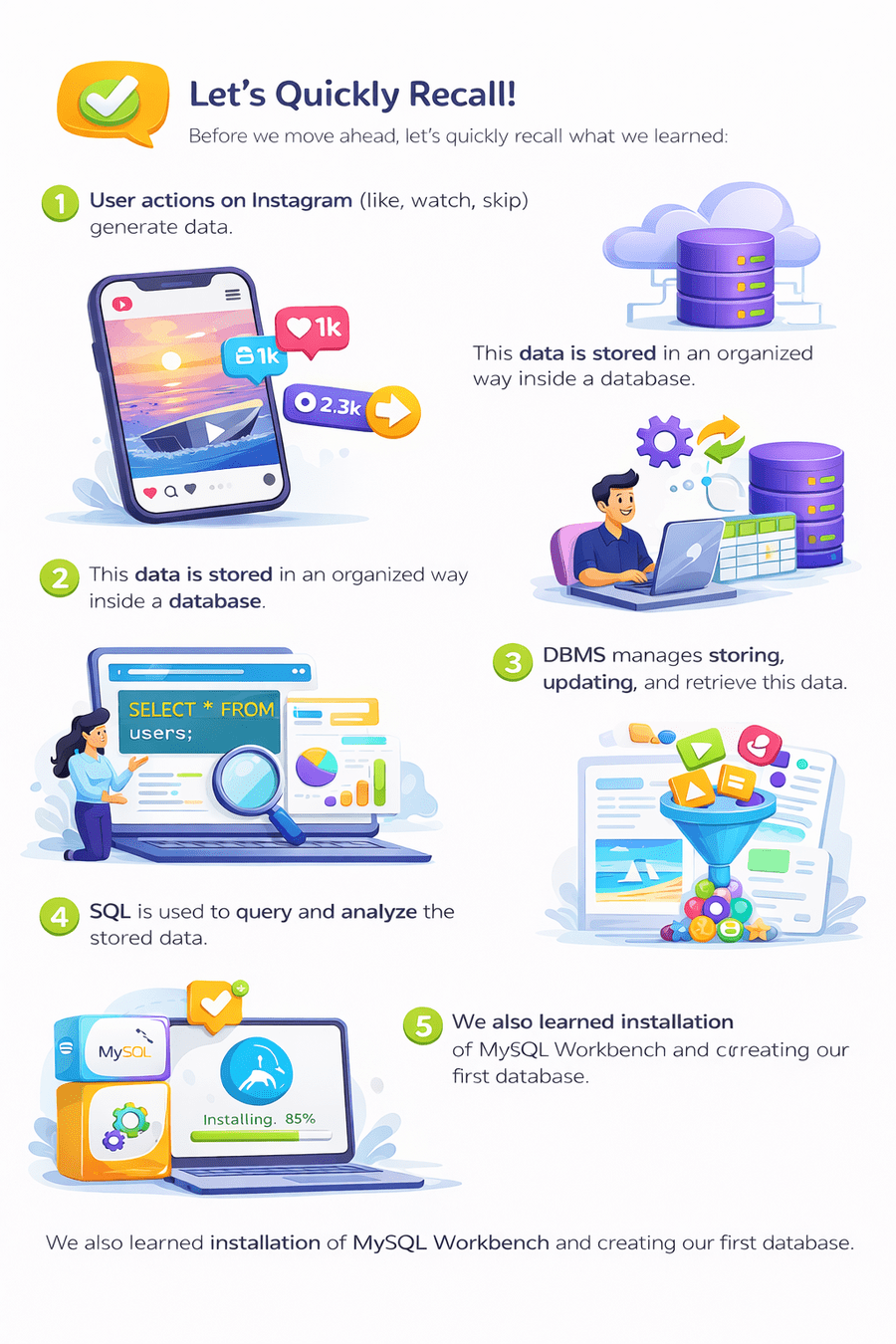
Before we move ahead, let’s quickly recall what we learned:
User actions on Instagram (like, watch, skip) generate data
1
This data is stored in an organized way inside a database

2
3
DBMS manages storing, updating, and retrieving this data


SQL is used to query and analyze the stored data

4
This data is stored in an organized way inside a database

5
6
We also learned installation of MySQL Workbench and creating our first database



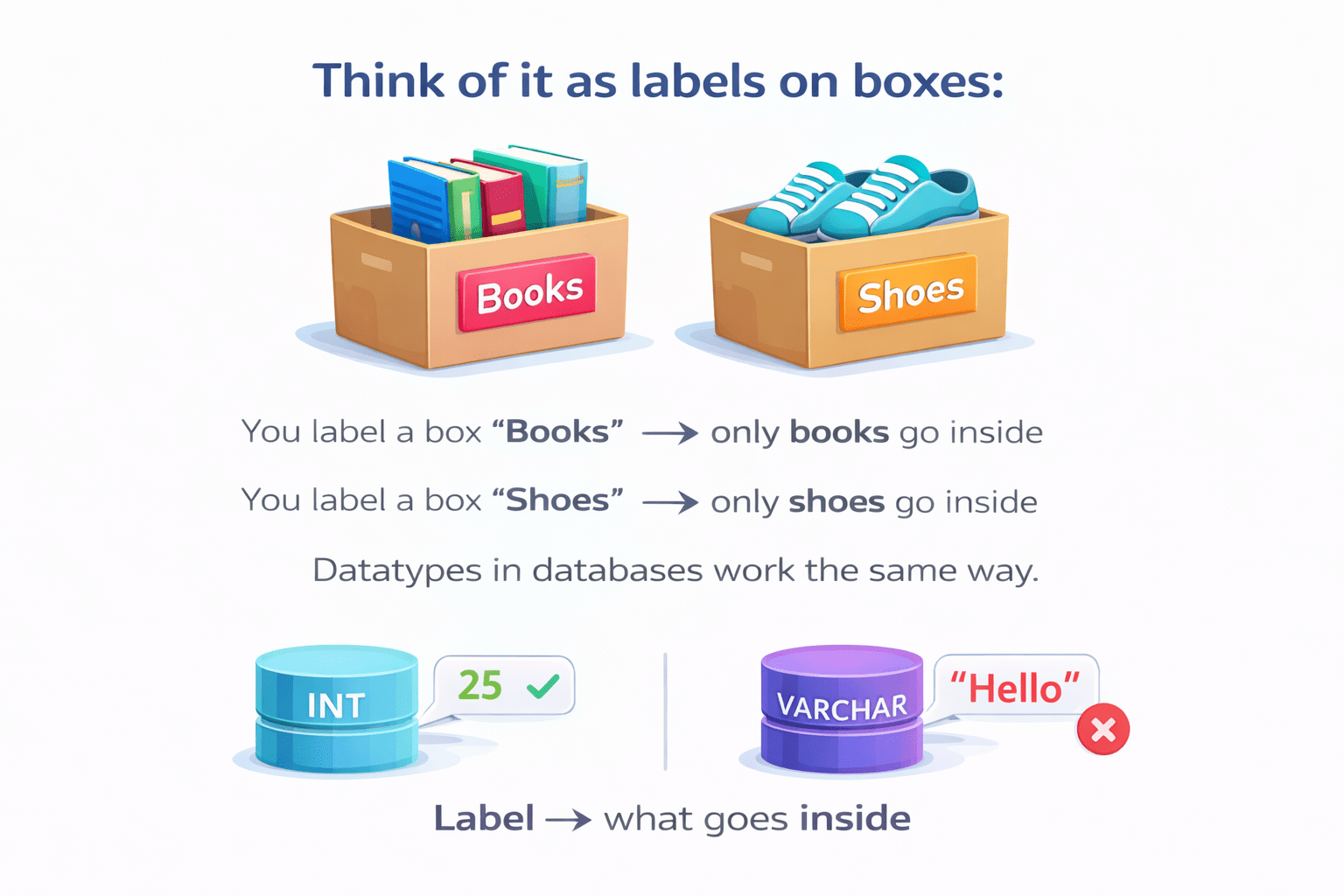
Think Datatypes as labels on boxes:
You label a box “Books”
only books go inside
You label a box “Shoes”
only shoes go inside
Datatypes in databases work the same way


Label → What goes inside

Now Think of a Instagram profile database:
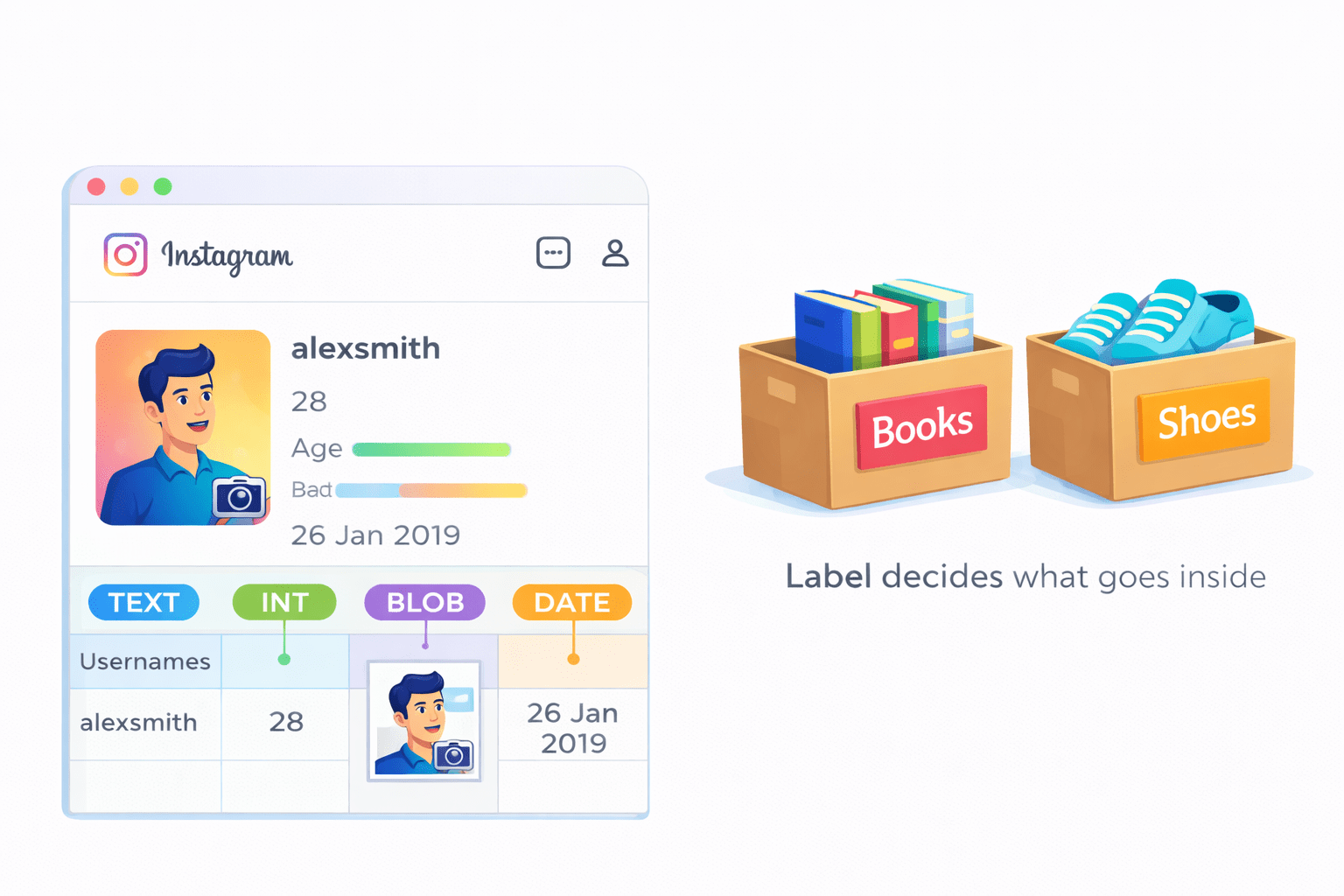
- Usernames → text
-
Age → numbers
-
Profile picture → file → BLOB
-
Account creation date → DATE

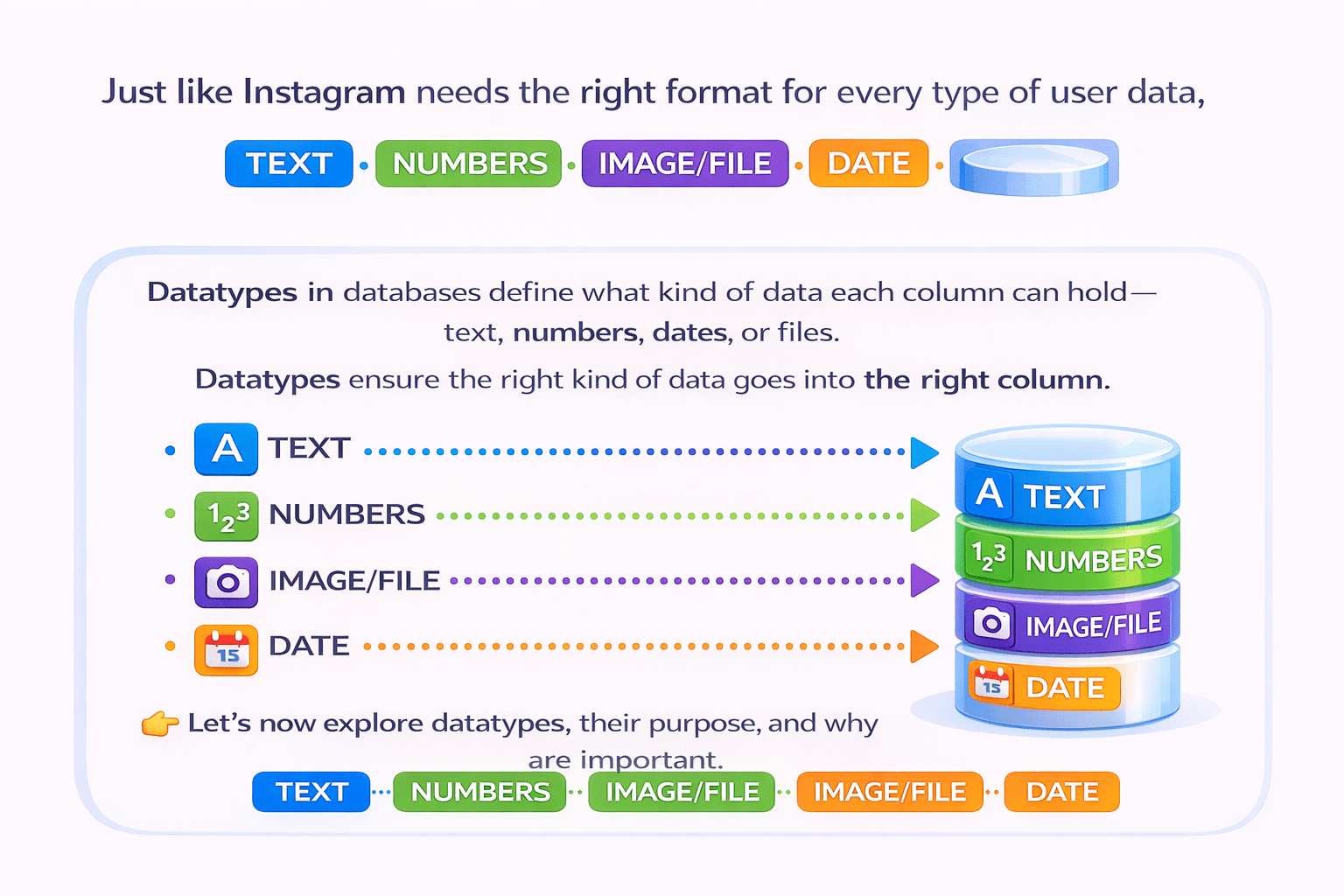
Just like Instagram needs the right format for every type of user data
Datatypes in databases define what kind of data each column can hold— text, numbers, dates, or files
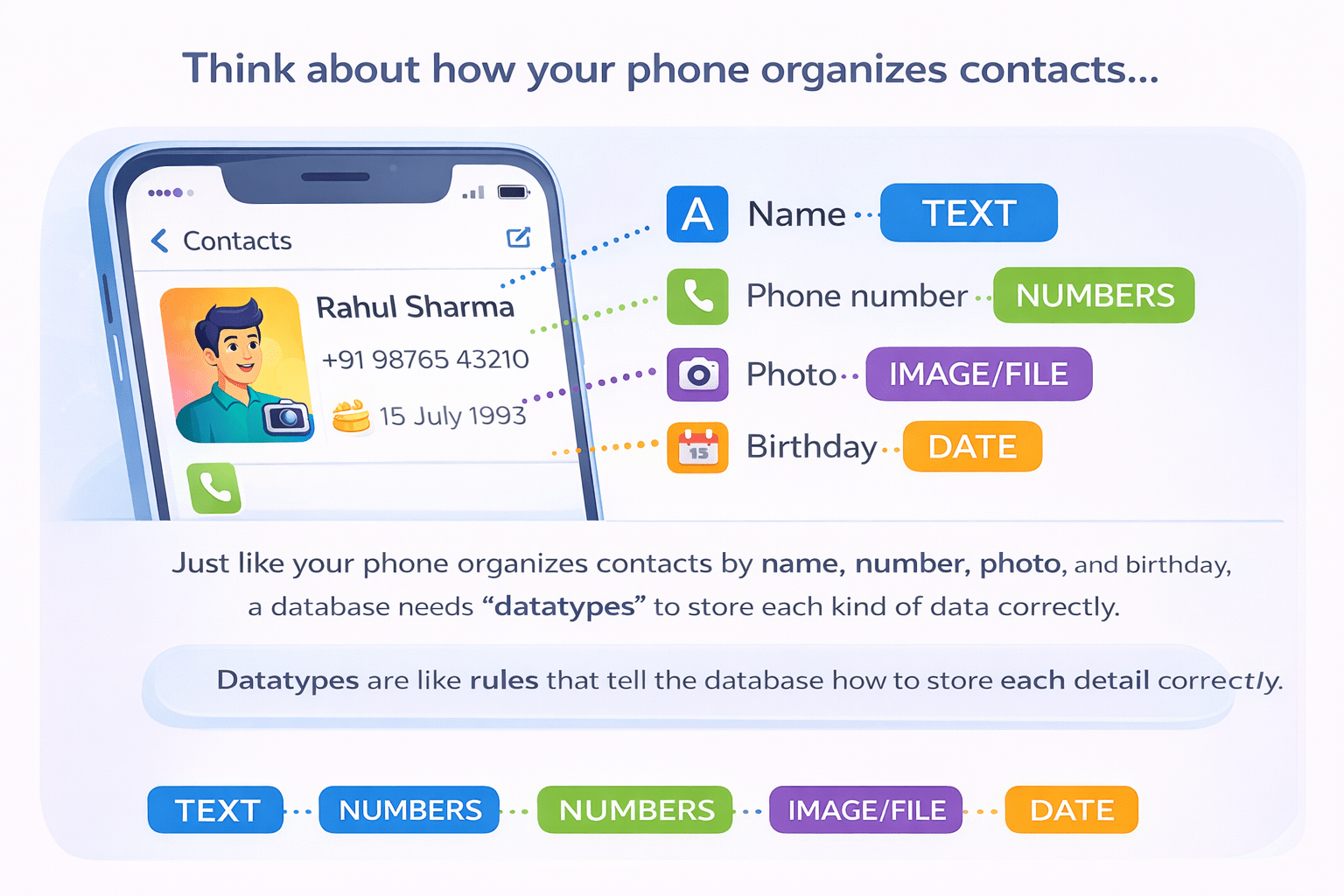

Now Think how your phone organizes contacts...

Just like your phone organizes contacts by name, number, photo, and birthday, a database needs “datatypes” to store each kind of data correctly.
Datatypes are like rules that tell the database how to store each detail correctly
Let’s now explore datatypes, their purpose, and why they are important.

What are Datatypes?
A datatype in a database defines the type of data a column can store.
It ensures that each column holds the right kind of data.
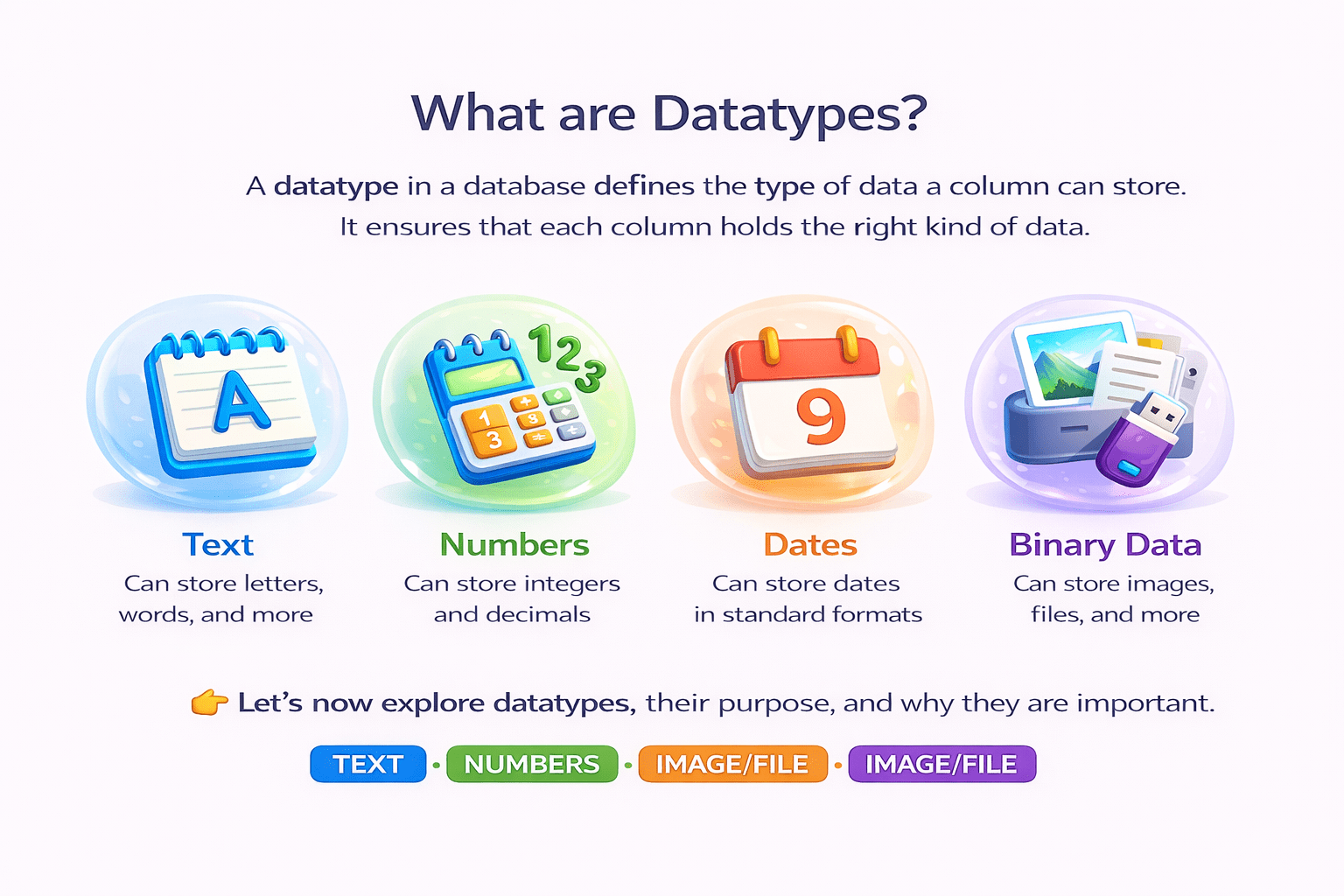
Text
can store letters, words, and more

Numbers
can store integers and decimals

Dates
can store dates in standard formagts

Binary data
can store images, files, and more

Purpose of Datatypes
- Datatypes serve several key purposes:

1. Data Integrity
-
Prevents storing the wrong kind of data in a column
- Example: Age column should only have numbers, not text

2. Efficient Storage
-
Databases allocate memory based on datatype
-
Example: INT takes less space than VARCHAR for numbers


3. Faster Operations
- Sorting, searching, and calculations are faster with proper datatypes.

4. Validation & Error Prevention
- Helps catch mistakes at the database level
- Example: Trying to insert a string into a numeric column will throw an error

5. Consistent Data Management
- Ensures uniformity across the database, making queries and reports accurate

Common MySQL Datatypes
1. Numeric Datatypes
| Datatype | Size / Storage | Description / Example |
|---|---|---|
| TINYINT | 1 byte | Small integers (-128 to 127) — e.g., user age |
| SMALLINT | 2 bytes | Medium-range integers (-32,768 to 32,767) |
| INT / INTEGER | 4 bytes | Standard integers (-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647) — e.g., likes count |
| BIGINT | 8 bytes | Large integers — e.g., user ID in a huge system |
| DECIMAL(p,s) | Variable (depends on precision) | Exact numbers with decimals — e.g., price 99.99 |

| Datatype | Size / Storage | Description / Example |
|---|---|---|
| FLOAT | 4 bytes | Approximate decimal numbers — e.g., ratings 4.5 |
| DOUBLE / REAL | 8 bytes | Larger approximate decimals — e.g., scientific data |

2. Text / String Datatypes
| Datatype | Max Size | Description / Example |
|---|---|---|
| CHAR(n) | n characters (fixed) | Fixed-length strings — e.g., country code “IN” |
| VARCHAR(n) | n characters (variable) | Variable-length strings — e.g., username, email |
| TEXT | Up to 65,535 chars | Long text — e.g., post comments, descriptions |
| MEDIUMTEXT | Up to 16,777,215 chars | Bigger text storage — e.g., blog content |
| LONGTEXT | Up to 4,294,967,295 chars | Very large text — e.g., entire articles |
Tip: Use VARCHAR for normal text, TEXT for long descriptions.


3. Date / Time Datatypes
| Datatype | Storage | Description / Example |
|---|---|---|
| DATE | 3 bytes | Stores date in YYYY-MM-DD — e.g., 2026-01-03 |
| DATETIME | 8 bytes | Stores date and time — e.g., 2026-01-03 15:30:00 |
| TIMESTAMP | 4 bytes | Auto-updates with current time — e.g., last login |
| TIME | 3 bytes | Time only — e.g., 15:30:00 |
| YEAR | 1 byte | Stores year only — e.g., 2026 |

4. Binary / Large Object Datatypes
| Datatype | Max Size | Description / Example |
|---|---|---|
| BLOB | 65,535 bytes | Binary large objects — e.g., images, videos |
| MEDIUMBLOB | 16,777,215 bytes | Bigger binary objects — e.g., larger videos |
| LONGBLOB | 4,294,967,295 bytes | Very large files — e.g., full-length movies |

Summary
5
Main categories: Numeric, Text, Date/Time, Binary.
4
Ensure consistent and reliable data management.
3
Help maintain data integrity by preventing wrong data.
2
They ensure correct and organized data storage.
1
Datatypes define the type of data a column can store.

Quiz
What is the main purpose of using datatypes in a database?
A. To increase table size
B. To store data randomly
C. To ensure correct type of data is stored
D. To delete unwanted data


Quiz-Answer
C. To ensure correct type of data is stored

A. To increase table size
What is the main purpose of using datatypes in a database?
B. To store data randomly
D. To delete unwanted data