Direct Connectivity in Power BI

Understanding Data Gateways


Learning Outcome
6
Monitor gateway health and troubleshoot failures
5
Manage data sources and access permissions
4
Install and configure a gateway
3
Differentiate between gateway types and modes
2
Understand how gateways work conceptually
1
Explain what a Data Gateway is and why it is required

Power BI Service works in the cloud


Reports are refreshed from datasets


Some data sources are on-premises


Scheduled refresh requires valid connectivity


Students already know:

Imagine Your report is ready.
Your visuals are perfect.
The cloud asks for the data.

The data refuses to leave

But the data lives here:
-
Inside a company server
-
Behind a firewall
- On a local machine

Now imagine a trusted messenger.
- It stays inside the building.
- It listens when the cloud asks.
- It sends data out, never lets the cloud come in.
- Secure.


- Controlled.
- Invisible.

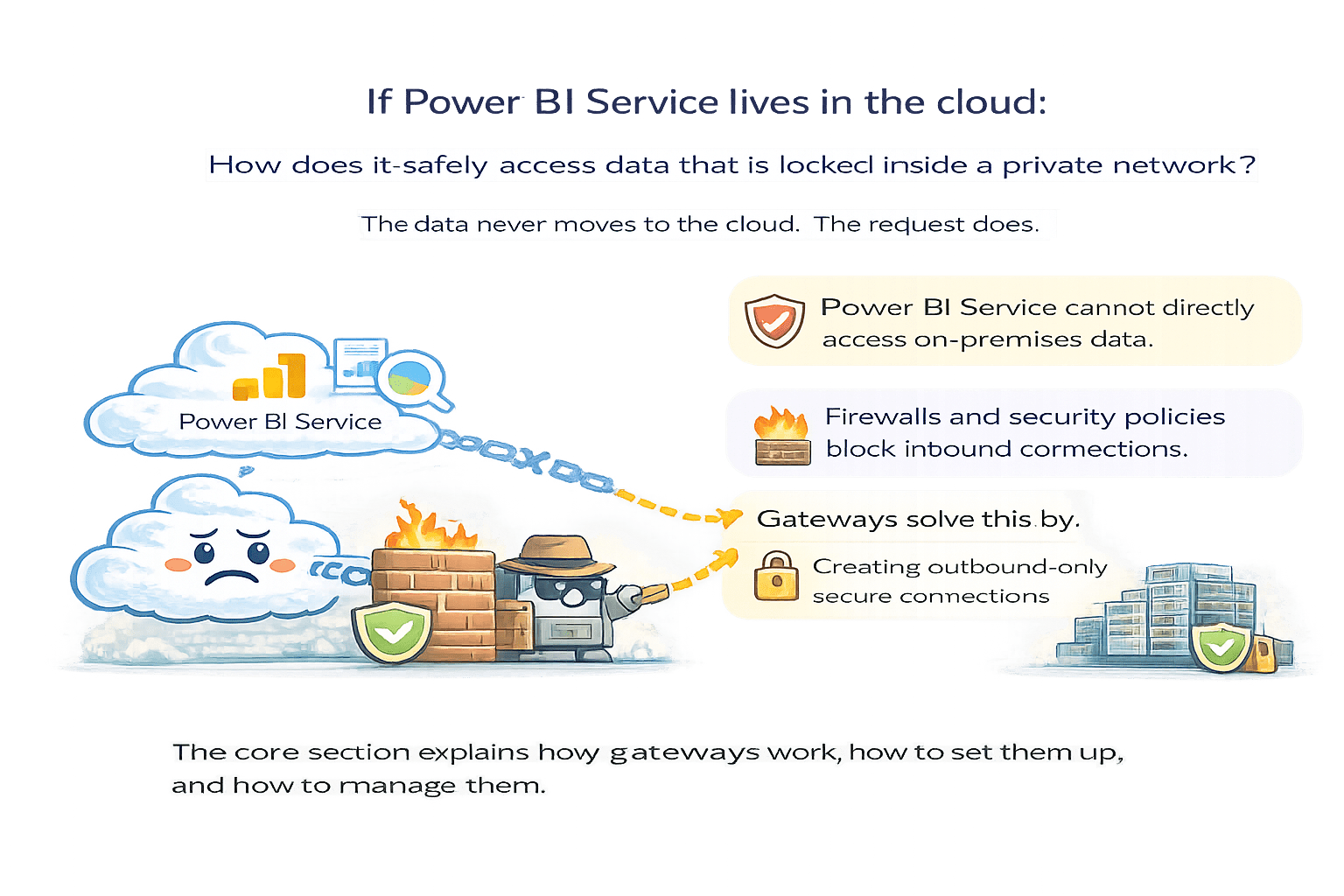
If Power BI Service lives in the cloud:
How does it safely access data
that is locked inside a private network?
The data never moves to the cloud.
The request does.
- That secure bridge is called a Data Gateway.
- Data Gateways let cloud reports talk to on-premises data safely.
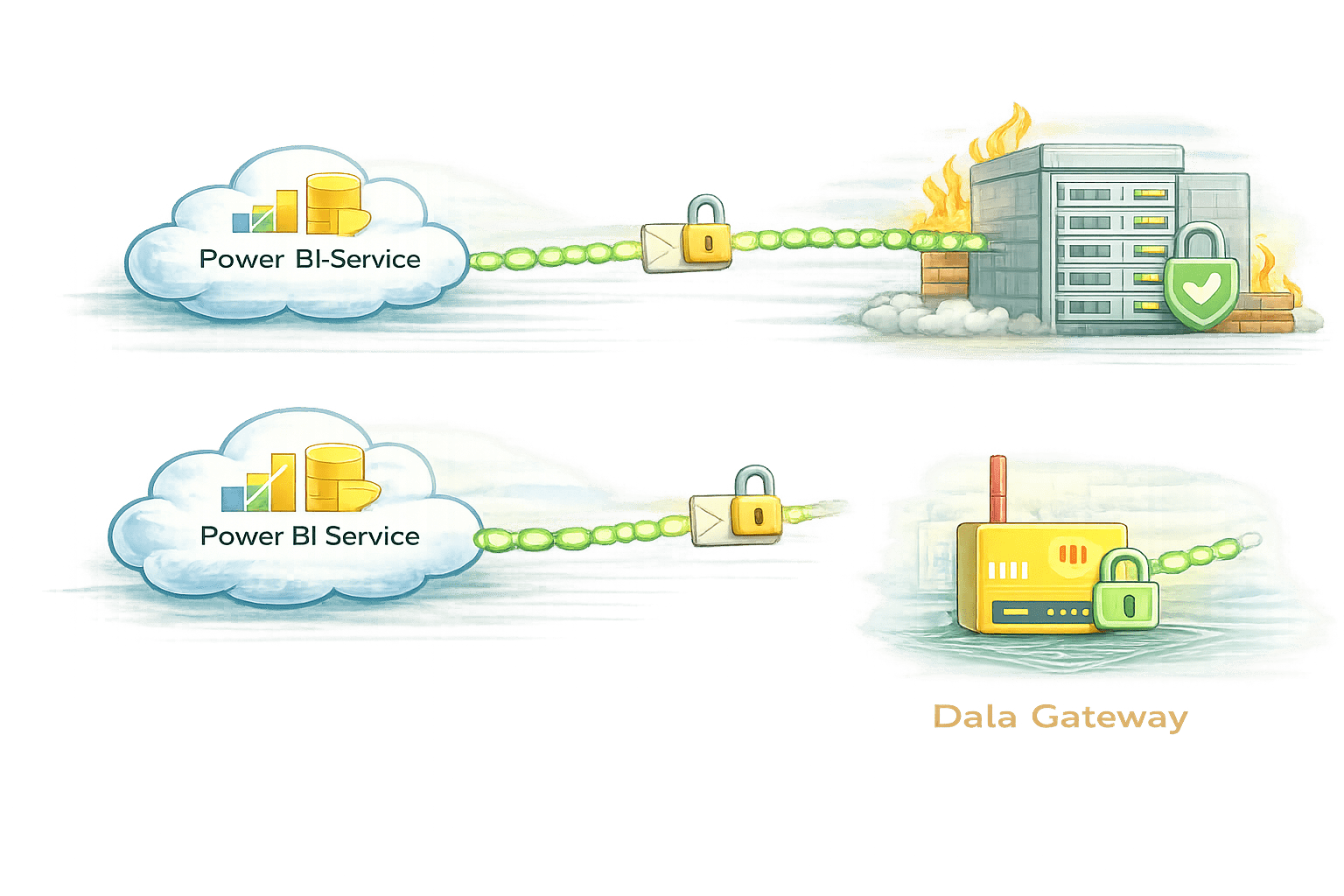


The core section explains how gateways work, how to set them up, and how to manage them
Power BI Service cannot directly access on-premises data
Firewalls and security policies block inbound connections
-
Gateways solve this by:
-
Creating outbound-only secure connections
-

Data Gateway
-
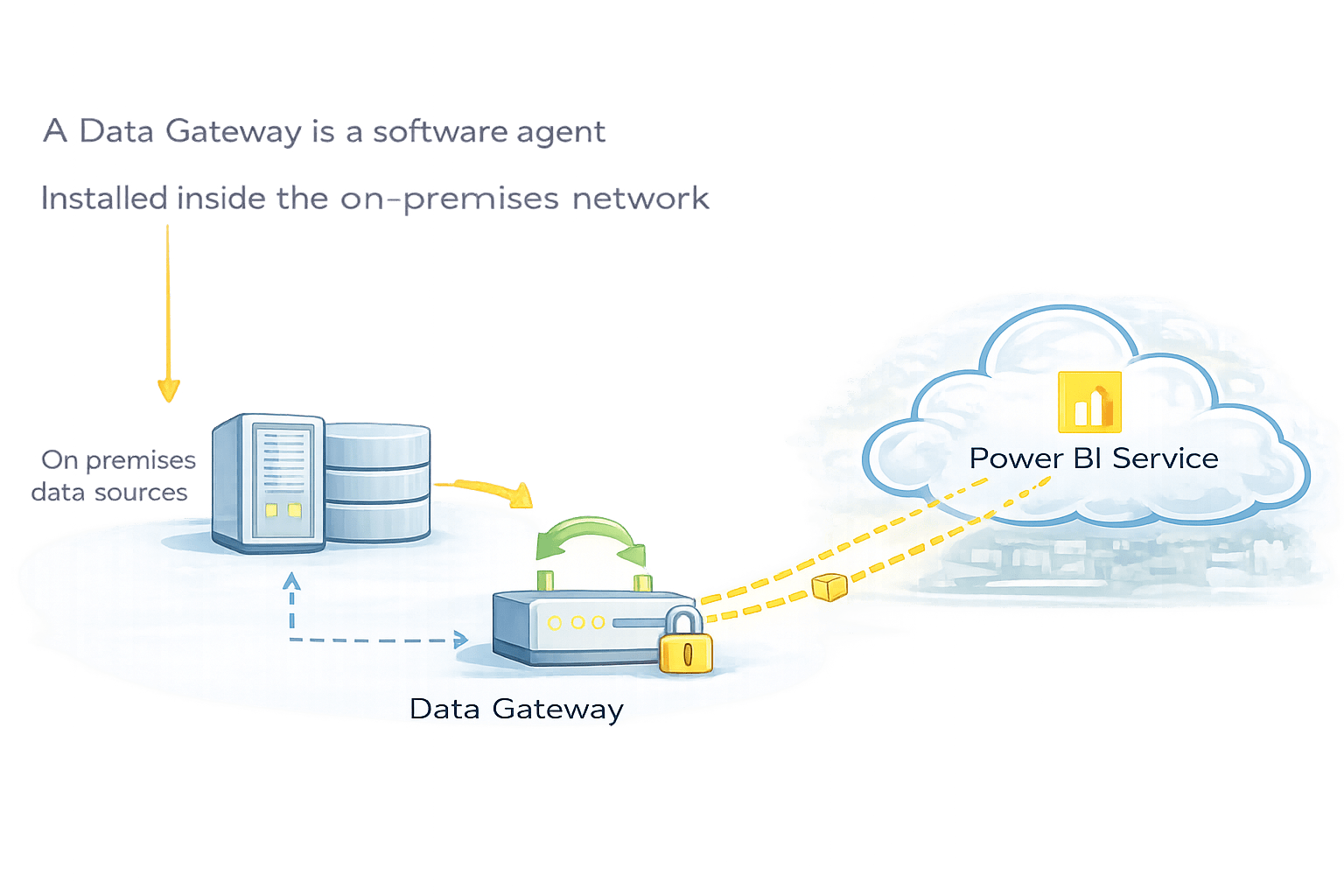
A Data Gateway is a software agent
-
Installed inside the on-premises network
-
Allows Power BI Service to:
-
Query local data sources
-
Refresh datasets securely
-
Power BI Service never directly enters the local network
Key Principle
-
Outbound communication only
-
No inbound firewall openings required
Key Principle

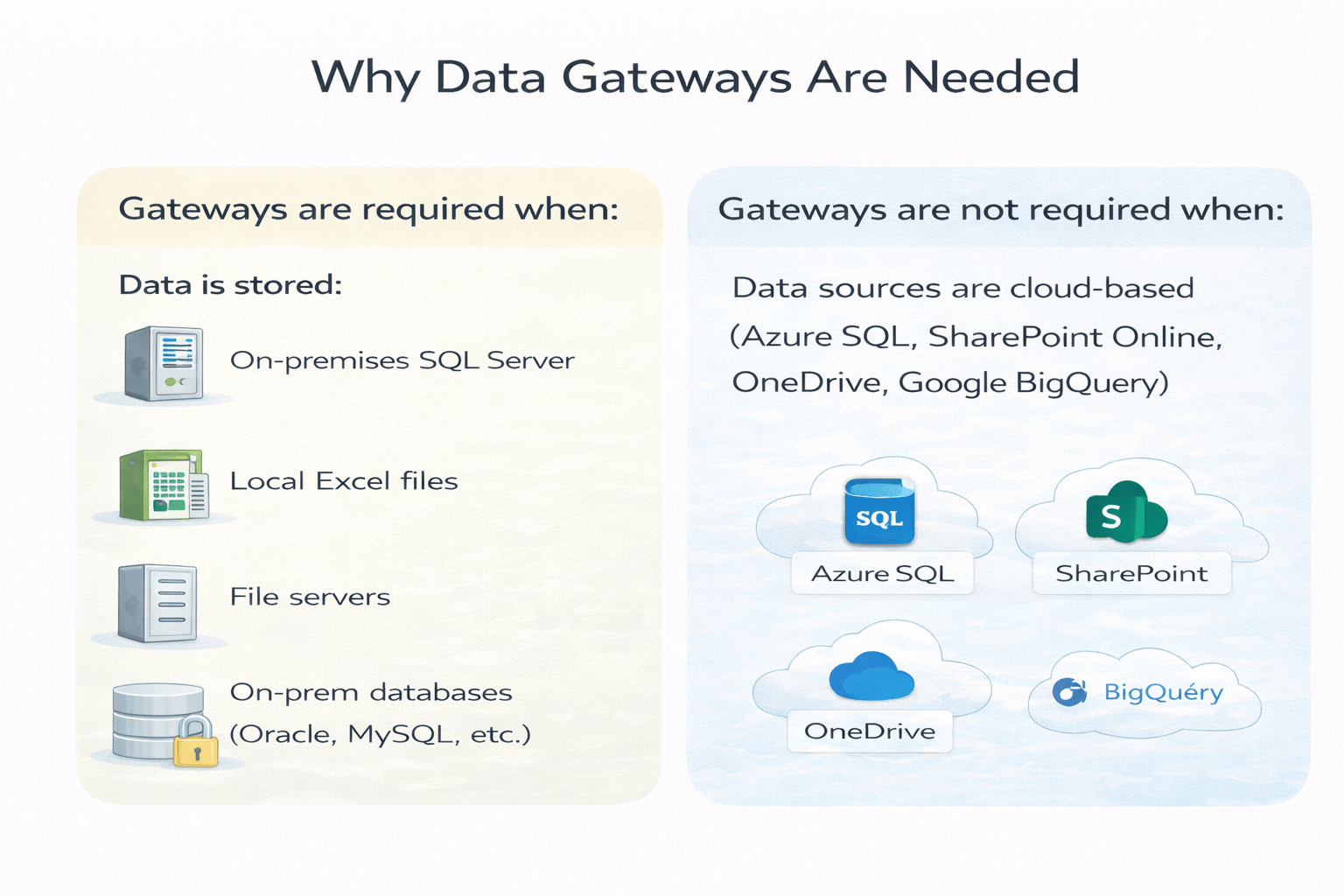

Why Data Gateways Are Needed

How Data Gateways Work
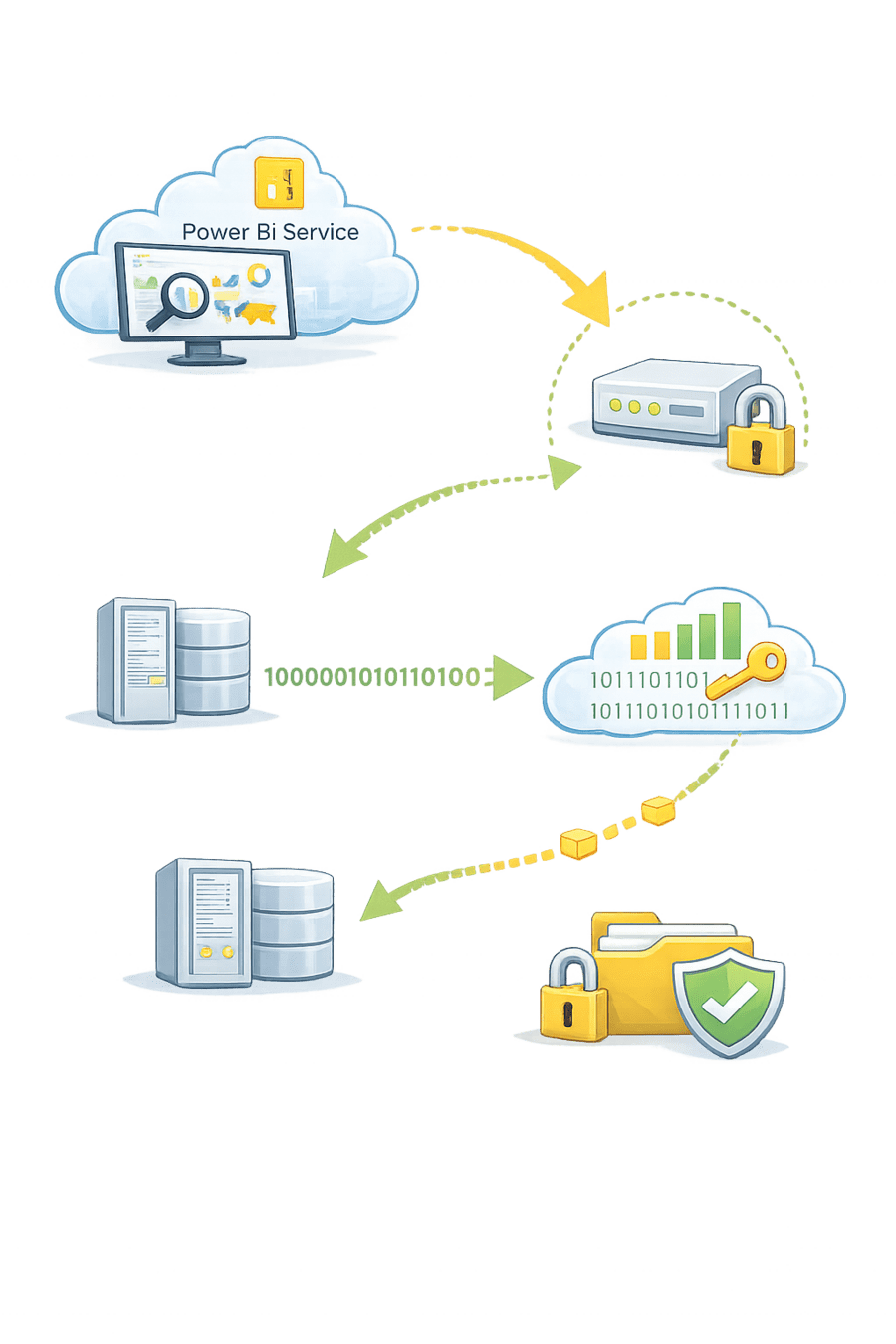
Power BI Service sends a refresh request



Gateway polls the service securely

Gateway connects to local data source
Data is encrypted and sent to Power BI Service

Dataset refresh completes
-
-
Credentials are stored securely
-
All traffic is encrypted
Security Insight

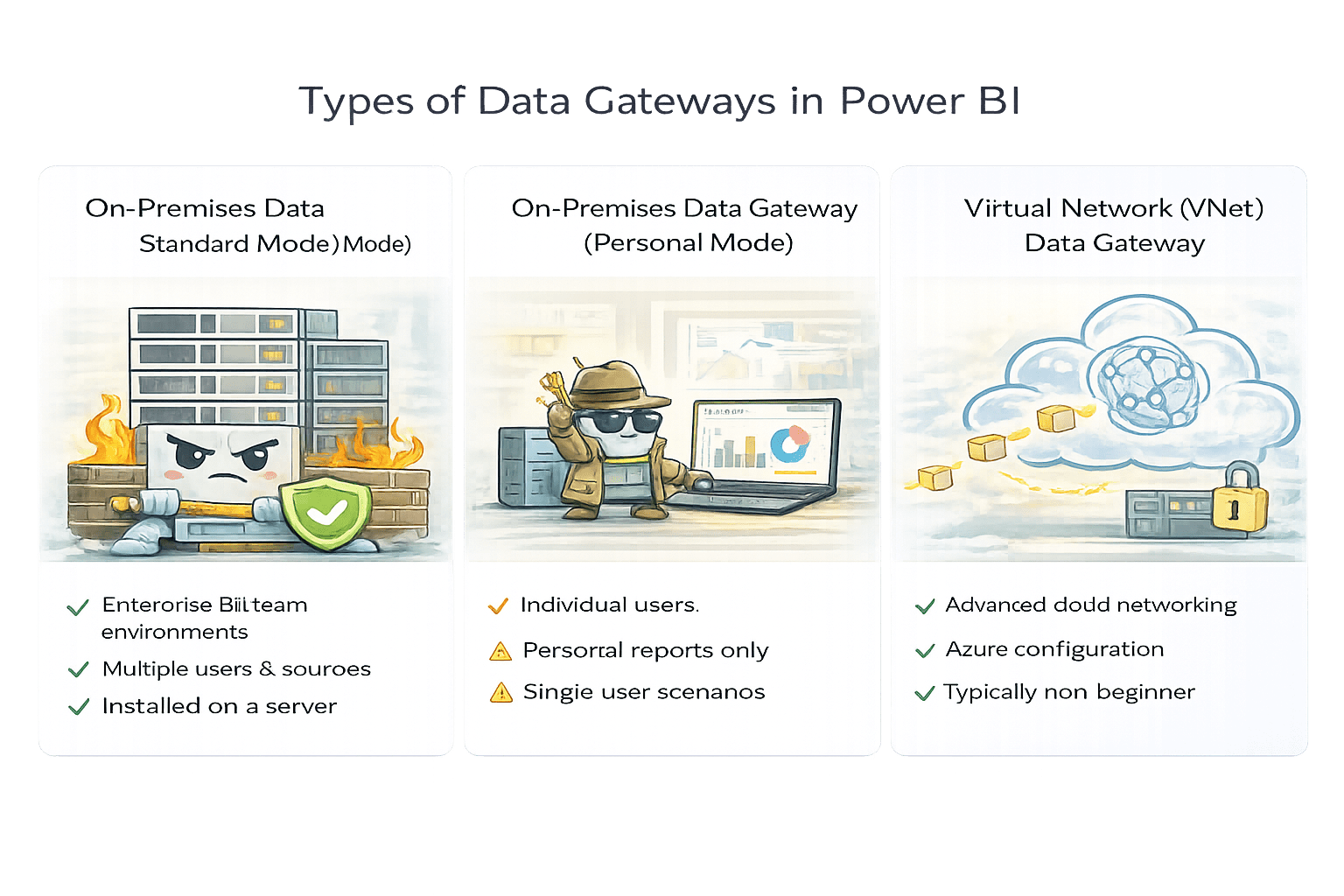


Types of Data Gateways in Power BI
-
Used in enterprise and team environments
-
Supports:
-
Multiple users
-
Multiple data sources
-
Shared datasets
-
- Installed on a server
-
Used by individual users
-
Limited to:
-
Personal reports
-
Single user scenarios
-
-
Not suitable for team collaboration
-
Used in advanced cloud networking scenarios
-
No local installation required
-
Requires Azure configuration
Typically outside beginner scope

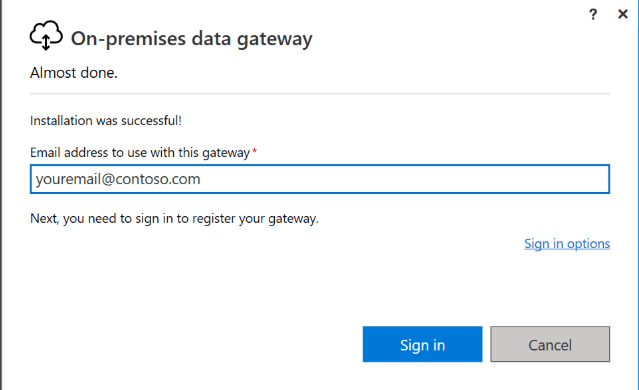
Installing the On-Premises Data Gateway
Steps
-
Go to Power BI Service
-
Download On-Premises Data Gateway
-
Install on:
-
A server or machine with access to SQL Server
-
-
Sign in using Power BI account
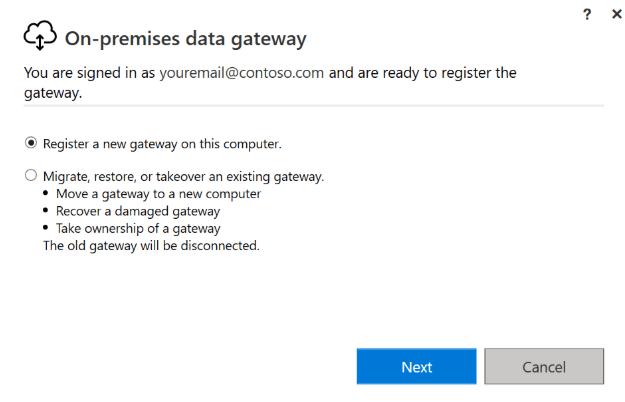
- Choose Standard Mode (recommended for teams)
-
Register the gateway
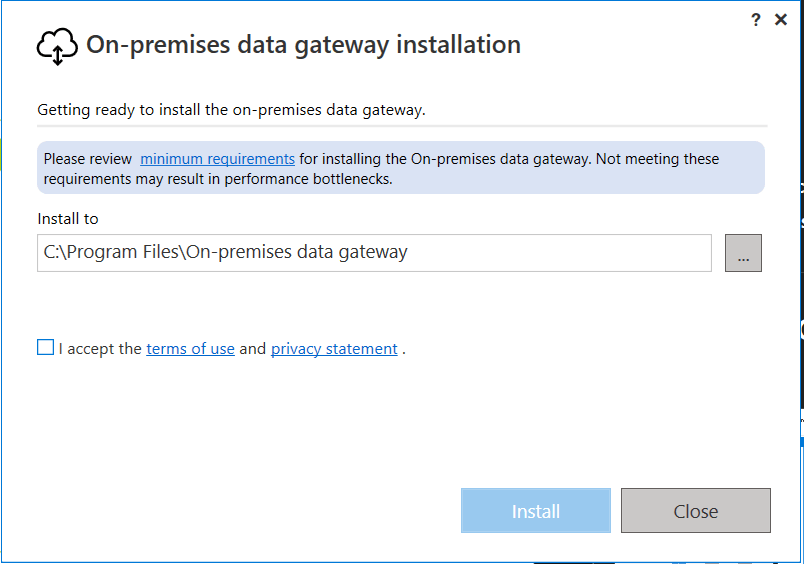
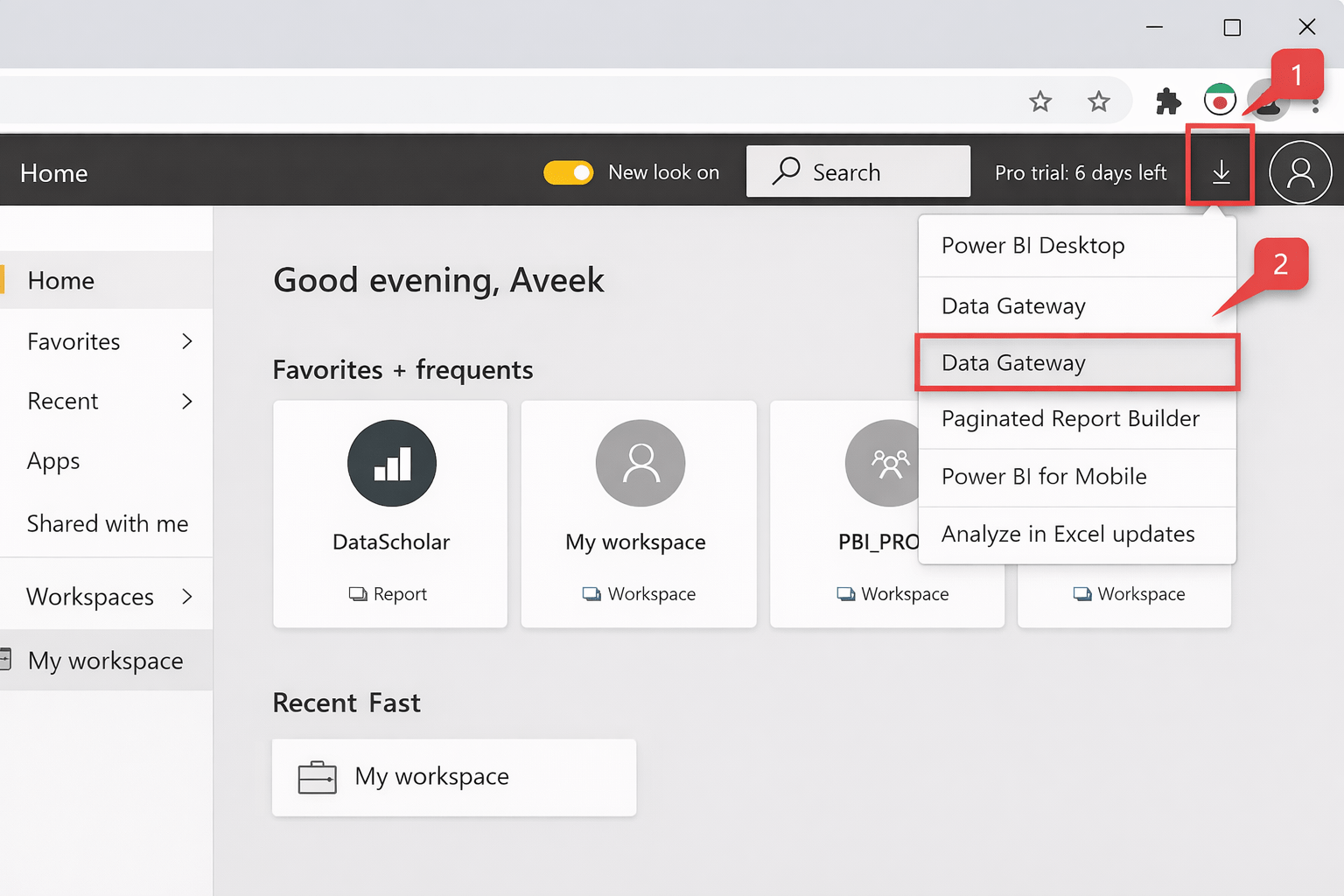
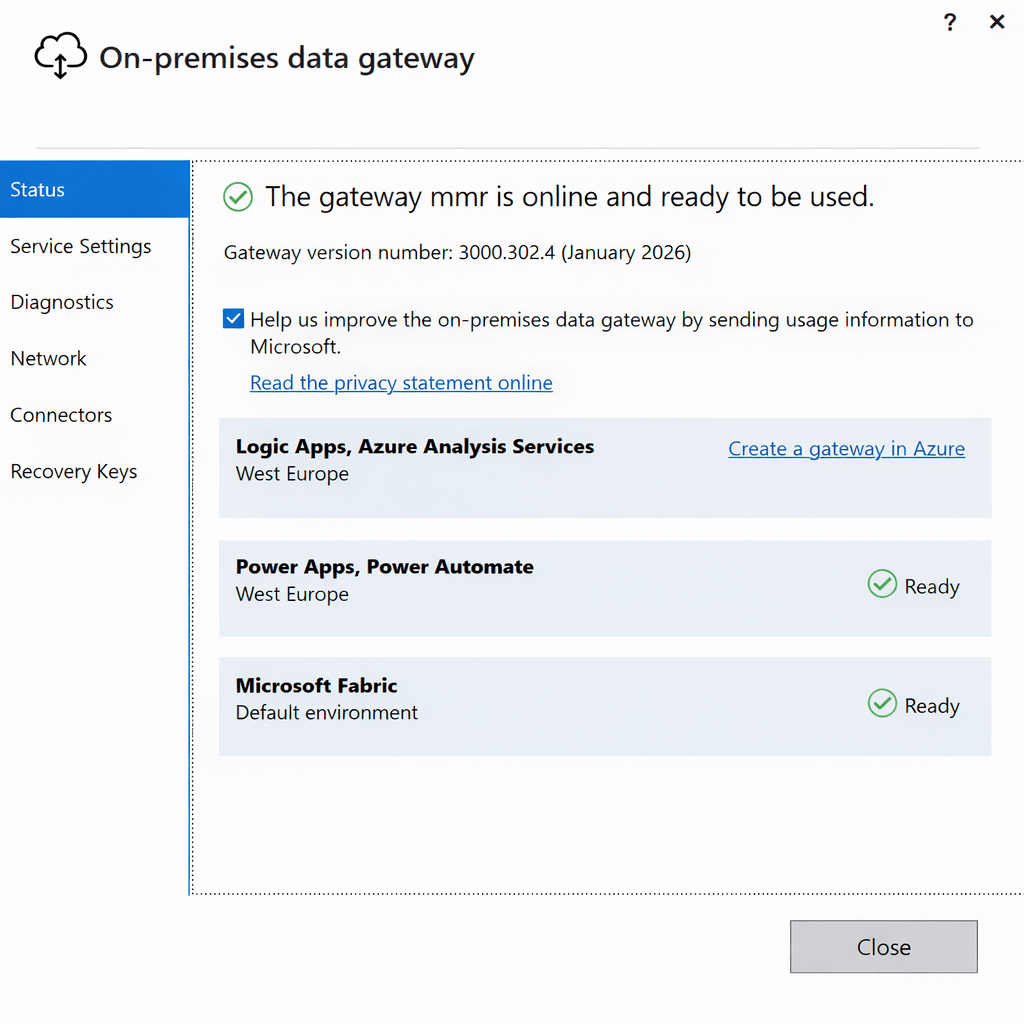
Install on a machine that:
- Is always online
- Has stable network connectivity

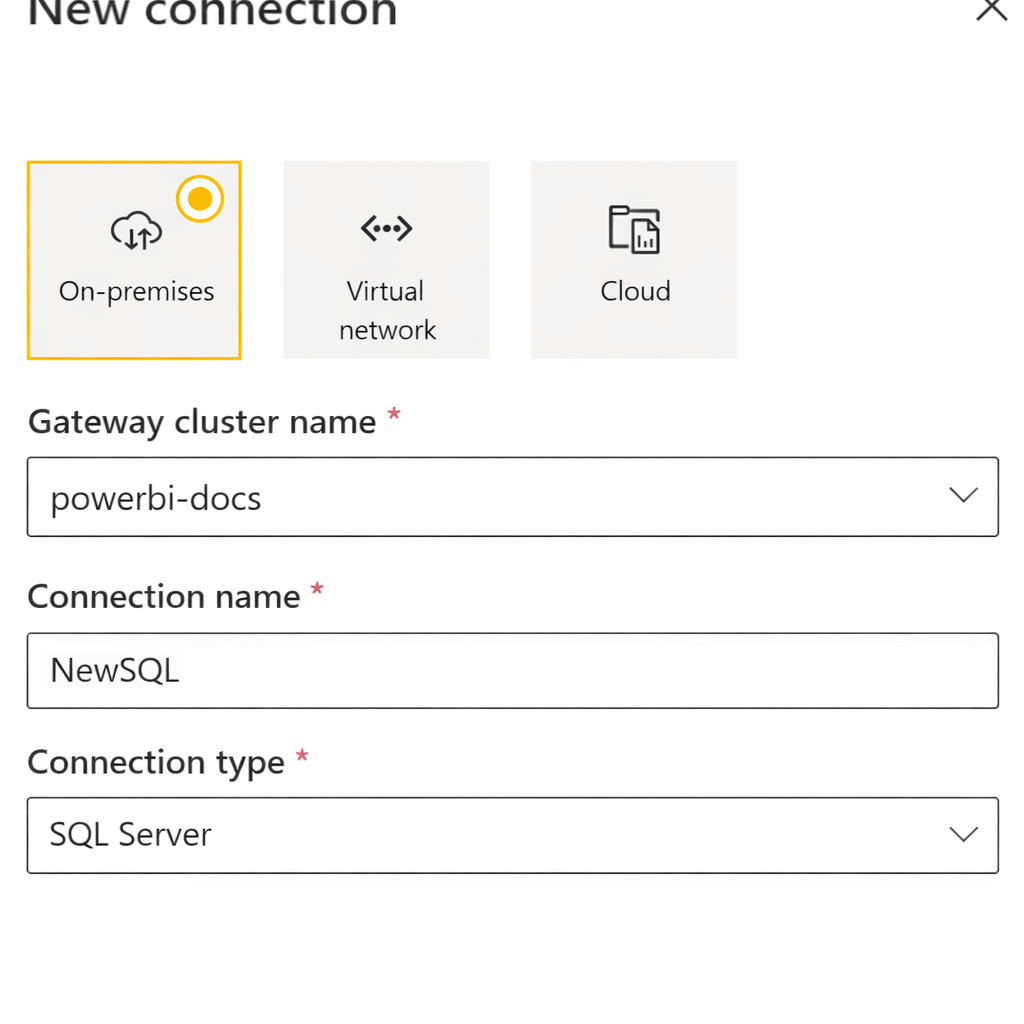
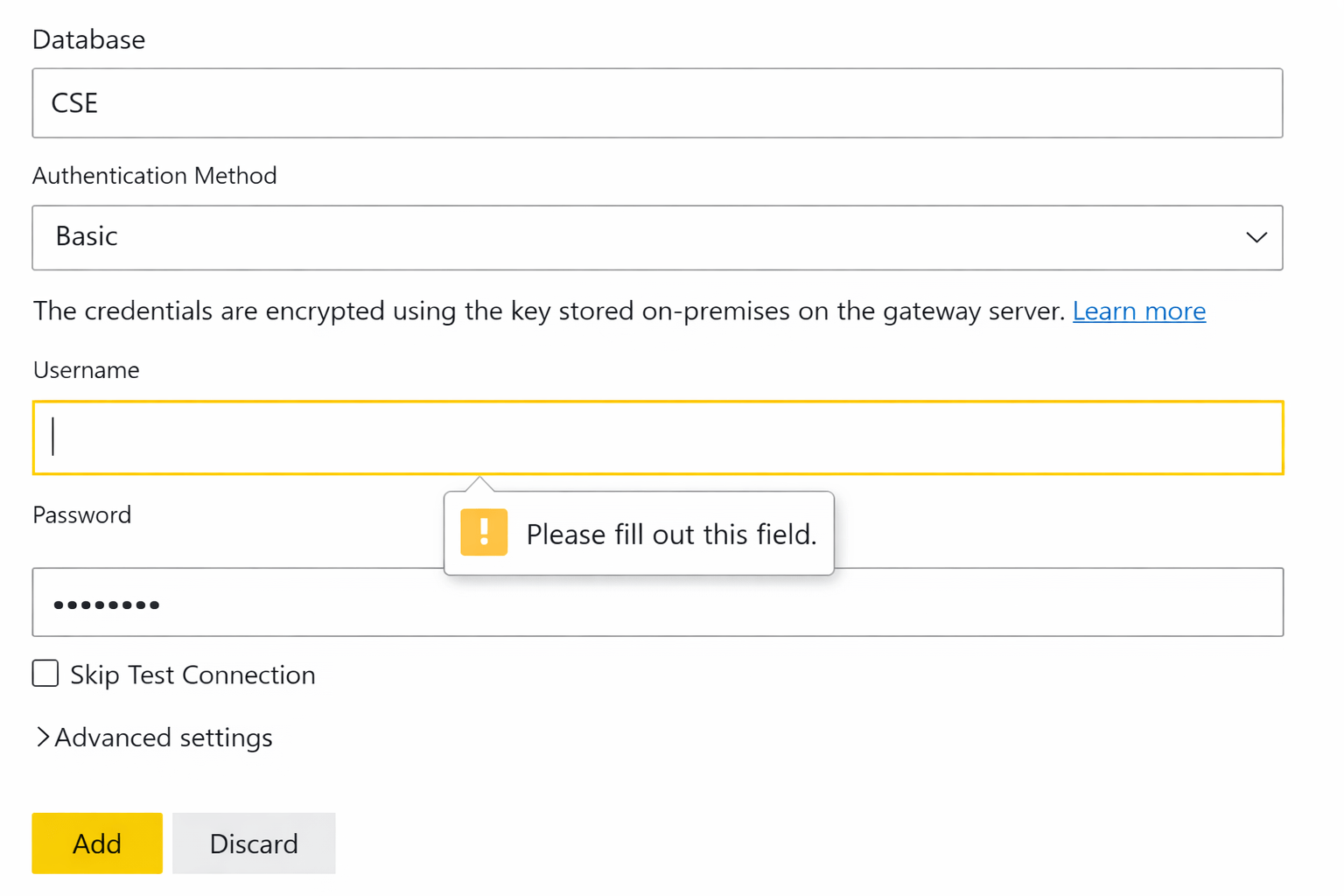
Configuring Data Sources in Gateway
Steps
- Go to Manage Gateways
- Select the installed gateway
Click Add data source
Choose:
- Data source type:
- Enter:
- Server name
- Database name
Enter credentials
- Test connection
- Save
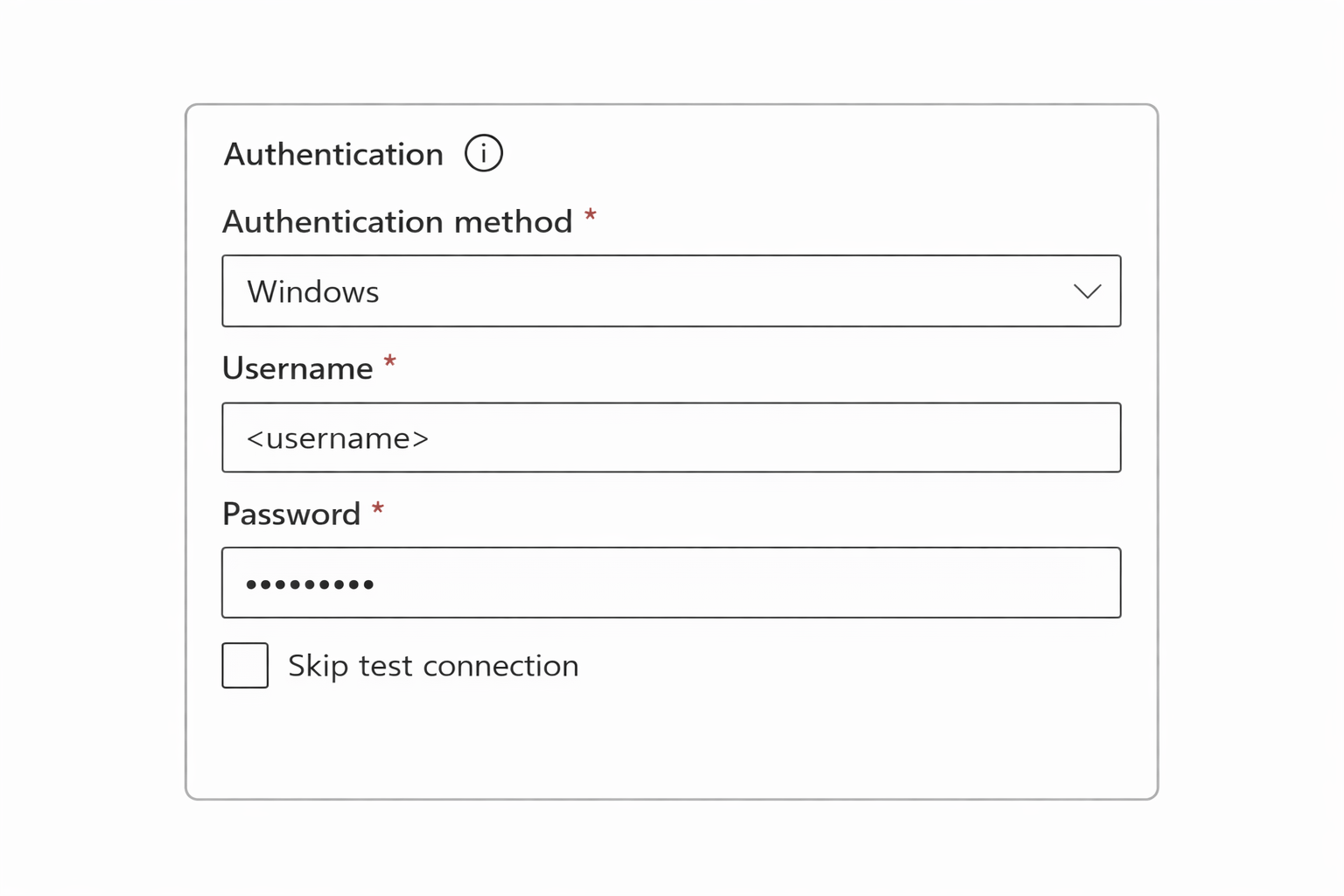


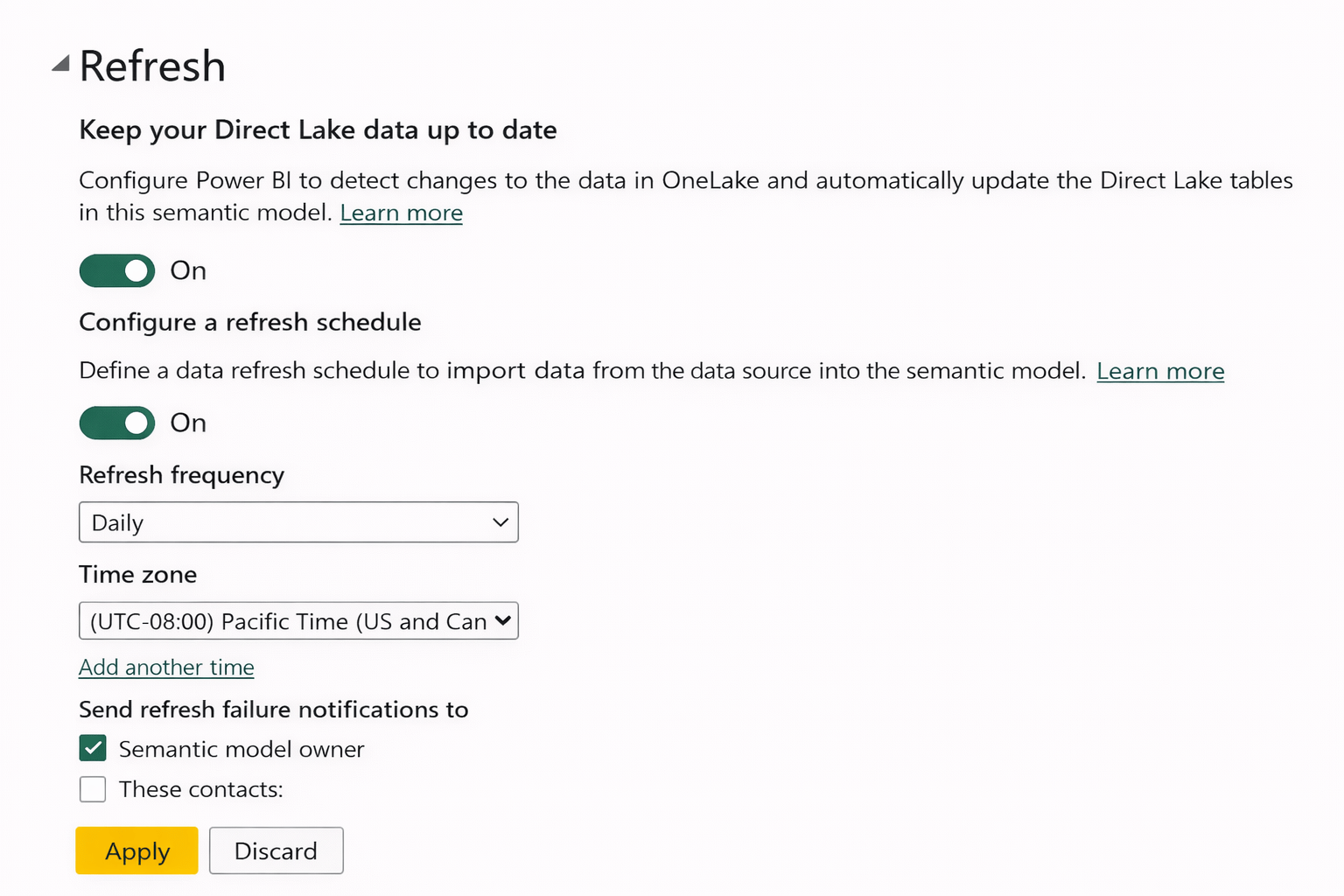
Using Gateway with Scheduled Refresh
Gateways enable scheduled refresh for on-prem data
Steps
-
Publish report to Power BI Service
-
Go to dataset settings
-
Map dataset to gateway data source
-
Enable scheduled refresh
-
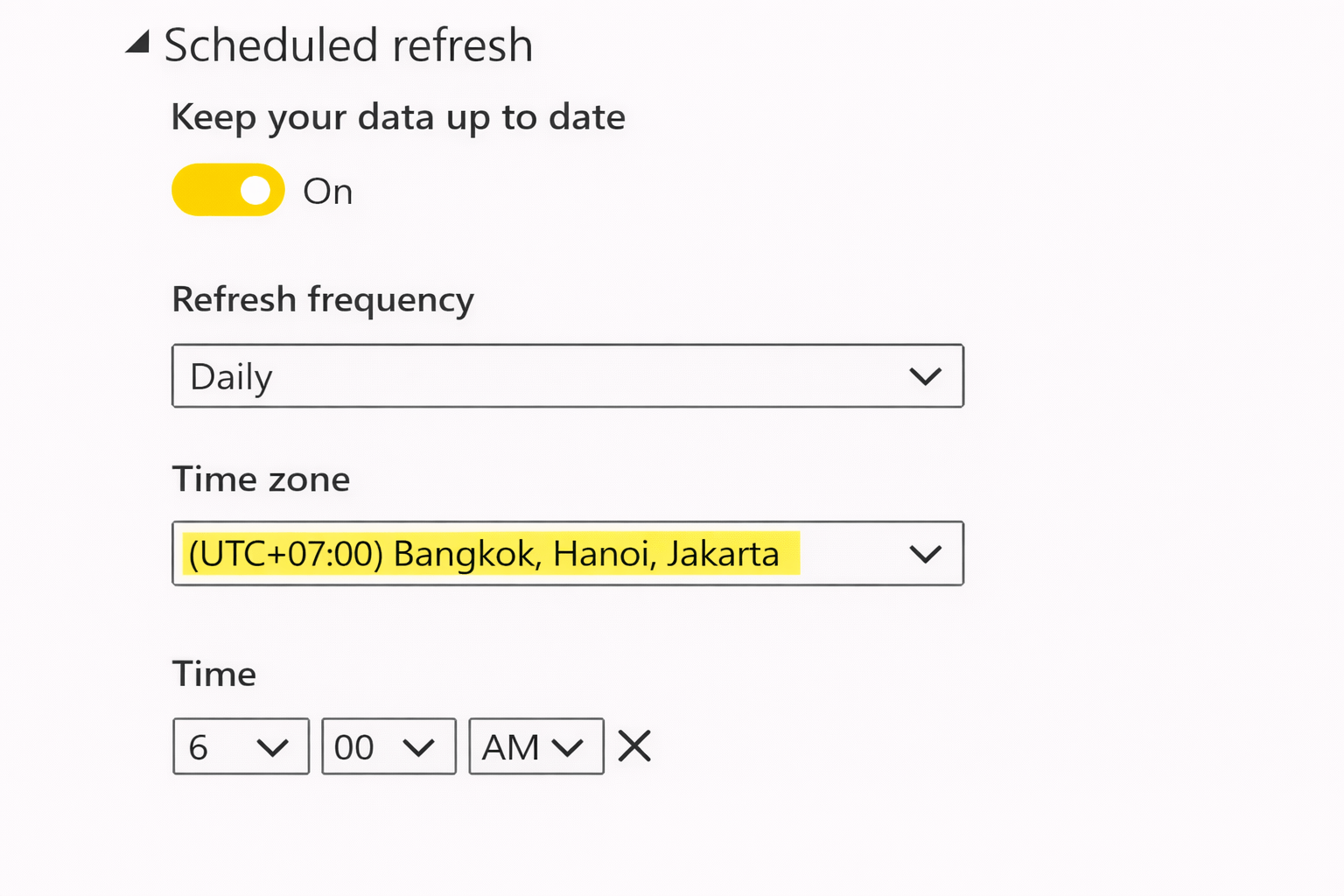
Set frequency and time
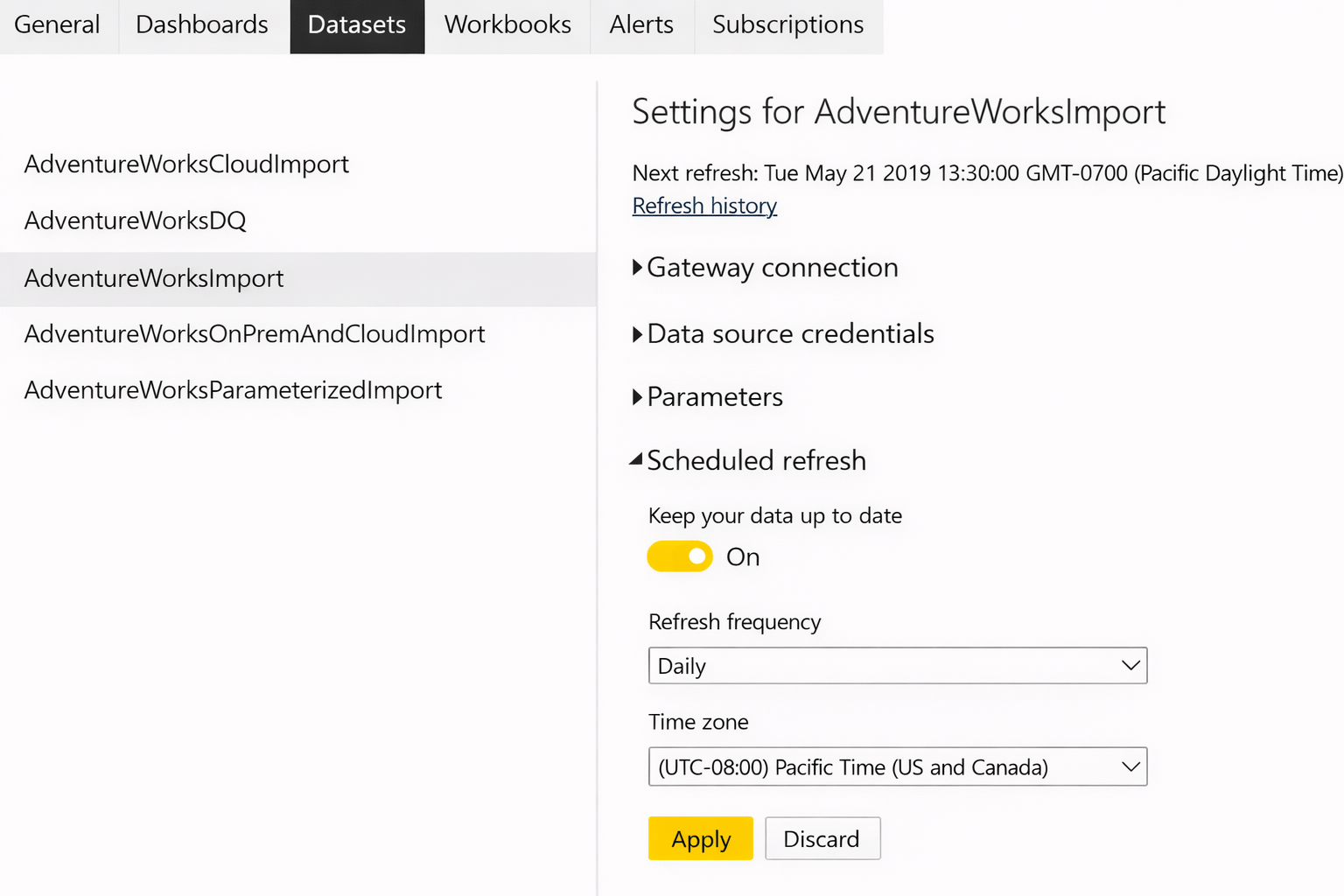



Monitoring and Maintaining Gateways
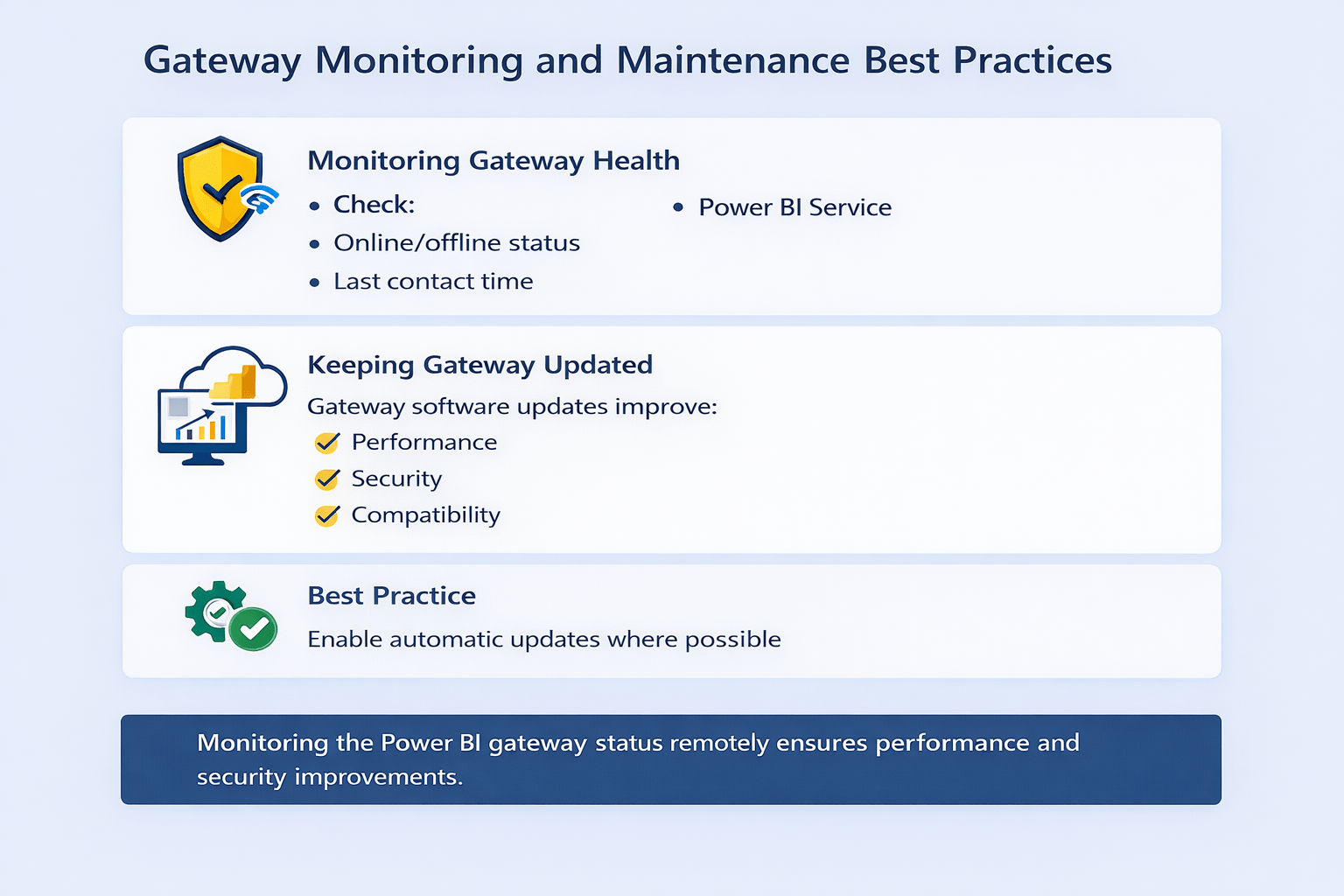




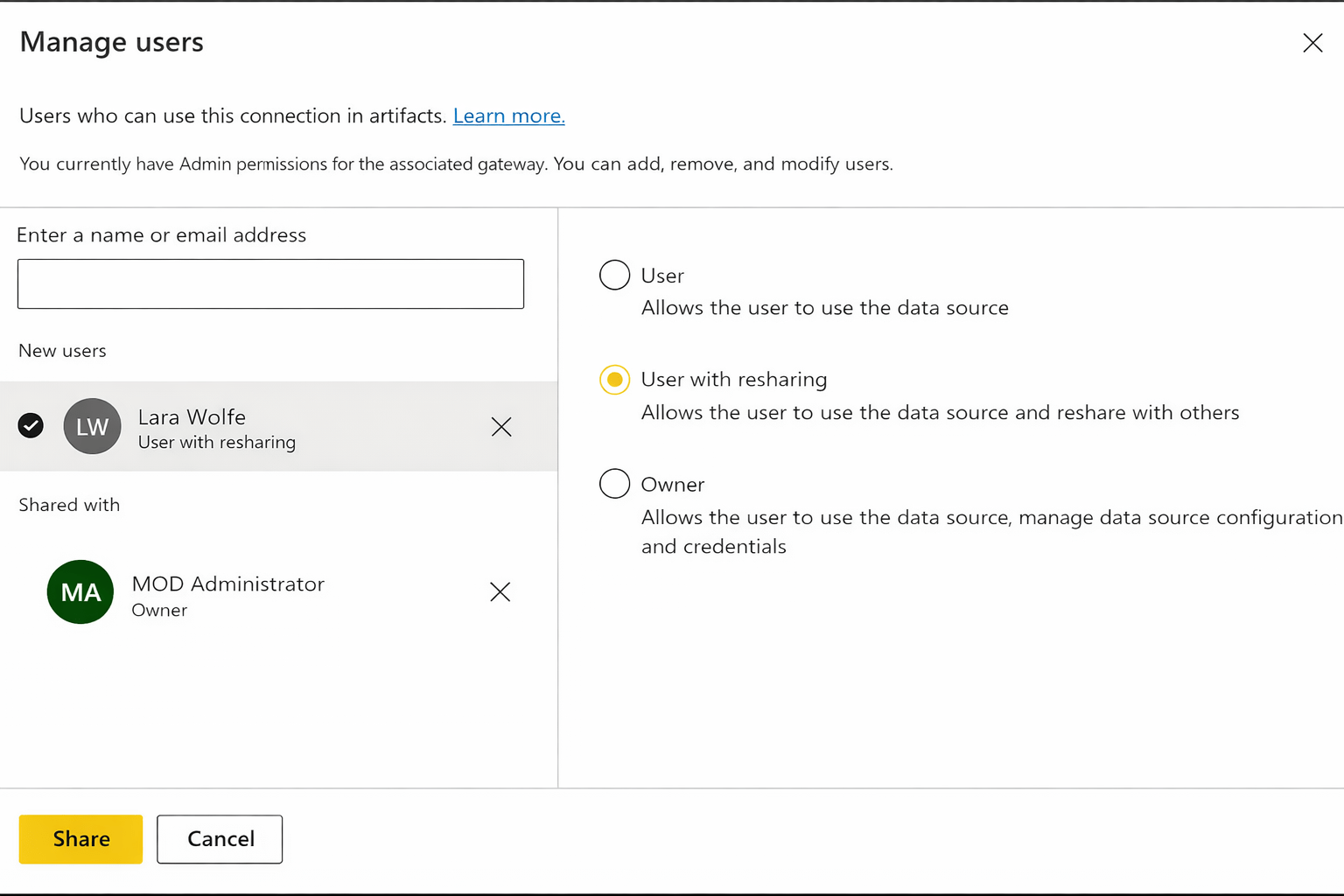
Managing Access
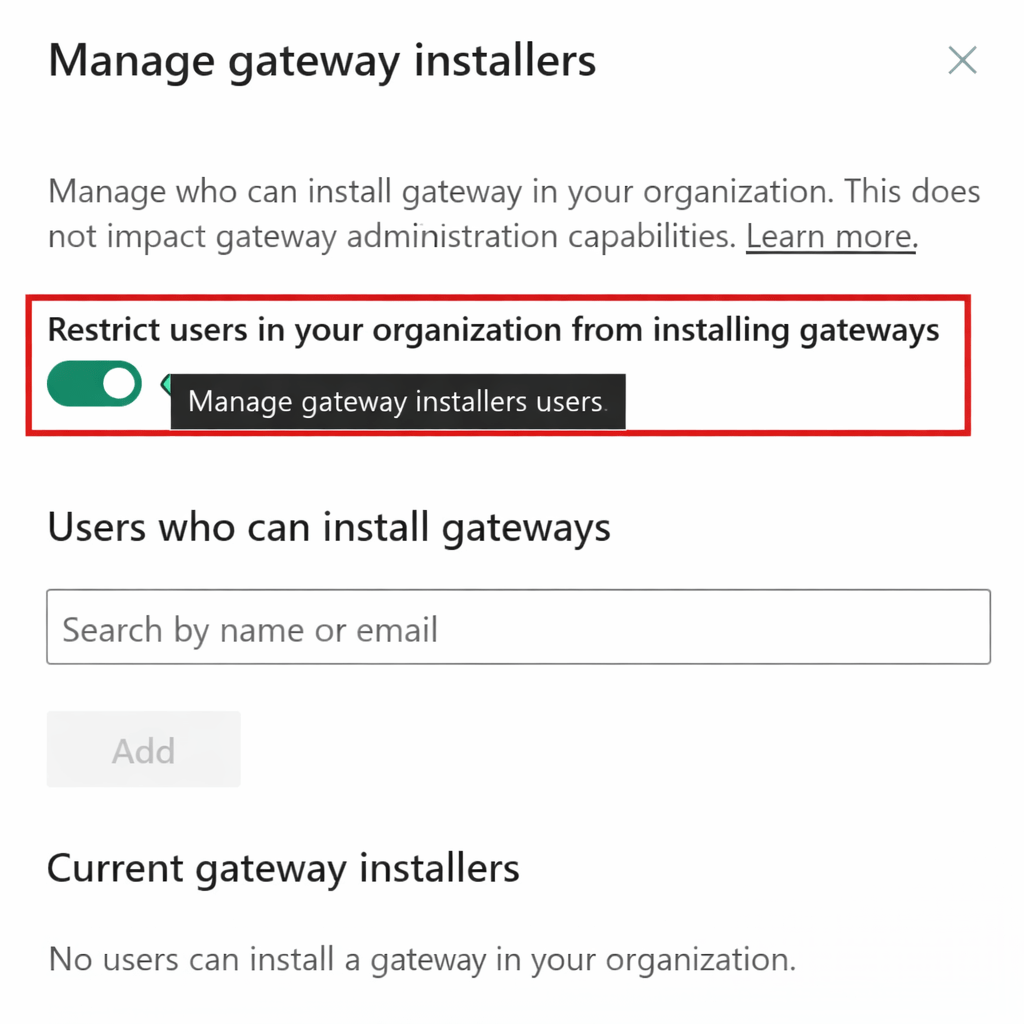
-
Control:
-
Who can use gateway
-
Who can add data sources
-
Power bi Service → Manage Gateway
Prevent unauthorized access
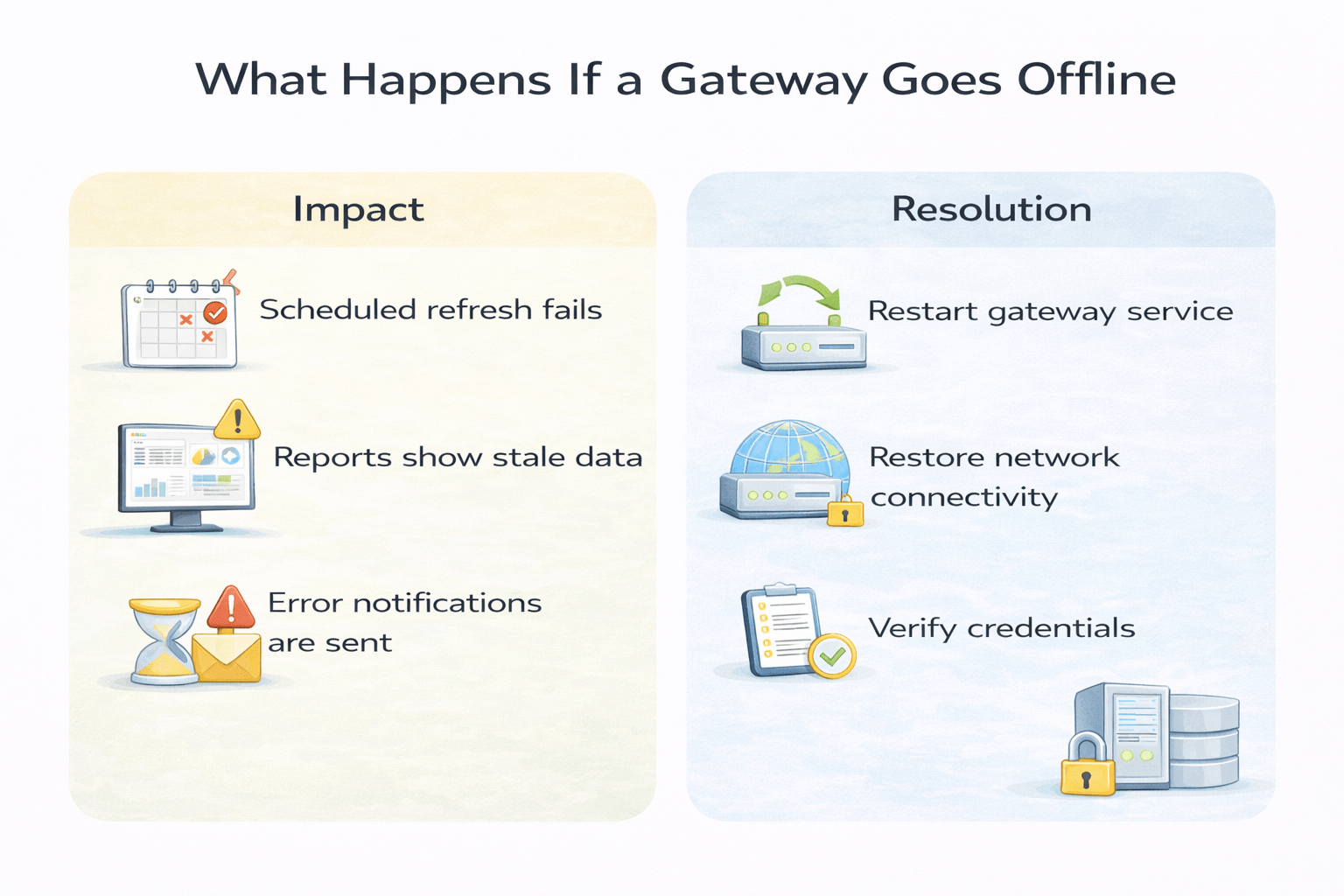

What Happens If a Gateway Goes Offline






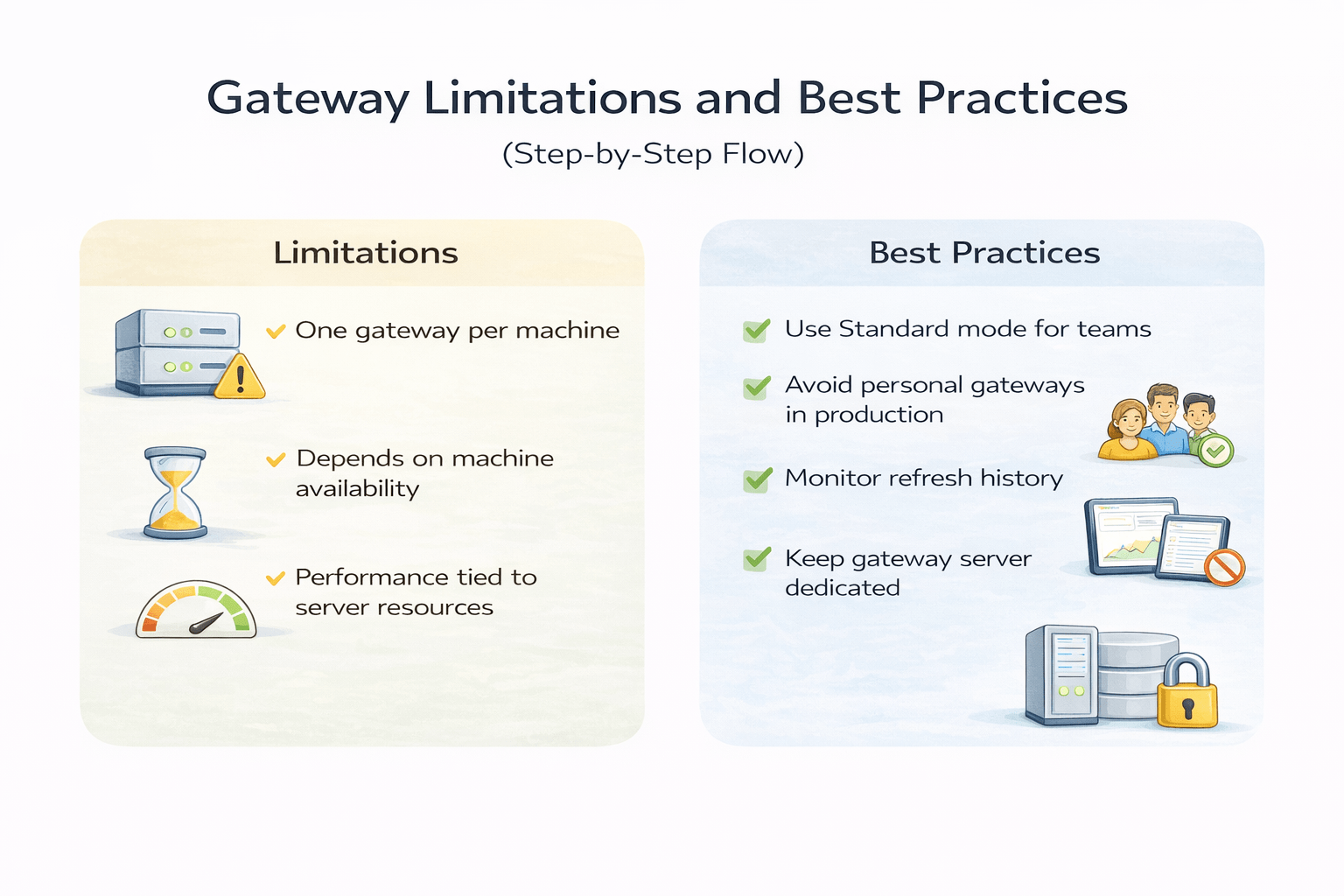

Gateway Limitations and Best Practices

Summary
5
4
3
2
1
Monitoring and maintenance ensure reliability
Gateways enable scheduled refresh
Standard mode supports teams and shared datasets
Required only for on-premises sources
Data Gateways securely connect cloud and on-prem data

Quiz
Why is a data gateway required?
A. To store data permanently in the cloud
B. To create dashboards and reports
C. To securely access on-premises data
D. To improve Power BI visual performance


Why is a data gateway required?
A. To store data permanently in the cloud
B. To create dashboards and reports
C. To securely access on-premises data
D. To improve Power BI visual performance
Quiz-Answer
