Wireframing
and
Prototyping
PV252
- UI components
- Visual guidelines
- Wireframes & mockups & prototypes
- Usability heuristics
- User flows
Agenda
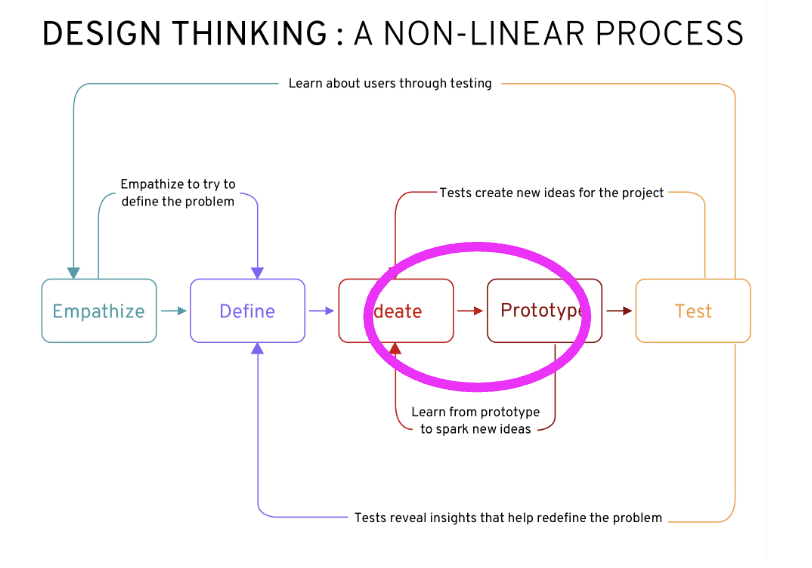
- A wireframe is a graphical skeleton of a website, helps designers and clients to discuss the details of the website building (like a blueprint)
- simple
- To communicate info structure/ layout/ content/ functionality
Wireframe

- Step-up from a wireframe
- Higher fidelity
- It incorporates seemingly realistic looking components.
- To discuss further with stakeholders
Mockup
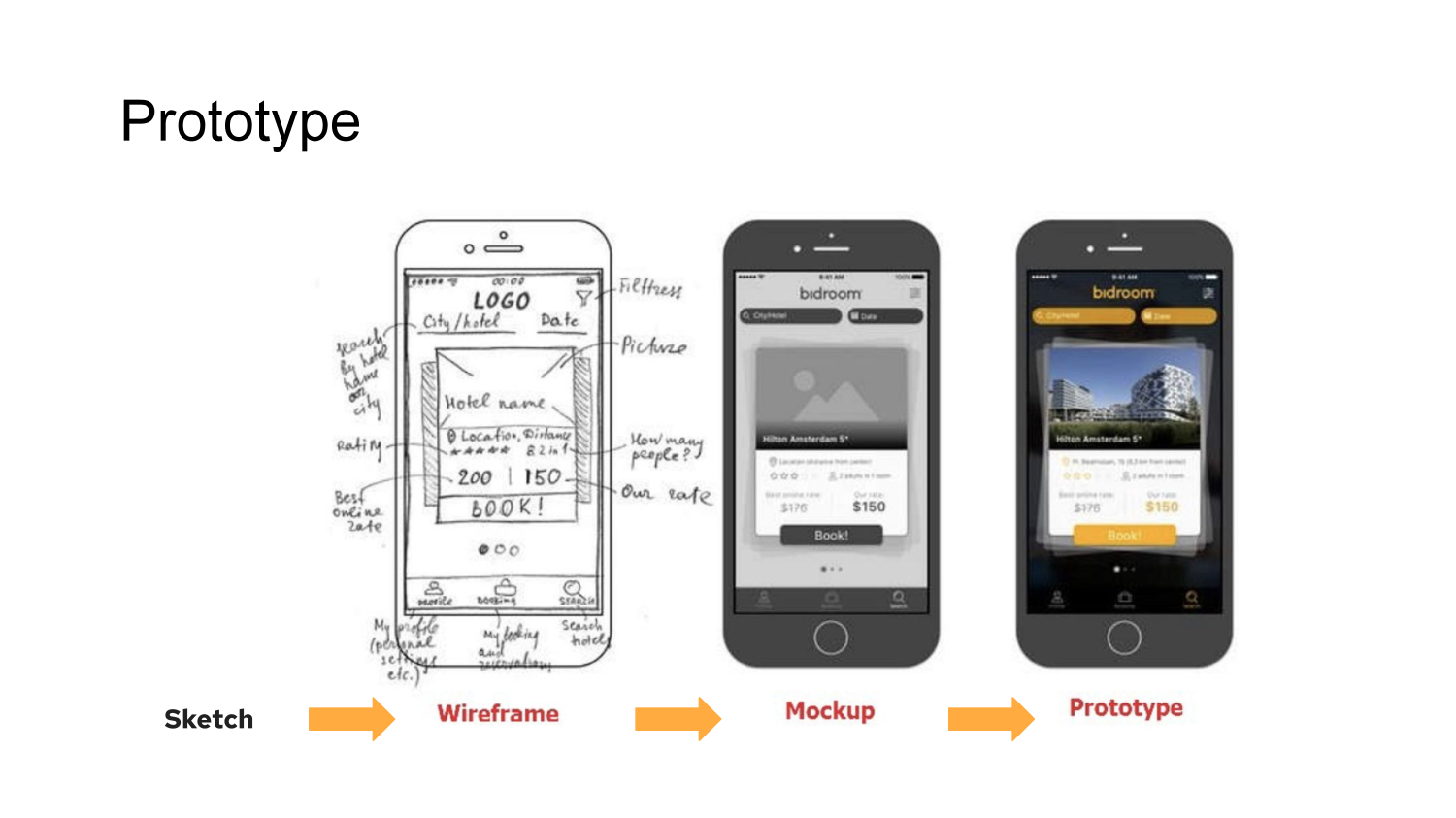
- Interactive simulation of a product (clickable or simulated by a person)
- Shows product functions and solves for a use case
- Great for validating product early. Ready to be tested with users.
- Different fidelity: low vs. high
- Validated prototypes are ready to be developed
Prototype
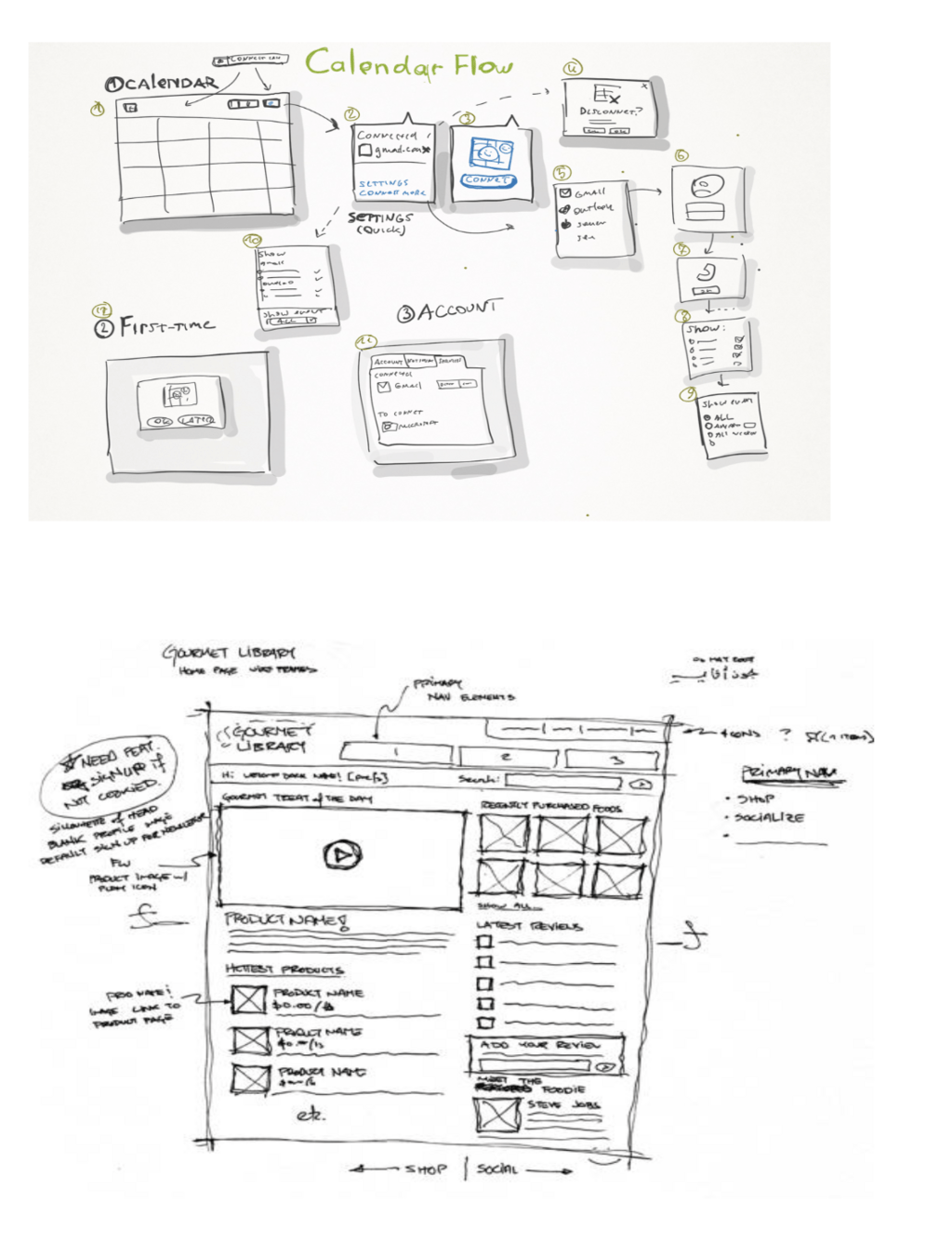
Low-fidelity
- Good for testing ideas
- Easy, cheap, fast
- Key concepts
- Can be interactive
- lacks realism


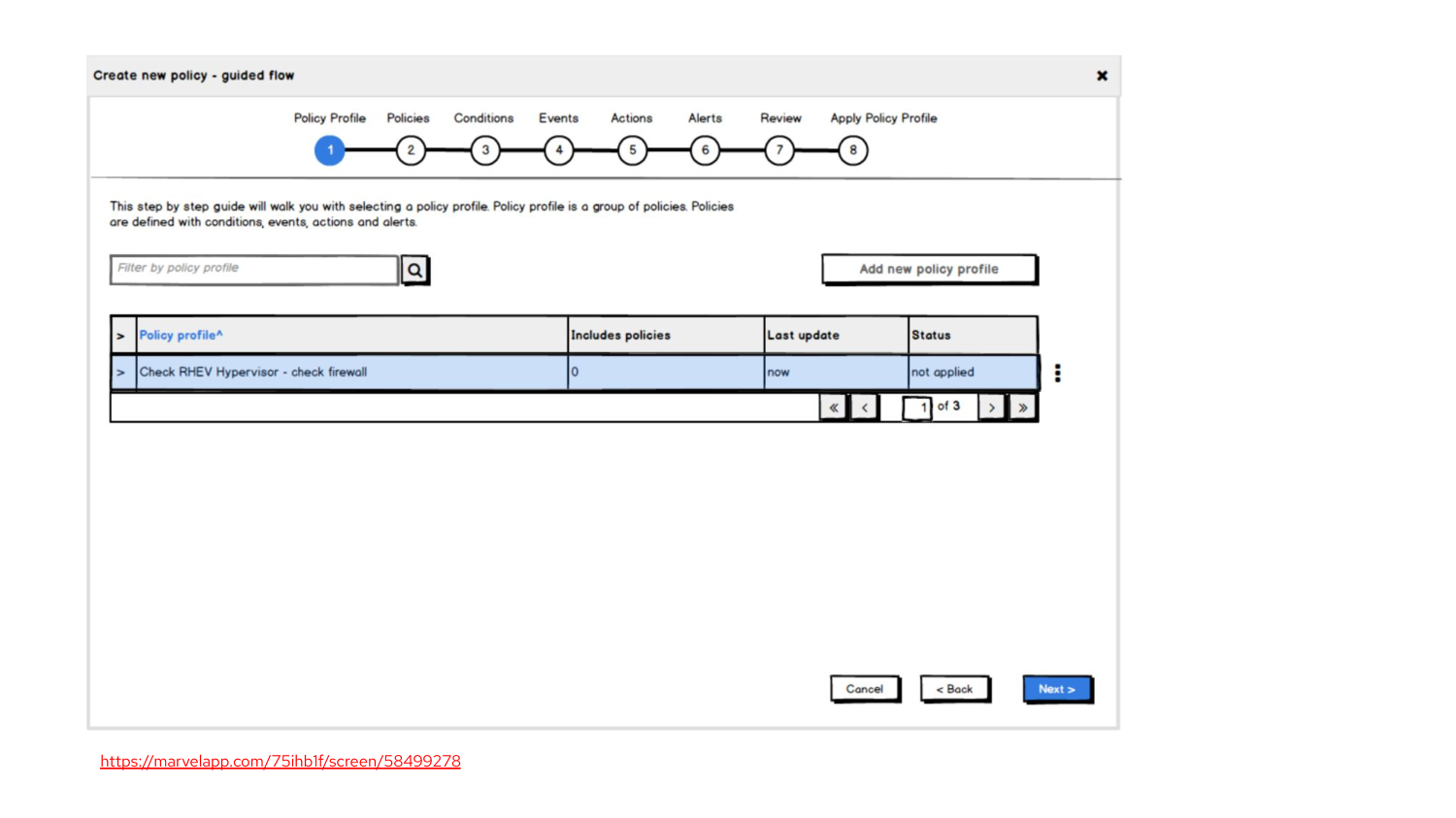
Low fidelity prototypes
Hi-fidelity
- highly realistic
- Great for testing
- Takes time and skill to create, expensive
- interactive

Vibe coding
- Instead of coding, you can focus on the user experience
- relatively easy to start
- quick prototyping
- instant feedback
- can use design system
- Quick idea prototyping (?)
- Risk of bugs, security, and scalability
- shareable/testable high-fi pixel prefect "idea"
- e.g. Gemini canvas, Cursor...
...tbd...
Activity
3 min

Sketching
Sketching
- It's a start...
- Anyone who can draw a circle, rectangle, wavy line can make a sketch
- The sketch doesn't have to be beautiful
- Quick idea generation, development of multiple ideas, verification, and visualization of the problem
- Contains only the main features
- The key is to focus on the content - what am I developing within the sketch?
- Fast and cheap




UI components
and some visual advices
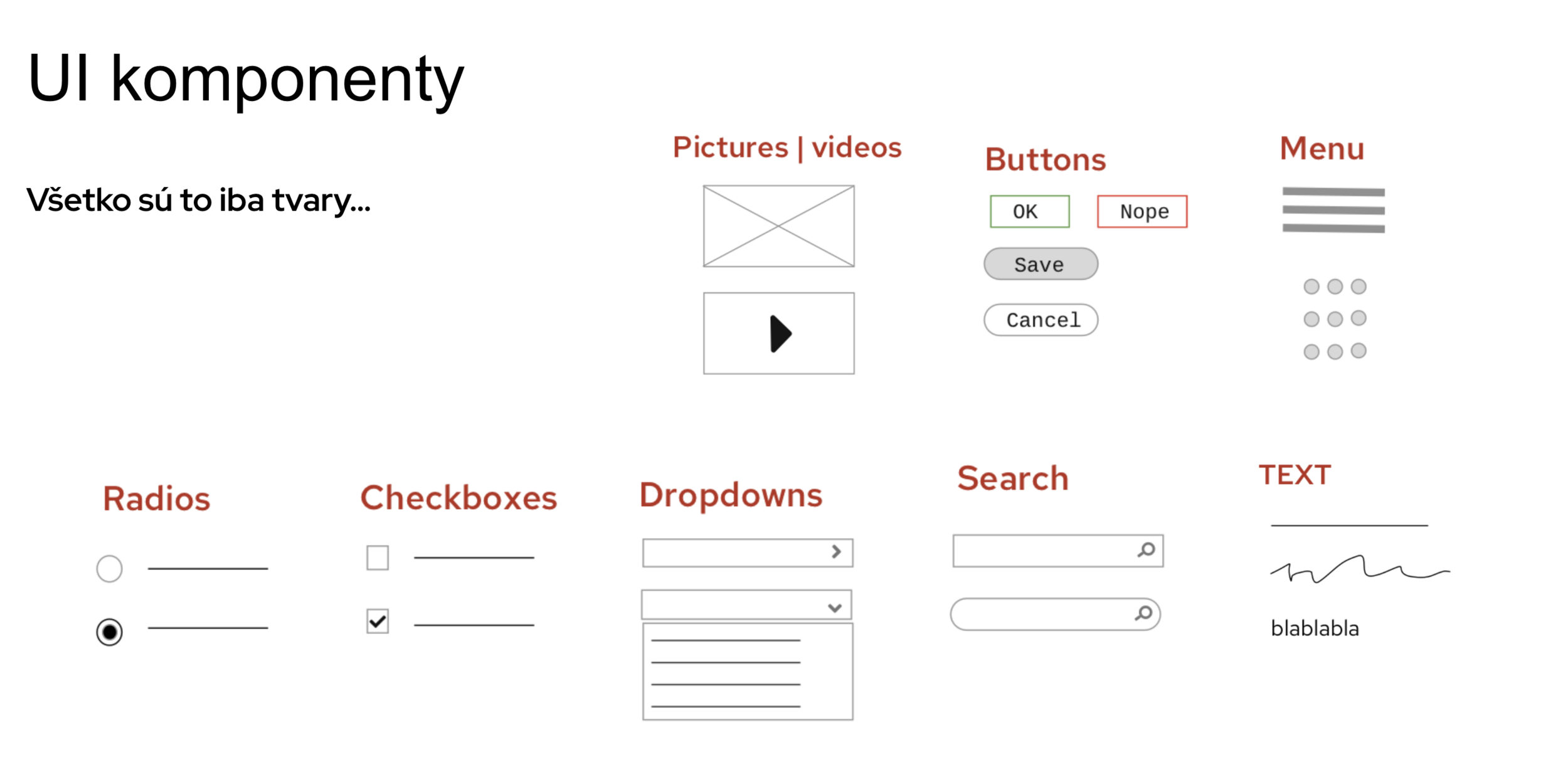
UI components
...are just shapes...
Imagine....
Activity
3 min

Size

Shapes

Colors
Pop up effect
Colors
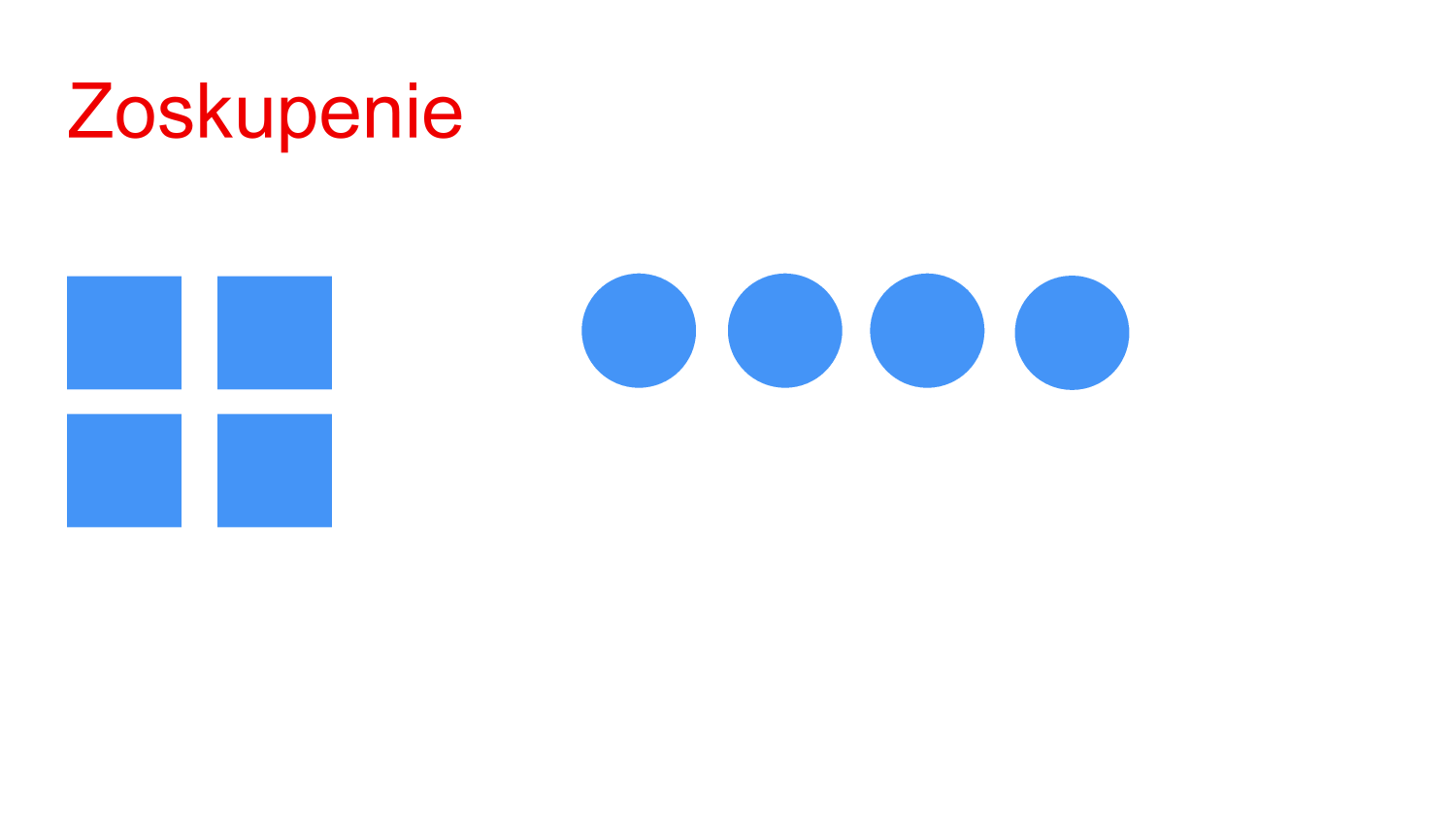
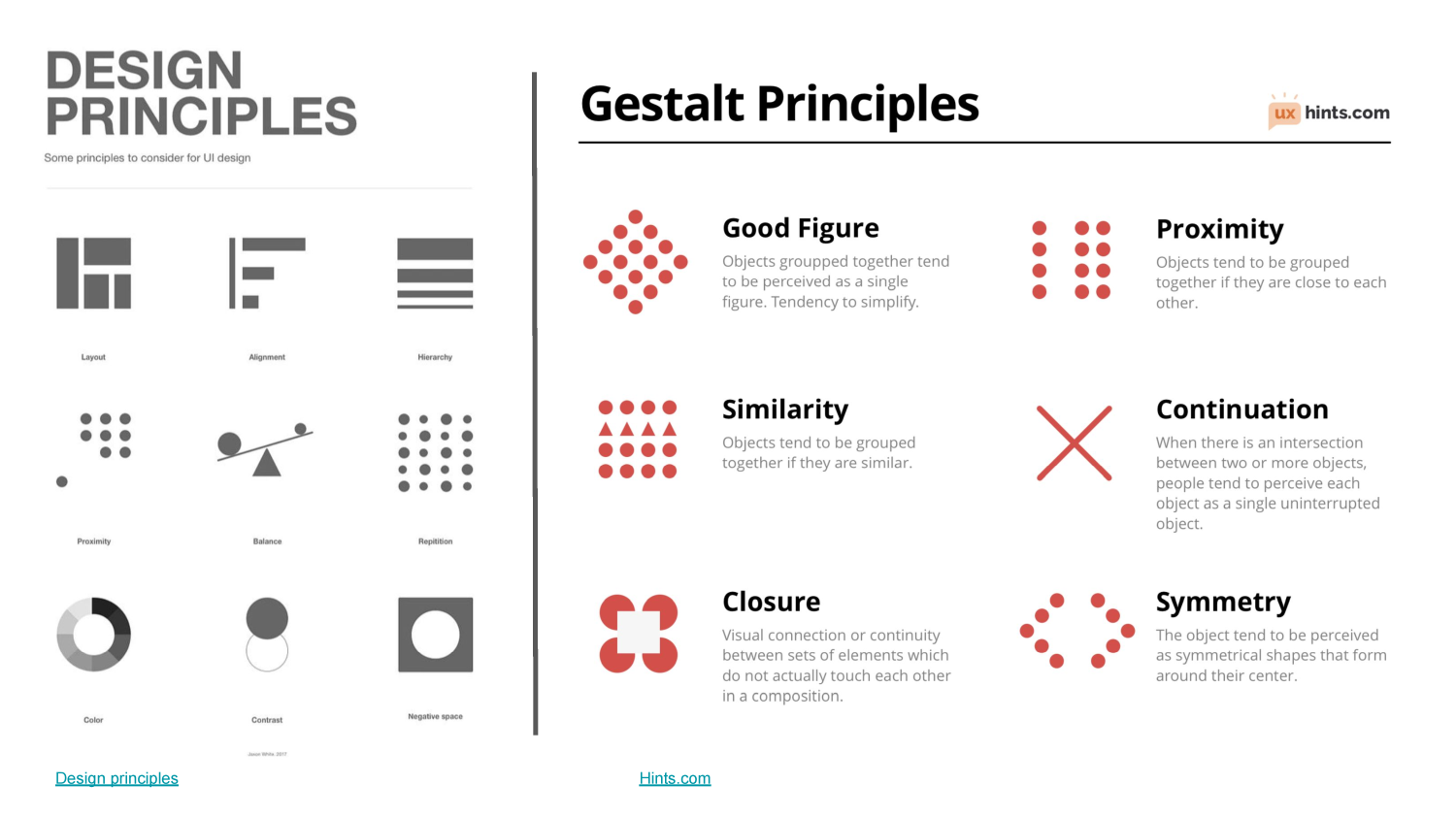
Grouping
- Creates a logical relationship between multiple elements (borders, background, proximity)
- Gestalth law of proximity and similarity
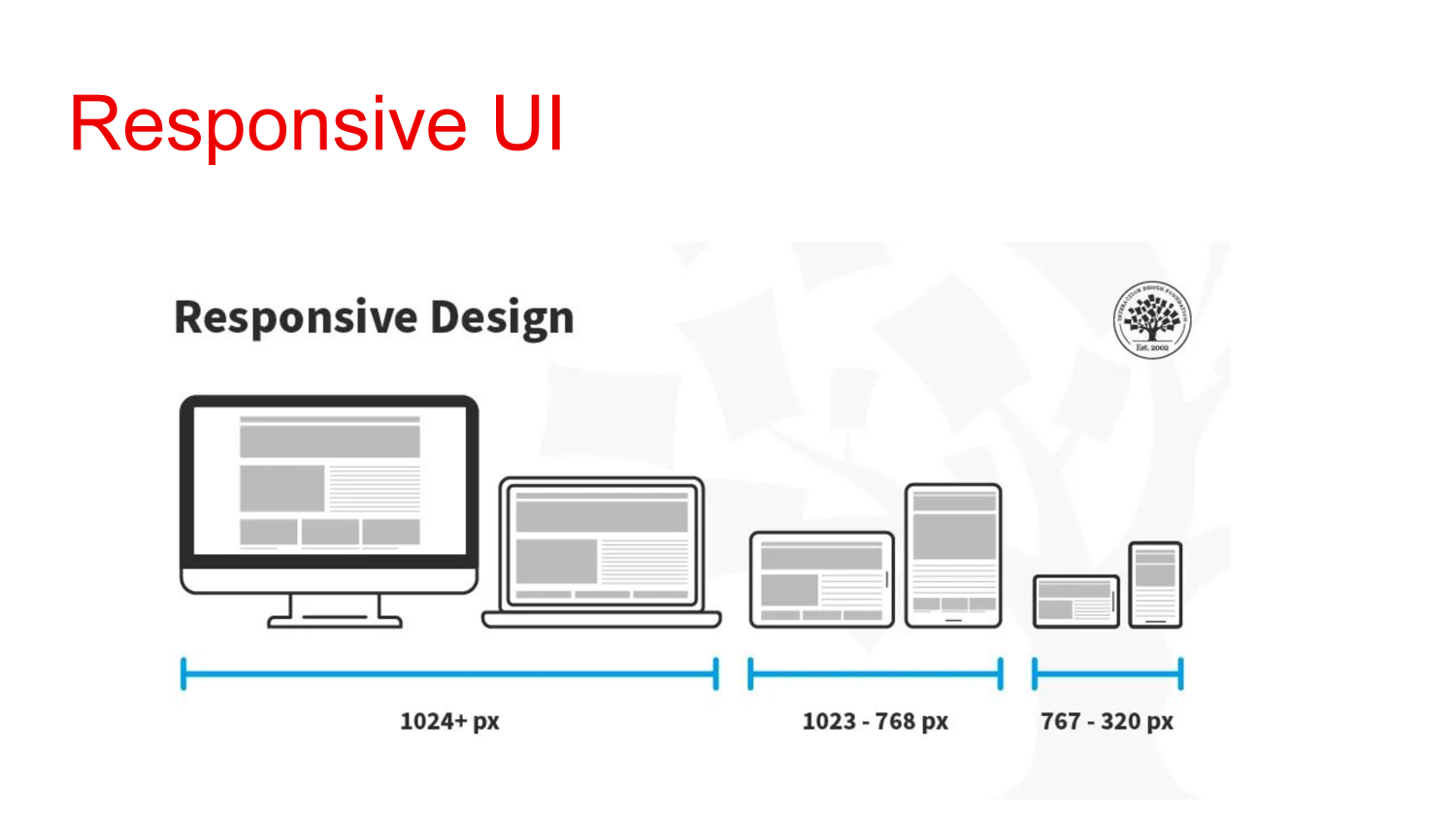
Responsiveness

Usability heuristics
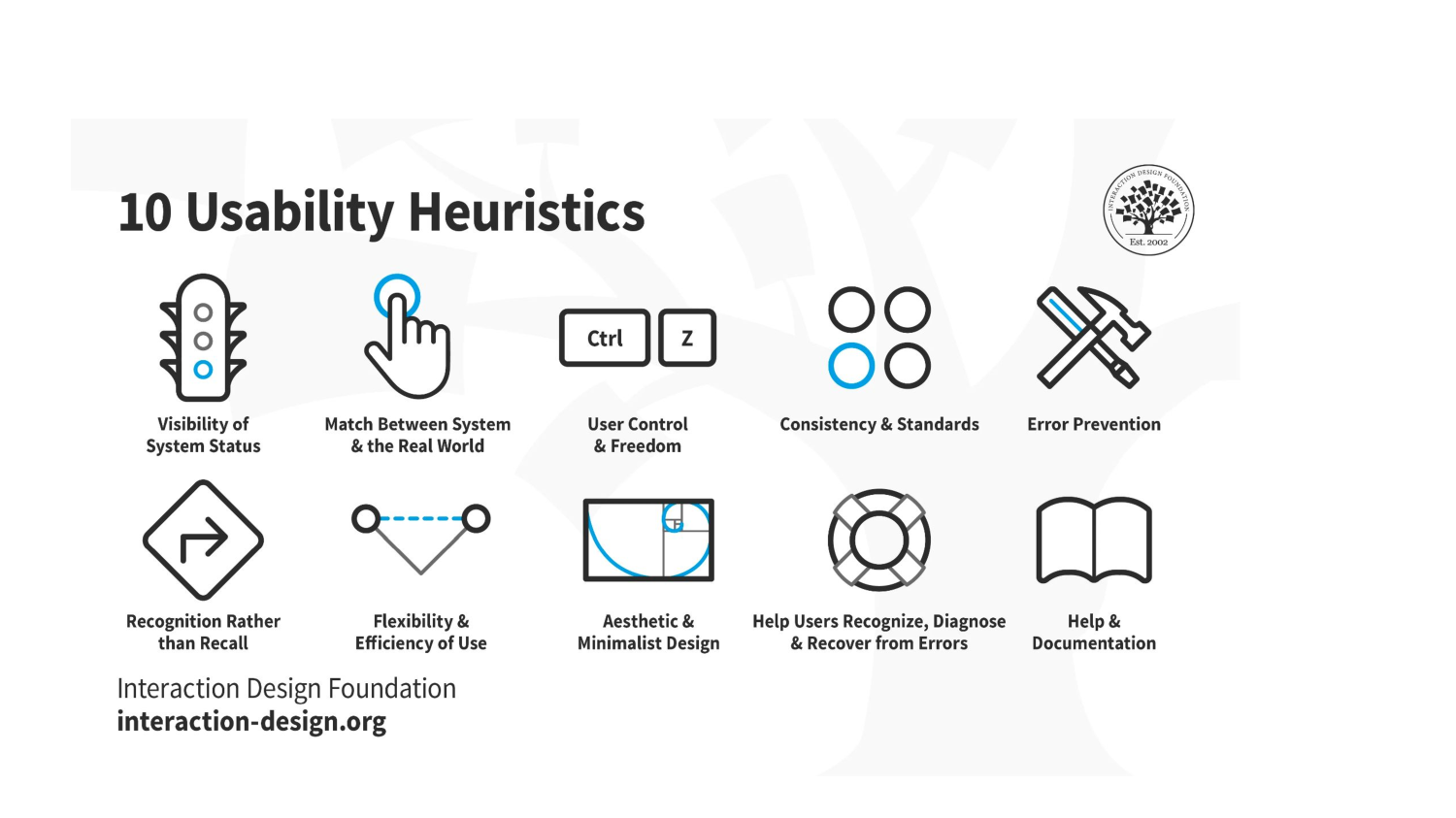
10 NN

5 usability principles
Activity
4 min


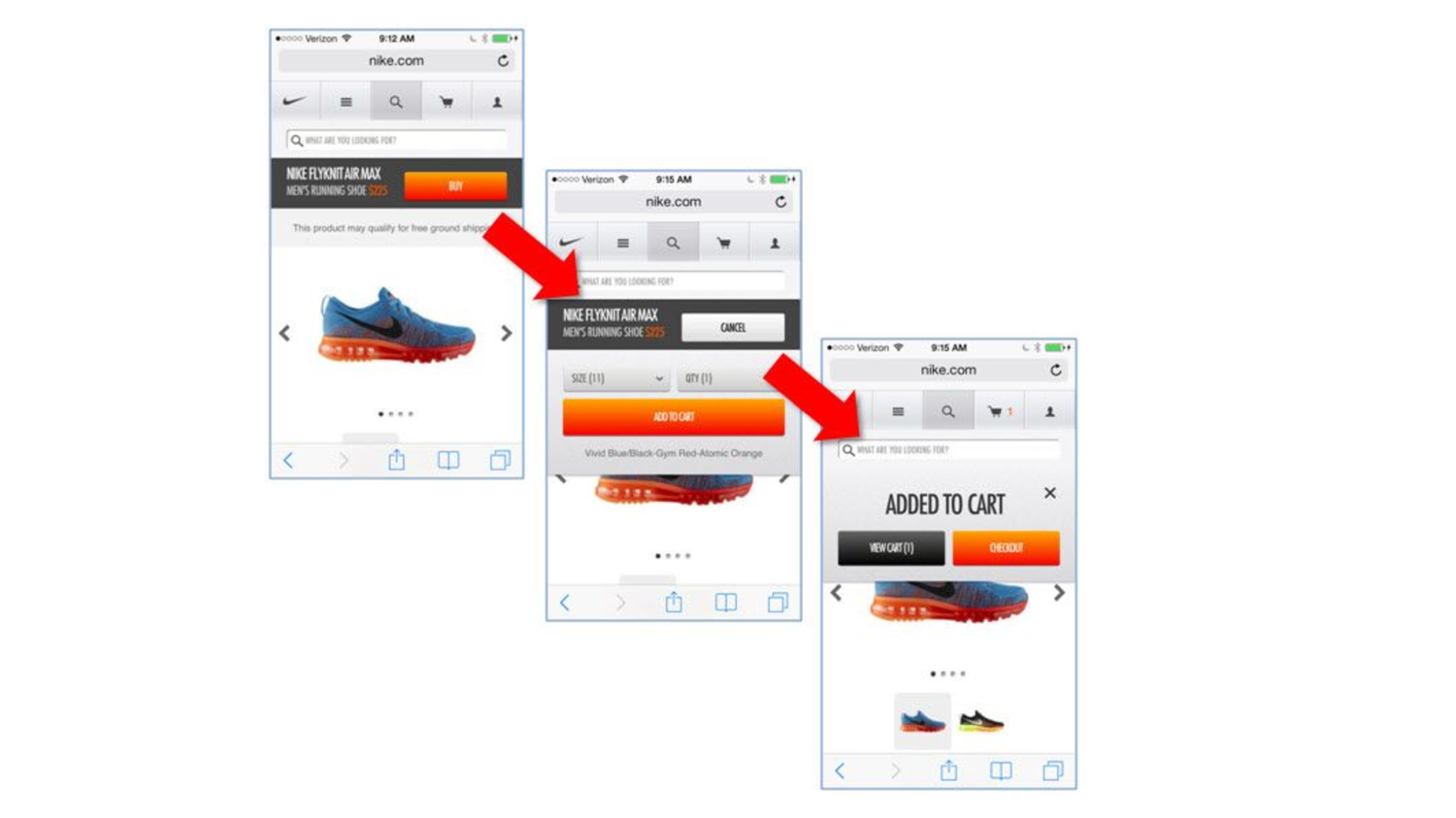
Nielsen's usability heuristics











Activity
8 min
In groups of 3 create the worst experience to rename a file





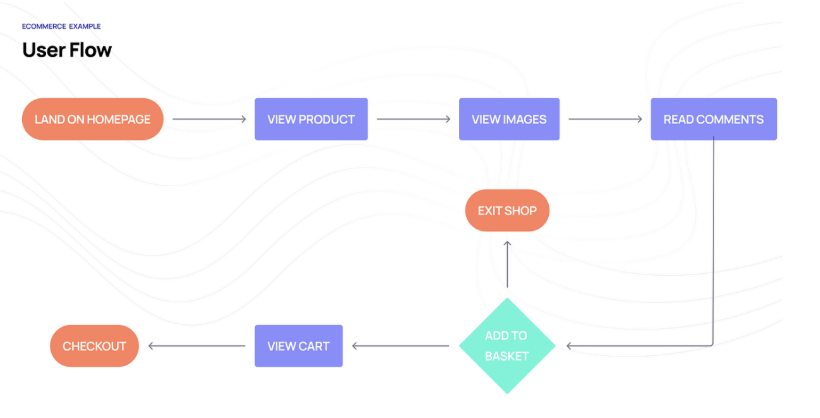
User flow
Text
- Visual representation of the steps a user takes to achieve a goal on a website or app.
- It maps out how users navigate through a product, helping you understand their journey from start to finish.
- Provides a bird’s-eye view of the user’s experience.
-
Helps designers anticipate user needs.
-
Ensures that the interface supports a seamless experience.
-
Identifies potential pain points and areas of friction in the user's journey.
-
What the user is trying to do???
User flow
-
Where the user begins (e.g., homepage, login screen).
-
Decision Points: Choices the user must make (e.g., "Login" or "Sign Up").
-
Actions/Tasks: What the user is trying to do (e.g., filling out a form).
-
End Point: The final goal (e.g., completing a purchase, submitting a form).
-
User flows are a crucial foundation for building wireframes and prototypes.
-
They help ensure your design is user-centered and goal-oriented.
-
Keep it simple and focused on the main task.
-
Think like the user—what steps do they want to take?
-
Don’t include solutions e.g. “clicks on the filter dropdown”.
-
Big picture
User flow
Example: Check the status of your systems
-
User visits homepage.
-
User logs in
-
User views system dashboard
-
User navigates to account settings.
-
User logs out.
User flow - example
Visit homepage
Log in
View
dashboard
Navigate to settings
Log out
Navigate to the Kino Scala page and attempt to purchase tickets for a movie of your choice.
Map the process.
Activity
3 min