PyMKS

Daniel Wheeler
What is PyMKS?
- Developed with Surya Kalidindi's group at GT
- ML library for microstrucutres
- Uses
- Localization
- Homogenization
- Graph based techniques
- Existential question when compared with neural nets
- Mostly using synthetic microstructures and building surrogate models
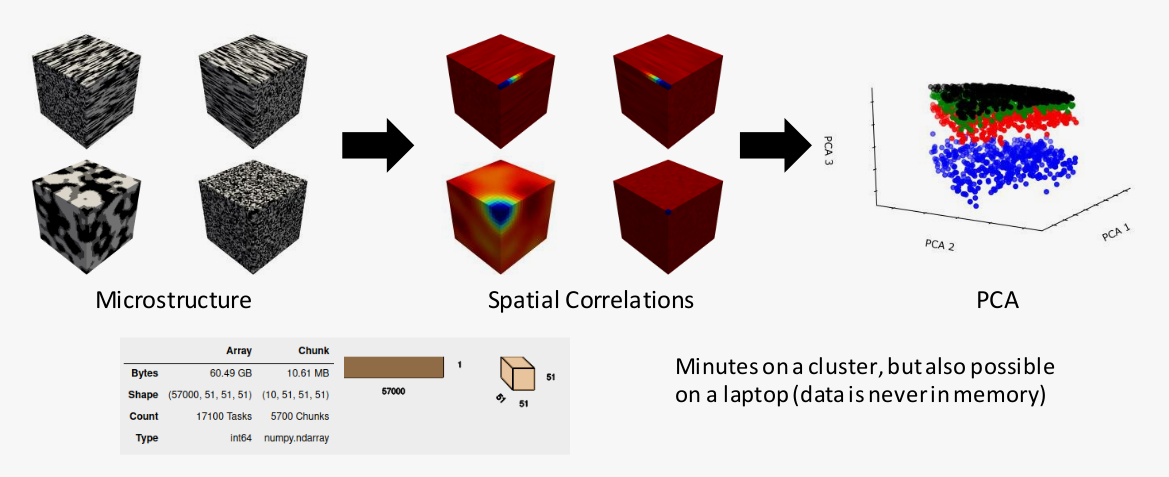
- Parallel + out of memory computations
Data
- Synthetic binary microstructures
- 8900 samples of 51x51x51
- Volume fraction from 25% to 75%
- 4 categories
Metamodel

n \Delta t
model
metamodel
Homogenization

Localization
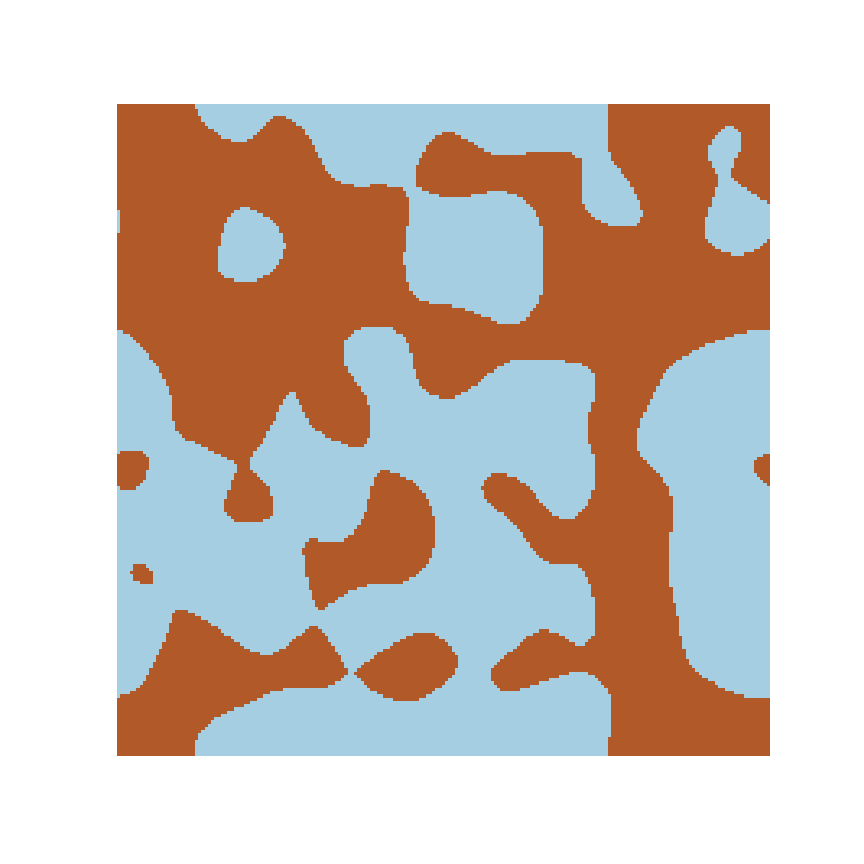
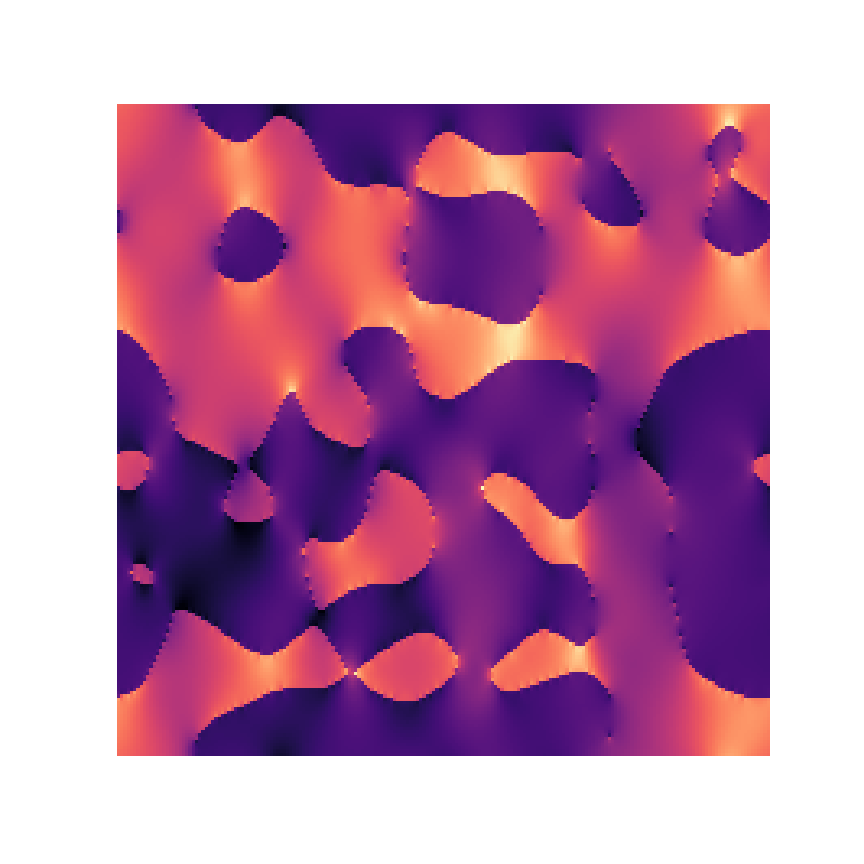
Microstructure
Response
1% displacement
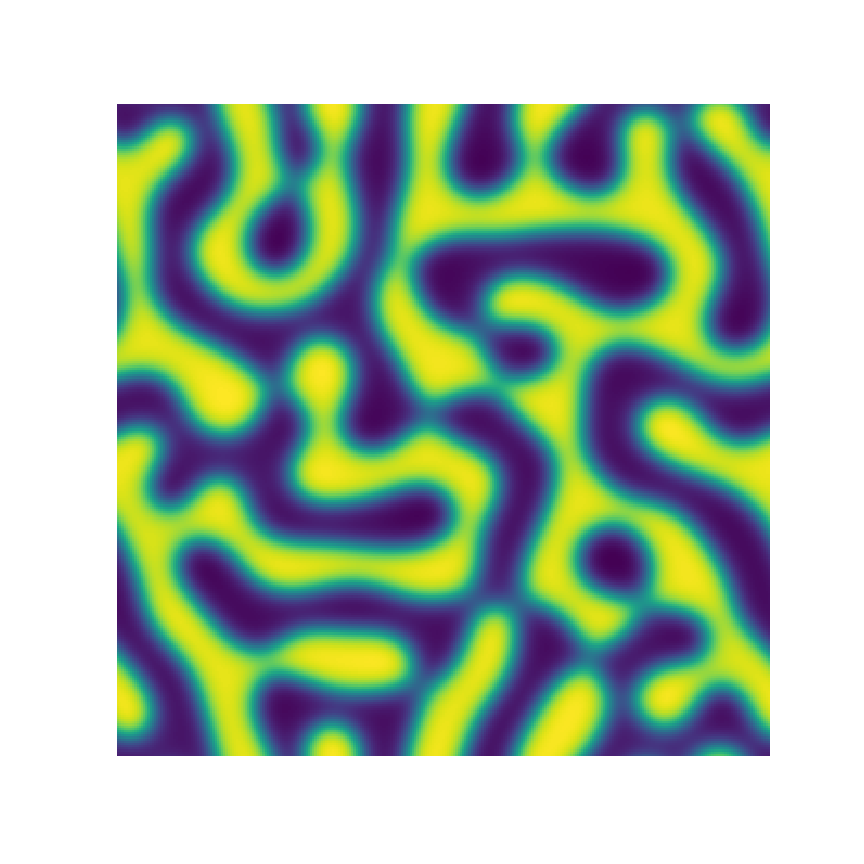
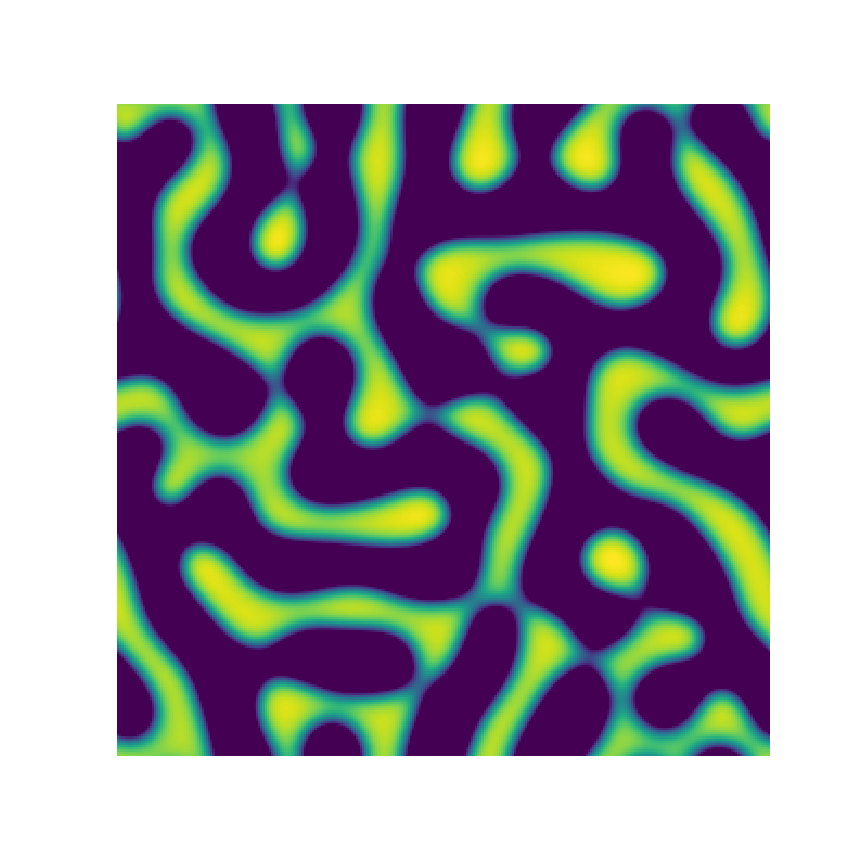
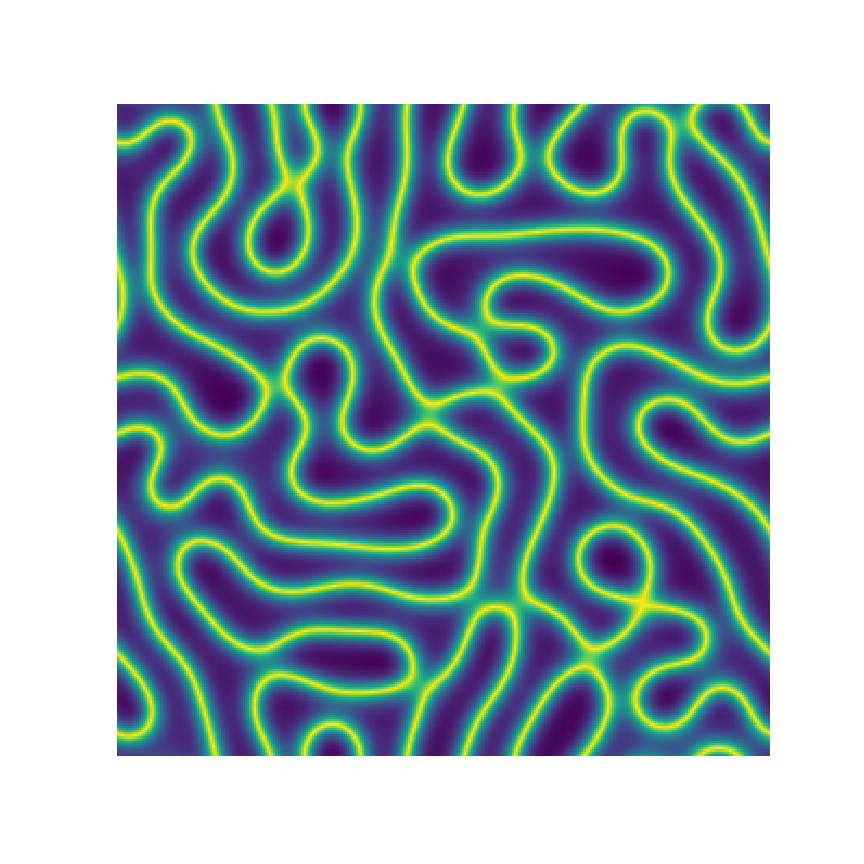
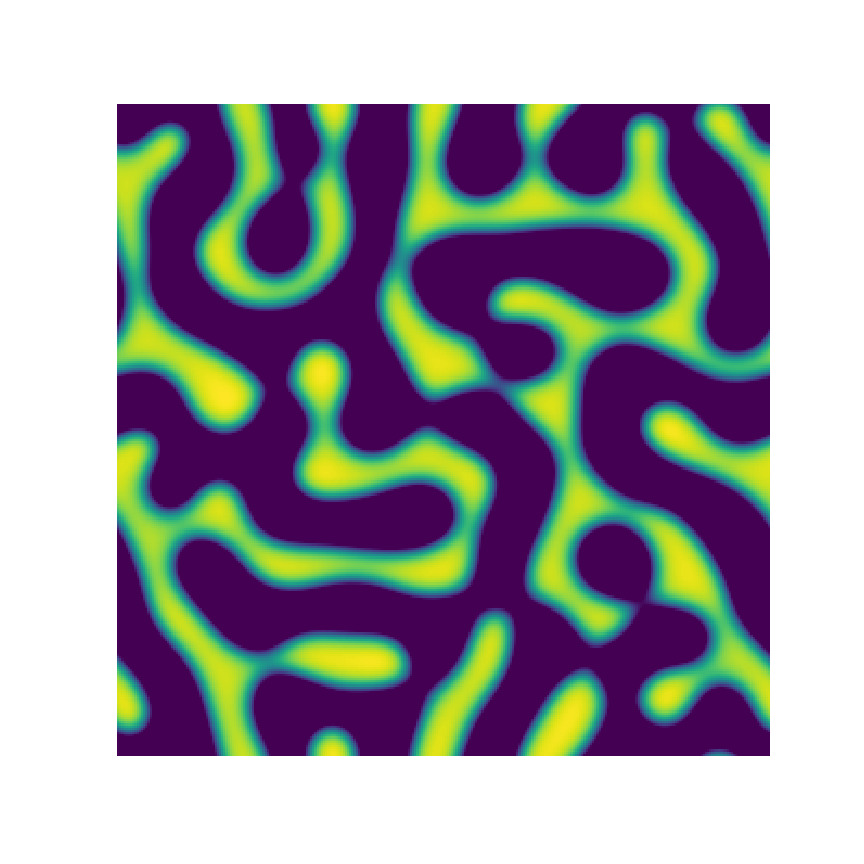
Channel 1
Channel 2
Channel 3
Microstructure Function
2-Point Statistics
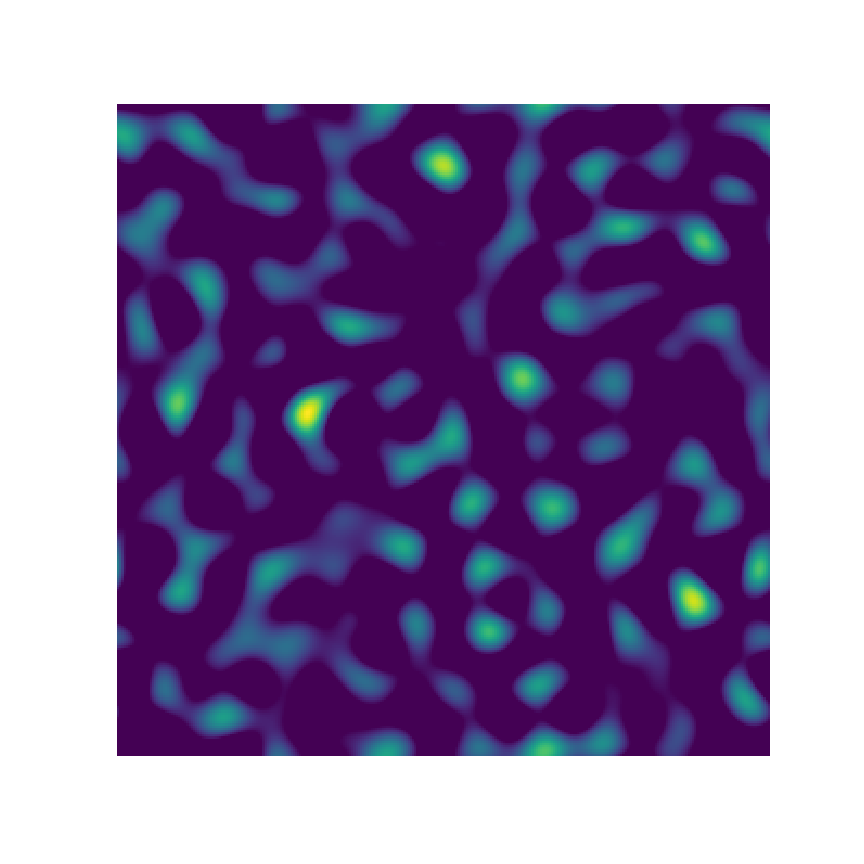
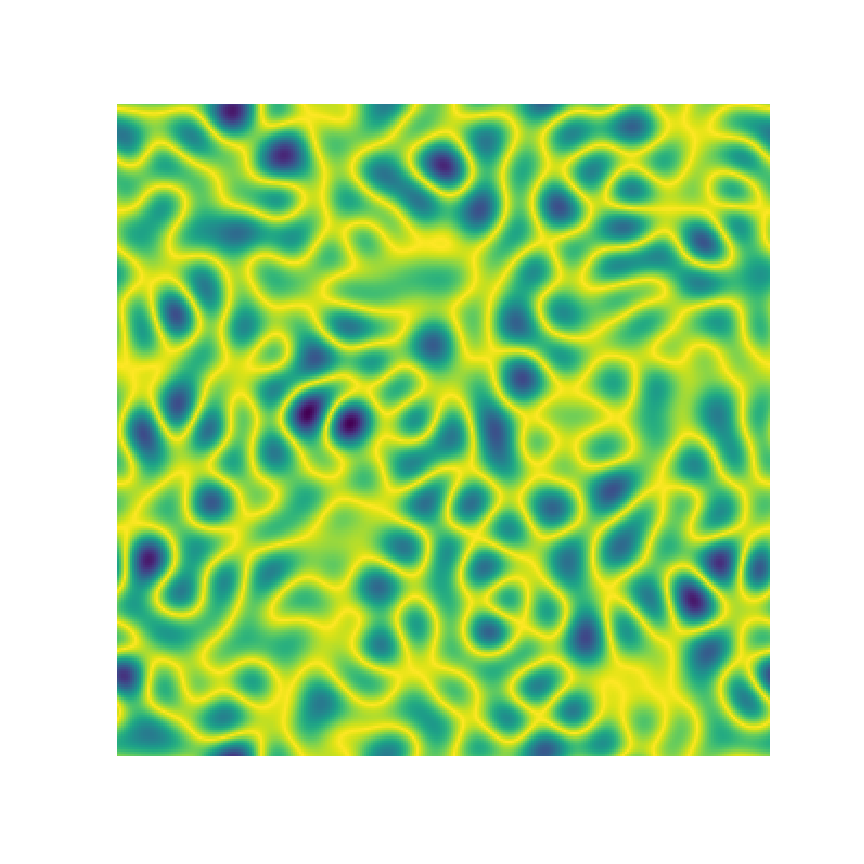

Microstructure Function
- Account for the stochastic nature of the local state
- Unified representation of the microstructure
- Create different mappings for different states
def get_model():
return Pipeline([
('reshape', GenericTransformer(
lambda x: x.reshape(x.shape[0], 51, 51,51)
)),
('discritize', PrimitiveTransformer(n_state=2, min_=0.0, max_=1.0)),
('correlations', TwoPointCorrelation(periodic_boundary=True, correlations=[(0, 0)])),
('flatten', GenericTransformer(lambda x: x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1))),
('pca', PCA(n_components=3, svd_solver='randomized')),#
('poly', PolynomialFeatures(degree=4)),
('regressor', LinearRegression(solver_kwargs={"normalize":False}))
])- All steps are Dask ML components
Pipeline
Graphs and Chunks
Samples v Features
\begin{pmatrix}
\begin{matrix}
m_{11} & m_{12} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{1n} \\
m_{21} & m_{22} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{2n} \\
\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & & & \vdots \\
\vdots & \vdots & & \ddots & & \vdots \\
\vdots & \vdots & & & \ddots & \vdots \\
m_{l1} & m_{l2} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{ln}
\end{matrix}
\end{pmatrix}
\begin{pmatrix}
\begin{matrix}
r_{1} \\
r_{2} \\
\vdots \\
\vdots \\
\vdots \\
r_{l}
\end{matrix}
\end{pmatrix}
Samples
Features



Microstructure
Response
Make New Features
\begin{pmatrix}
\begin{matrix}
m_{11} & m_{12} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{1n} \\
m_{21} & m_{22} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{2n} \\
\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & & & \vdots \\
\vdots & \vdots & & \ddots & & \vdots \\
\vdots & \vdots & & & \ddots & \vdots \\
m_{l1} & m_{l2} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{ln}
\end{matrix}
\end{pmatrix}





New features
n \gg l
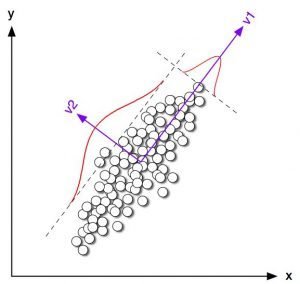
Dimensionality Reduction
\begin{pmatrix}
\begin{matrix}
m_{11} & m_{12} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{1n} \\
m_{21} & m_{22} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{2n} \\
\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & & & \vdots \\
\vdots & \vdots & & \ddots & & \vdots \\
\vdots & \vdots & & & \ddots & \vdots \\
m_{l1} & m_{l2} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{ln}
\end{matrix}
\end{pmatrix}
Reduce features
l \gg n
n \gg l
Learning
\begin{pmatrix}
\begin{matrix}
m_{11} & m_{12} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{1n} \\
m_{21} & m_{22} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{2n} \\
\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & & & \vdots \\
\vdots & \vdots & & \ddots & & \vdots \\
\vdots & \vdots & & & \ddots & \vdots \\
m_{l1} & m_{l2} & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & m_{ln}
\end{matrix}
\end{pmatrix}
l \gg n
\begin{pmatrix}
\begin{matrix}
r_{1} \\
r_{2} \\
\vdots \\
\vdots \\
\vdots \\
r_{l}
\end{matrix}
\end{pmatrix}
Microstructure
Response
Microstructure
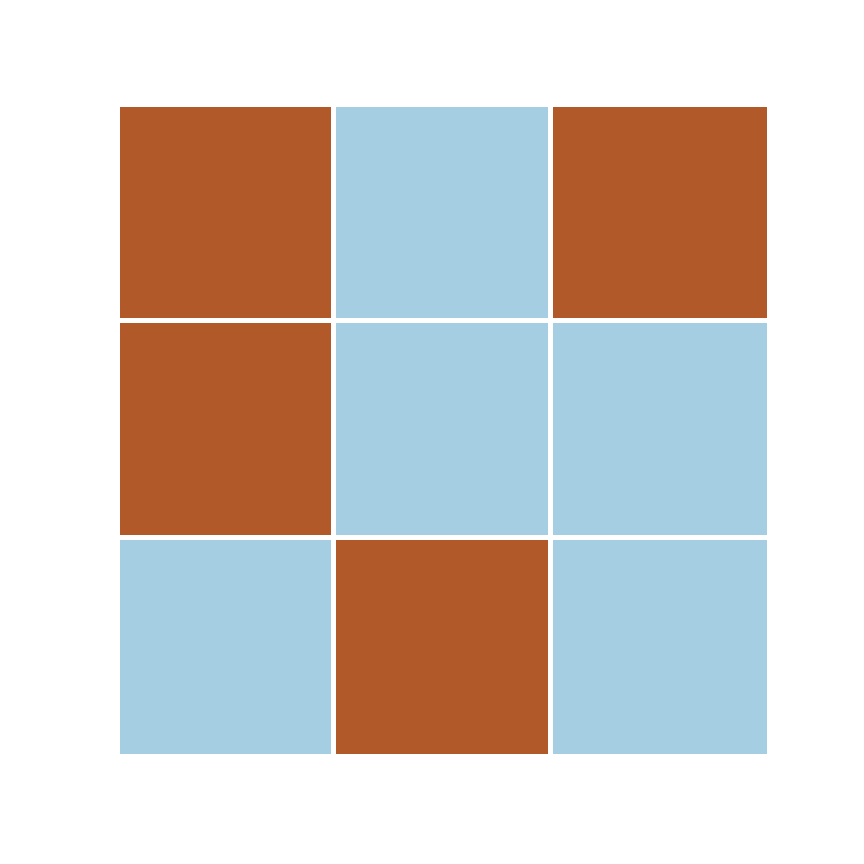
s = [0, 0]
s = [1, 0]
s = [2, 0]
s = [2, 1]
s = [1, 1]
s = [0, 1]
s = [0, 2]
s = [1, 2]
s = [2, 2]
\phi_k(\vec{s})
continuous:
discrete:
\phi_k[[i, j]]
\phi_k[[0, 0]] = 0
\phi_k[[0, 2]] = 1
categorical data
Microstructure
s = [0, 0]
s = [1, 0]
s = [2, 0]
s = [2, 1]
s = [1, 1]
s = [0, 1]
s = [0, 2]
s = [1, 2]
s = [2, 2]
\phi_k[[0, 1]] = 0.9
\phi_k[[0, 2]] = 0.1
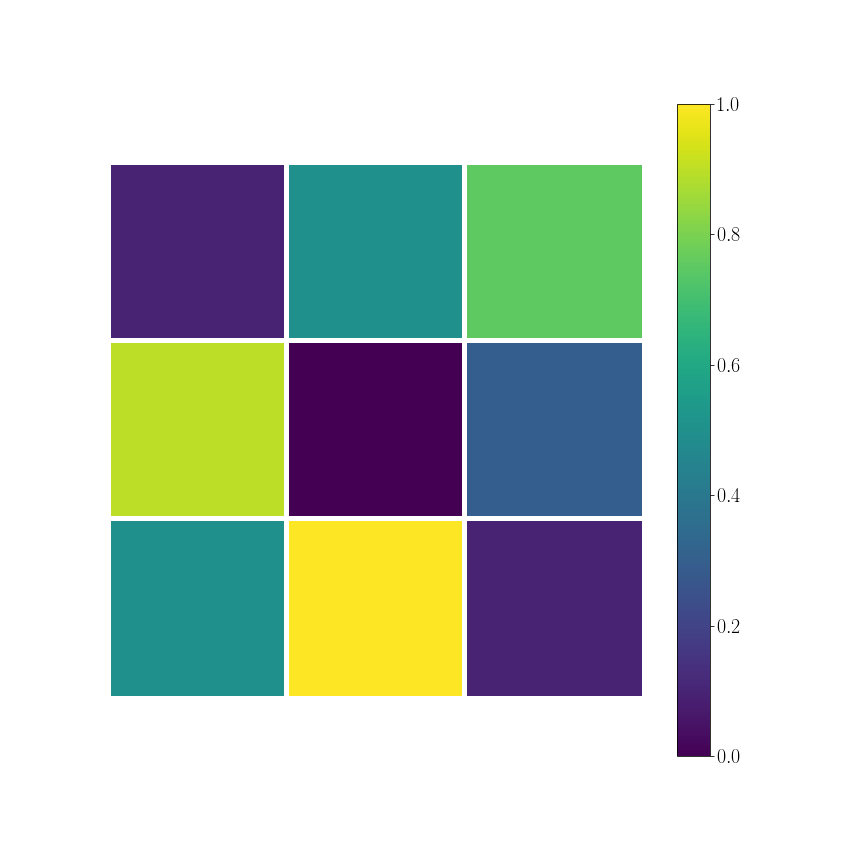
continuous data
Microstructure Function
\phi_k(\vec{s})
m_k(h; \vec{s})
\phi_k(\vec{s}) = \int_H h \; m_k(h; \vec{s}) \; dh
\int_H m_k(h; \vec{s}) \; dh = 1
m_k(h; \vec{s}) = \delta(h - \phi_k(\vec{s}))
Microstructure Function
\phi_k[s]
m_k[h; s]
m_k[h; s] = \delta[h - \phi_k[s]]
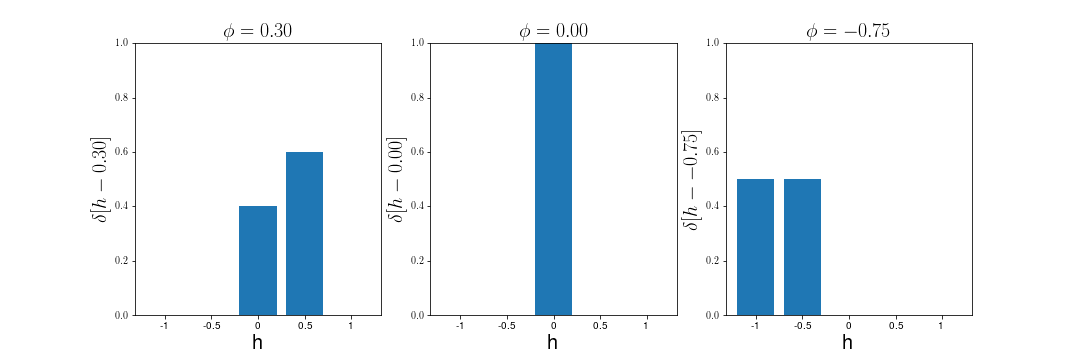
\delta [x] = \max \left( 1 - \left|\frac{x}{\Delta h}\right|, 0 \right)
Microstructure Function

s = [0, 0]
s = [1, 0]
s = [2, 0]
s = [2, 1]
s = [1, 1]
s = [0, 1]
s = [0, 2]
s = [1, 2]
s = [2, 2]
\phi_0[[0, 2]] = 1 \;\;\; m_0[0; [0, 2]] = 0
\phi_0[[0, 2]] = 1 \;\;\; m_0[1; [0, 2]] = 1
\phi_0[[0, 0]] = 0 \;\;\; m_0[0; [0, 0]] = 1
\phi_0[[0, 0]] = 0 \;\;\; m_0[1; [0, 0]] = 0
2-Point Stats

s = [0, 0]
s = [1, 0]
s = [2, 0]
s = [2, 1]
s = [1, 1]
s = [0, 1]
s = [0, 2]
s = [1, 2]
s = [2, 2]
f_k[h, h';r] = \frac{1}{\Omega_j[s]} \sum_{s \in S} m_k[h; s] m_k[h'; s + r]
f_0[0, 0; [0, 0]] = 5 / 9
f_0[1, 1; [0, 0]] = 4 / 9
f_0[0, 1; [0, 0]] = 0 / 9
f_0[1, 0; [2, -1]] = 3 / 9
f_0[1, 1; [2, -1]] = 1 / 9