Go testing
Different test cases
Unit testing
Functional testing
E2E testing
Fuzzing
Unit testing
Unit testing is a software development process in which the smallest testable parts of an application, called units, are individually and independently scrutinized for proper operation
Unit testing
go test -v ./...Unit testing
=== RUN TestMyPassed
--- PASS: TestMyPassed (0.00s)=== RUN TestMyFailed
--- FAIL: TestMyFailed (0.00s)Unit testing
package demo
var the_var = "the_value"
func awesome() (s string) {
if the_var == "the_value" {
s = "working"
}
if len(the_var) == 0 {
s = "empty"
}
if the_var == "bypass" {
s = "bypass"
}
if called(the_var) {
s = "called"
}
return
}
Unit testing
func Test_awesome(t *testing.T) {
if awesome() != "working" {
t.Errorf("The awesome function must return `working` while passed initial value, %s given", awesome())
}
the_var = ""
if awesome() != "empty" {
t.Errorf("The awesome function must return an empty string while passed empty value, %s given", awesome())
}
the_var = "bypass"
if awesome() != "bypass" {
t.Errorf("The awesome function must return `bypass` string while passed `bypass` value, %s given", awesome())
}
the_var = "another_valid"
if awesome() != "called" {
t.Errorf("The awesome function must return `called` string while passed `another_valid` value, %s given", awesome())
}
}Unit testing
func Test_awesome_working(t *testing.T) {
if awesome() != "working" {
t.Errorf("The awesome function must return `working` while passed initial value, %s given", awesome())
}
}
func Test_awesome_empty(t *testing.T) {
the_var = ""
if awesome() != "empty" {
t.Errorf("The awesome function must return an empty string while passed empty value, %s given", awesome())
}
}
func Test_awesome_bypass(t *testing.T) {
the_var = "bypass"
if awesome() != "bypass" {
t.Errorf("The awesome function must return `bypass` string while passed `bypass` value, %s given", awesome())
}
}
func Test_awesome_called(t *testing.T) {
the_var = "another_valid"
if awesome() != "called" {
t.Errorf("The awesome function must return `called` string while passed `another_valid` value, %s given", awesome())
}
}Unit testing
ok my_package 0.155s coverage: 92.9% of statements
my_package/main.go:5: called 80.0%
my_package/main.go:17: awesome 100.0%
total: (statements) 92.9%go test ./... -coverprofile cover.out && \
go tool cover -func cover.outUnit testing
func Test_called_valid(t *testing.T) {
if !called("valid") {
t.Errorf("The called function must return `true` while passed a valid value, %v given", called("valid"))
}
}ok my_package 0.180s coverage: 100.0% of statements
my_package/main.go:5: called 100.0%
my_package/main.go:17: awesome 100.0%
total: (statements) 100.0%Unit testing
Les race conditions
A race condition occurs when multiple threads try to access and modify the same data (memory address).
Unit testing
var sharedInt int = 0
var unusedValue int = 0
func runSimpleReader() {
for {
var val int = sharedInt
if val%10 == 0 {
unusedValue = unusedValue + 1
}
}
}
func runSimpleWriter() {
for {
sharedInt = sharedInt + 1
}
}
func startSimpleReadWrite() {
go runSimpleReader()
go runSimpleWriter()
time.Sleep(10 * time.Second)
}Unit testing
go run -race .==================
WARNING: DATA RACEFuzzing
In programming and software development, fuzzing or fuzz testing is an automated software testing technique that involves providing invalid, unexpected, or random data as inputs to a computer program
Fuzzing
Fuzzing
Introduced in Go 1.18
Differ from classic testing.T
Implement fuzzing interface testing.F
Fuzzing
go test -v -fuzztime=2s ./...Fuzzing
package demo
import "testing"
func FuzzThis(f *testing.F) {
f.Fuzz(func(t *testing.T, a string) {
if value(a) {
t.Error("The value is equal to `this is my value`.")
}
})
}package demo
import "testing"
func value(v string) bool {
return v == "this is my value"
}Fuzzing
=== RUN FuzzThis
=== RUN FuzzThis/04358d4af4e8ef32223beec89298ad6721bfc244a75b77a139bd898d3bb3cbcc
=== RUN FuzzThis/28e3bb38264eccee98122f81aa5be66182144a75e42aa783fcf10509c2127083
=== RUN FuzzThis/43b9989630564313daa99fbd4cbb4ee155f698e3332d7af823ab87b5a1897618
--- PASS: FuzzThis (0.00s)
--- PASS: FuzzThis/04358d4af4e8ef32223beec89298ad6721bfc244a75b77a139bd898d3bb3cbcc (0.00s)
--- PASS: FuzzThis/28e3bb38264eccee98122f81aa5be66182144a75e42aa783fcf10509c2127083 (0.00s)
--- PASS: FuzzThis/43b9989630564313daa99fbd4cbb4ee155f698e3332d7af823ab87b5a1897618 (0.00s)
PASS
ok something 0.156s
Fuzzing
package demo
import "testing"
func FuzzThis(f *testing.F) {
f.Add("this is my ")
f.Fuzz(func(t *testing.T, a string) {
if value(a) {
t.Error("The value is equal to `this is my value`.")
}
})
}package demo
import "testing"
func value(v string) bool {
return v == "this is my value"
}Fuzzing
=== RUN FuzzThis
=== RUN FuzzThis/seed#0
base_test.go:12: The value is equal to `this is my value`.
=== RUN FuzzThis/04358d4af4e8ef32223beec89298ad6721bfc244a75b77a139bd898d3bb3cbcc
=== RUN FuzzThis/28e3bb38264eccee98122f81aa5be66182144a75e42aa783fcf10509c2127083
=== RUN FuzzThis/43b9989630564313daa99fbd4cbb4ee155f698e3332d7af823ab87b5a1897618
--- FAIL: FuzzThis (0.00s)
--- FAIL: FuzzThis/seed#0 (0.00s)
--- PASS: FuzzThis/04358d4af4e8ef32223beec89298ad6721bfc244a75b77a139bd898d3bb3cbcc (0.00s)
--- PASS: FuzzThis/28e3bb38264eccee98122f81aa5be66182144a75e42aa783fcf10509c2127083 (0.00s)
--- PASS: FuzzThis/43b9989630564313daa99fbd4cbb4ee155f698e3332d7af823ab87b5a1897618 (0.00s)
FAIL
FAIL something 0.206s
FAILFuzzing
More complex fuzzing
https://github.com/google/gofuzz
https://github.com/dvyukov/go-fuzz
Functional testing
Test your feature according to the specifications
Functional testing
I developed an API
I want to test the behavior
I will write a service mock
I send an HTTP request to my API
Wait and see...
Functional testing
req := httptest.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, "/handled", nil)
app.ServeHTTP(res, req)database := mockDatabase()database.get("Something", "VALUE")Functional testing
{
debug
}
:4443
route /mock-my-external-route-empty-body {
header Content-Type application/json
respond "{}"
}
route /mock-my-external-route-filled-body {
header Content-Type application/json
respond "{\"is_filled\": true}"
}Functional testing
Mock the external services
Reduce dependencies
Ensure the app resilience
E2E tests
test the functionality and performance of an application under product-like circumstances and data to replicate live settings
E2E tests
Postman / Insomnia
Cypress / Selenium
Postman
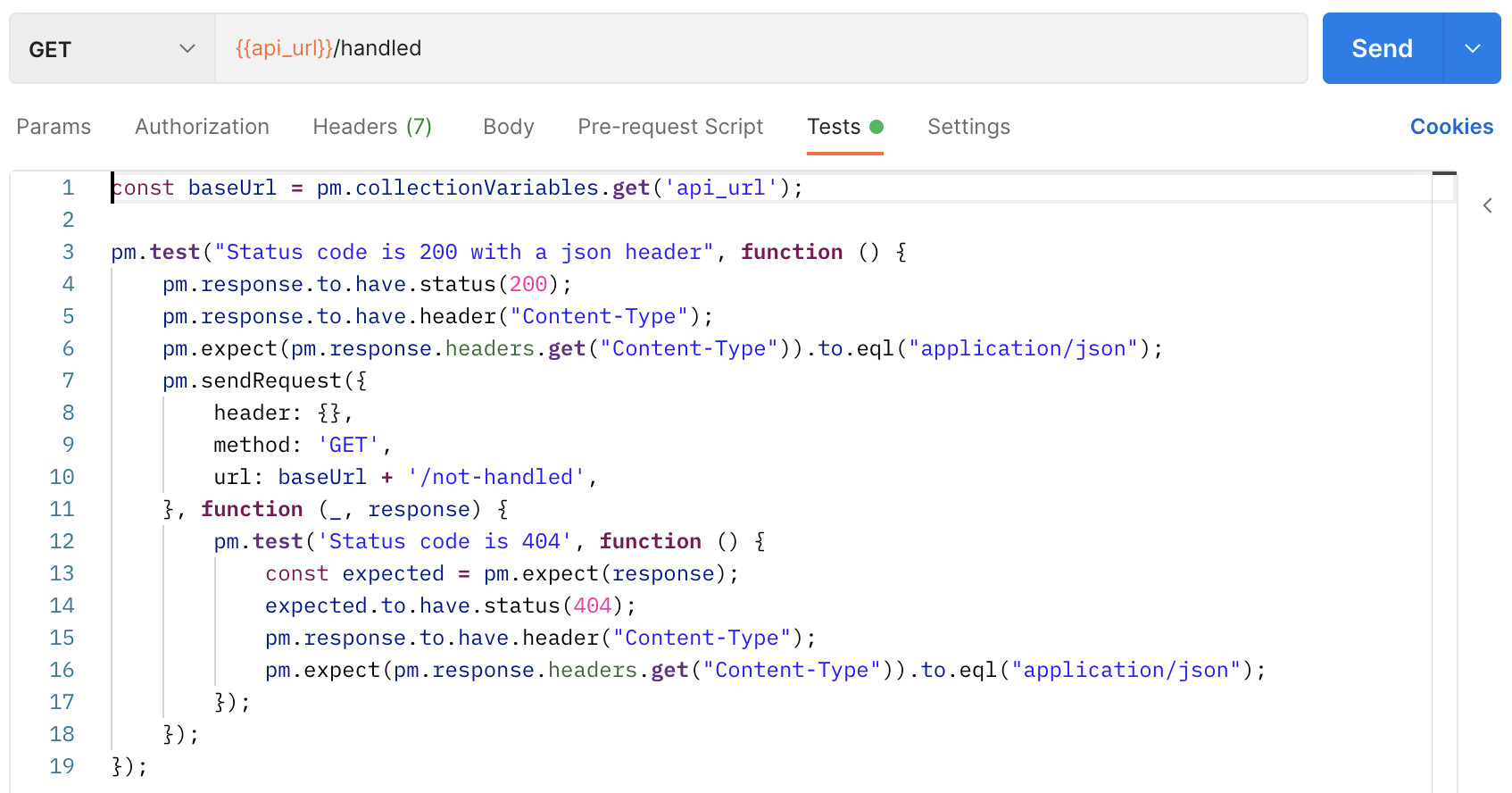
Postman
npm install -g newman
newman run my-collection.jsonPostman
version: v1.0
name: cds_goes_bruh
jobs:
- job: Run newman/E2E tests
steps:
#...
- script:
- '#!/bin/bash'
- npm install -g newman
- newman run my-collection.json
requirements:
- binary: npmDid I hear CDS?
I don't know if it's really working