Winter School in Political Economy
Seminar 1
Intro
Let's meet
- We will split into small groups
- Name your favourite movie, play, record, painting or book
- Think of a Political Economy angle in this work (of art)
- Return to the main channel and introduce your ideas
- Let's sketch them on a white-board
Let's meet
- What is your name?
- What is your story?
Set-up of the seminar
- Introduction to (the theory of) Political Economy
- Course overview
- Group discussion
- Format: 45 / break / 45 / break / 25
Political Economy
What is PE
and why is it worth studying?

Discipline:
Political economy addresses real-world concerns in a way that emphasizes the connections between economic problems, social structures and political processes (Stilwell, p.9, 2012)
Focus:
- State-market interaction
- Markets as design
- Embeddedness
- Capitalism (and crisis)
- Development (and the West)
- Conflict and Cooperation
Covid-19
- Intertwined relation between policy-makers and markets
- Political decisions influence (or not) economic performance
- Economic performance influences political decisions
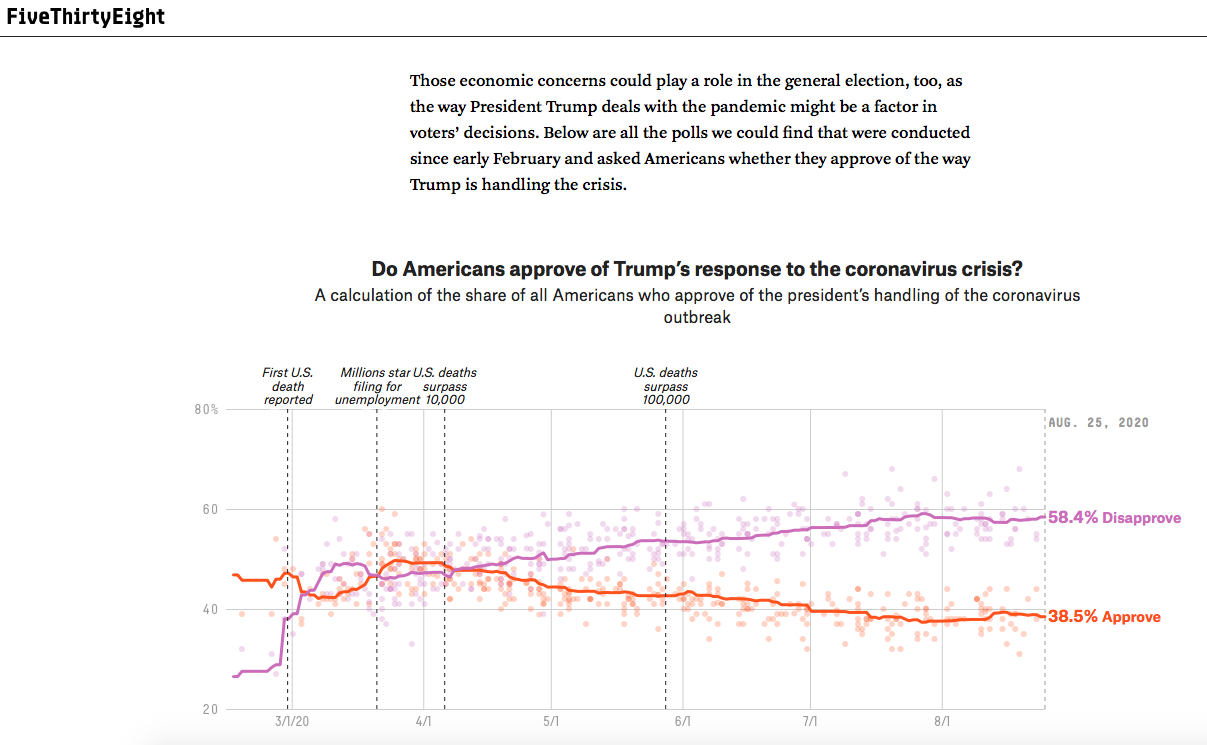
Covid-19
- Reveals the ability of different political regimes to address a major health crisis (and associated economics crisis)

Theory in PE
What is (neo)mercantilism and liberalism, and what are the critical perspectives?

Realism
Premises
- Anarchic international system
- Primacy of the state;
- but constrained by domestic actors and structure of international relations
- Importance of relative gains
- Focus on Plenty, as a mean for Power
- Distinction between scholarship and policy
Neomercantilist policy
- Hamilton and List
- Positive blance of trade
- Protectionism temporary and targeted, but not for agriculture
- Free trade in the long run
- Russia, China and US
Q&A on mercantilsm
- What are the strengths and weakness of the neomercantilist perspective?
- What is hegemony and how theories differ in their views regarding the current status of the USA?
Smith on mercantilism
Viner, J. (1948) Power Versus Plenty as Objective of Foreign Policy in the 17th and 18th Century. World Politics, 1(1), pp.1-29.

Liberalism
Premises
- Free trade and comparative advantage
- Absolute gains
- Role of international organisations
- Think about WHO today
- Interdependance
- Cooperation
Q&A on liberalism
- What are the differences and similarities between orthodox, interventionist and institutional liberalism?
- What is neoliberalism?
Critical Schools
Dependency theory
- Originates in Marxism and Latin American Structuralism
- Rejection of Marx's view that South benefits from capitalist economic relations with the North
- Workers in the South only increase their dependance on North
- Relations of exchange rather than relation of production
- Import-substitution industrialisation
Q&A on critical perspectives
- What are the similarities and differences between Marxism and dependency theory?
- How gender issues should be addressed in IPE?
- What is the relation between environmentalism and the main perspectives in IPE?
Let's work on an assignment together

Complete the table
| Realism | Liberalism | Historical materialism | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actors | |||
| Structure | |||
| Argument | |||
| Cooperation | |||
| Varieties | |||
| Authors |
Now let's work it out together
| Realism | Liberalism | Historical materialism | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actors | State | Many | Class, gender |
| Structure | Anarchy | Interdependence | Hierarchy |
| Argument | Competition | Cooperation | Exploitation |
| Cooperation | Strategic | Voluntary | Class-based |
| Varieties | (neo)mercantilism | Orthodox | Marxism |
| Authors | Krasner | Keohane | Cox |
Break
Individual assignment
Atlas of Economic Complexity
Please spend the next 10 minutes browsing through the AEC data. Look for changes, patterns and dynamics. It can be states, products, trade flows or regions – or an interaction of these.

Group assignment
Brining data and theory together
- In small groups over the next 20 minutes
- Return to the Atlas of Economic Complexity
- Select an interesting empirical dynamic
- Reflect on it from the perspective of a theory of PE; think about:
- who are the actors?
- how do they interact?
- what kind of constraints do they face?
- is there a conflict and if yes, of what nature?
- are there any patterns emerging in the data?
Course overview
Course overview
- How we will work
- two seminars – live
- four lectures – recoded
- Q&A – live
- Canvas is crucial
- Three graded assignments
- preparatory assignment (done)
- podcast
- final paper
House rules
- Be prepared
- Read
- Ask questions (really)
- Late arrival
- Zoom etiquette
Important
- Podcast
- due on Tuesday 24 Jan 2023 at 23:59 (CET)
- worth 30% of the final grade
- 6-8 minutes in length
- more information in Week 1 (lecture)
- Final essay
- due on Friday 24 Feb 2023 at 23:59 (CET)
- worth 50% of the final grade
- 3,000 words
- more information in Week 2 (lecture)
- proposal of the essay (800 words) due on Friday 10 Feb 2023 for peer-review and comments from me
Questions?

Break
Disscussion
What drives development?
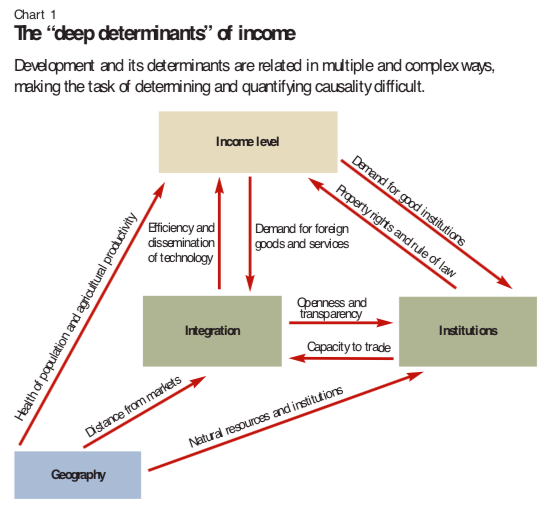
- Institutions through property rights an rule of law increase income levels
- What about reverse causality?
- Are the mechanisms correctly specified (think PL or HU)
Whiteboard
- Let's keep some of the ideas on the whiteboard
- Let's try to identify puzzles or research questions