Active Inference with Semi-markov models

Dimitrije Marković
Theoretical Neurobiology Meeting
01.03.2020
Active inference and semi-markov decision processes
-
(Part I) Active inference in multi-armed bandits
- Empirical comparison with UCB and Thompson sampling.
- https://slides.com/dimarkov/ai-mbs
-
(Part II) Active inference and semi-Markov processes
- Hidden semi-Markov models and a representation of state duration.
- Learning the hidden temporal structure of state transitions.
- Application: Reversal learning task.
-
(Part III) Active inference and semi-Markov decision processes
- Extending policies with action (policy) duration.
- Decision about when actions should be taken and for how long.
- Applications: Temporal attention, intertemporal choices.
Active inference and semi-markov decision processes
-
(Part I) Active inference in multi-armed bandits
- Empirical comparison with UCB and Thompson sampling.
- https://slides.com/dimarkov/ai-mbs
-
(Part II) Active inference and semi-Markov processes
- Hidden semi-Markov models and a representation of state duration.
- Learning the hidden temporal structure of state transitions.
- Application: Reversal learning task.
-
(Part III) Active inference and semi-Markov decision processes
- Extending policies with action (policy) duration.
- Decision about when actions should be taken and for how long.
- Applications: Temporal attention, intertemporal choices.
-
(Part II) Active inference and semi-Markov processes
- Hidden semi-Markov models and a representation of state duration.
- Learning the hidden temporal structure of state transitions.
- Application: Reversal learning task.
Semi-Markov processes
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markov_renewal_process#Relation_to_other_stochastic_processes
- State space S
- Jump times \(T_n\) and states \( X_n\)
- Inter-arrival time \( \tau_n = T_n - T_{n-1}\)
- The sequence \( [(X_0, T_0), \ldots, (X_n, T_n), \ldots]\) is called a Markov renewal process if:
If \( Y_t \equiv X_n \) for \( t \in \left[T_n, T_{n+1} \right)\) then the process \(Y_t\) is called a semi-Markov process
Semi-Markov processes
State space \( S\)
\( \ldots\)
\( \ldots\)
Time
Special cases
For exponentially distributed iid waiting times we have a continuous time Markov chain
A discrete time Markov chain has geometrically distributed waiting times
Hidden Semi-Markov models
Shun-Cheng Yu, "Hidden semi-Markov Models: Theory, Algorithms and Applications", Elsevir 2016.
A graphical representation of HSMM
Latent variables
outcomes
Example
\( f \in \{1, 2, 3\}\)
time step
\( s \in \{A, B\}\)
Example
\( f \in \{1, 2, 3\}\)
time step
\( s \in \{A, B\}\)
Phase transitions
\[p(f_t|f_{t-1})\]
M Varmazyar, et al., Journal of Industrial Engineering International (2019).
Discrete phase-type distribution

\(\ldots\)
Phase transitions
\[p(f_t|f_{t-1})\]
M Varmazyar, et al., Journal of Industrial Engineering International (2019).
Discrete phase-type distribution
Duration distribution
Negative binomial
\[p(\tau) = {\tau + n - 2 \choose \tau-1}(1-\delta)^{\tau-1}\delta^n\]

\(\ldots\)
Phase transitions
\[p(f_t|f_{t-1})\]
State transitions
State transitions
\( p(s_t|s_{t-1}, f_{t-1})\)
A
B
A
B

\(\ldots\)
negative binomial distribution

Active Inference
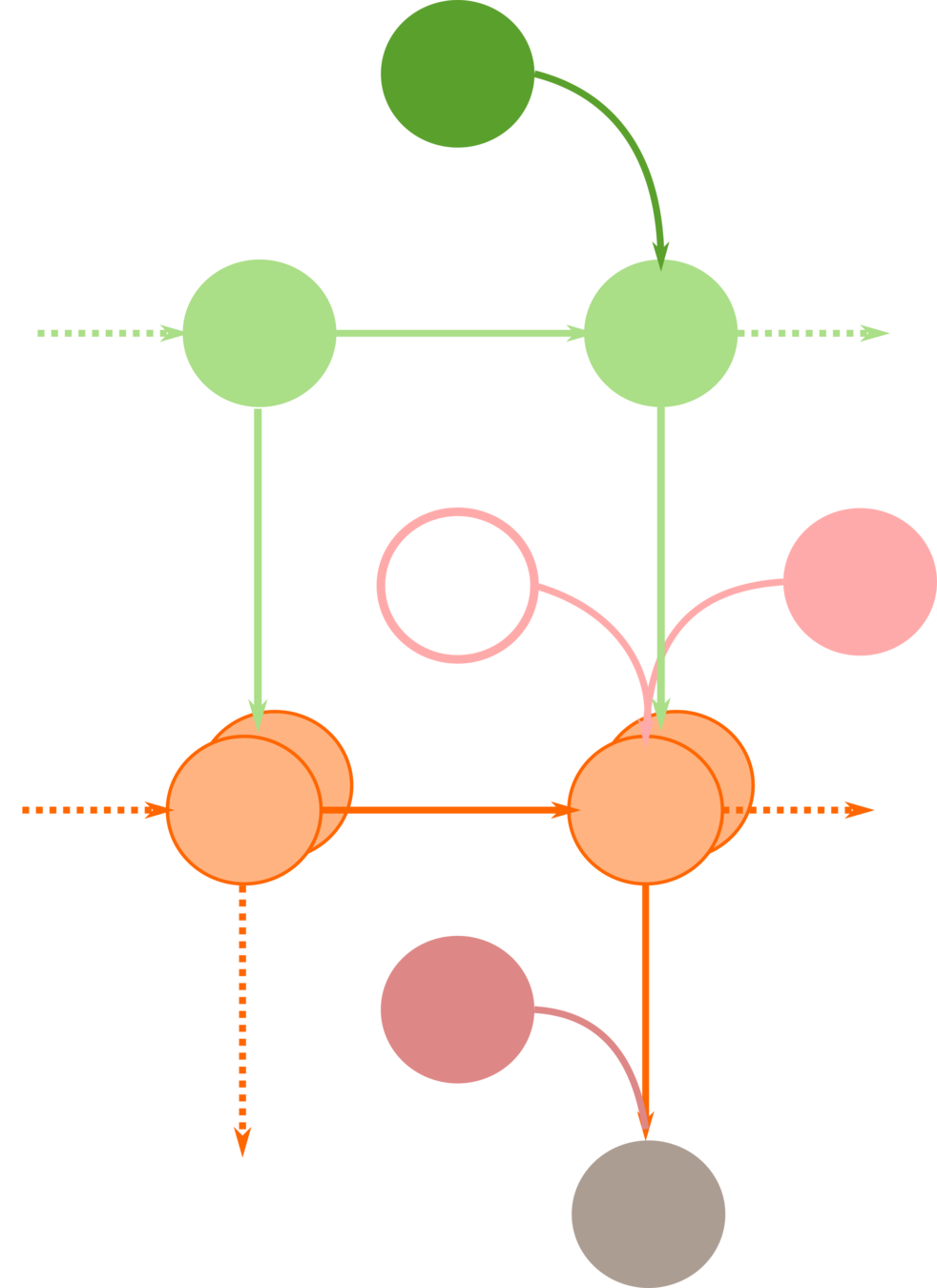
Belief updating and learning
History of past outcomes \( O_t = (o_1, \ldots, o_t) \)
Marginal likelihood
Predictive prior
Action selection
When simulating behaviour \( \gamma \rightarrow \infty \)
For data analysis \( \gamma \) is a free parameter
Probabilistic reversal learning



Probabilistic reversal learning



Probabilistic reversal learning
Model parameters
\( f \in \{1, \ldots, n_{max} \} \)
\( \otimes \)

\( \otimes \)
loss
gain
cue A
cue B
\(P(o_t^1) = [\frac{1}{3}, \frac{1}{3}, \frac{1}{3}] \)
\(P(o_t^2) = [\rho_1, \rho_2, \frac{\rho}{2}, \frac{\rho}{2}] \)

Performance
Trials Until correct (TUC)

In SILICO
Is the experimental setup useful?
- Can the temporal structure be learned?
- Will different temporal beliefs reflect different behaviour?
- How well can we differentiate between agents with different temporal beliefs?
In SILICO
Process:
- Fix priors, and action precision \(\gamma\)
- Simulate behaviour in both conditions with different \(n_{max}\)
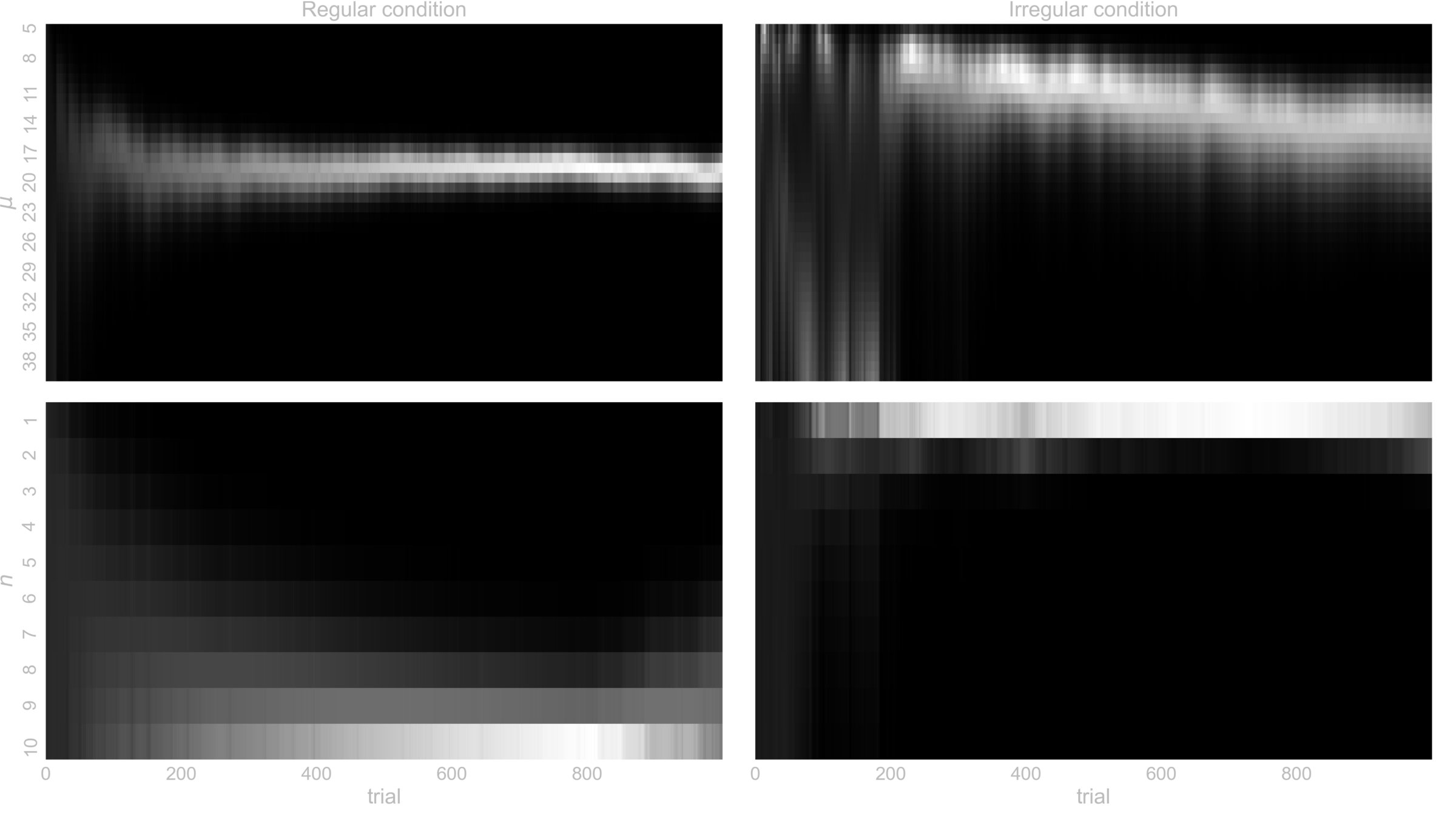
- Illustrate, performance, TUC, and the learning of the latent temporal structure \( (\mu, n) \)
- Model inversion, and confusion matrix for \(n_{max}\)
In SILICO - Behavioural metrics

In SILICO - Learning latent temporal structure
In SILICO - Confusion matrix

In SILICO - Confusion matrix

Behavioural data
- 50 healthy volunteers (20-30 years old):
- 27 subjects in the condition with regular reversals
- 23 subjects in the condition with irregular reversals
- 40 trials long training with a single reversal
Performance-tuc trajectories

Model comparison

Labeled trajectories

conclusion
- Modelling and assessing influence of temporal-expectations on decision-making in dynamic environments.
- How people learn temporal expectations could also be addressed with this approach, but some challenges remain.
- Linking the underlying representation of the temporal structure to behaviour provides a novel method for computational cognitive phenotyping.
Thanks to:
- Andrea Reiter
- Stefan Kiebel
- Thomas Parr
- Karl Friston


https://slides.com/dimarkov/active-inference-semi-markov
https://github.com/dimarkov/pybefit
https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?rev=2&id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006707