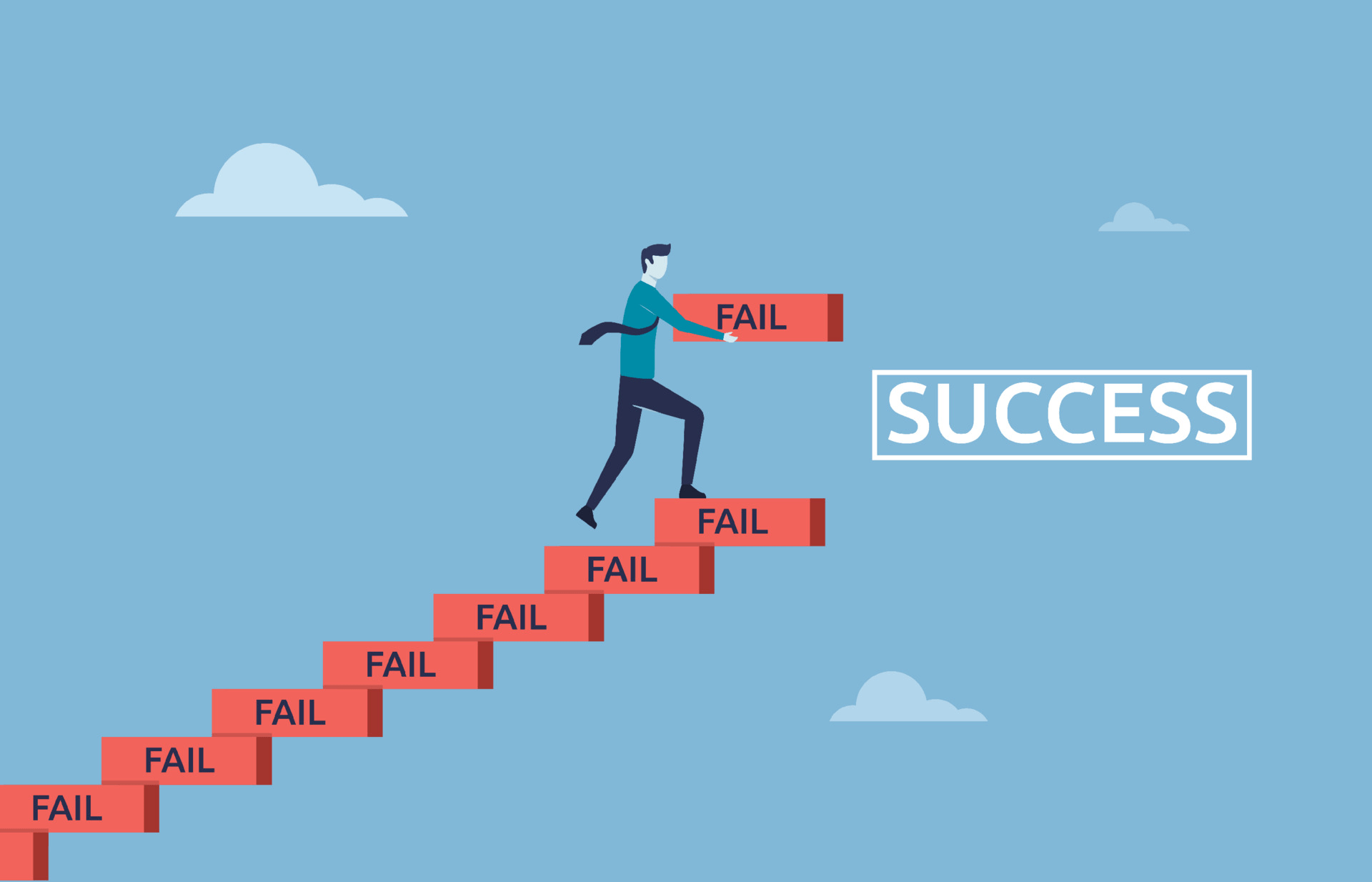
How Machines Learn
By: Saanvi Chugh
Goal: Baby dragon learns to breathe fire perfectly




What do you think the baby dragon is doing wrong?
Too smokey
Too hot
Too little
Perfect!
Dragon = neural network
Mentor's feedback = backpropagation
Trying again = updating weights
Neural network = a machine learning model that learns how to turn raw inputs into useful patterns and then uses those patterns to make predictions
Its ancestor is the linear model y = mx + b
How it works
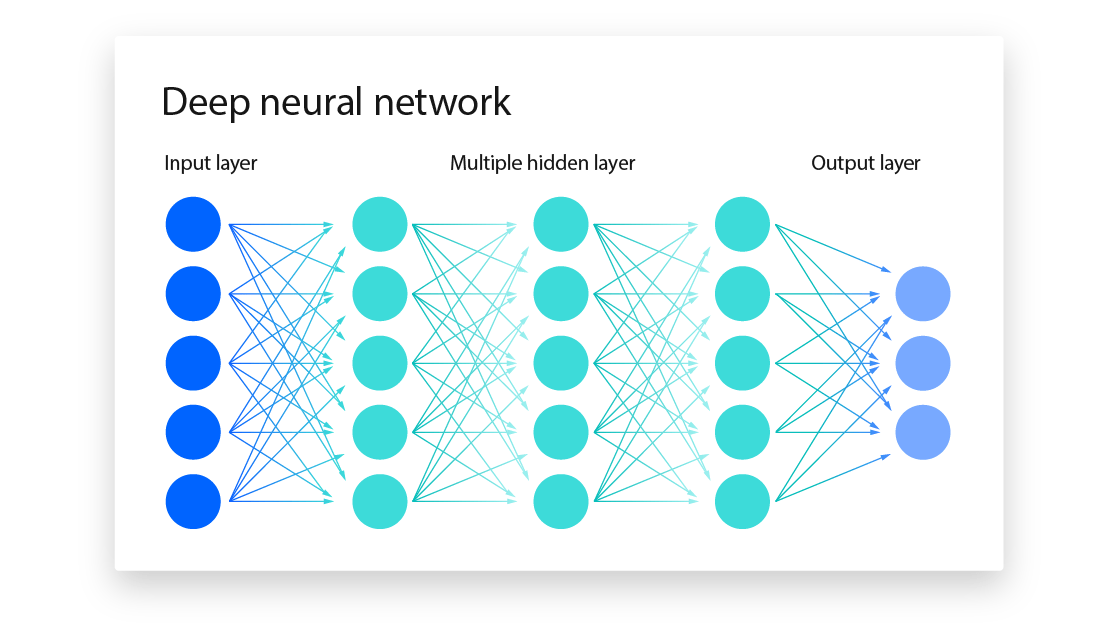
Early layers figure out which parts of the input matter most
Middle layers mix those pieces together to recognize bigger ideas (context/tone)
The final layer uses all of that to calculate the probability of possible predictions
Weights = dials that control how strongly each input feature influences the decision
Biases = built-in values that let the neuron “shift” when it decides to activate, even if inputs are weak
By adjusting these values, the network gradually learns to make accurate predictions.
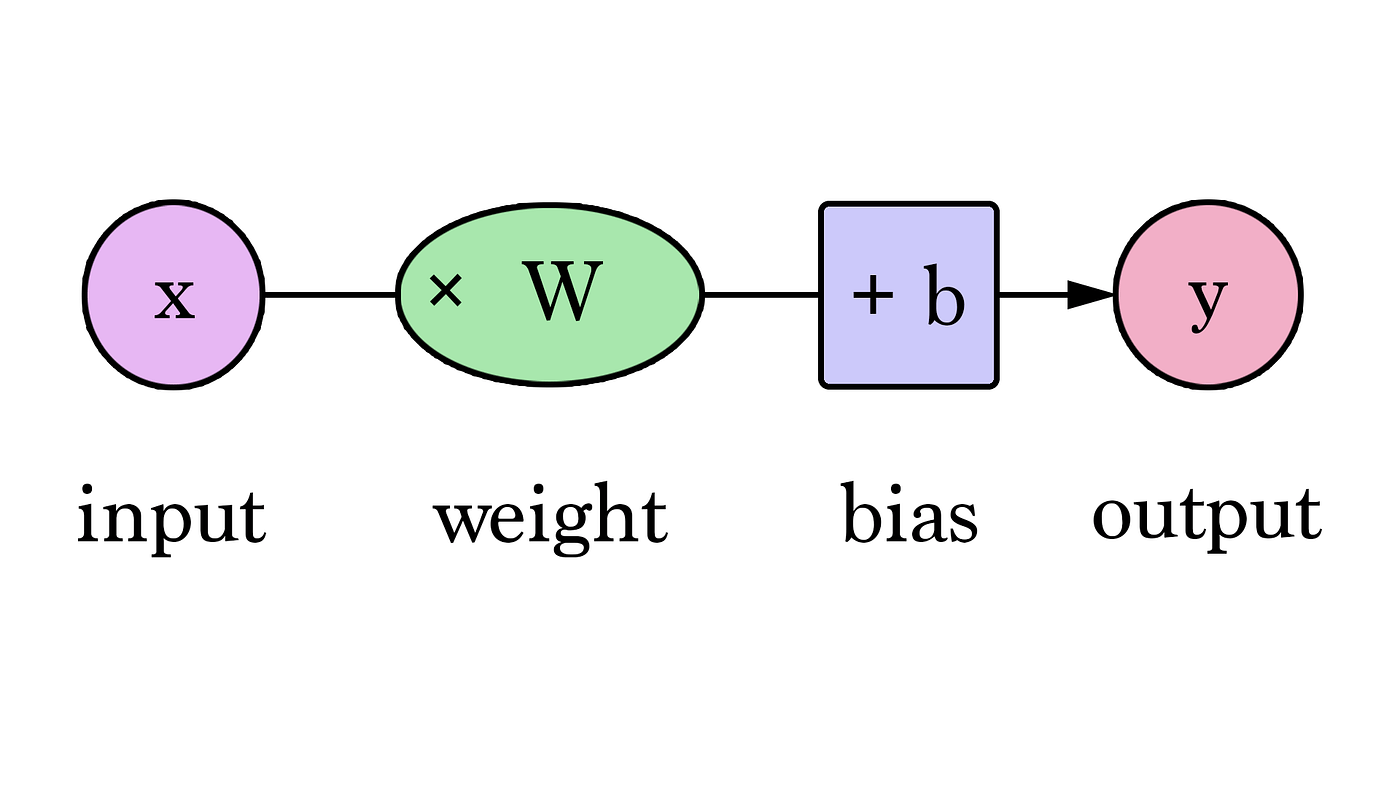
f(x) obtained by mapping X = (x1, x2, x3...) to predict a response Y
1. Input layer holds input features (X1, X2, X3, ...)
2. Hidden leayers consist of artificial neurons that transform inputs using weights and biases
3. Output layer produces the final prediction
Spam Detection Example
Inputs: "prize" "money" "dear" "hello" "win"
"prize" is given more weight than "hello," meaning it contributes more to the overall prediction
Eventually, the neural network will accurately predict whether an email is spam or not
Back Propagation
Back propagation = an algorithm used to learn the correct weights and biases
-
Compares prediction Y to true Y and uses a loss function to measure the error
-
At each neuron, the algorithm uses calculus to determine how much each weight and bias contributed to the error


Real World Applications
Computer Vision + Medical Imaging

Chatbots/LLMs
Forcasting

Speech Recognition
Machines learn from their mistakes just like humans do!