AC-Circuits
Alternating Current
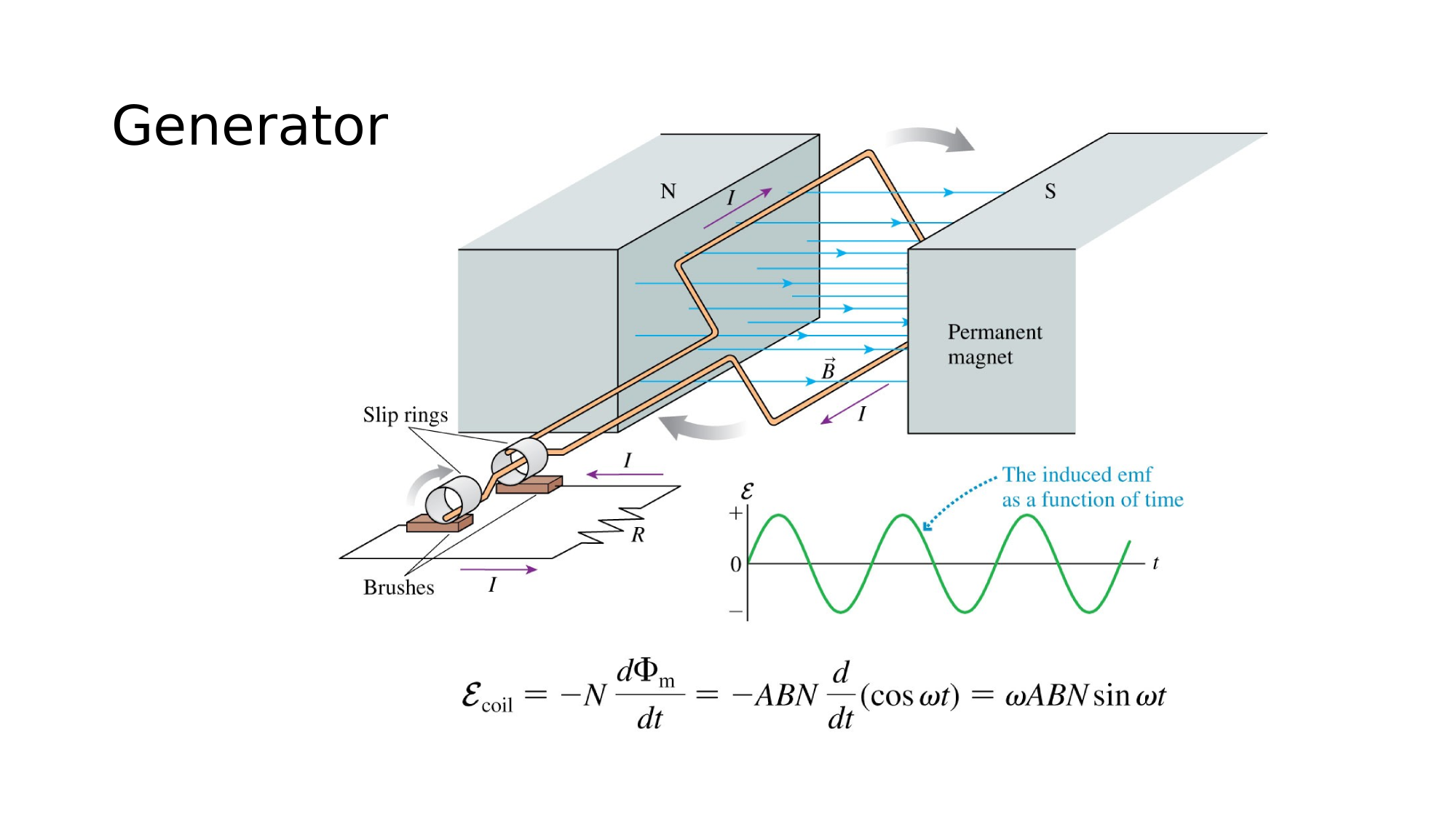
AC-generator
AC-Circuits
Alternating current
AC-circuits
AC-generator
Induced EMF
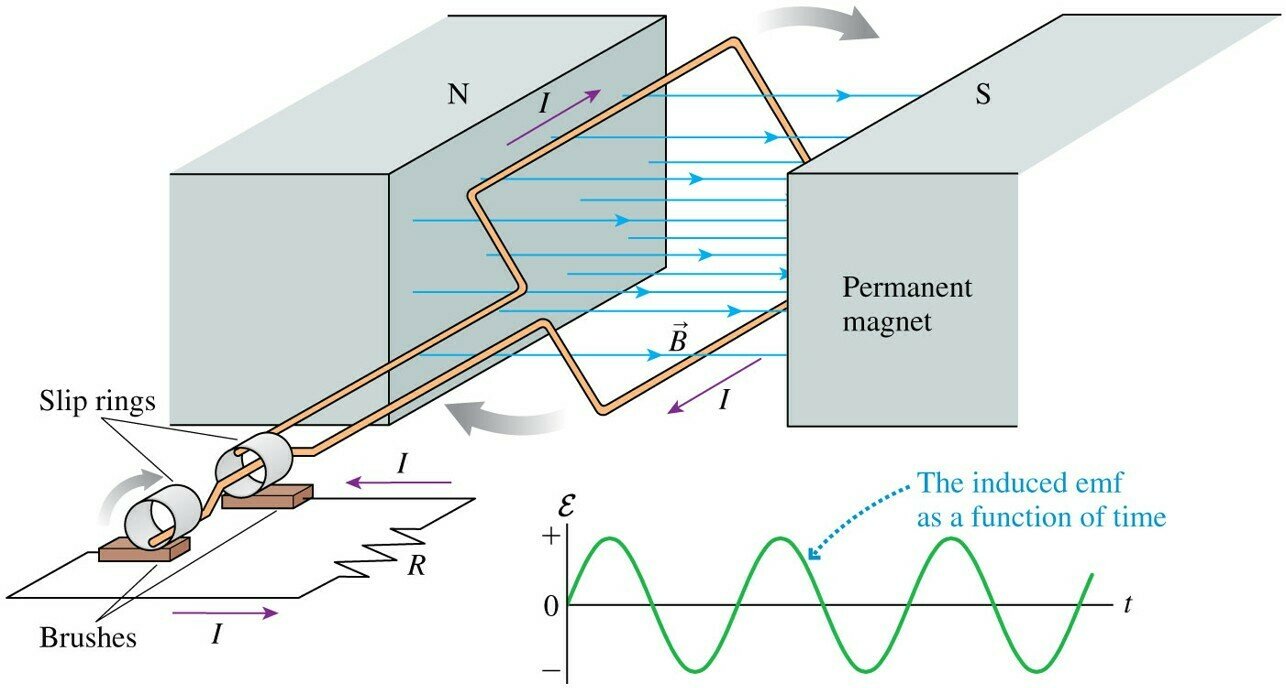
for
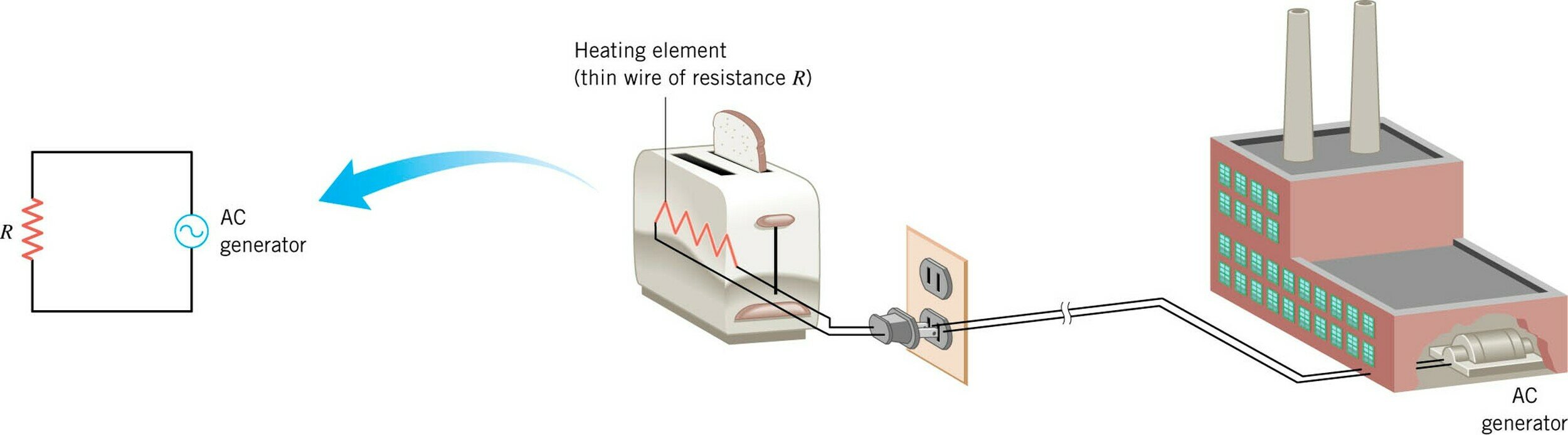
AC-circuits
AC-generator
Experimental results
For constant
AC-circuits
AC-generator
.
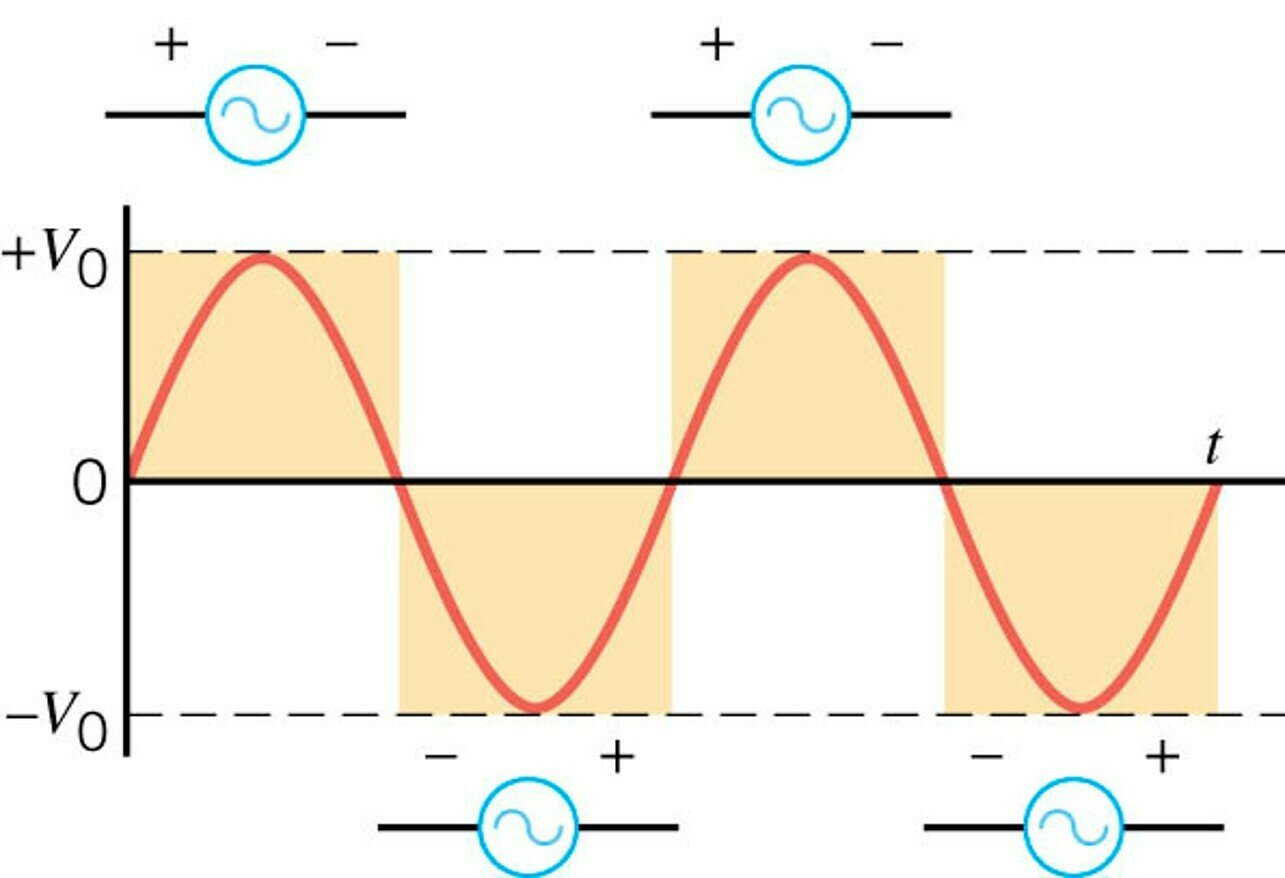
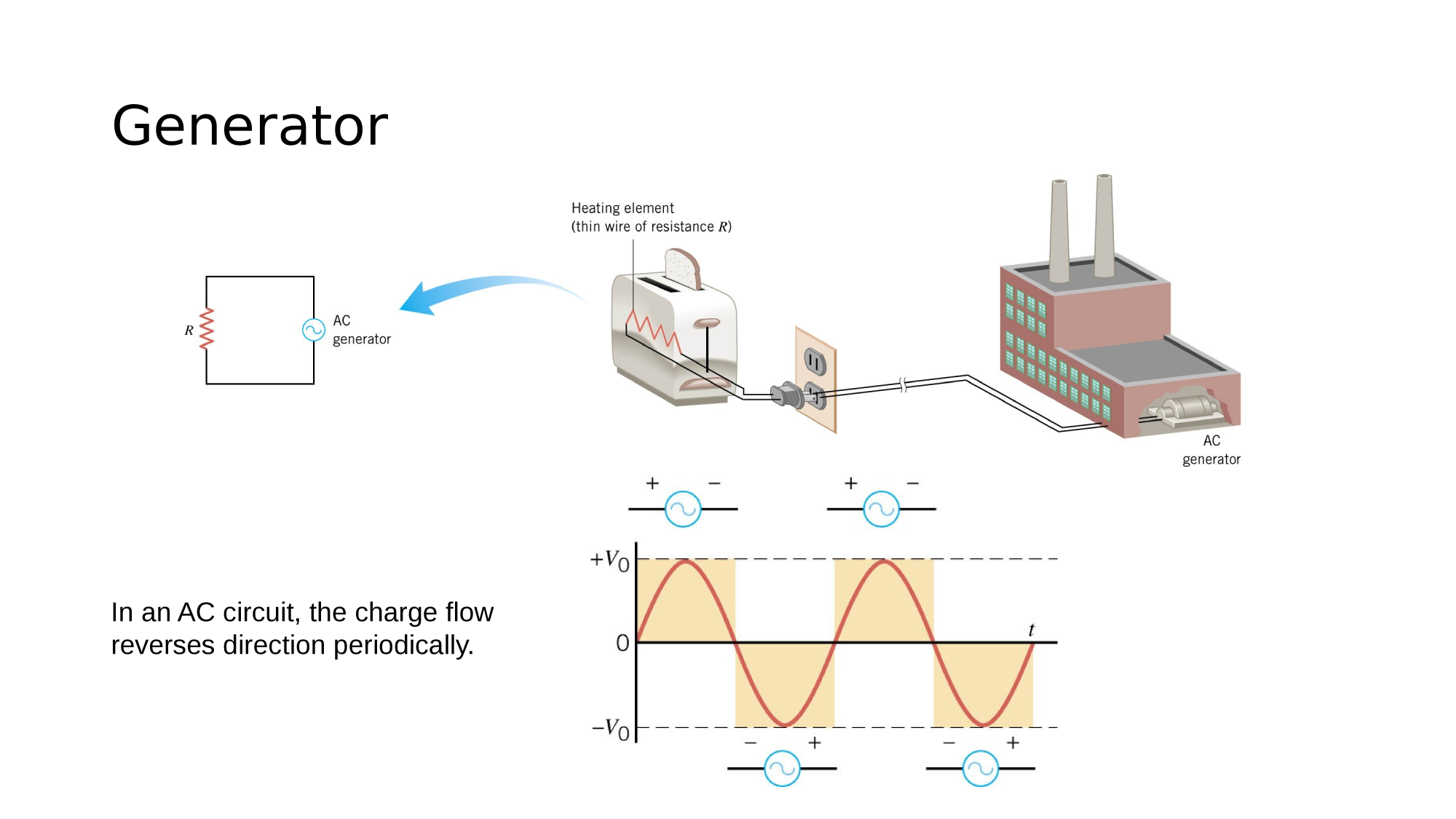
The output of an AC source flips polarity periodically.
The output of an DC source has a fixed polarity.


AC-circuits
AC-generator
AC-source
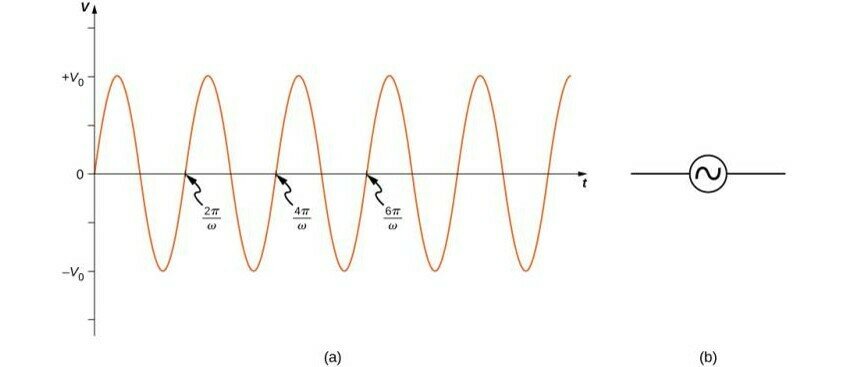
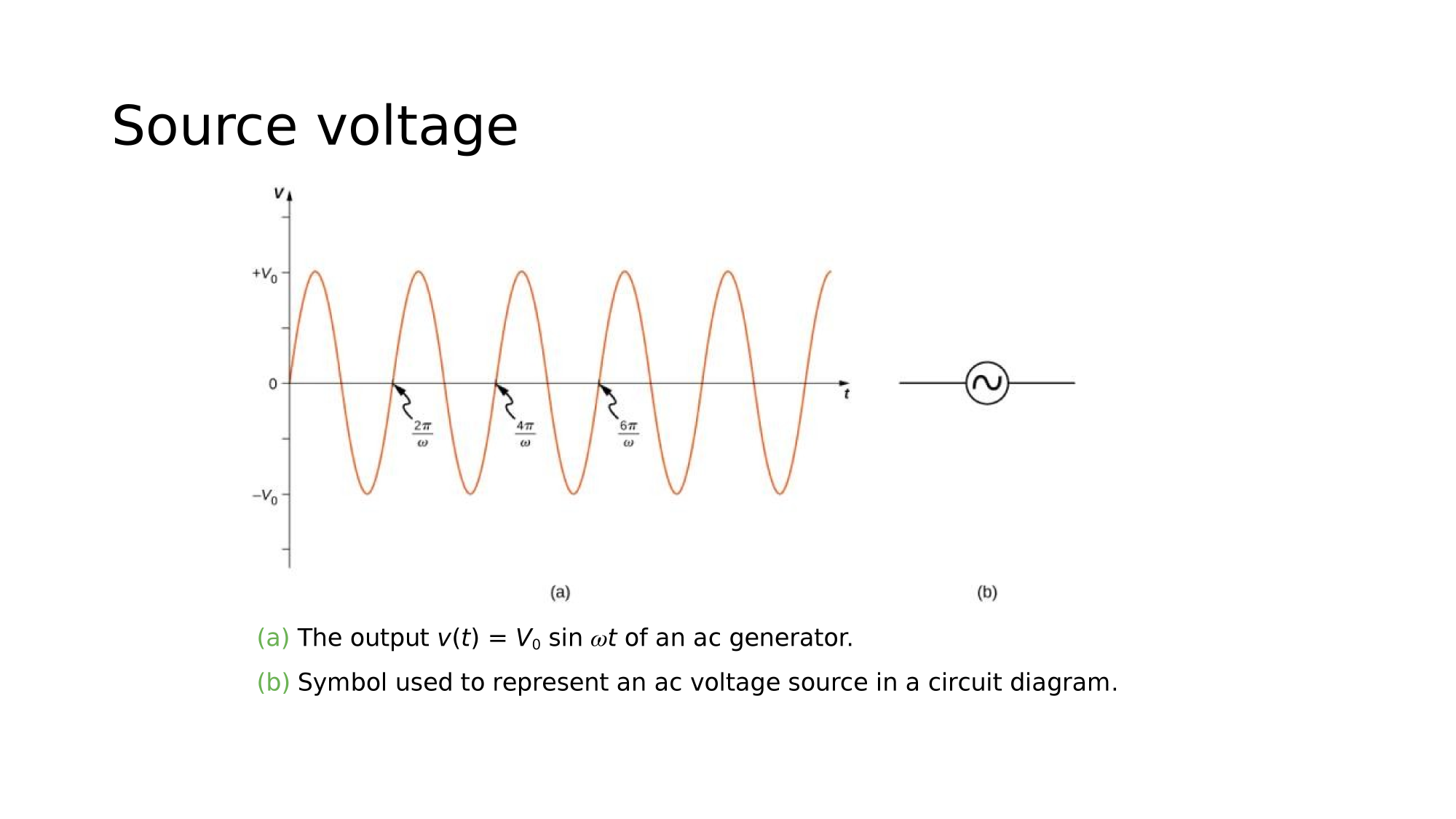
(a) The output of an AC generator:
(b) Symbol used to represent an AC voltage source in a circuit diagram.
Parameters of an AC-source:
Peak EMF (Volt)
Angular Frequency (rad/s)
Frequency (1/s = Hz)
Period (seconds)
AC-circuits
AC-generator
.

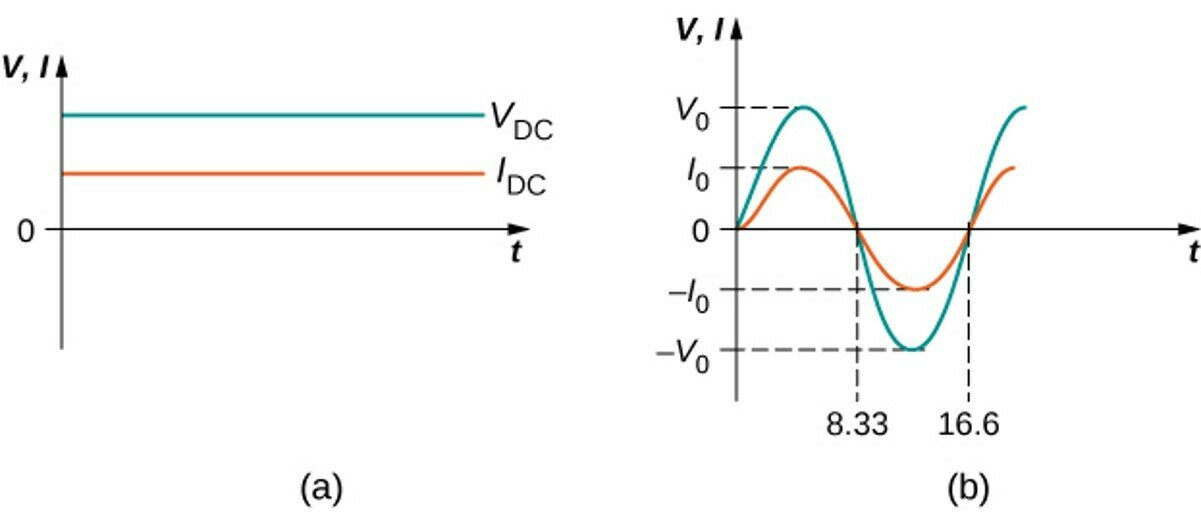

(a) The dc voltage and current are constant in time (once the current is established.)
(b) The voltage and current versus time are quite different for ac power. In this example, which shows 60-Hz ac power and time t in milliseconds, voltage and current are sinusoidal and are in phase for a simple resistance circuit.
AC-circuits
AC-generator
AC Sources
simple AC-circuits
AC-Circuits
Alternating current
AC-circuits
AC-circuits
Section 15.2
AC-circuits
AC-circuits
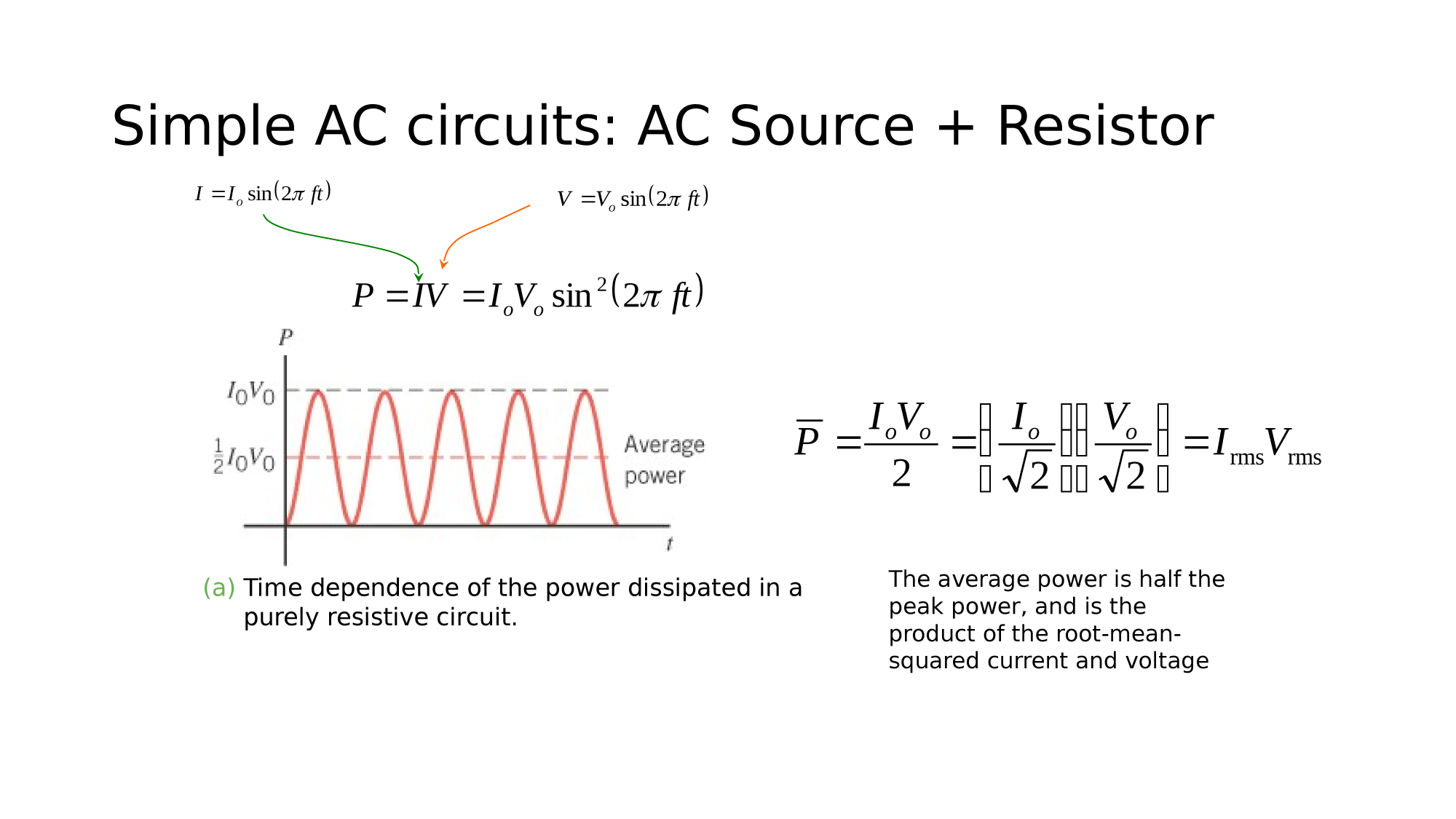
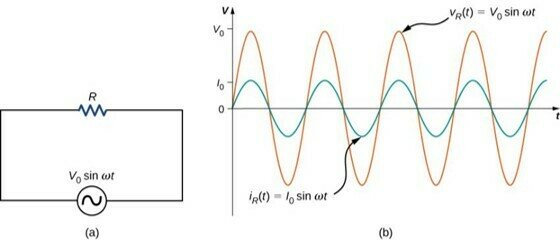
AC-source + Resistor
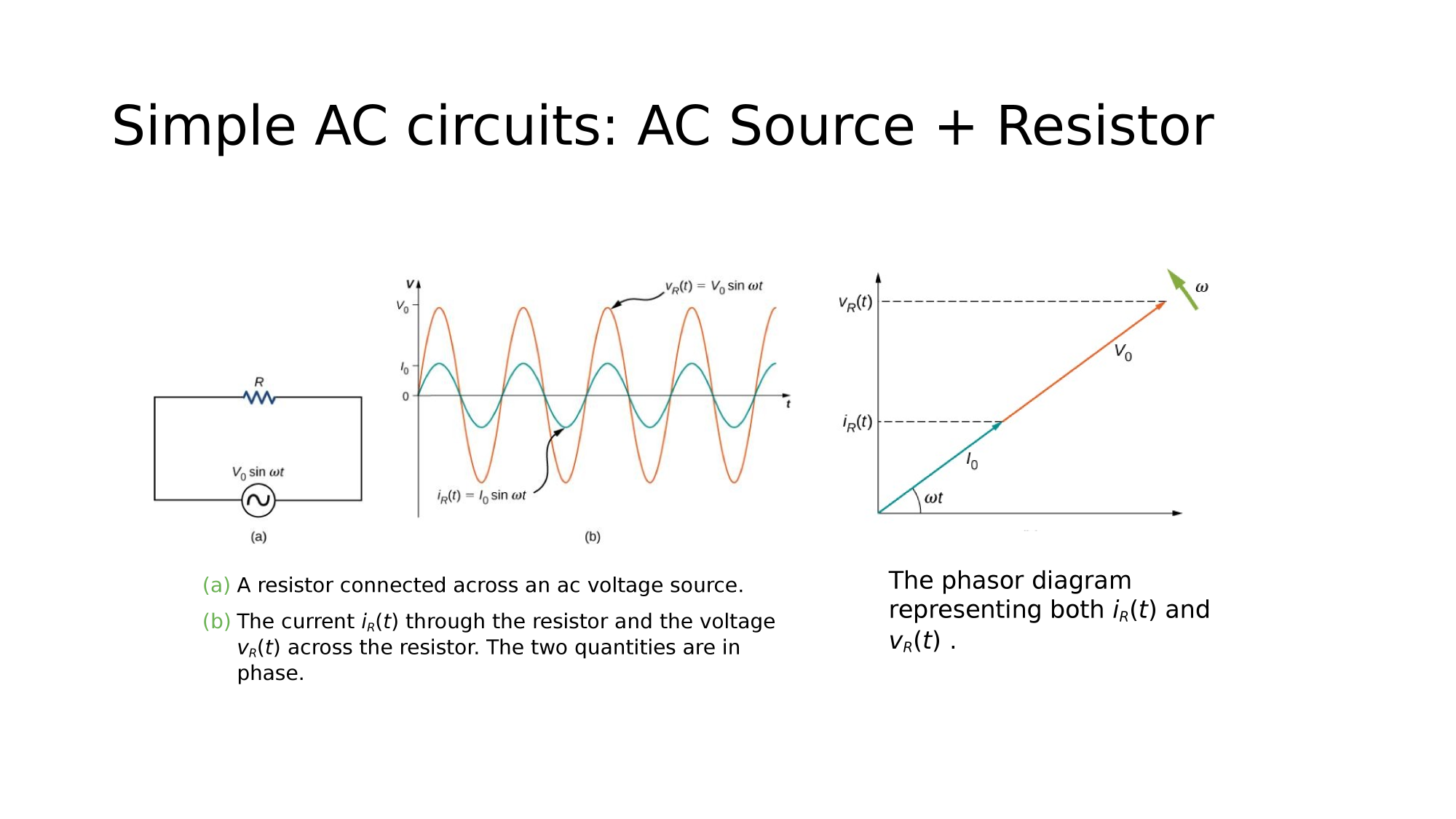

AC-circuits
AC-circuits
AC-source + Resistor

AC-circuits
AC-circuits
AC-source + Capacitor
Current Leads Voltage by
AC-circuits
AC-circuits
AC-source + Capacitor
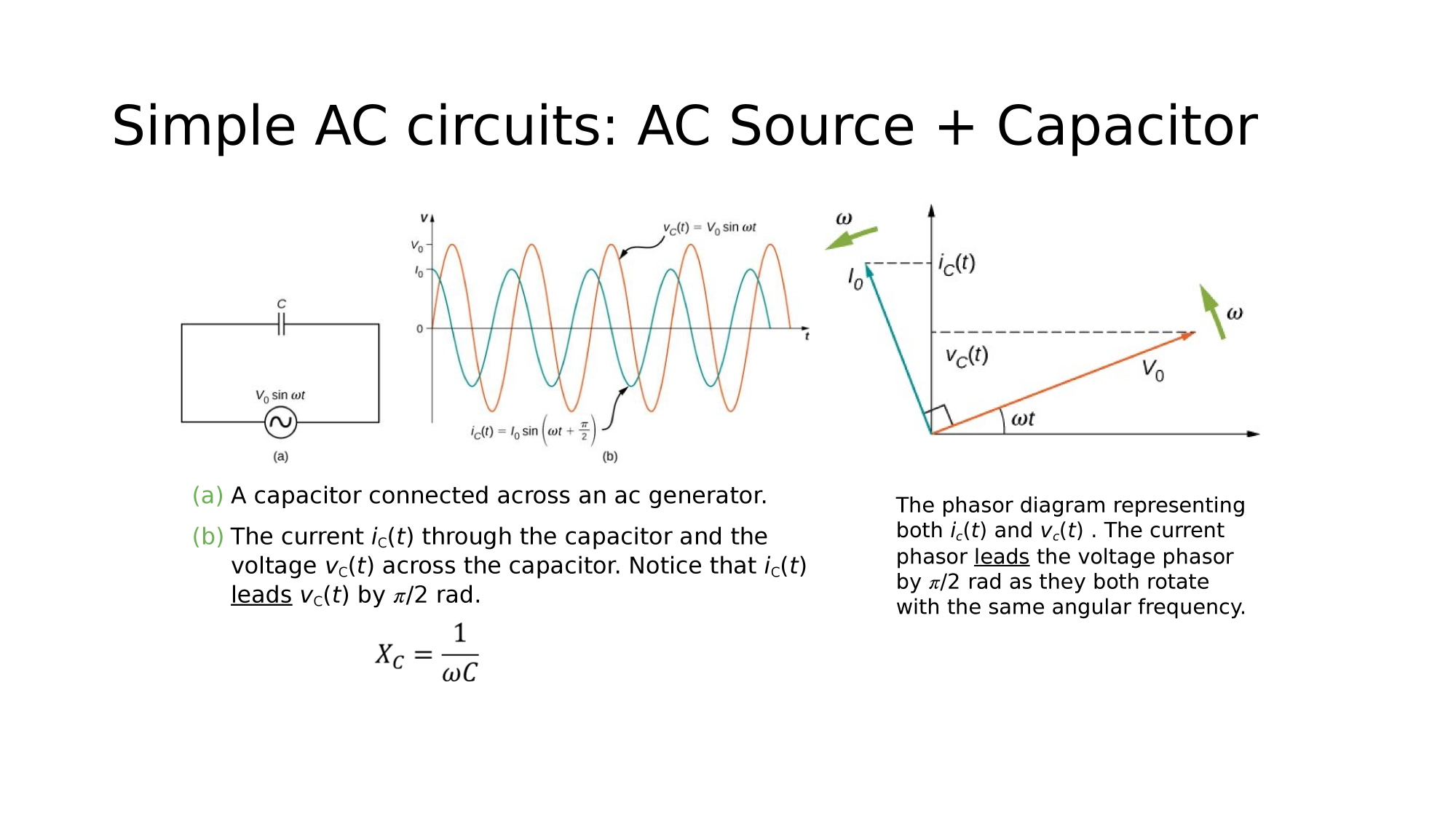
AC-circuits
AC-circuits
AC-source + Inductor
Current Lags Voltage by
AC-circuits
AC-circuits
AC-source + Inductor
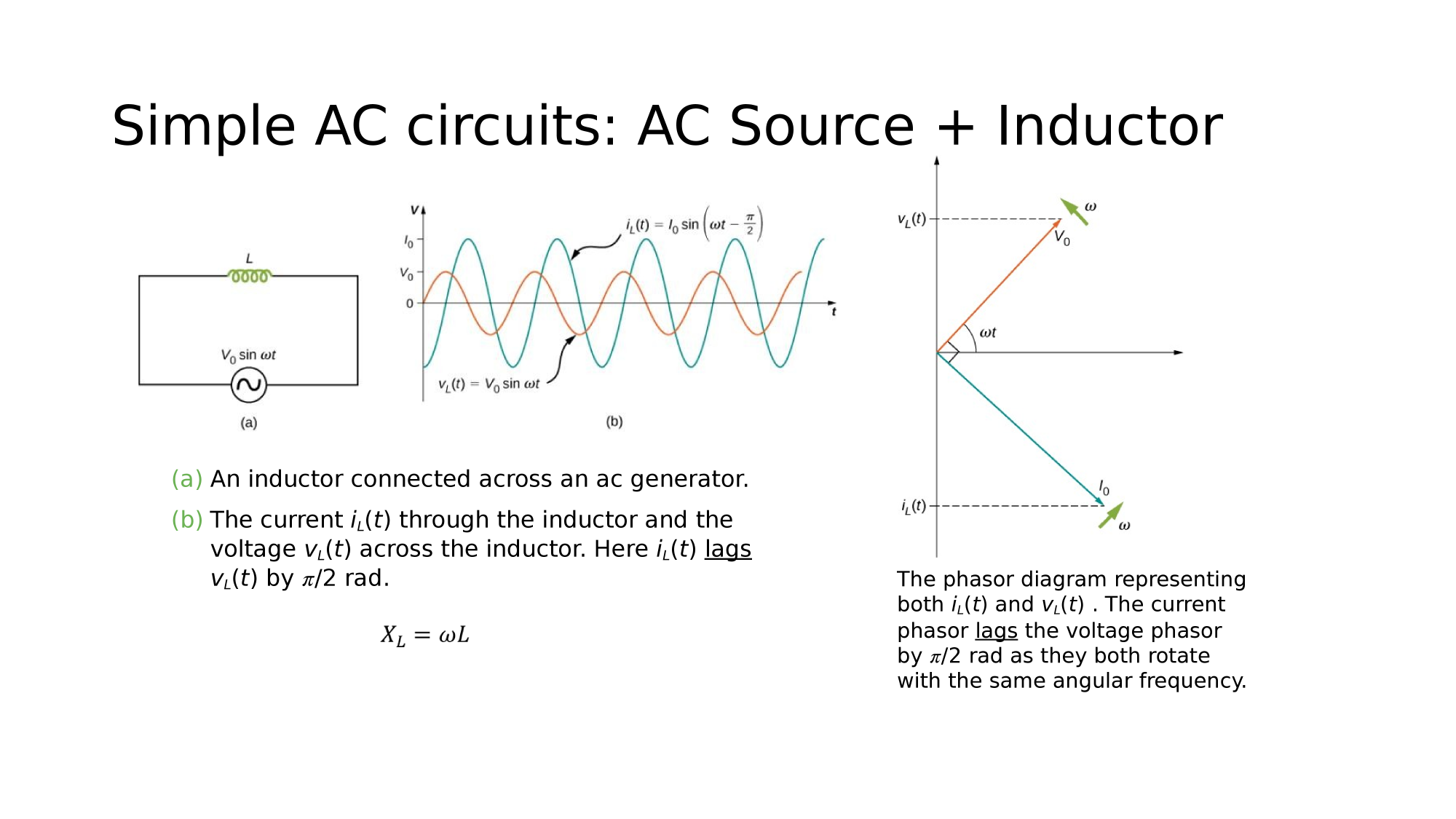
AC-circuits
AC-circuits
Summary
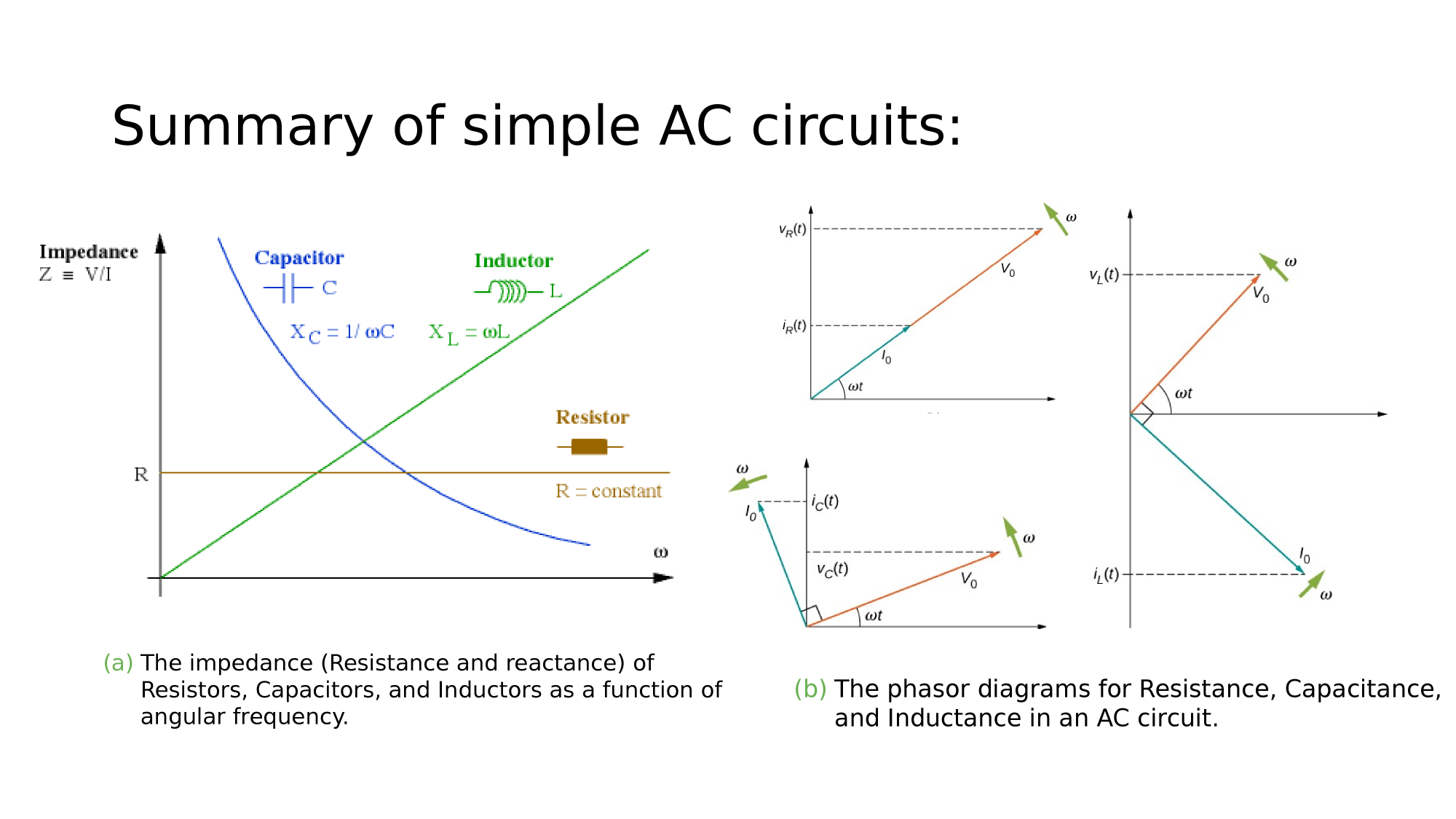
RLC-circuits
AC-Circuits
Alternating current
AC-circuits
RLC-circuits
Section 15.3
AC-circuits
RLC-circuits
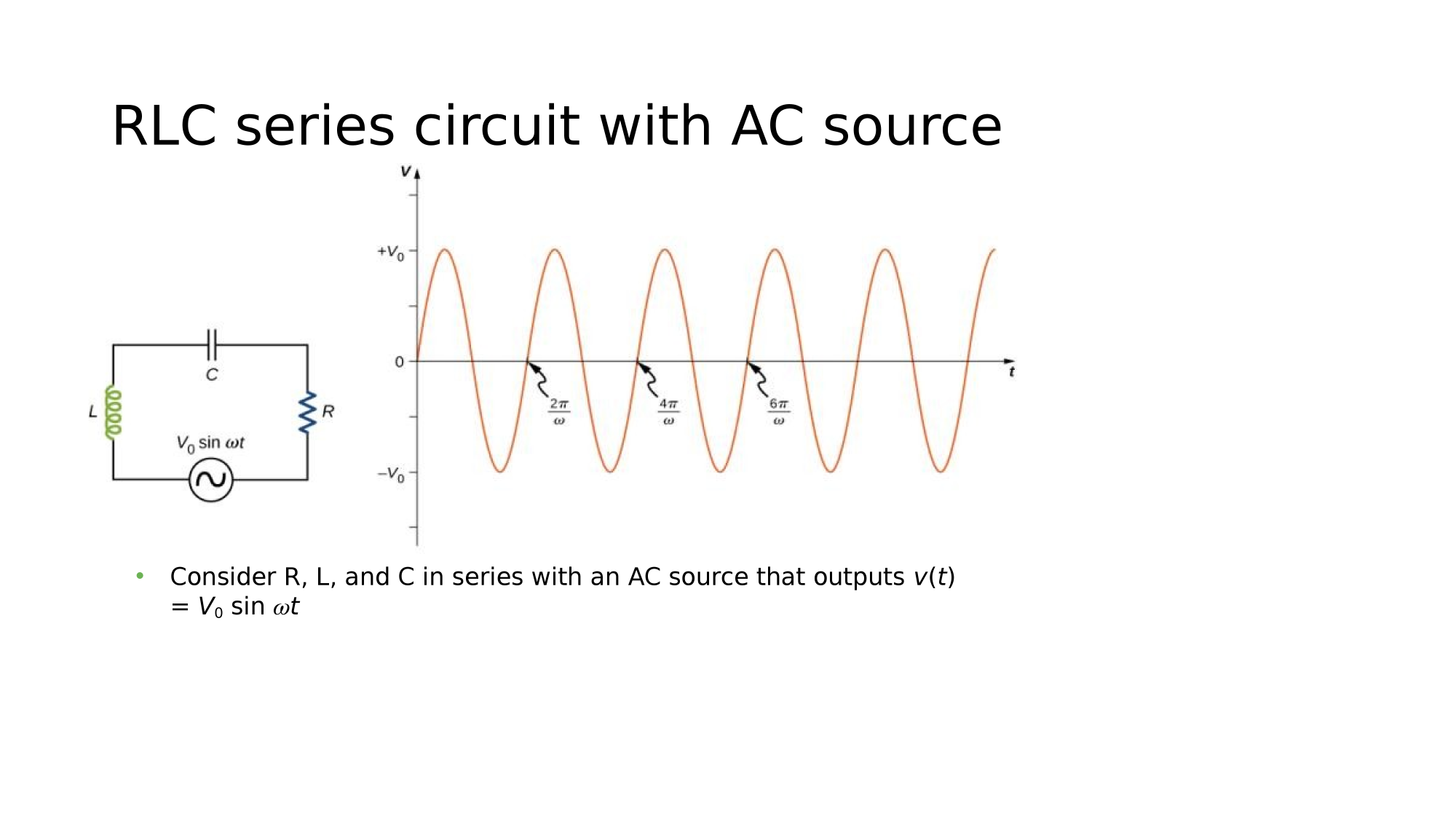
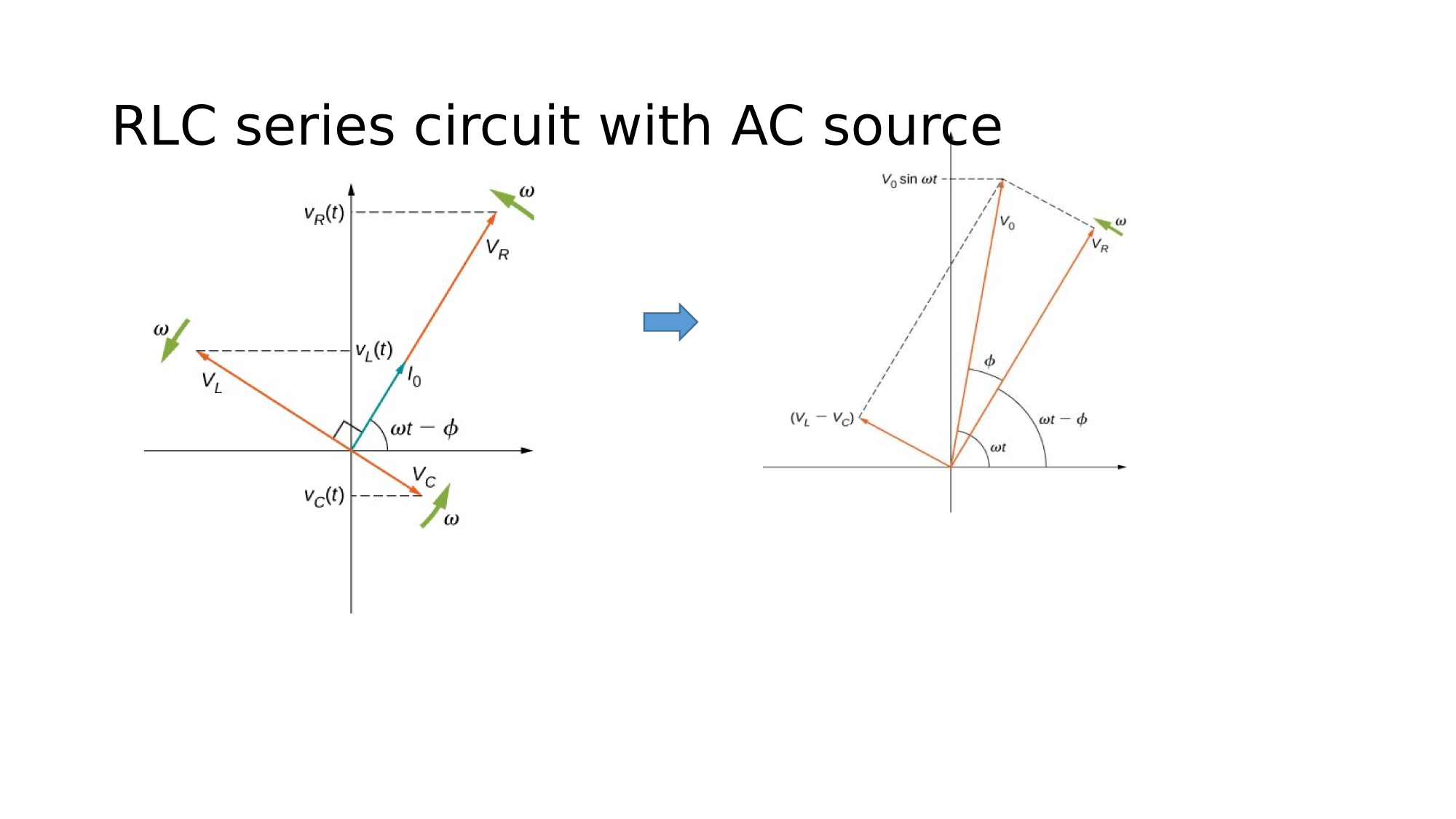
RLC in series
Consider a circuit where R, L, and C are in series with an AC-source. What is the electric current response?
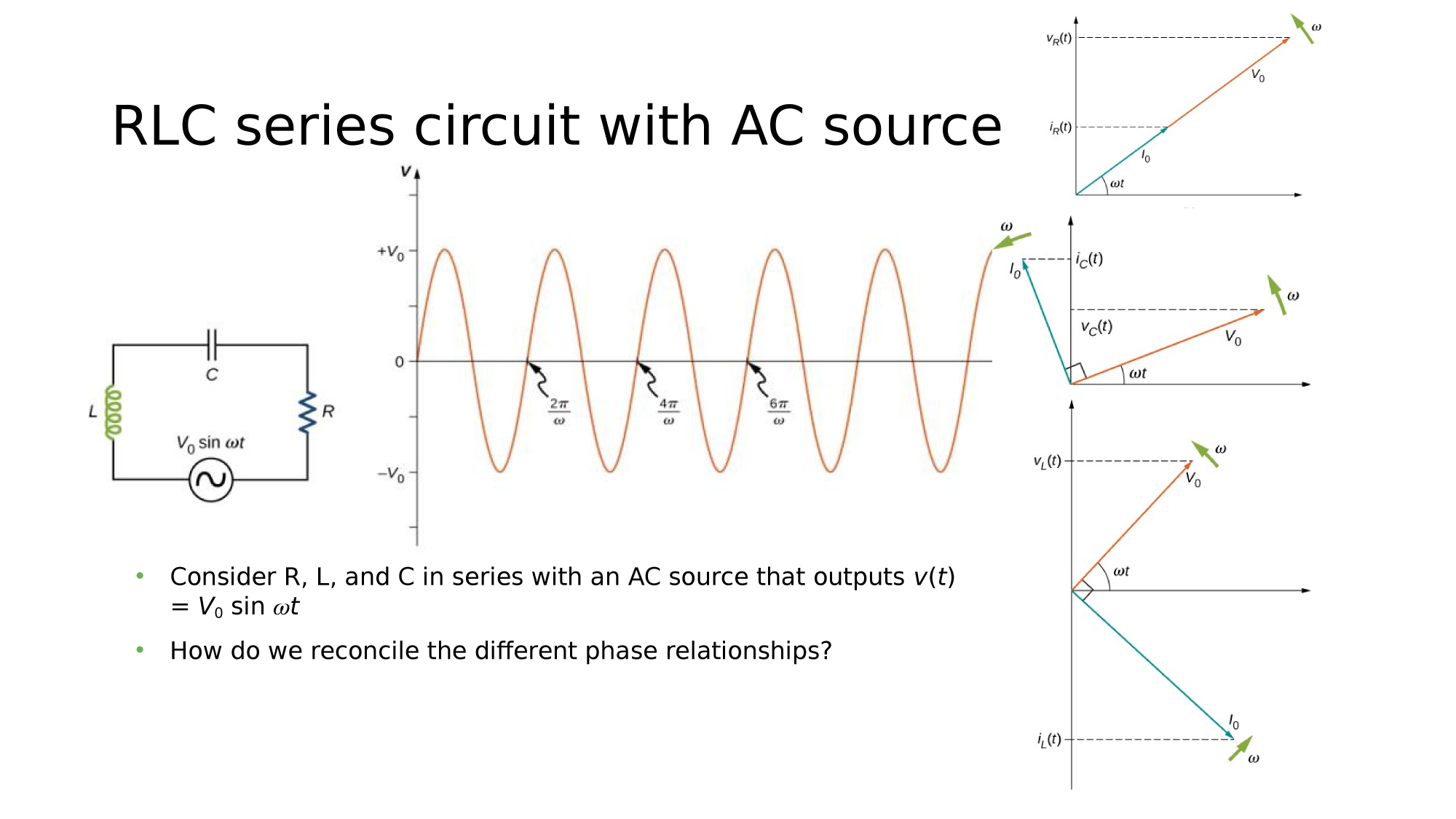
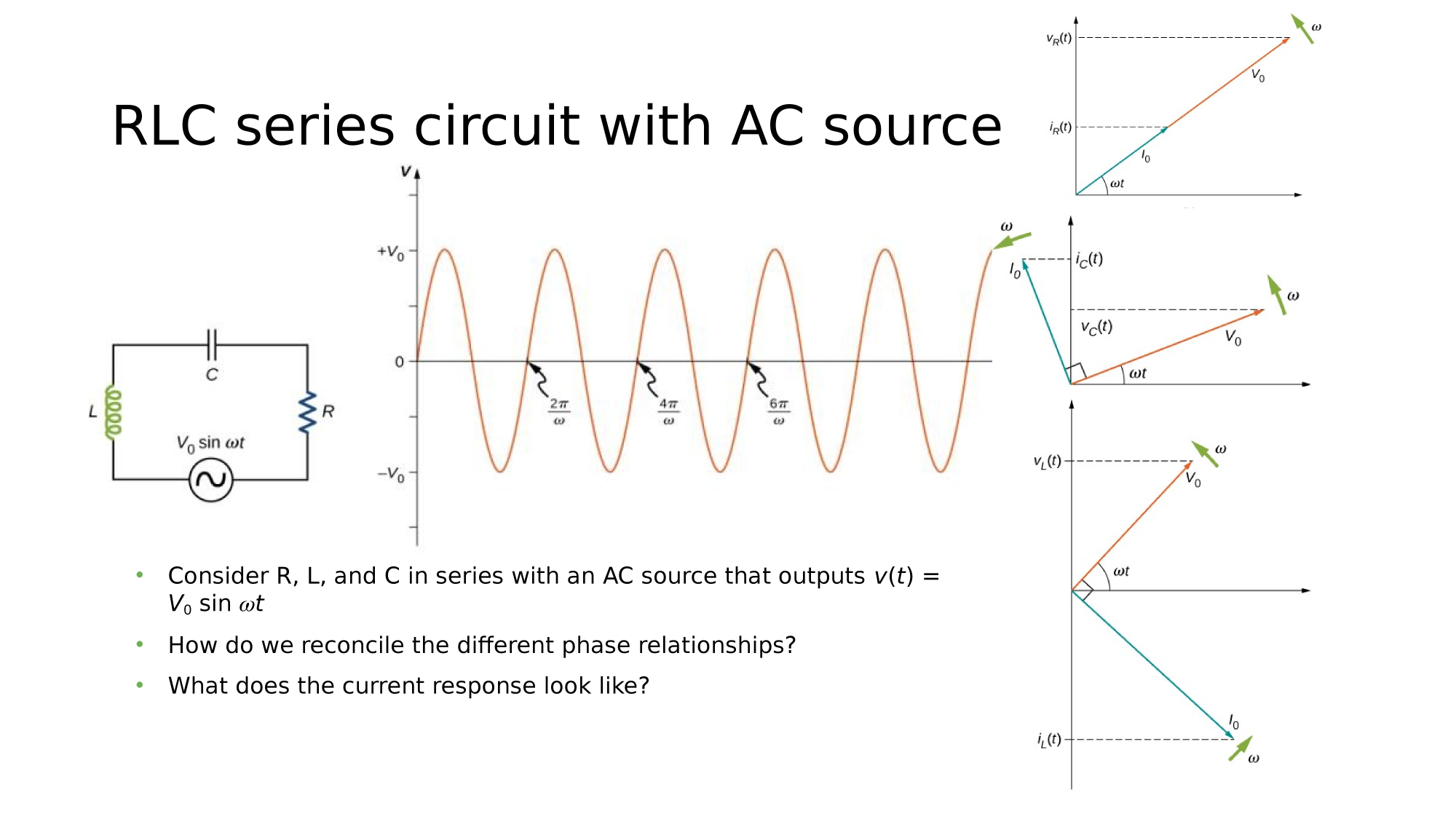
How do we reconcile the different phase relationships?

AC-circuits
RLC-circuits
RLC in series
Consider a circuit where R, L, and C are in series with an AC-source. What is the electric current response?
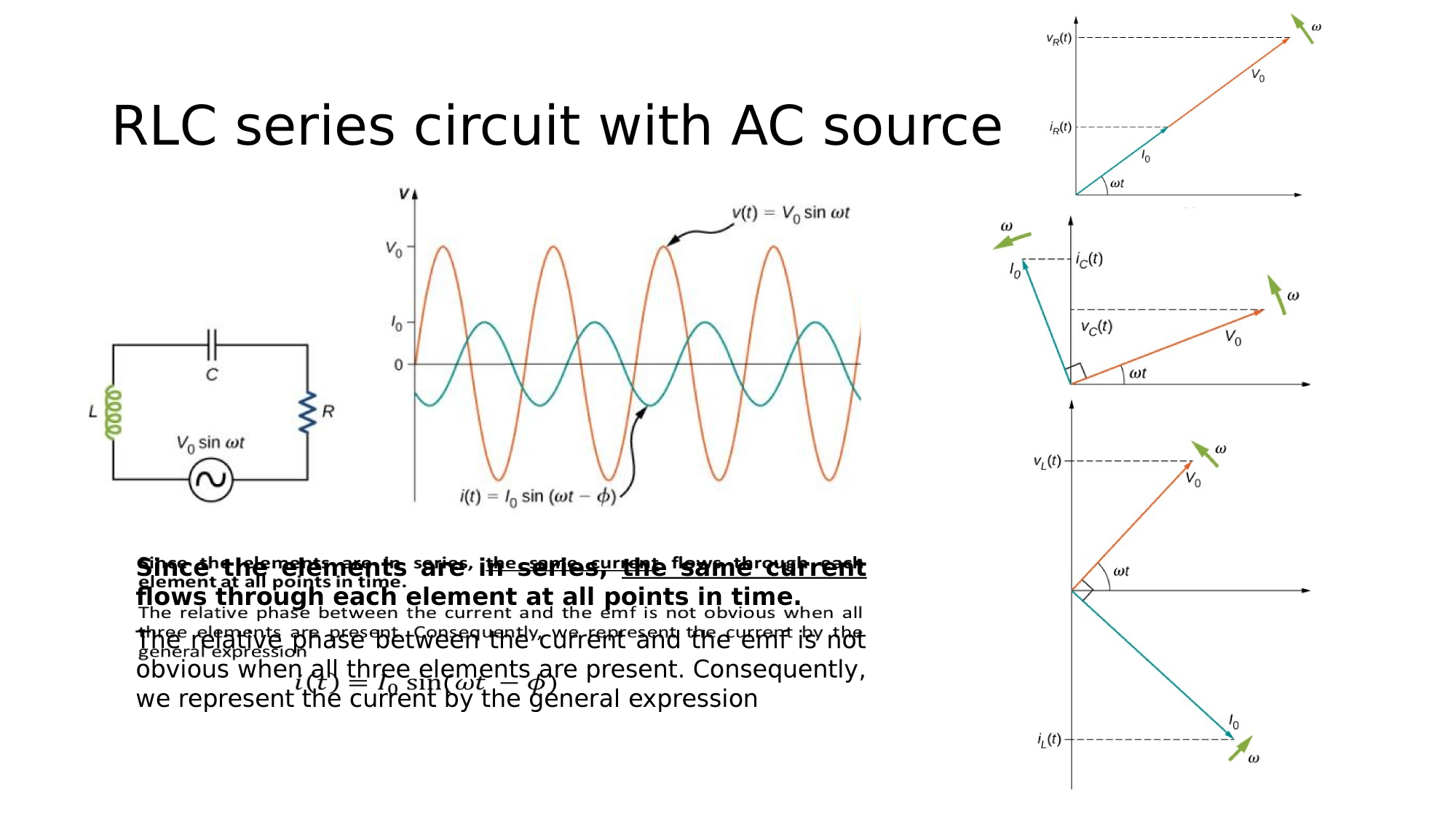
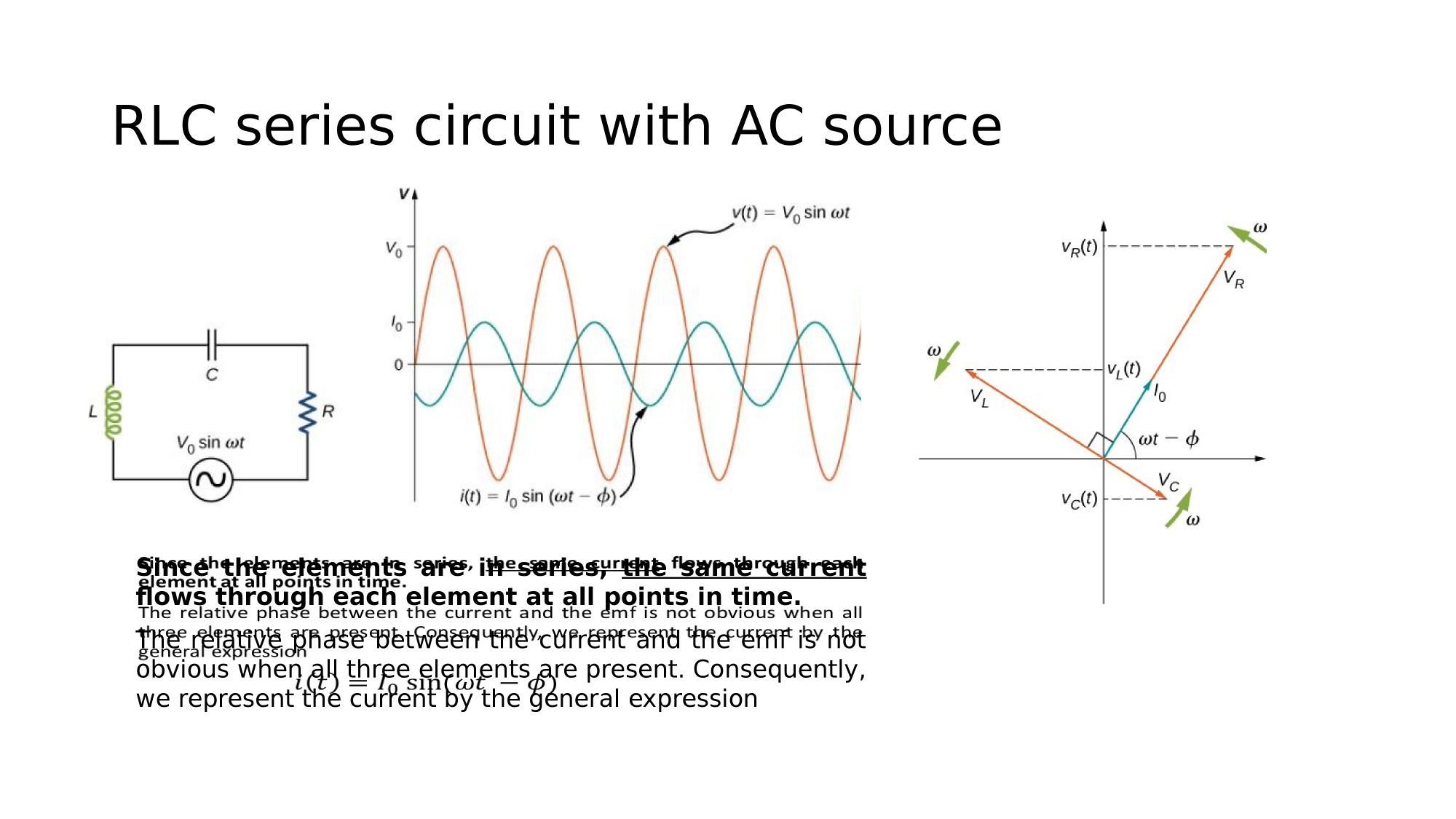
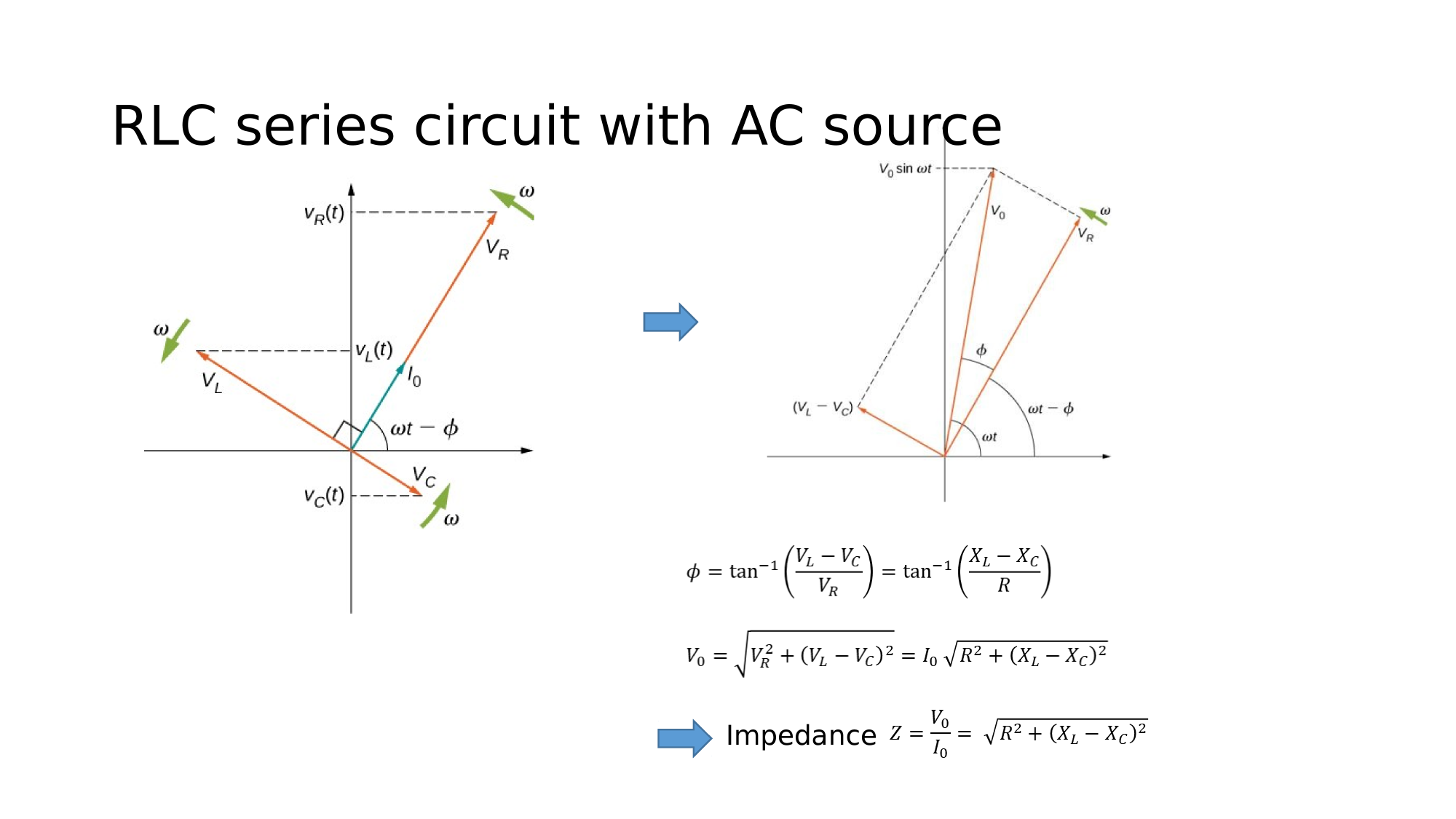
Since the elements are in series, the same current flows through each element at all points in time.
The relative phase between the current and the emf is not obvious when all three elements are present. Consequently, we represent the current by the general expression:
where the peak current and the phase-shift are unknowns.
AC-circuits
RLC-circuits
RLC in series
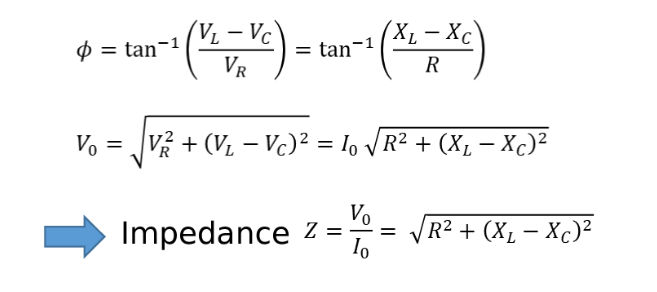
Power
AC-Circuits
RLC
AC-circuits
Power in AC-circuits
Section 15.4
AC-circuits
Energy & Power
Power dissipated in resistor
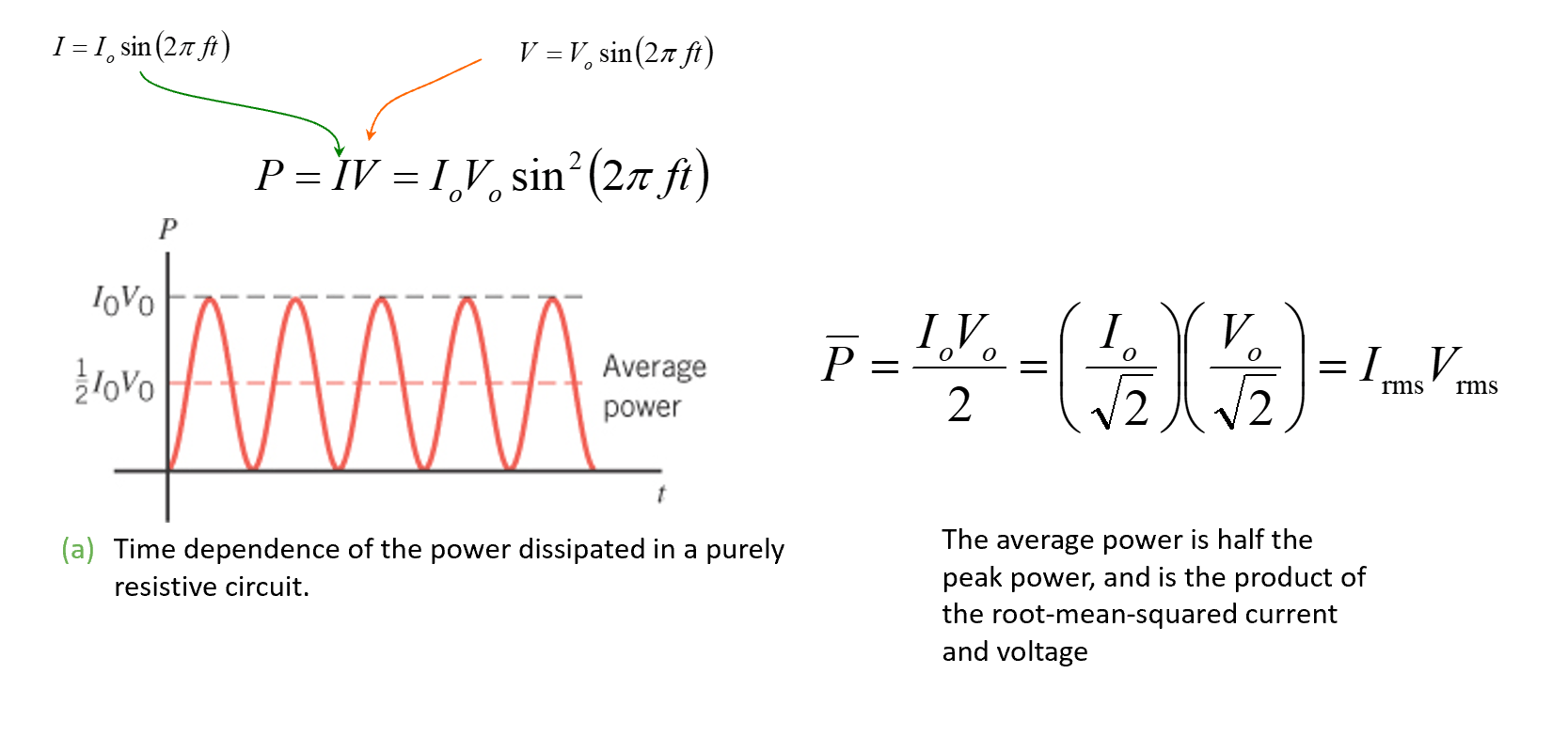
AC-circuits
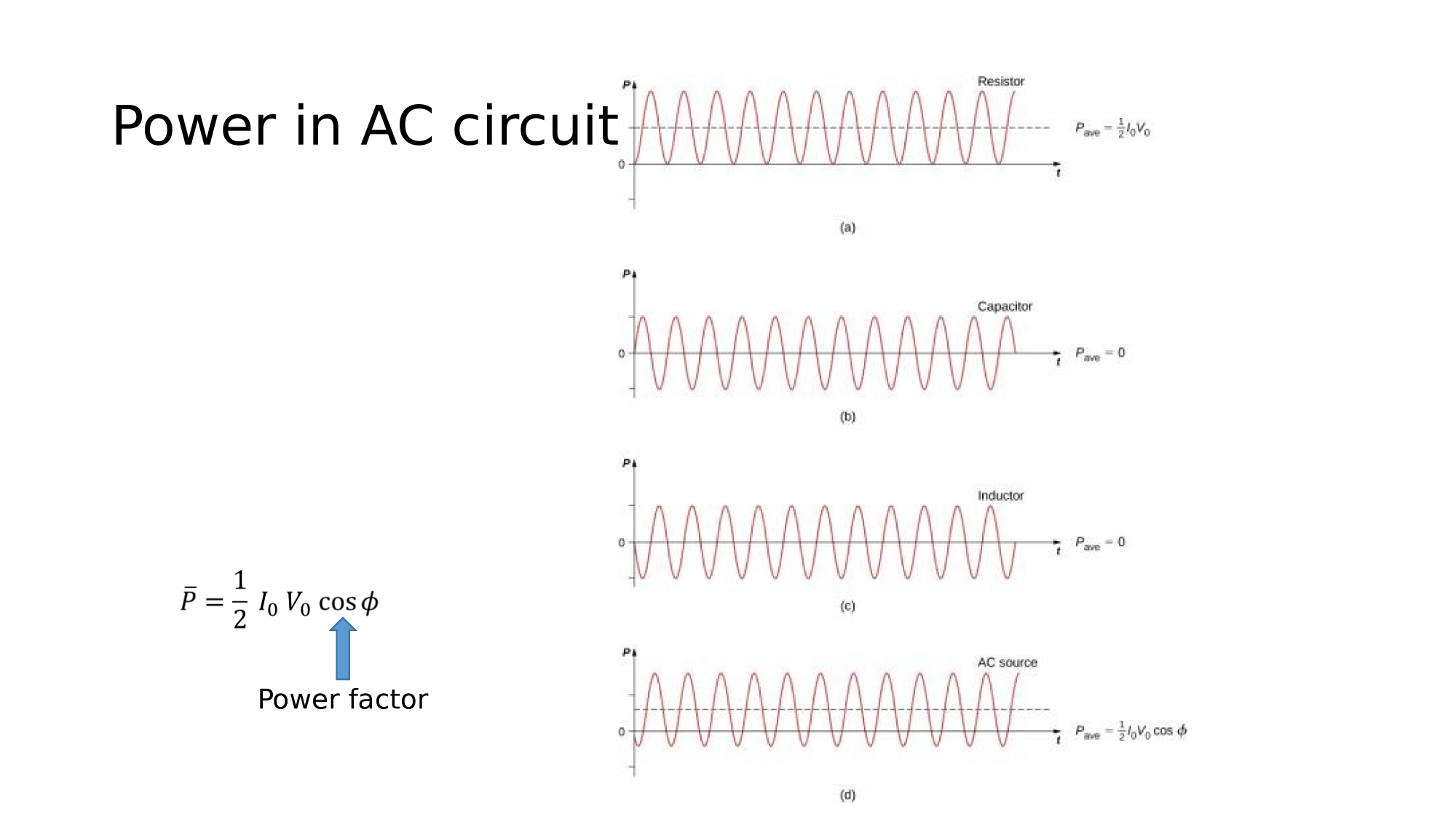
Energy & Power
Power in various components
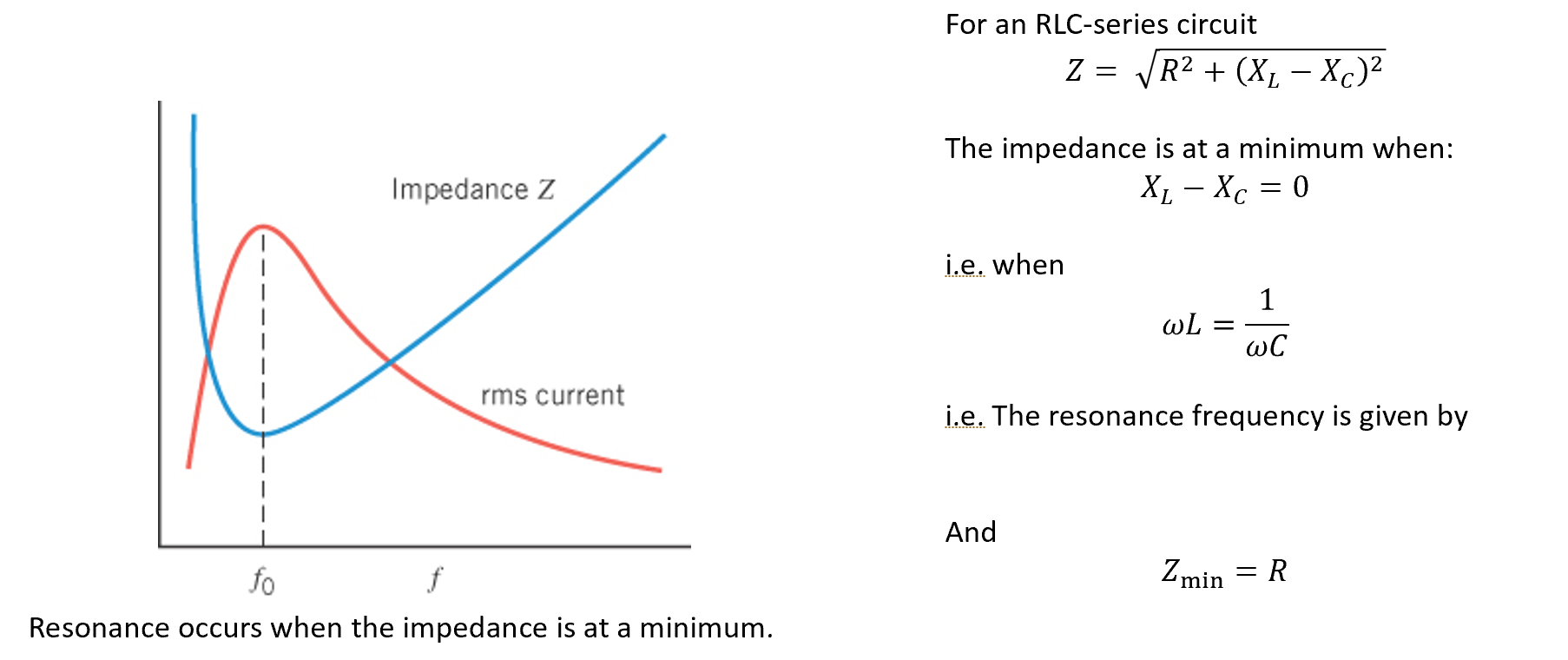
Resonance
AC-Circuits
RLC
AC-circuits
Resonance in AC-circuits
Section 15.5
AC-circuits
Resonance in AC-circuits
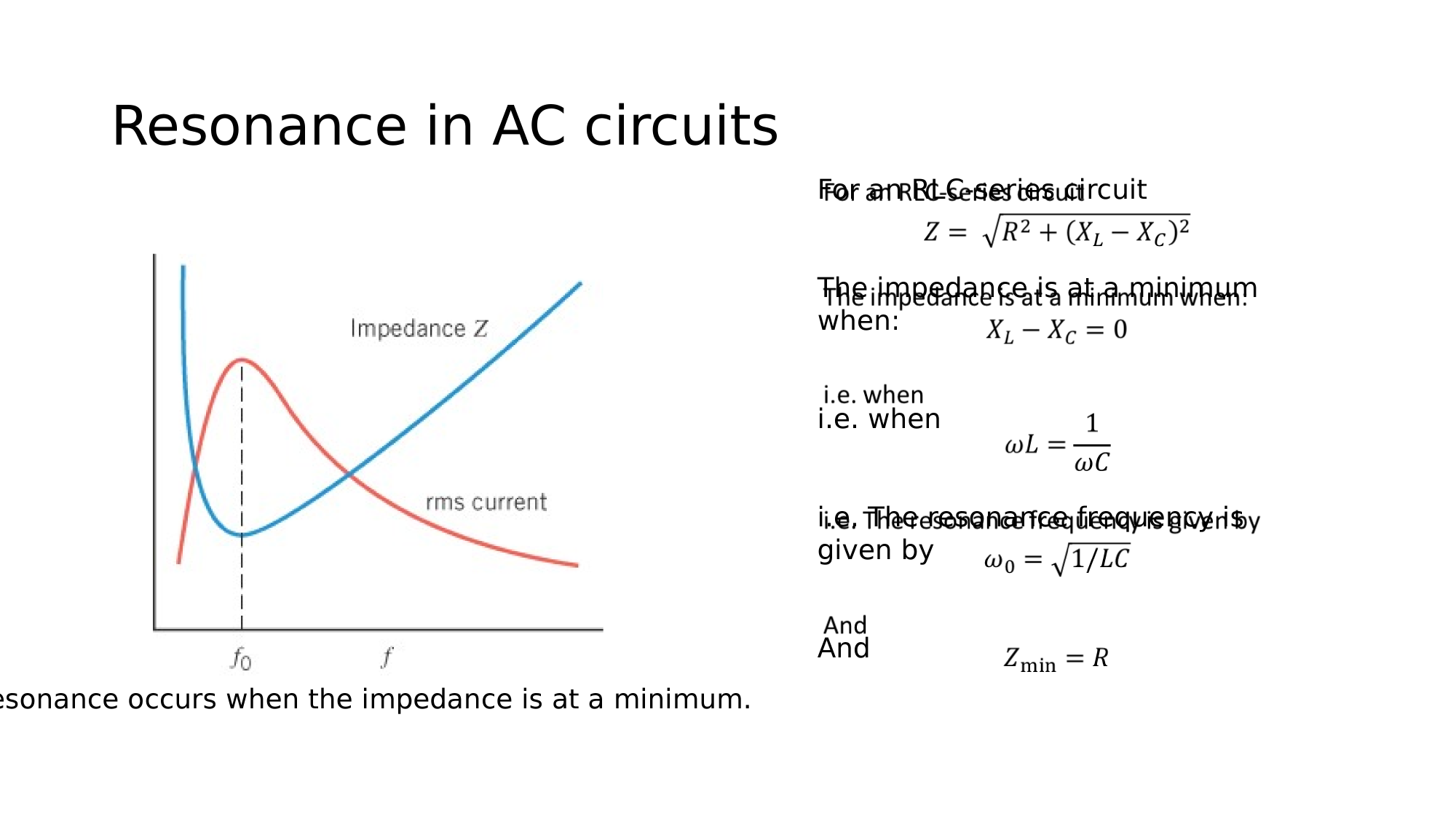
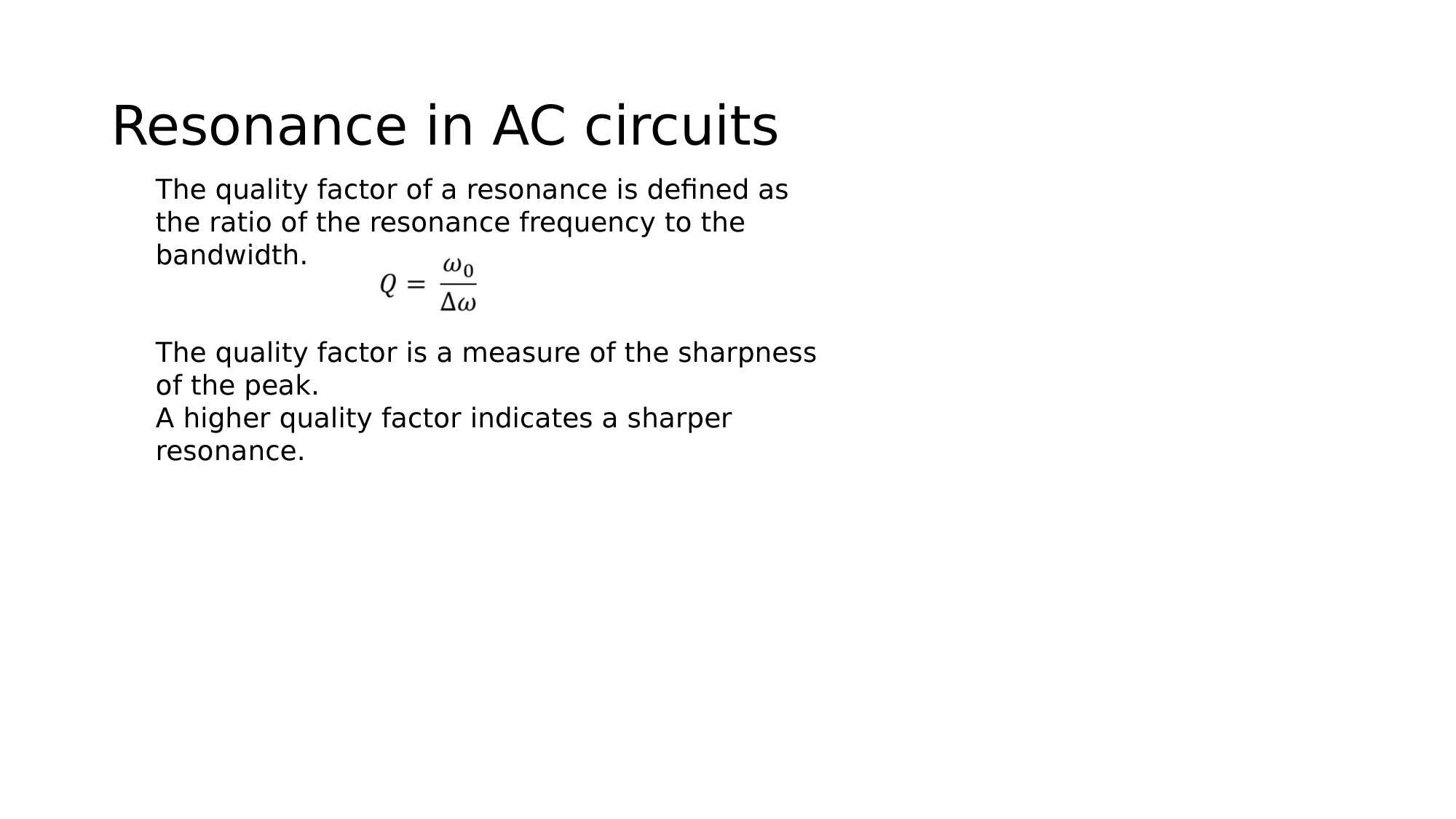
Condition for resonance
AC-circuits
Resonance in AC-circuits
[CA] Resonance
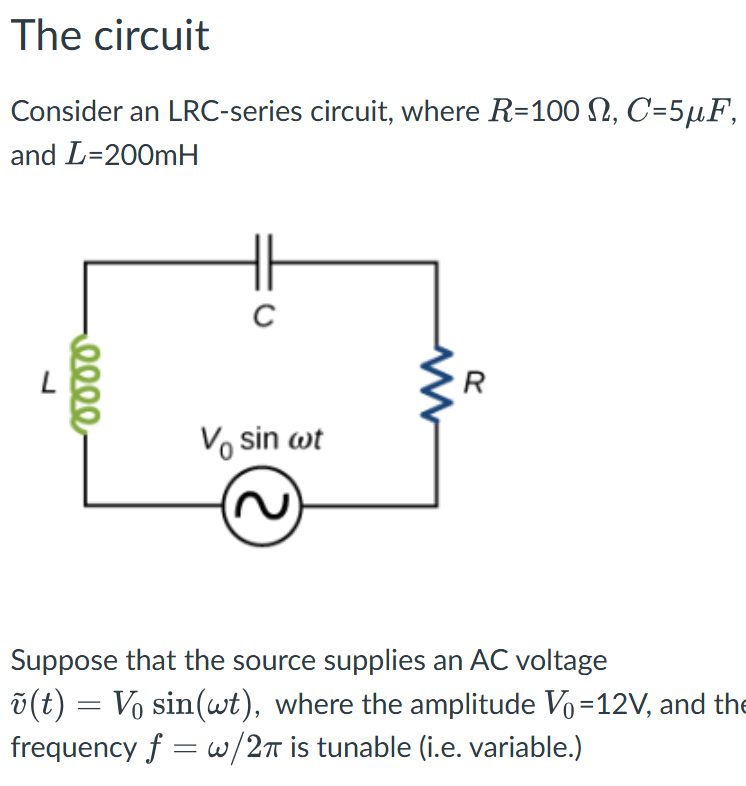

AC-circuits
Resonance in AC-circuits
[CA] Resonance


AC-circuits
Resonance in AC-circuits
[CA] Resonance


AC-circuits
Resonance in AC-circuits
[CA] Resonance


AC-circuits
Resonance in AC-circuits
[CA] Resonance


AC-Circuits