EM-waves
more on EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
EM-waves
Energy
The energy stored in the electric field in the volume between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor is given by
EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
The energy density stored in the electric field:
EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
The energy density stored in the magnetic field:
EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
For an electromagnetic wave, for a sample volume, which field carries more share of the energy (E or B) ?
EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
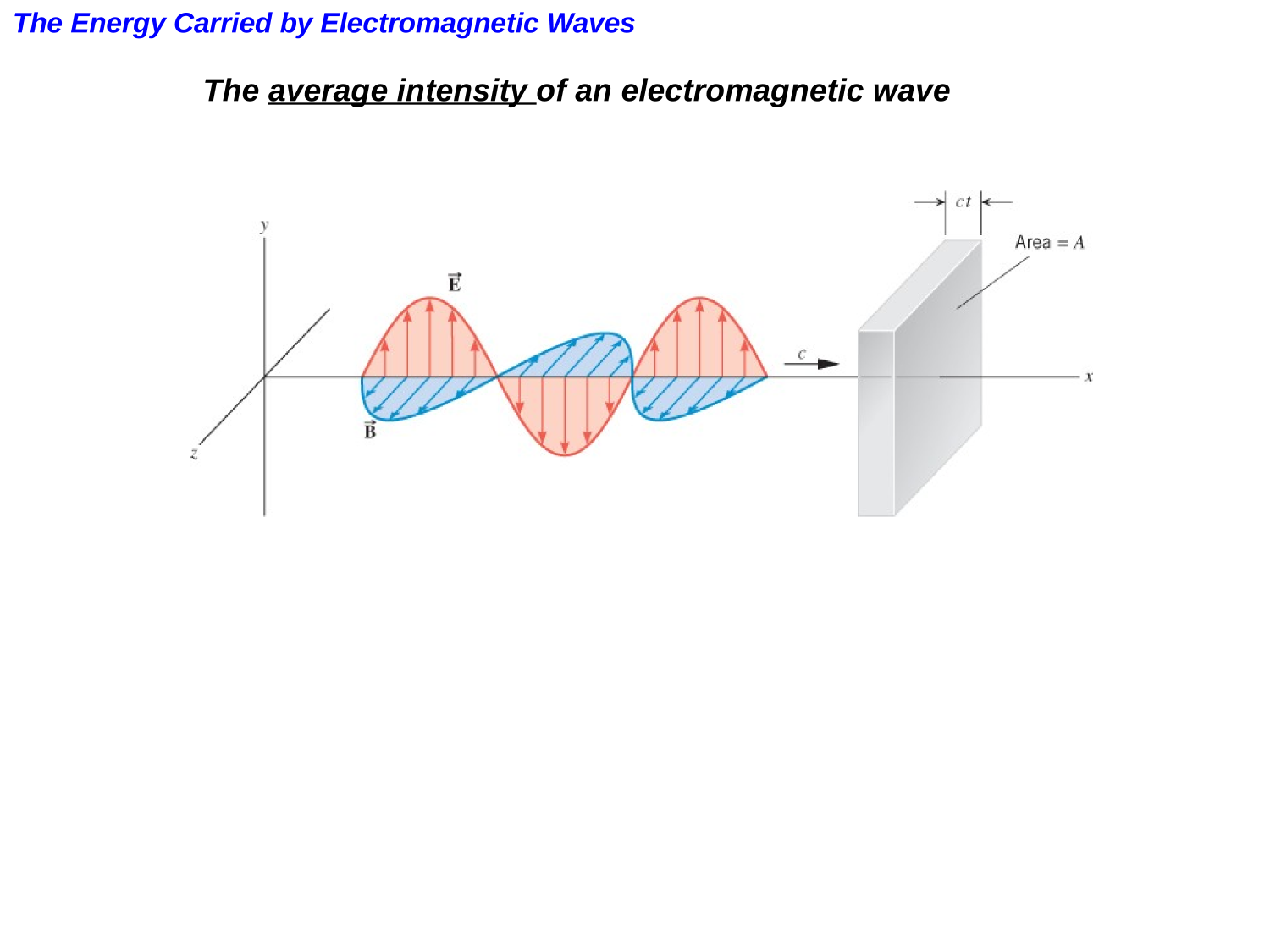
The energy carried by the wave per unit area per unit time is called the energy flux S:
EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
Taking the direction of propagation into account, we get the Poynting vector:
For an electromagnetic wave given by:
EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
We define the intensity as the average flux density over one cycle
EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
A plane electromagnetic wave travels northward. At one instant, its electric field has a magnitude of 6.0 V/m and points eastward. What are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at this instant?
The electric field, the magnetic field, and the Poynting vectors are mutually orthogonal. Curl from E (east) to B (downwards), to get S (north)
EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
The beam from a small laboratory laser has a radius of 2.0mm and a power of 15.0 mW. Assuming that the beam is composed of plane waves, calculate the amplitudes of the electric and magnetic fields in the beam.

EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
A light bulb emits 5.00 W of power as visible light. What are the electric and magnetic fields from the light at a distance of 3.0 m?

EM-waves
Energy & Intensity
How much energy does an EM wave carry?
A 150-W lightbulb emits 5% of its energy as electromagnetic radiation. What is the magnitude of the average Poynting vector 10 m from the bulb?

Wave Interference
EM-waves
Other phenomena
Suppose that two sources are generating two waves with similar properties:
EM-waves
Interference
Introduction
The waves arriving from multiple sources will have different phases:
Case I: the two waves arrive in phase
EM-waves
Interference
Introduction
Case II: the two waves arrive out of phase
Case I: the two waves arrive in phase
EM-waves
Interference
Introduction
Case II: the two waves arrive out of phase
Case I: the two waves arrive in phase
EM-waves
Interference
Introduction
Case II: the two waves arrive out of phase
Huygen's principle
EM-waves
Other phenomena

EM-waves
Huygen's Principle
Introduction
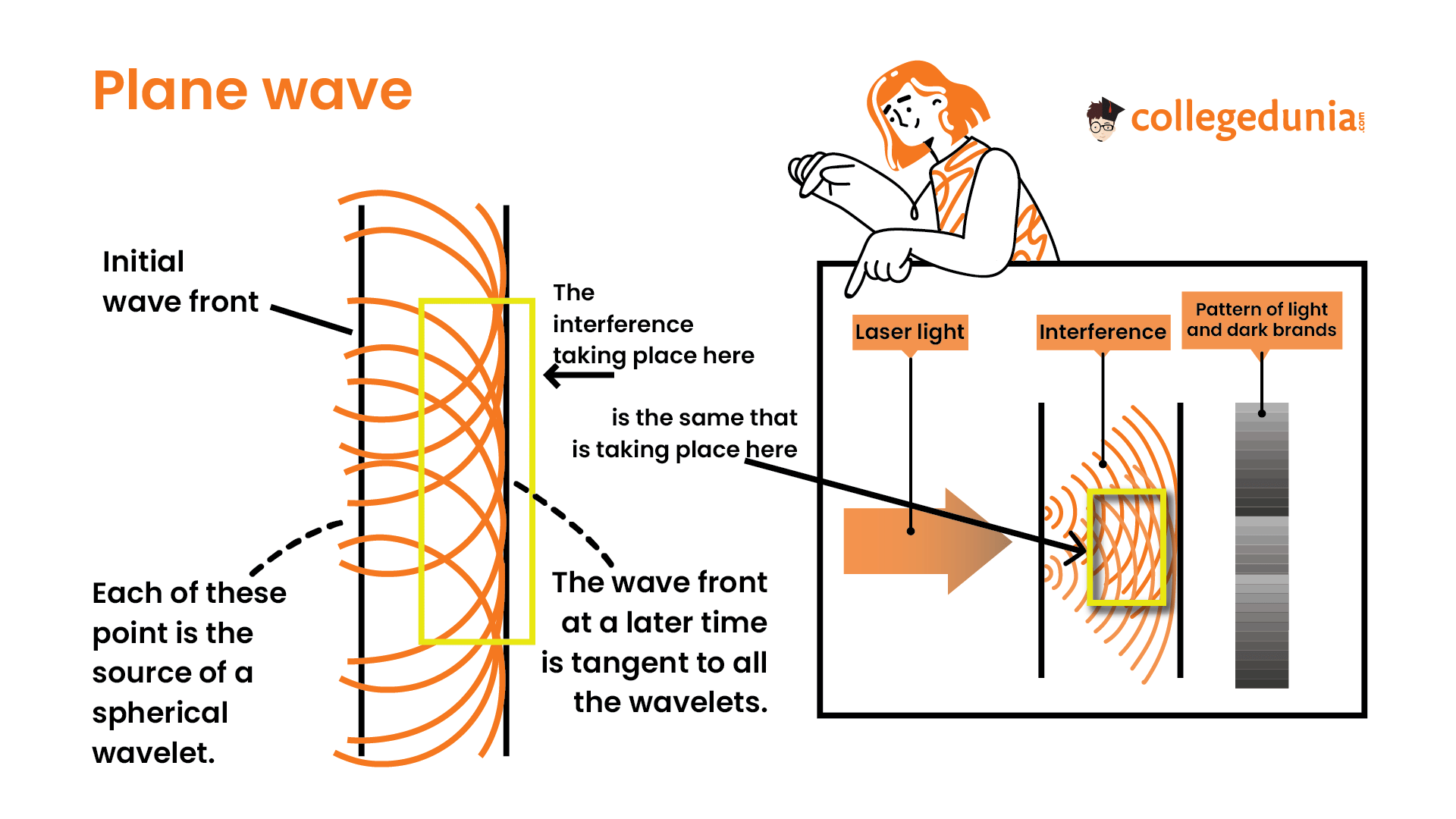
The Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens (1629–1695) developed a useful technique for determining in detail how and where waves propagate.
Huygens’s principle states that every point on a wave front is a source of wavelets that spread out in the forward direction at the same speed as the wave itself. The new wave front is tangent to all of the wavelets.
EM-waves
Huygen's Principle
Textbook examples
EM-waves
Huygen's Principle
Textbook examples
Forward propagation of plane waves
EM-waves
Huygen's Principle
Textbook examples

Outward propagation of spherical waves
EM-waves
Huygen's Principle
Textbook examples
Reflection of a plane wave by a plane mirror
EM-waves
Huygen's Principle
Textbook examples
Diffraction through an opening
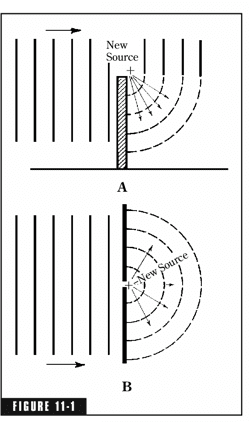
EM-waves
Huygen's Principle
Extra Resources

Diffraction
EM-waves
Other phenomena
EM-waves
Diffraction
Introduction
The phenomenon of diffraction is observed when a wave is incident on an opening.
EM-waves
Diffraction
Single slit diffraction
When the wavelength of the incident wave is comparable to the size of the opening, a single slit diffraction pattern is observed
EM-waves
Diffraction
Single slit diffraction
Analysis
(a) All rays are in phase; big bright peak at 0
(b) For each ray in the top half of the opening, there is a ray from the bottom half of the opening that destructively interferes with it.
EM-waves
Diffraction
Single slit diffraction
destructive interference for a single slit
for
EM-waves
Diffraction
Single slit diffraction
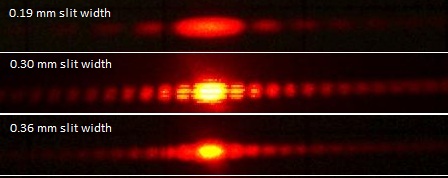
EM-waves
Diffraction
Double slit diffraction
The double-slit pattern is a product of the diffraction and the interference patterns
EM-waves
Diffraction
Babinet's Principle
Babinet's principle states that the diffraction pattern from an opaque body is identical to that from a hole of the same size and shape except for the overall forward beam intensity.
i.e. the diffraction pattern from a thin strip is the same as that from a thin slit.
EM-waves
Diffraction
[CA] Single slit diffraction
Find the thickness of a human hair.
Step 1.
The Doppler Effect
EM-waves
Other phenomena


The Doppler Effect for Sound Waves


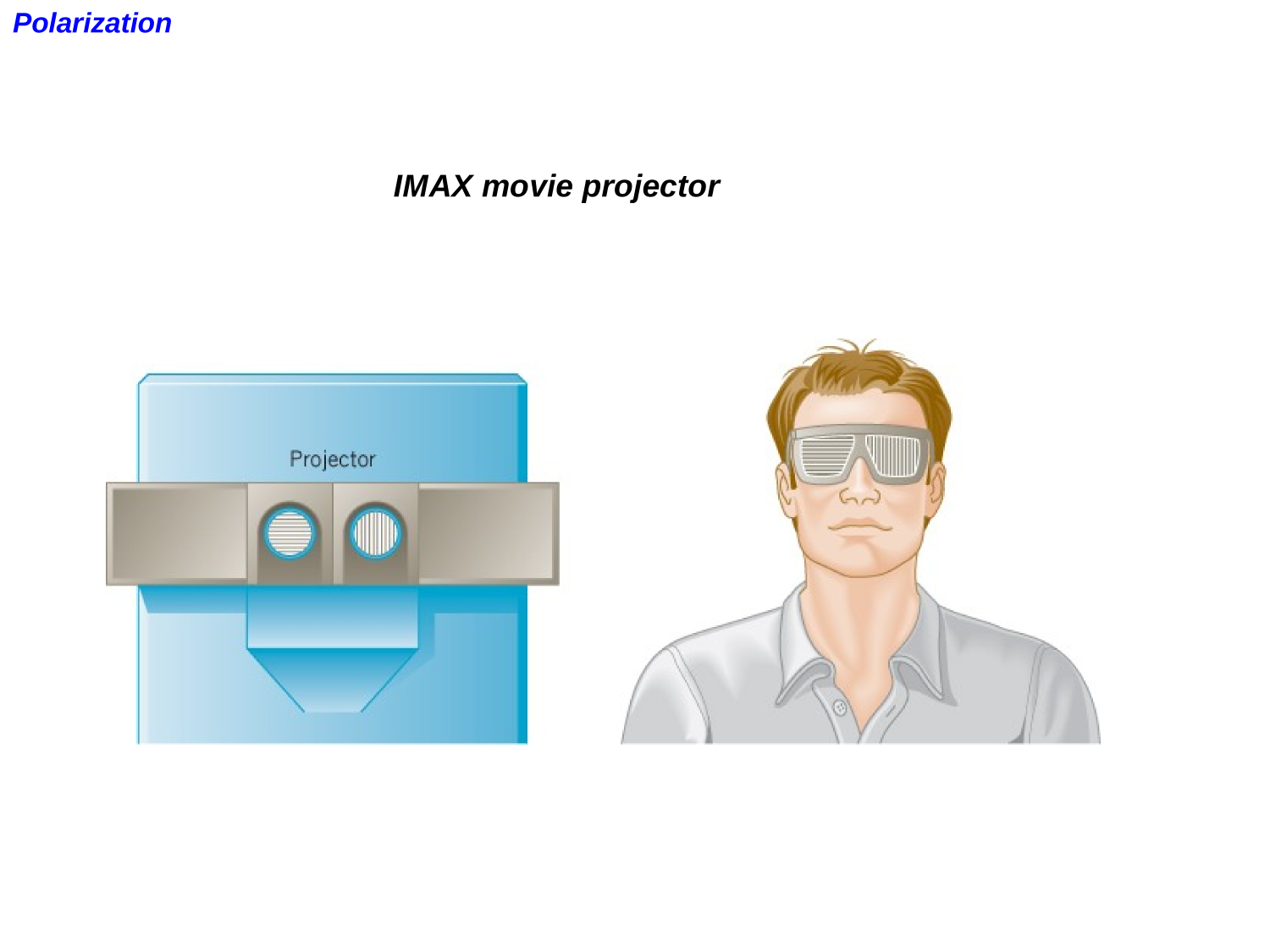
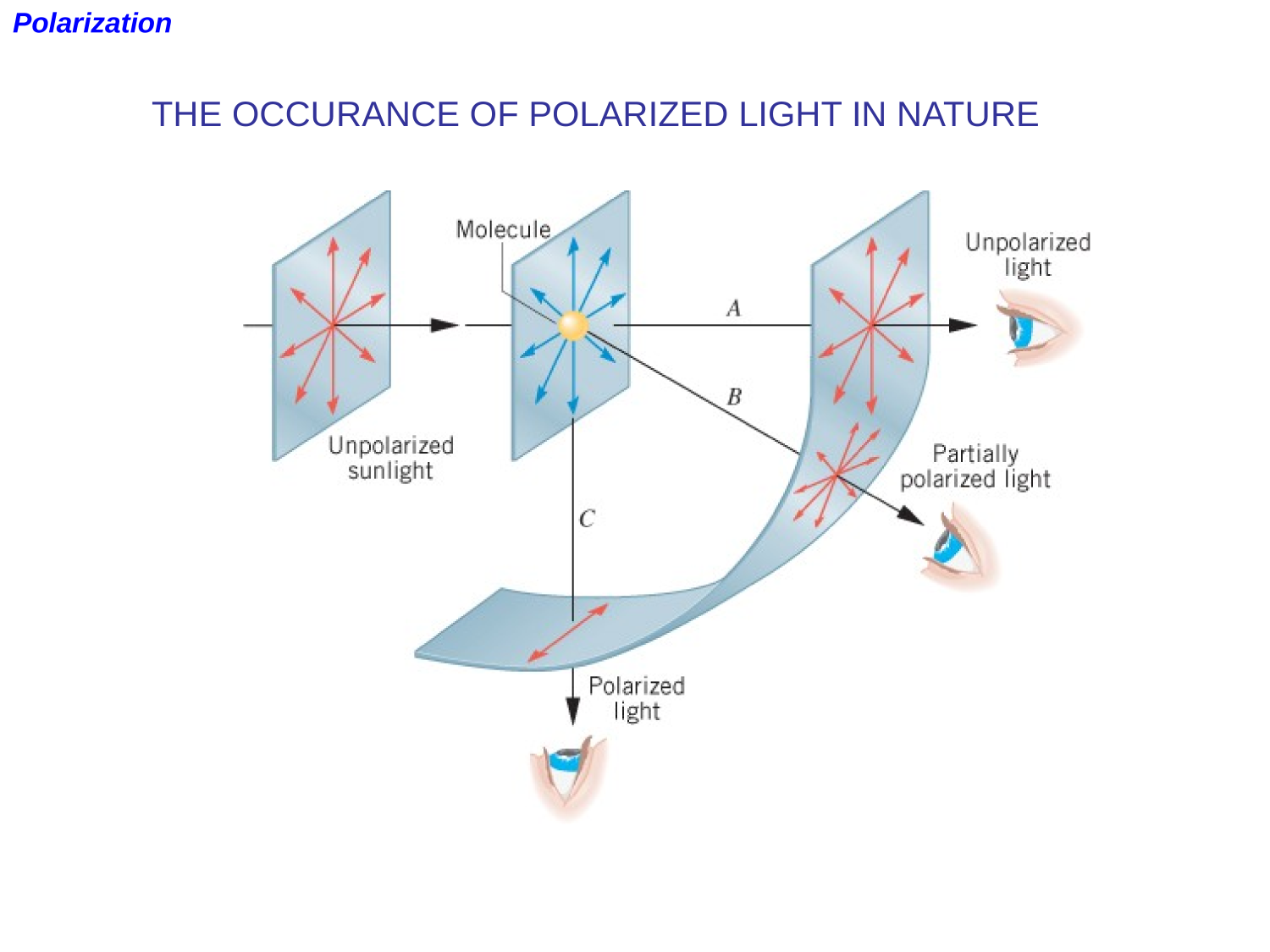
Polarization
EM-waves
Other phenomena

EM-waves
Polarization
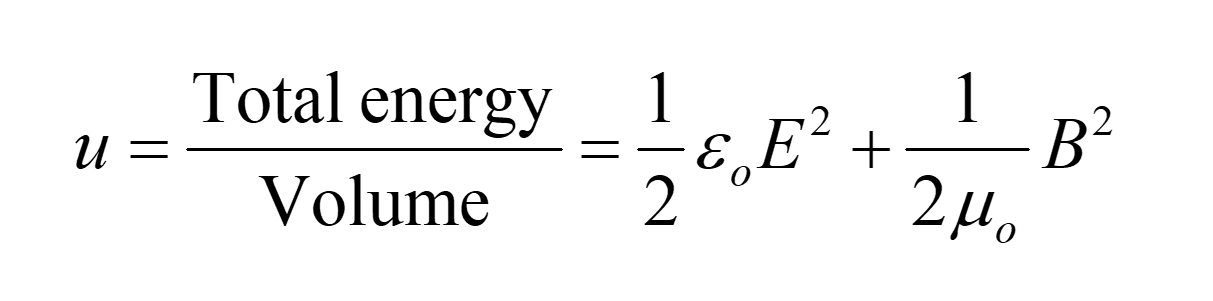
EM-waves
Polarization
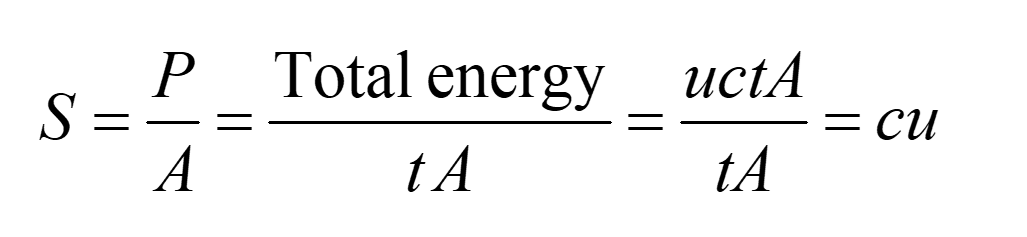
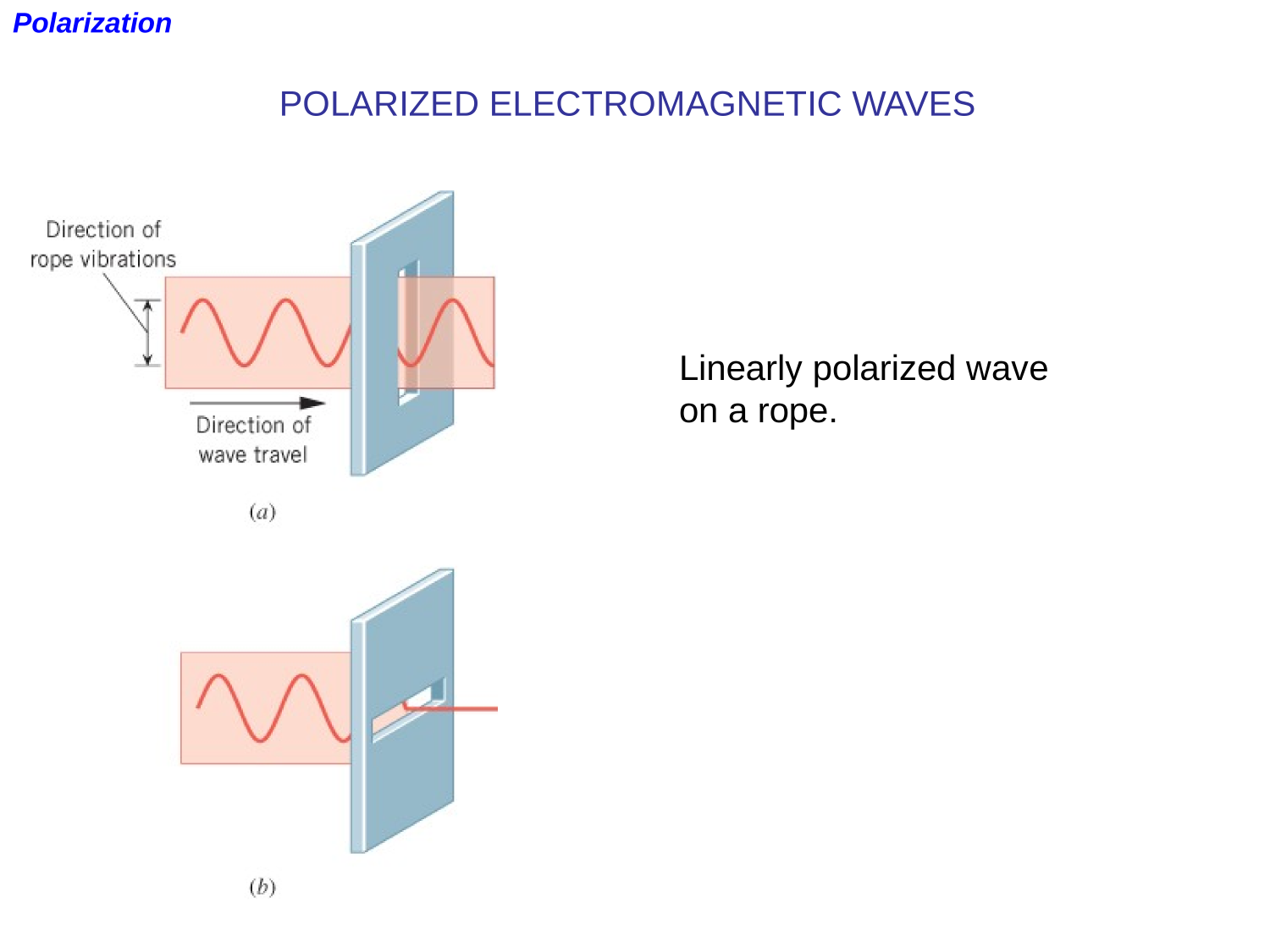
EM-waves
Polarization
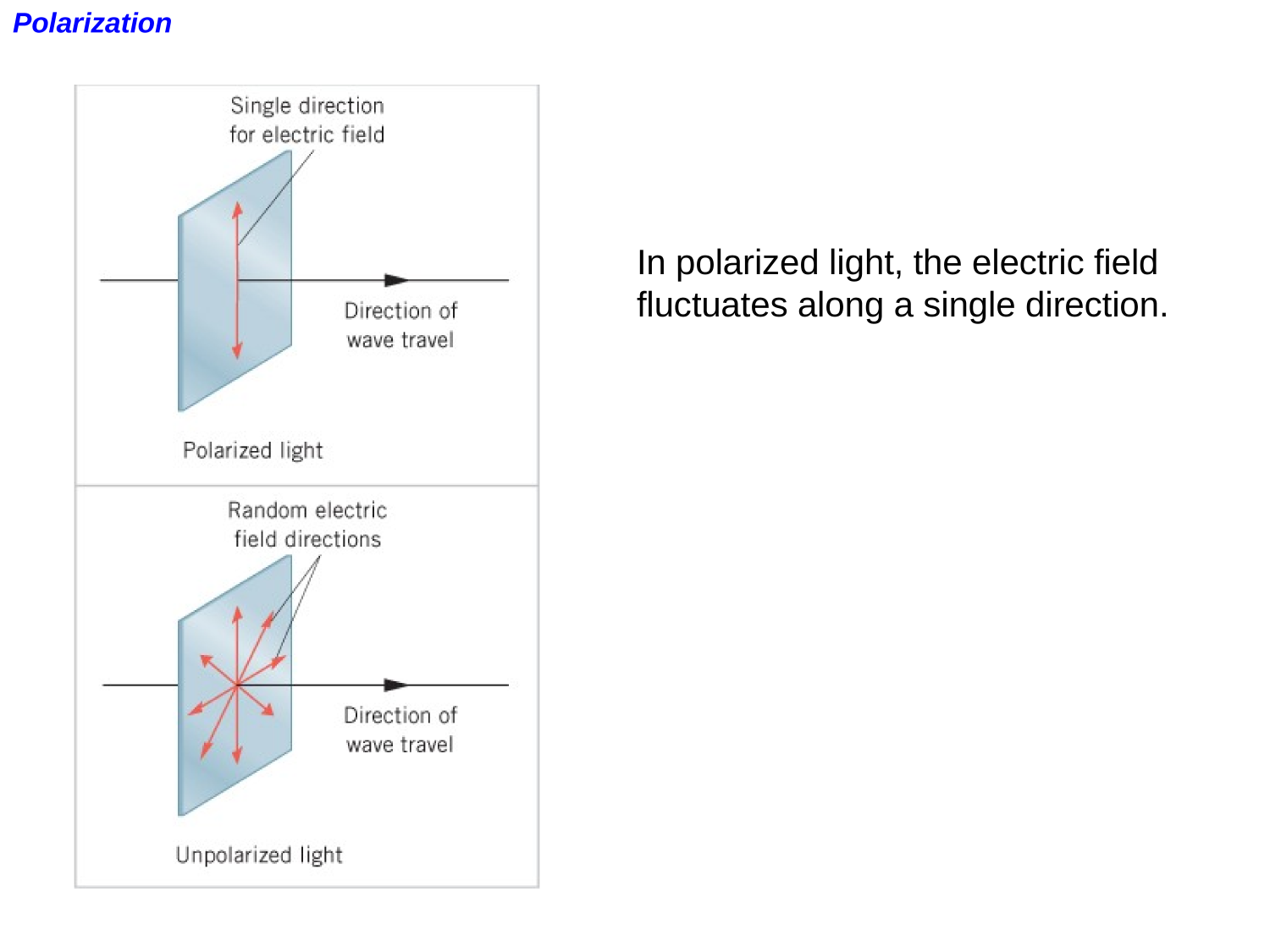
EM-waves
Polarization
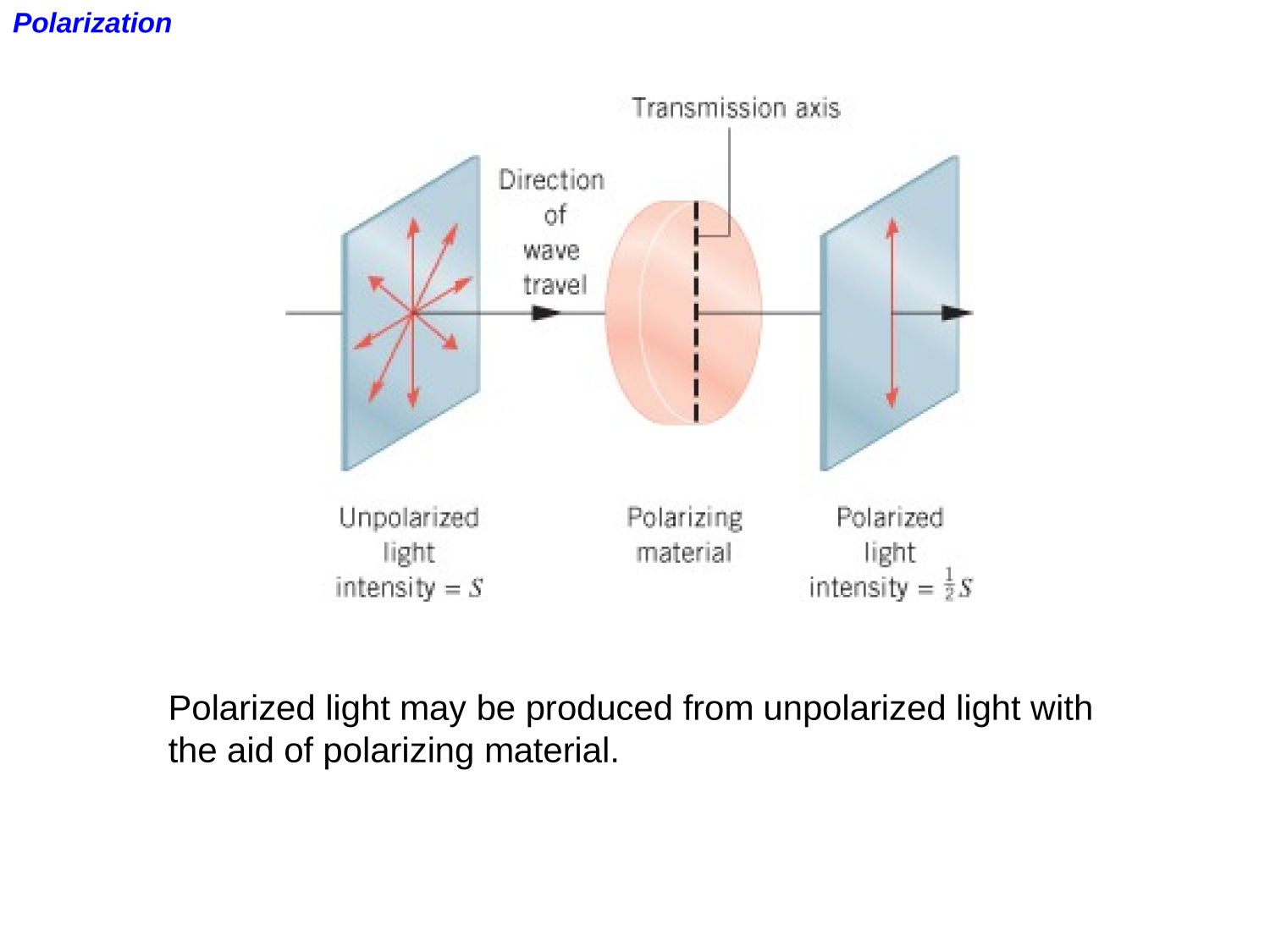
EM-waves
Polarization
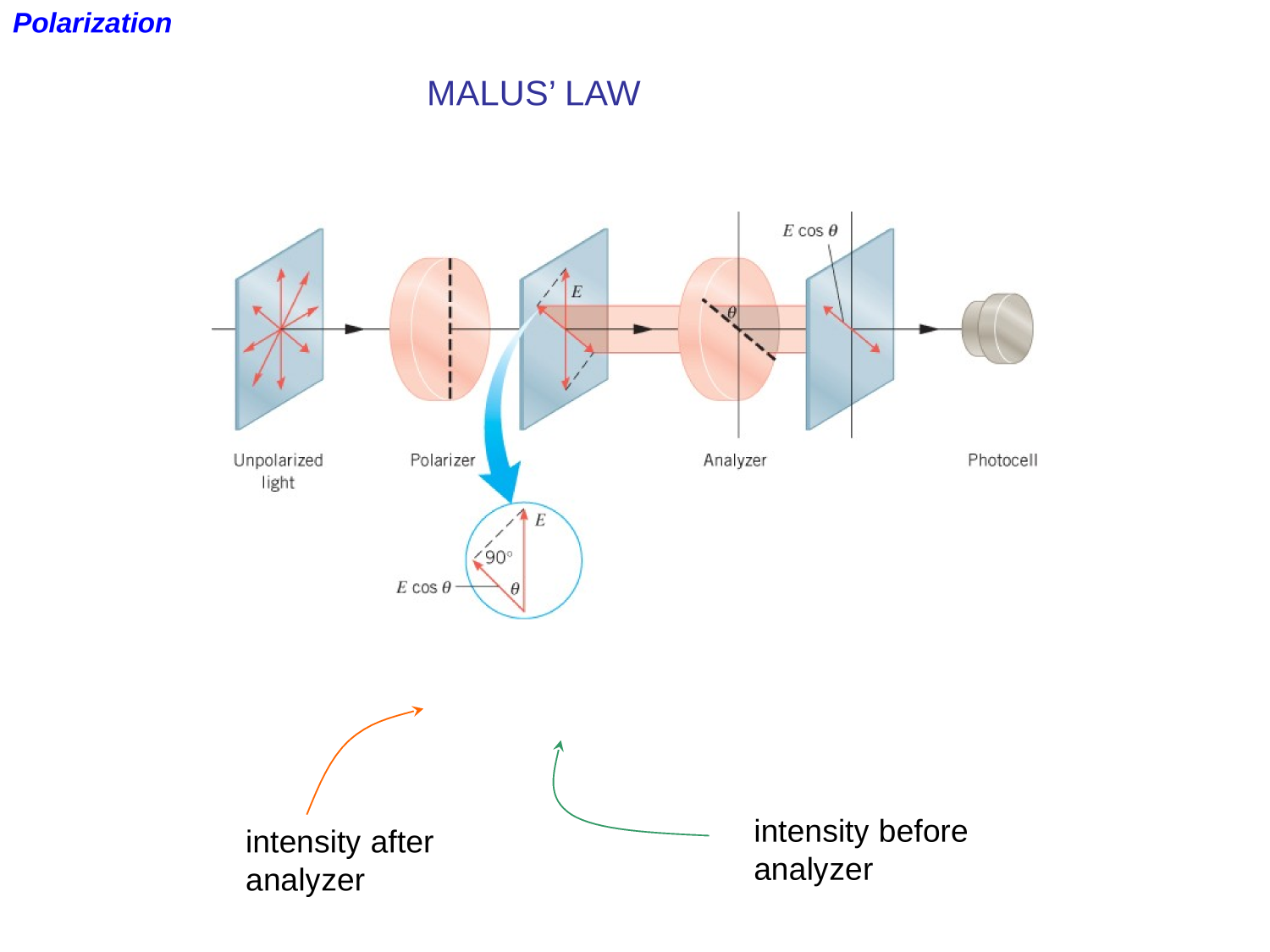
EM-waves
Polarization
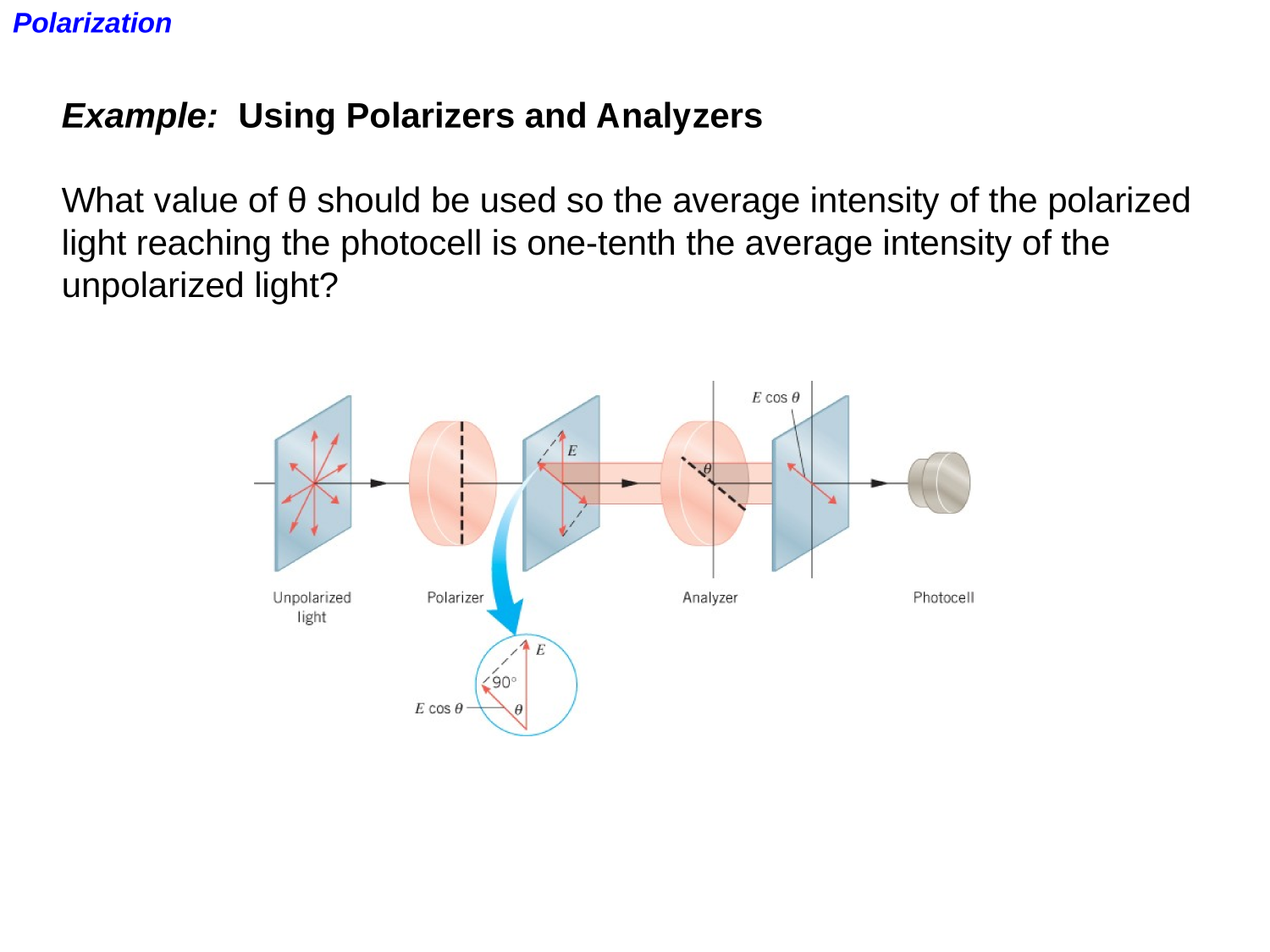
EM-waves
Polarization
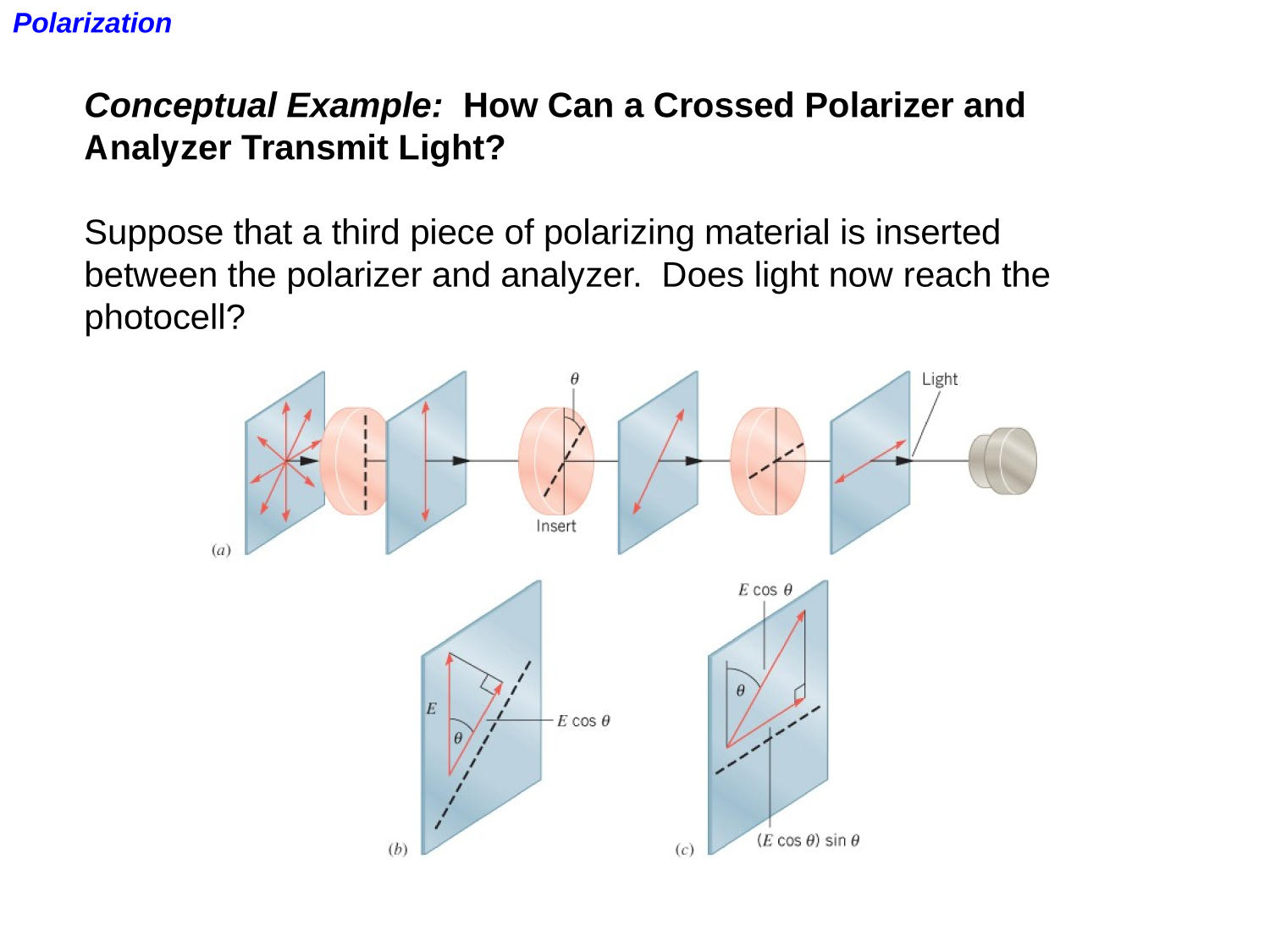
EM-waves
Polarization
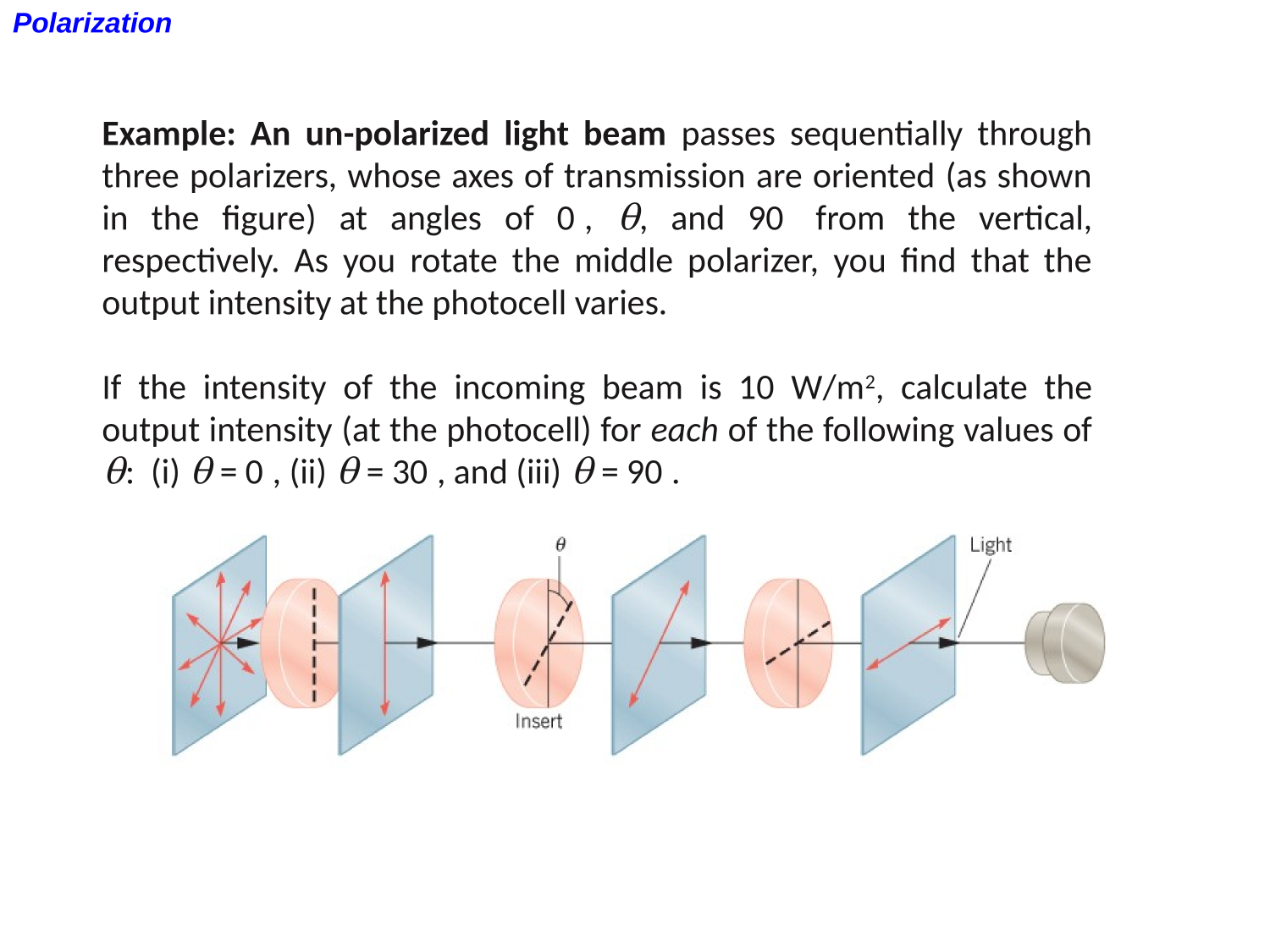
EM-waves
Polarization

EM-waves
Polarization