GL 9 IFR Enroute

Rev 02/2025
Disclaimer

Students should use their textbooks, syllabus, and Airman Certification Standards (ACS) as their primary sources of information. EcFlight is an online training tool designed to simplify and enhance your ground school learning experience. However, it is not a substitute for FAA- or school-approved study materials. Before using these slides for study, always refer to your officially approved resources, such as the Jeppesen physical or electronic book and other FAA-approved materials.
Reference Books
- Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge(FAA-H-8083-25B). (2016). Oklahoma City, OK: United States Department of Transportation, Federal Aviation Administration, Airman Testing Standards Branch.
- Instrument Flying Handbook faa-h-8083-15B. (2012). Oklahoma City, OK: United States Department of Transportation, Federal Aviation Administration, Airman Testing Standards Branch.
- Instrument Pilot Syllabus (10001785-003). (2015). Englewood, CO: Jeppesen.
Reference Multimedia
- IFR Enroute Aeronautical Charts and Planning. (2019, March 08). Retrieved from https://www.faa.gov/air_traffic/flight_info/aeronav/digital_products/ifr/
- IFR Enroute Aeronautical Charts and Planning. (2019, March 08). Retrieved from https://www.faa.gov/air_traffic/flight_info/aeronav/digital_products/ifr/
- https://www.faa.gov/air_traffic/flight_info/aeronav/acf/media/Presentations/16-01-RD303_ARR-DEP_Routes_on_TACs_Duke.pdf
Index
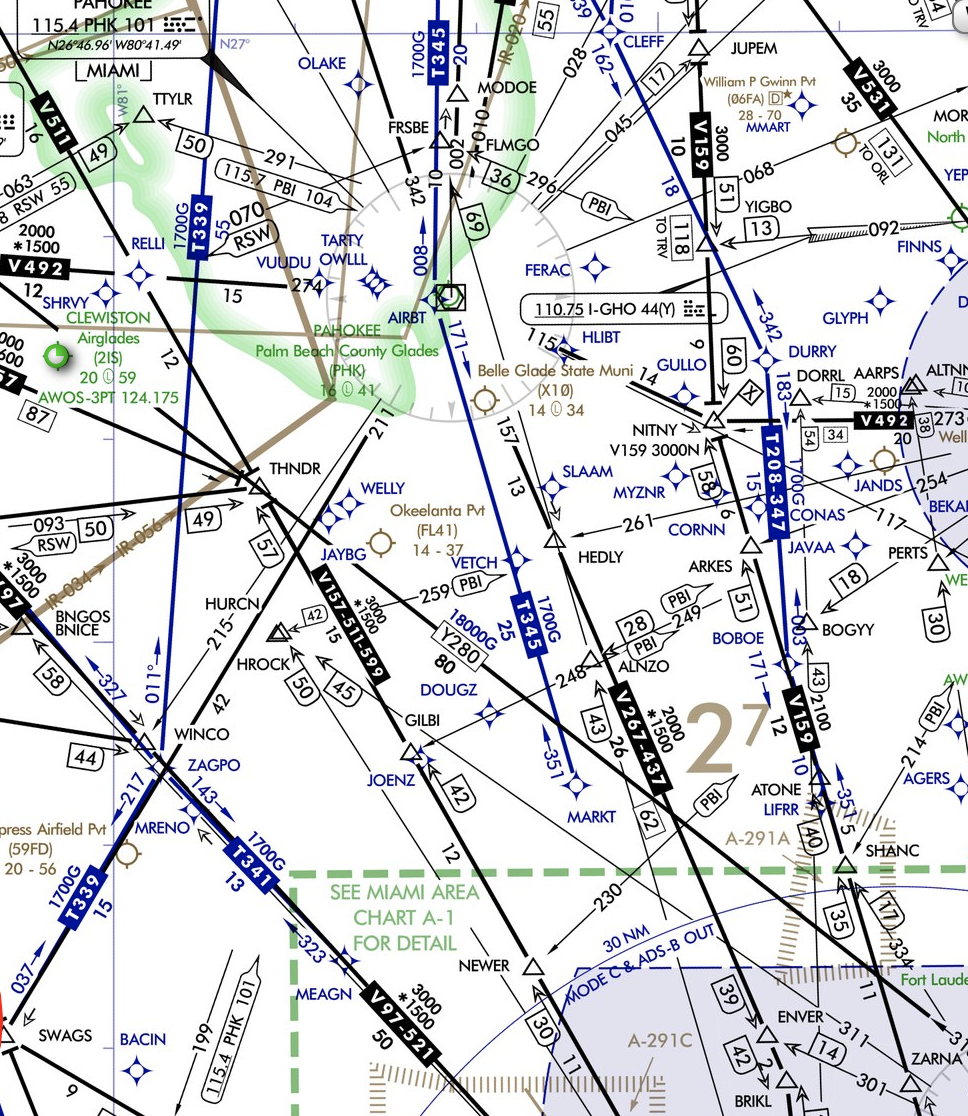
Enroute and Area Chart
Enroute Charts
Enroute charts are divided into:
- Low Altitude airways (Below 18,000 feet MSL).
- High altitude airways (Above 18,000 feet MSL).
- Surface features are shown are major bodies of water and airports.
- Clearance and reception are guaranteed by flying the minimum IFR altitudes.
Front Panel


- Major cities and state boundaries are shown on the diagram to help you find the appropriate chart more easily.
- Charts expire every 56 days.
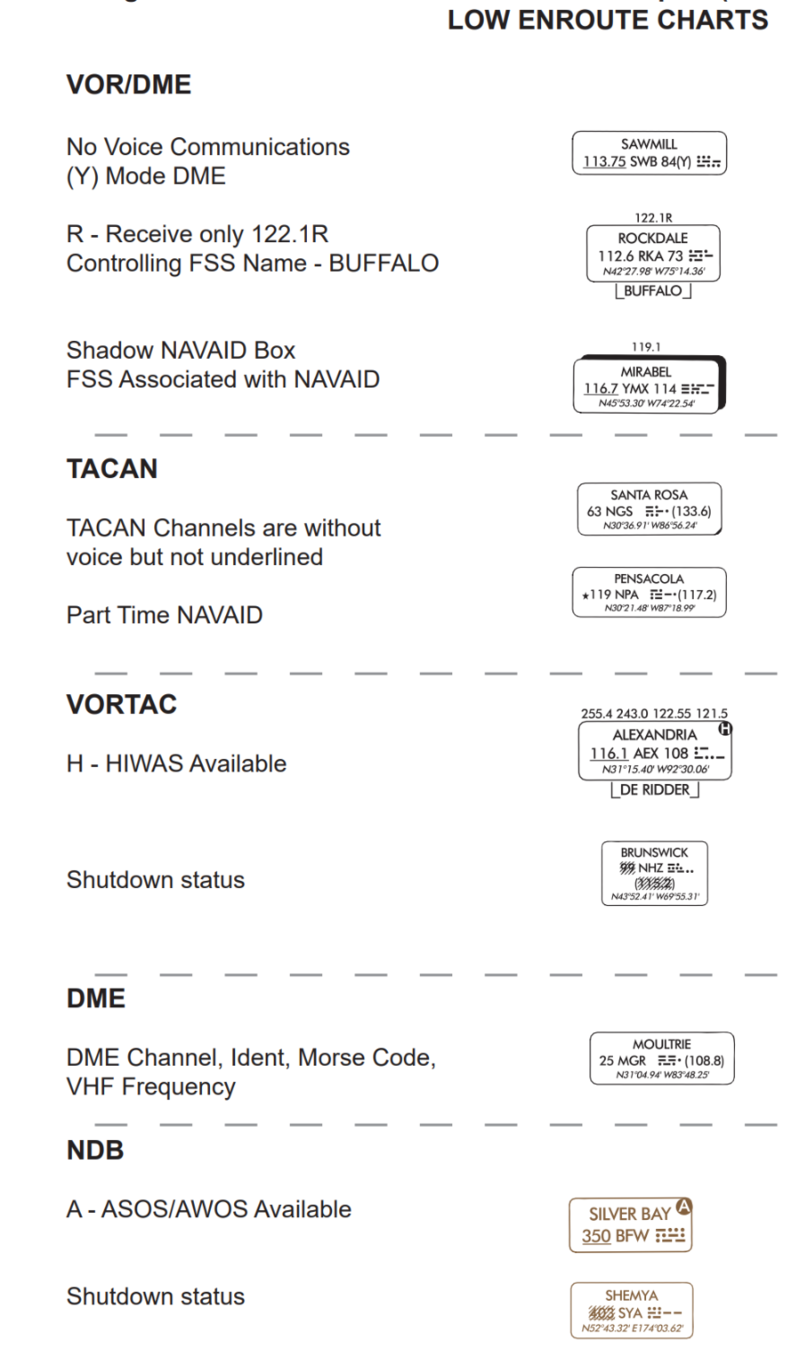
Navigation Aids

Victor Airways
- Victor airways are connected in between with VOR, VORTAC, and VOR/DME.
- The width of a victor airway is usually 8 nautical miles.
- The number of Victor Airway indicates its general direction. Example:
Even = East and West direction. Odd = North and South direction"
When to switch VORs?
When you see the following:
Change of course
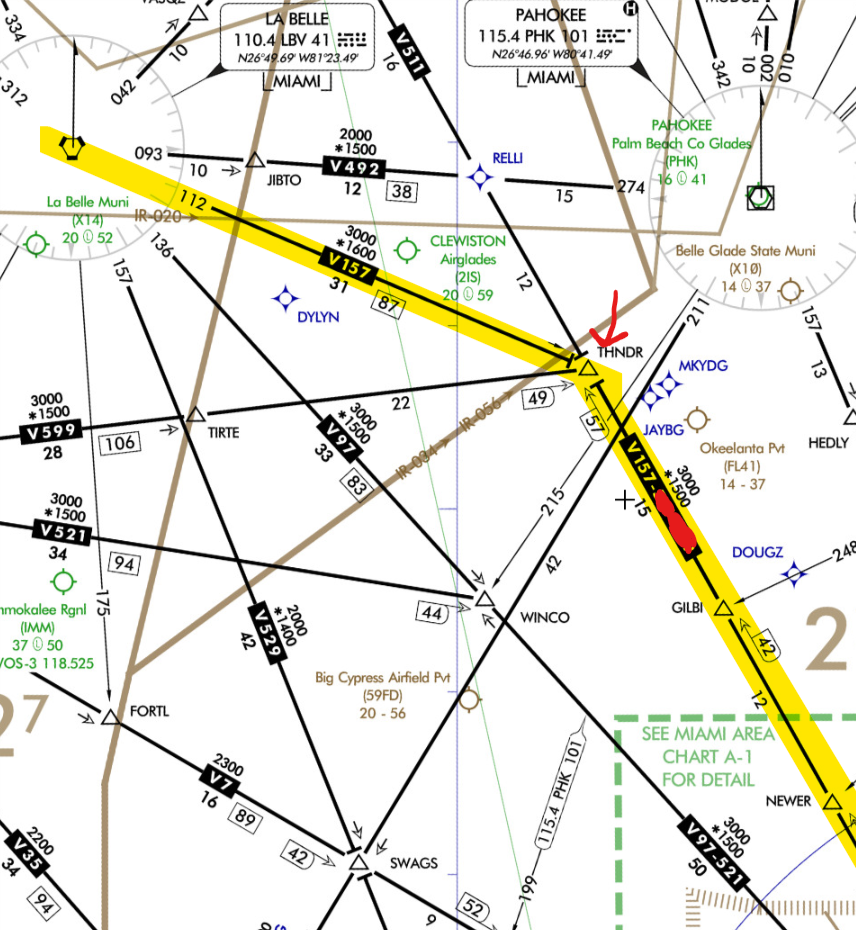
- While Flying NW on V157 switches to R-112 from La belle above THNDR intersection.
Milage Break point
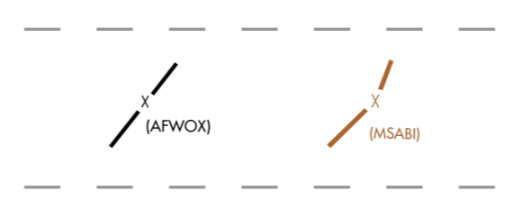
- Indicates a point on the airway where the course changes direction and no intersection is designated.
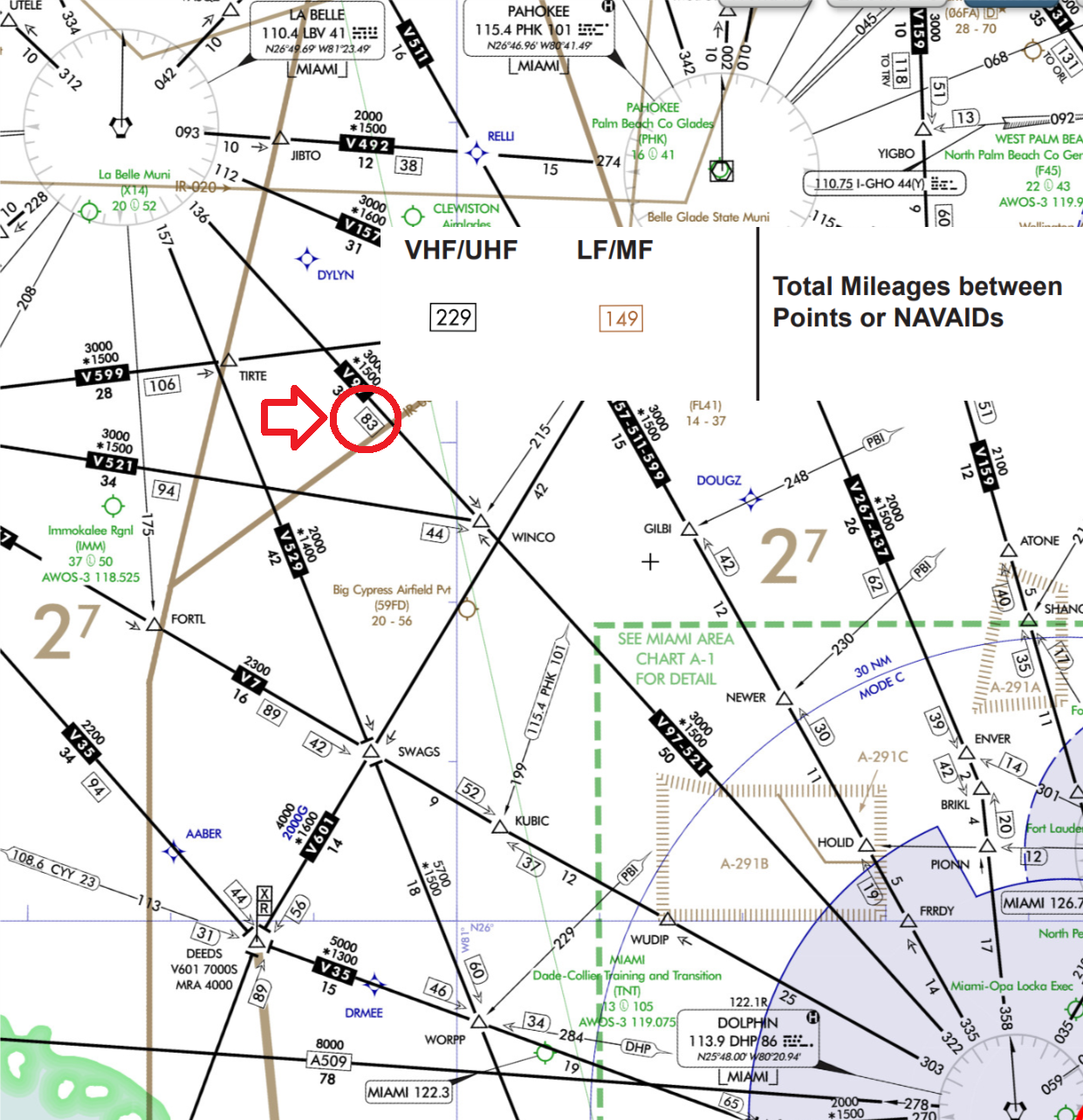
Half Distance of the V-Airway
- V97 (between LBV and DHP) has a total distance of 83 NM. The VORs will be changed approximately 41 nautical miles from each other.
Changeover Point
- A changeover point (COP) is established when a change must be made somewhere other than the midpoint.
Intersections
- Intersections are points along an airway that provide aircraft's position information to ATC.
- Can be identified by:
- Two VOR radials
- DME distance
- Other navaids like localizer or NDB
Minimum Enroute Altitude (MEA)
- Guarantees adequate navigation signal reception and obstruction clearance (2,000 ft mountainous areas and 1,000 ft elsewhere).
- MEA may have gaps in between and will not provide signal coverage up to 65 NM, this gap will be charted.

Minimum Obstruction Clearance Altitude (MOCA)
- Guarantees adequate navigation signal reception within 22NM and obstruction clearance (2,000 ft mountainous areas and 1,000 ft elsewhere).

Off-Route Obstruction Clearance Altitude (OROCA)
- Guarantees obstruction clearance for each quadrangle of latitude and longitude (2,000 feet for mountainous terrain and 1,000 feet elsewhere within a radius of 4 nautical miles).


In this case, if not flying on top of an airway, the pilot should fly at least the OROCA (2,700 ft).
Maximum Authorized Altitude (MAA)
An MAA is a published altitude representing the maximum usable altitude or flight level for an airspace structure or route segment. It is the highest altitude on a Federal airway or RNAV route.
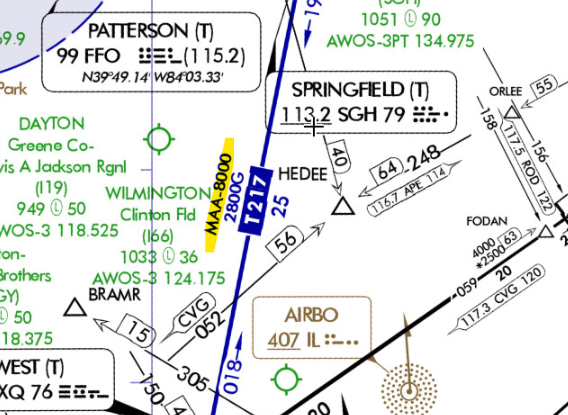
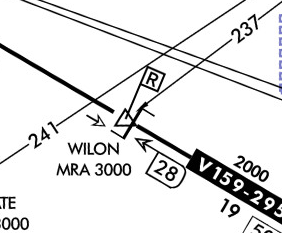
Minimum Reception Altitude (MRA)
The MRA establishes the minimum altitude the navigation signal can be received for the route and for off-course NAVAID facilities that determine a fix.
When the MRA at the fix is higher than the MEA, an MRA is established for the fix and is the lowest altitude at which an intersection can be determined.
The bar symbol indicates a change of MEA, MOCA and MAA after crossing the fix.
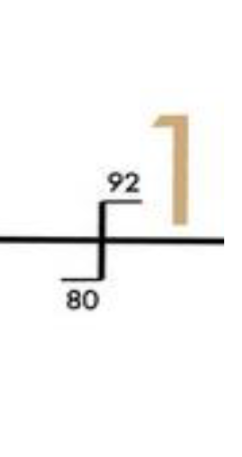
Minimum Crossing Altitude (MCA)
- An MCA is the lowest altitude at certain fixes at which the aircraft must cross when proceeding in the direction of a higher minimum enroute IFR altitude.
- MCAs are established in all cases where obstacles intervene to prevent pilots from maintaining obstacle clearance during a normal climb to a higher MEA after passing a point beyond which the higher MEA applies.
Example of MCA
RNAV Routes
RNAV Routes
- The RNAV routes will provide more direct routing for IFR aircraft and enhance the safety and efficiency of the National Airspace System.
- The aircraft is required to be equipped with IFR approved GNSS.
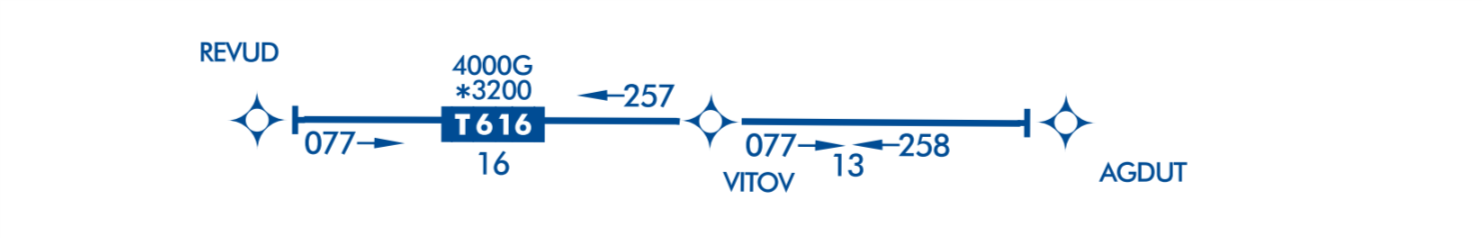
RNAV only routes are identified by the prefix "T"
Communication
- Ground stations are also capable of transmitting voice.
- FSS communication frequencies are on top of the NAVAID box.
Airports
- Facilities in BLUE or GREEN have an approved Instrument Approach Procedure and/or RADAR MINIMA published.
- Those in BLUE have an Instrument Approach Procedure and/or RADAR MINIMA published at least in the High Altitude DoD FLIPs. Facilities in
- BROWN do not have a published Instrument Procedure or RADAR MINIMA.

Airspace
Air Route Traffic Control Centers (ARTCC) are established to provide Air Traffic Control to aircraft operating on IFR flight plans within controlled airspace.


Class B
Mode C Veil
Class C

A letter C will identify the aiport
For Example:
- FLL is located in a Class C airspace, we have seen that within the dash blue lines, but there is no letter C depicted.
- Refer to the Chart Supplement and you will find more information such as frequencies, type of airspace.
Class D
Special Use of Airspace
Confines certain flight activities, restricts entry, or cautions other aircraft operating within specific boundaries.
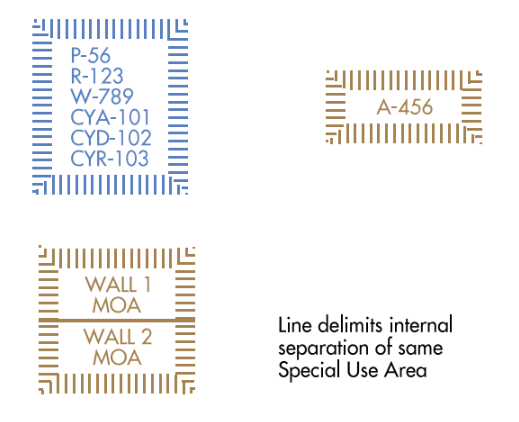
Prohibited
Restricted
Warning
Military
Operation
Areas
Alert Area
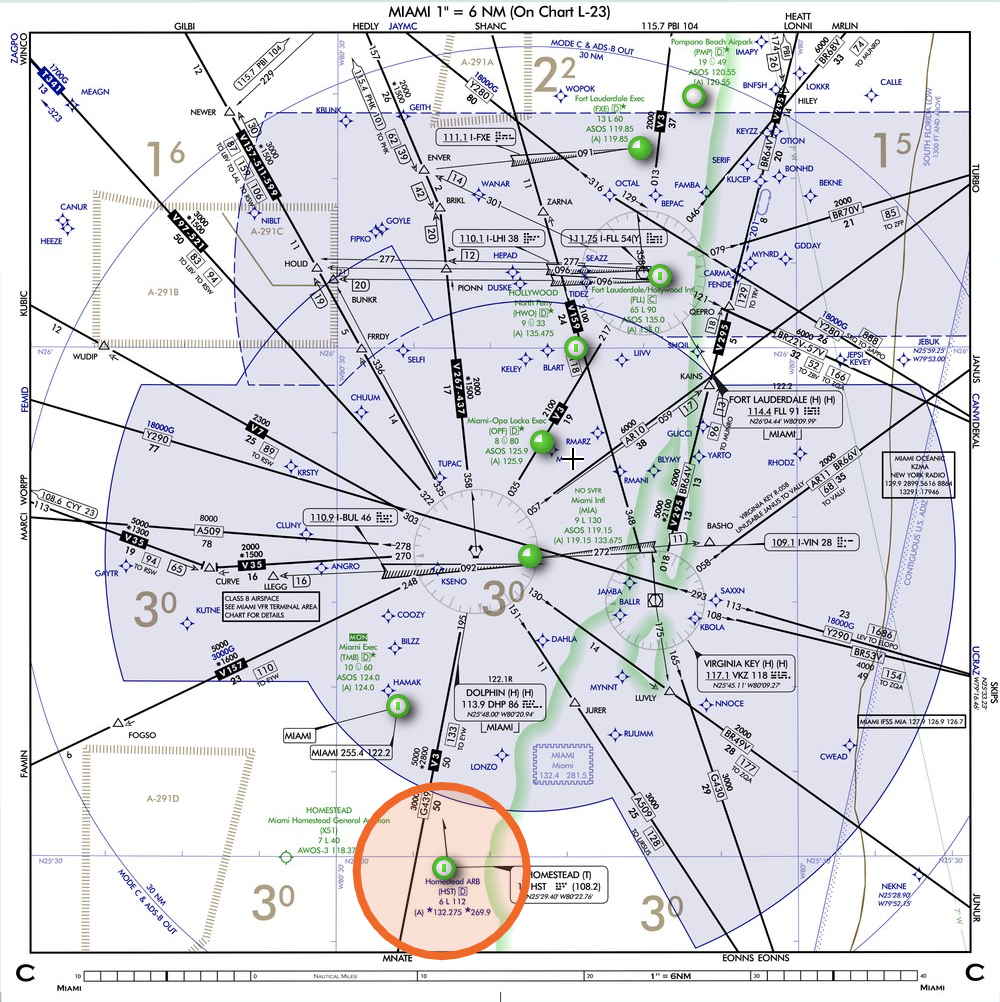
Area Chart
- Area charts are created to display locations on a larger scale, to improve readability and provide more detail to the pilot.
- Area charts do not provide approach or departure information but can help with the transition from departure to the enroute structure, and from enroute to approach.
Miami Area Chart
Enroute Procedures
- The enroute phase of an IFR flight involves more than just flying to your destination. Staying in communication with ATC, making necessary reports, and responding to clearances takes up a good portion of your time.
- The pilot also should monitor the aircraft's position and stay informed of any changes to the airplane’s equipment status or weather.
Enroute Radar Procedures
- Continuously monitor an appropriate center or control frequency.
- As your flight leaves the departure controller’s airspace, you will be instructed to contact the center.
- The instructions include the name of the facility, the appropriate frequency, and any pertinent remarks.
- Always acknowledge the information provided for a handoff to another controller
Communication
- When getting handoff to the next controller, advise the controller with heading and altitude.
- In case you cannot establish communication with the next controller, return to the previously assigned and request an alternate frequency.
Reporting Procedures
There are reports that you should make without a specific request from ATC: some during radar contact, others if radar has been terminated or lost.
M
A
O
U
R
S
E
V
V
L
R
F
500
Missed Approach
Airspeed Change of 5% or 10KTAS
Reaching a holding fix (report time & altitude)
VFR on top
ETA change ±2 min (Non-radar)
Leaving a holding fix/point
Outer marker (Non-radar)
Unforecasted weather (Non-radar)
Safety of flight
Vacating an altitude/FL
Final approach fix (Non-radar)
Radio/Nav failure
unable climb/descent 500 fpm
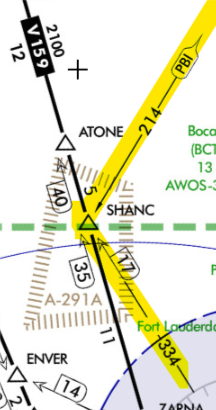
Reporting Items
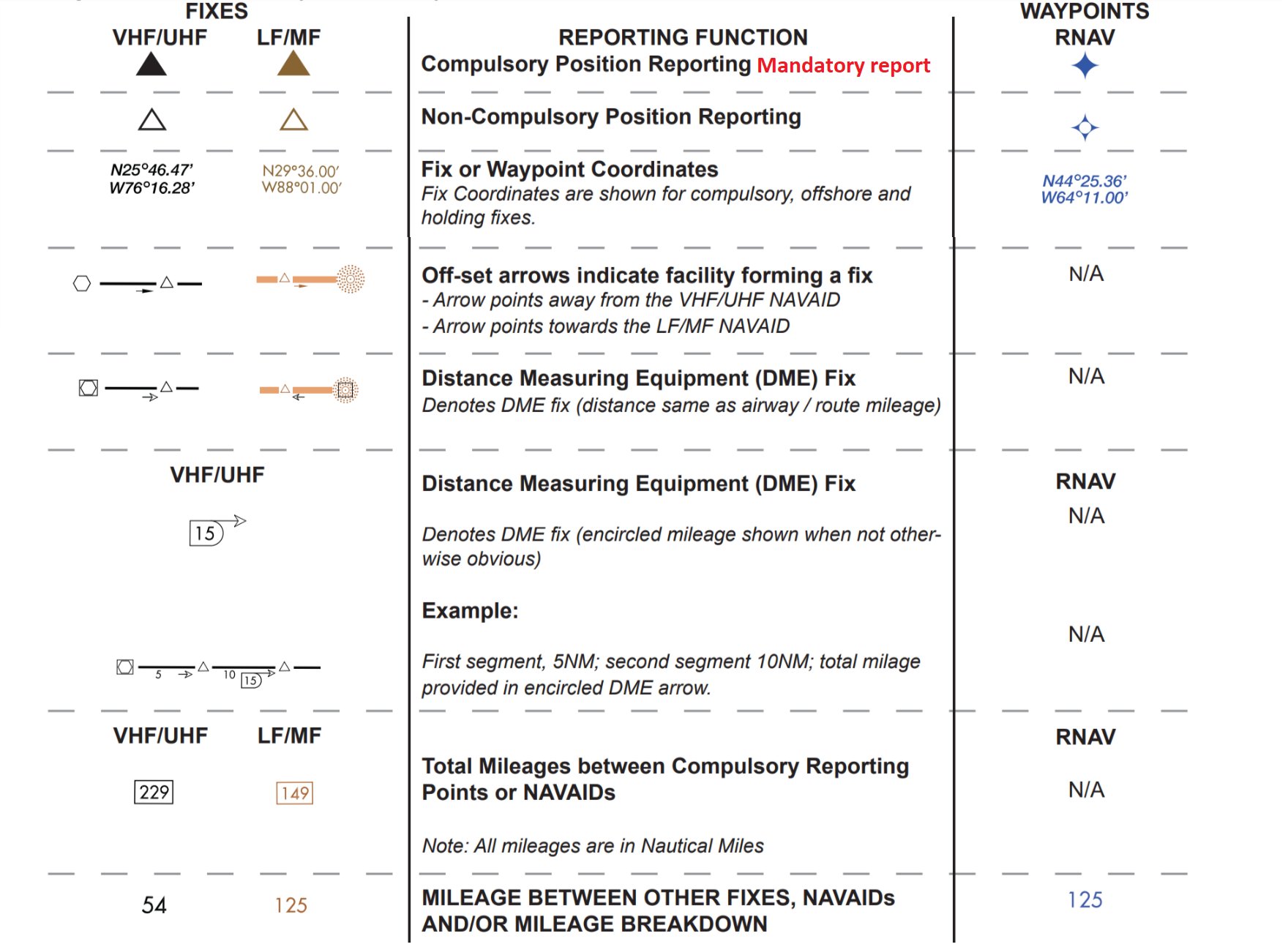
These compulsory reporting points are depicted on IFR enroute charts
by solid triangles.
Enroute Navigation Using GPS
- If the IFR GPS is not equipped to receive a wide area augmentation system (WAAS) correction signal, your aircraft must be equipped with an alternate means of navigation, such as VOR, appropriate to the flight.
- The alternate navigation system is not required for WAAS-equiped IFR approved GPS system.
- Active monitoring of alternate equipment is not required if the GPS has RAIM.
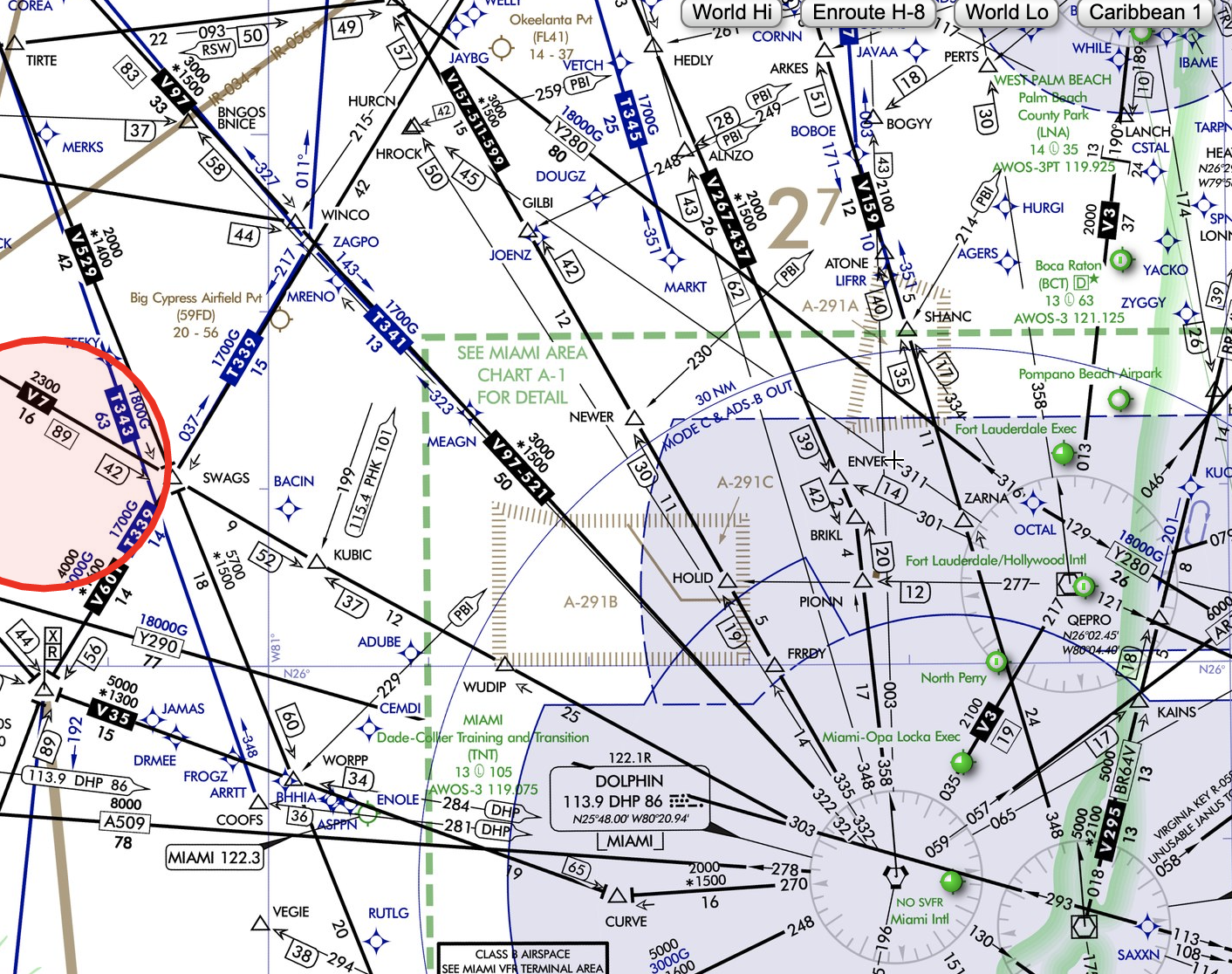
RNAV Routes
- RNAV routes are depicted in blue on aeronautical charts and are identified by the letter T or Q followed by the airway number.
- T-routes, or Tango routes, are depicted on Low altitude enroute charts, and reduce ATC workload, and these routes are around or through Class B and Class C airspace.
- Q-routes can be found on high-altitude enroute charts and help IFR traffic on long-range direct flights within congested airspace areas, such as the East and West Coasts of the U.S.
RNAV Routes
T341RNAV MEA is 1,700ft
T-Route
Q-Route
IFR Cruising Altitudes
FAR §91.179
Example: Magnetic Course 340°. Altitude should be 4,000, 6,000, FL240.
Reduced Vertical Separation Minimums (RVSM)
Descending from the Enroute Segment
- When ATC issues a Descend Clearance, the pilot needs to descend at the optimum rate for the specific aircraft until he/she is within 1,000 feet above the assigned altitude.
- The last 1.000 feet should be made at a rate of 500 to 1,500 FPM
- When ATC issues a Descend at pilot's discretion the descend may begin whenever he considers to.
- The pilot is also authorized to level off, temporary, at any intermediate altitude during the descent. However, once the pilot leaves an altitude, he may not return to it.
N.....Cross PHK VOR at or above 10,000, Descend and maintain 4,000.
- This clearance authorizes the pilot to descend from the assigned altitude whenever he chooses as long as he crosses the PHK VOR at or above 10,000 feet MSL.
- After that, the pilot should descend at a normal rate until reaching the assigned altitude of 4,000 feet MSL.
For example:
click here