Creative
Computation
for Visual
Communication
Design
WEEK 2 DAY 2
Coding Workshop 2.2
PROBLEM:
HOW TO ROTATE SHAPES?
Transformations
-
In drawing software like Illustrator, moving, rotating and scaling objects is easy
-
Transformations affect individual shapes
-
-
With code you are drawing the entire frame at once
-
Transformations affect all the following shapes
-
Transformations are reset when frame is refreshed
-
Transformations
translate(x,y);
rotate(rad); //default is radians
scale(x,y); //decimal percentage- Transformations move, rotate and scale the entire coordinate system
translate(100,-50); //move origin point to (100,-50)
rotate(3); //rotate coordinates 3 radians (~180°)
scale(1,2); //scale y-axis to 200%Transformations: Translate
- Moves the point of origin
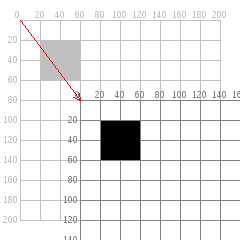
rect(20,20,40);
rect(80,100,40);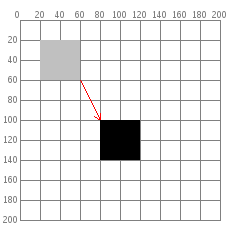
rect(20,20,40);
translate(60,80);
rect(20,20,40);Transformations: Translate
-
Translating is useful when drawing the same complicated shape in different locations
-
Define the coordinates in relation to the origin, then move the origin and repeat drawing
-
“Grouping shapes”
-
-
Translating is also necessary when rotating shapes!
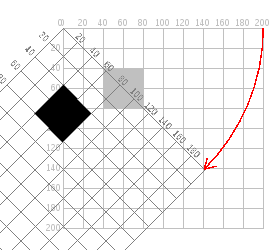
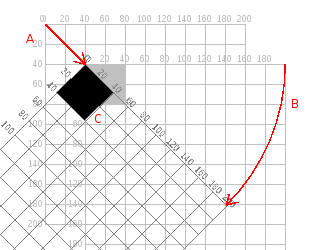
Transformations: Rotate
-
Rotates the coordinate system around the point of origin
-
Default unit is radians
-
Use angleMode(DEGREES) for degrees
-
- To rotate a shape in place, first translate, then rotate!
Transformations: Scale
-
Scales the coordinate system in relation to the origin
-
X and Y axis can be scaled individually
-
-
Unit is decimal percentage
-
scale(2.5) increases the size 2.5 times larger than original (=250%)
-
- Affects also strokeWeight and other effects
rect(20,20,40);
scale(2);
rect(20,20,40);Push and Pop
-
Transformations are cumulative and affect all the following drawing commands
-
Drawing styles eg. fill() also affect all following drawing commands
-
-
We can save and restore transformations and styles with push and pop functions
- Always use push and pop together!
-
Indenting your code makes it more legible!
-
push(); //start new drawing state
fill(0); //change fill to black
translate(100,100); //move origin
rect(0,0,50,50); //draw rectangle at new origin
pop(); //restore the original drawing state and styleExercise 1: Simple rotation
Exercise 2: Solar system
- Try adding more planets and moons!
Exercise 3: Rotating Arm
function setup(){
createCanvas(500,500);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw(){
background(255,200,255);
strokeWeight(30);
stroke(255,100,0);
//translate the origin to center of canvas
//rotate around origin using the value of mouseX
//draw a line from the origin point to 100px on the right
//translate the origin to the end of the line
//rotate around the new origin point using the value of mouseY
//draw a line from the new origin point to 100px on the right
noStroke();
fill(255,100,0);
//draw a circle at the end of the line
}VARIATION: Exercise 4: Spirograph
-
Start from the solar system example, but don’t update the background in draw()!
-
Play with changing values of rotation and translation to get cool patterns!
Basic concepts in computation
-
MEMORY
-
Storing data and accessing it later
-
Variables, arrays, objects
-
-
-
SEQUENCE
-
Running instructions in order
-
Functions, algorithms
-
-
-
SELECTION
-
Making choices
-
Conditionals and logic (if, else, and, or)
-
-
-
REPETITION
-
Doing the same thing more than once
-
Loops (for, while)
-
-
Loops
ellipse(0, 250, 50);
ellipse(100, 250, 50);
ellipse(200, 250, 50);
ellipse(300, 250, 50);
ellipse(400, 250, 50);
ellipse(500, 250, 50);PROBLEM:
HOW TO MAKE REPETITION EASIER?
Reasons to use computation
-
AUTOMATION
-
Using computational power to complete tasks that are laborious for humans.
-
-
OPTIMISATION
-
Seeking solutions for complex problems that are beyond human cognition.
-
-
IDEATION
-
Reaching unexpected outcomes by setting into motion an autonomous process
-
LOOPS!
Loops
ellipse(0, height/2, 50);
ellipse(100, height/2, 50);
ellipse(200, height/2, 50);
ellipse(300, height/2, 50);
ellipse(400, height/2, 50);
ellipse(500, height/2, 50);WE ARE ADDING 100 TO X EVERY TIME...

Loops
let x = 0;
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100; // x is 100
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100; // x is 200
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100; // x is 300
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100; // x is 400
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100; // x is 500
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);WE ARE REPEATING IDENTICAL LINES!

Loops
let x = 0;
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100; // x is 100
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100; // x is 200
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100; // x is 300
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100; // x is 400
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100; // x is 500
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);REPEAT THIS UNTIL X IS 500

While loop
while(condition){
//repeat while condition is true
}
let x = 0; //define variable
while(x <= 500){ //repeat while condition is true
ellipse(x, height/2, 50); //draw ellipse
x += 100; //increment variable
}
boolean expression
curly brackets
While loop
let x = 0; //define variable
while(x <= 500){ //repeat while condition is true
ellipse(x, height/2, 50); //draw ellipse
x += 100; //increment variable
}
- Beware the infinite loop!
- The condition must become false at some point or the loop will never finish!
- The value of the boolean expression has to change!
- Remember to increment!
Recipe for loops
let x = 0;
while(x <= 500){
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
x += 100;
}
INCREMENT
INITIAL STATE
CONDITION

For loop
for(initial state; condition; increment){
//code block to be repeated
}indent
semicolons between statements
curly brackets

For loop
for(initial state; condition; increment){
//code block to be repeated
}executed when loop starts
condition for repeating the loop
executed after each repetition
for(let x = 0; x <= 500; x += 100){
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
}
let x has local scope inside the loop!
Exercise 6a: Simple for loop
For loop
for(let i = 0; i < 6; i++){
ellipse(i*100, height/2, 50);
}
for(let x = 0; x <= 500; x += 100){
ellipse(x, height/2, 50);
}
LOOPING ACROSS THE DISTANCE
Reapeat until x > width
LOOPING A NUMBER OF TIMES
Repeat until we have done 6 loops
THESE DO THE SAME THING IN A DIFFERENT WAY
Exercise 6b: For loop
While vs. for


When you don’t know how many times you have to repeat the code
When you know how many times you want to repeat the code
WHILE
FOR
Understanding loops

LOOPING
!=
"ANIMATING"
Understanding loops
-
Loop diverts the program flow
-
"Top to bottom, inside out"
-
-
Loop structures inside draw() are completed before the frame is refreshed
-
Loop does not appear as animated!
-
function draw(){
//this stuff happens first
for(let i = 0; i < 10; i++){
//this stuff happens until loop ends
}
//this stuff happens last
}
Exercise 6c: Better for loop
VARIATION: Exercise 10: Animated loop
VARIATION: Exercise 7: Anni Albers


Mapping
PROBLEM:
HOW TO CONSTRAIN VALUES?
Mapping
map(value, start1, stop1, start2, stop2);let x = map(mouseX, 0, width, 180, 360);-
Converts values from one range to another
-
VALUE: the incoming value to be converted
-
START1: lower bound of the value's current range
-
STOP1: upper bound of the value's current range
-
START2: lower bound of target range
-
STOP2: upper bound of target range
-
- You should know the incoming number's range!
Exercise 8: Map
VARIATION: Exercise 9: Gradients
Recap
//transformations
translate(x,y); //move point of origin
rotate(rad); //rotate around origin, default in radians
scale(p); //scale coordinate system in decimal percents
push(); //save previous transformations and drawing styles
pop(); //reset to previous transformations and styles
angleMode(MODE); // set angle unit to DEGREES or RADIANS
//while-loop
while(condition){
//repeat while condition is true
}
//for-loop
for(initial state; condition; increment){
//code block to be repeated
}
//converting values from one range to other
map(value, start1, stop1, start2, stop2);Coding Assignment II: Clock
Coding Assignment II: Clock
-
Make a program that visualises time.
It could be:- An abstract visualisation that shows the passing of time OR
- A literal clock that counts seconds, minutes and/or hours
- CONSTRAINT: The visualisation should change over time.
Coding Assignment II: TIPS
-
We have looked at different methods to create change over time, including:
- randomness
- rotation
- frameRate
- incrementation
-
Consider how to use these methods to create an engaging visualisation
- It does not have to be a literal, traditional clock! Let your imagination run free!
Coding Assignment II: TIPS
- New functions that might be helpful:
- Coding Train clock tutorial
- You don't have to use these!
Coding Assignment II: INSTRUCTIONS
-
Comment your code well!
-
Add your name and date on the top
-
Explain how the code works
-
Explain the key features of your clock. How does it visualise time?
-
-
If you borrow code, include references and be explicit how you have modified it!
-
Submit a web editor link to your sketch in MyCourses by Tuesday
To do before next Tuesday
-
Weekly Reading II
- Coding Assignment II
