Learning CSS
Cascading Stylesheets
and how they work with HTML
body {
background-color: #e6e6e6;
color: #031B3F;
font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif;
padding:15px;
line-height:1.4em
}Sample Code!
- It helps to learn by looking at sample code for other websites!
- We have a model website with HTML and CSS code posted on the introDH-Hub here:
https://github.com/newtfire/introDH-Hub/tree/master/docs
- Feel free to browse and apply our sample code to your projects!
CSS syntax
Selector {declaration;
declaration; }
Image credit: https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_syntax.asp
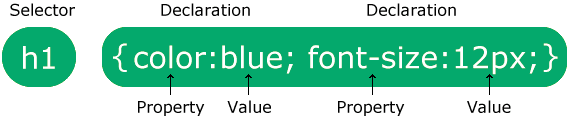
Selector {property: value;
property: value;}
Stacking the code
body {
background-color: #e6e6e6;
color: #031B3F;
font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif;
padding:15px;
line-height:1.4em
}One CSS declaration per line: keep your code tidy and legible!
Commenting on the code
body {
background-color: #e6e6e6; /*#C5D3D3*/ /*#B4D6B4*/
/*trying different shades of grey-green */
color: #031B3F;
font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif;
padding:15px;
line-height:1.4em
}- "Comment out" values you're experimenting with.
- Or write comments to explain what you're trying to do.
How to connect CSS to your HTML:
Three ways
- inline HTML (not recommended, makes "code bloat"):
<p style="color:blue;">....</p>
- "Separation of concerns":
- Good for one HTML page only: a <style> element inside an HTML <head>
- Good for an entire website: a separately linked .css file:
<link> element in the HTML <head>
How to connect CSS to your HTML:
<style> element inside the <head>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>My Webpage</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: #e6e6e6 /*#C5D3D3*/ /*#B4D6B4*/;
color: #031B3F;
font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif;
padding:15px;
line-height:1.4em
}
p { padding: 2em;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>..some text...</p>
</body>
</html>
How to connect CSS to your HTML:
<link> element inside the <head>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>My Webpage</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/syllsched.css" />
</head>
<body>
<p>..some text...</p>
</body>
</html>
- Preferred for a whole website: Update once, updates everywhere!
-
Relative file association: This one is saved in a folder named "css" in my web folder
- docs/
- index.html
- css/
- syllsched.css
- docs/
How to link a separate CSS Stylesheet
- <link/> element: for linking a CSS file
- <script> element can link a JS file
Inside the <head>.....</head>
<head>
<title>My Portfolio Site</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css"/>
</head>
CSS Inheritance
- Put CSS declarations for styling across your entire page on top-level HTML elements like <body>. . . </body>
- Examples: set a background-color, set a font or font-family, set your normal font color
- Inheritance: the declarations you set for one element are passed down the HTML tree (to the elements nested inside it.)
CSS Box Model
- To CSS, every element is a box
- This includes the block and inline HTML elements
- The box has a structure with several properties you can control with CSS:
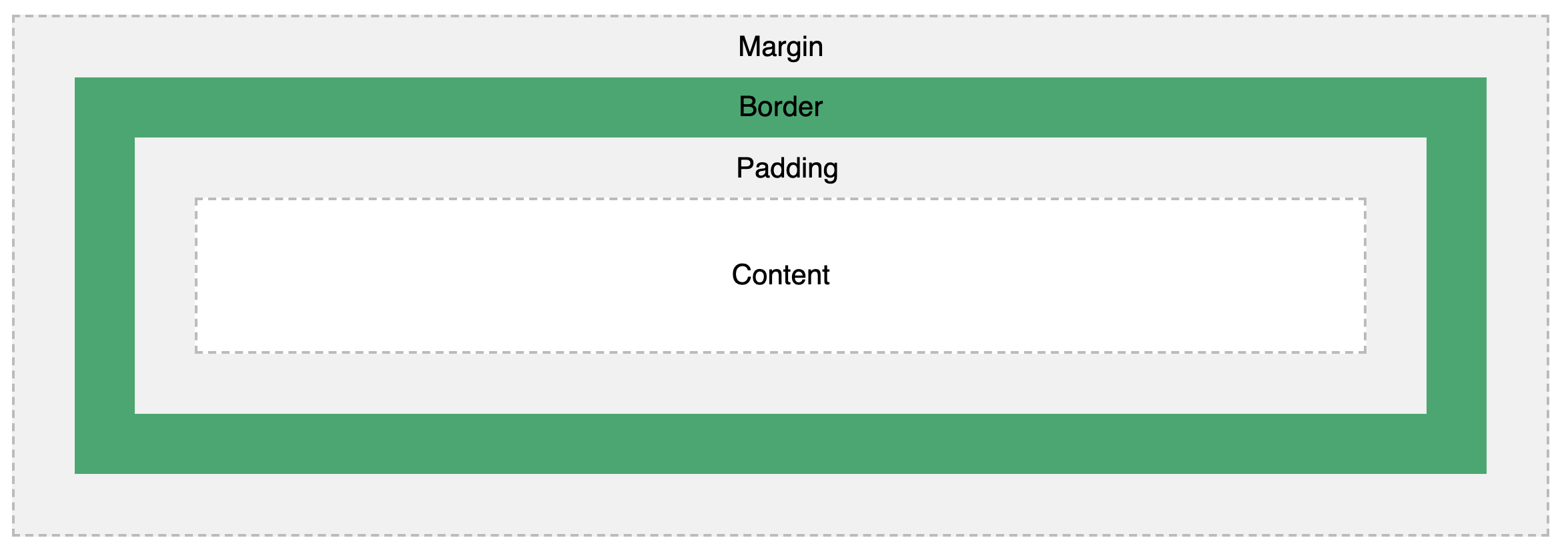
- To adjust how much space goes around your HTML elements, work with
CSS Box Model: Properties

- content: literally takes up the space needed for text, image, etc.
- padding: a little room inside the box, just outside the content. By default, transparent.
- border: this can be made visible around your content (draw the box!)
- margin: area outside the border. By default, transparent.
- Details: w3schools Box Model Demo
CSS: Units of “length”
Reference: w3schools on CSS units
- Absolute (cm or mm) vs. Relative lengths
- Why we prefer relative lengths!
Some length units we use most:
- em: literally the size of the standard letter “m” in the default font you're using
- vw: a percentage of the width of the viewport window (much smaller than an em)
- px: technically an absolute dimension: 1 device pixel or ”dot” in your display. Pixel size depends on the device!
Writing CSS Demands
Looking Stuff Up!
Favorite resources for ALL available CSS properties:
- Plus: Lets you try as you go
-
Minus: Often has inline CSS examples (learn to adapt)
- All properties in alphabetical order for lookup!
CSS: Color!
How to reference colors:
- by name:
- as in, tomato
- 140 Color Names supported across all web browsers
- RGB values:
- Red / Green / Blue values
- scale from 0 to 255
- rgb(0,0,255) = most intense blue
- rgb(0,0,0) = black
- rgb(255,255,255) = white
- rgb(20,20,20) (or make all the values equal): something grey
See w3C colors tutorial for more details.
CSS: Color! Hexadecimal values
- Hex value looks like this: #RRGGBB
- On base 16 scale: 0 -10, A, B, C, D, E, F
- lowest value: 00
- highest value: FF
- Can refer to them in threes or sixes
- #FF0000 = red
- #F00 = same red
See w3C colors tutorial for more details.
Combinations of CSS properties in declarations
body {
background-color:SlateBlue;
color: black;
}
h1 {
padding: 2px;
border: 1px solid violet;
}CSS: Working with Accessible Color Schemes
- Color on the web: notoriously variable!
- How do individuals see color?
- How do monitors display it?
- Design with variable experience in mind
- Reference WebAIM: Web Accessibility in Mind
- WebAIM feature on color blindness
- Try the Toptal Colorblind Webpage filter on your site (plug in your website address)
CSS: Resources for Choosing Color Schemes
- Experimenting with color palettes: Paletton
- Foreground against Background color testing: WebAIM Contrast Checker
- Tests foreground/background with fonts and font sizes: ColorSafe
HTML @class, @id and CSS
-
@ (short for attribute)
as in @href in:
<a href="https://behrend.psu.edu/">Penn State Erie</a>
- Any HTML display element can hold @class and @id
- @class : creates a shared category for group of elements
- everything associated with a topic, or to be arranged
in a certain area of the page -
Multiple elements can share an @class value.
- everything associated with a topic, or to be arranged
-
@id : marks an element as unique, different from all the others.
- Each @id attribute has a unique value (cannot be used again anywhere else on the page).
-
You can have lots of elements with @id on your page, but each one has its own unique value.
-
These attributes are useful for CSS styling.
- Write CSS rules for all elements of a particular @class
- Write CSS rules for a specific element with a distinct @id
HTML with @id and @class for a navigation bar
<nav id="menu">
<div class="button"><a href="index.html">Home</a></div>
<div class="button"><a href="resume.html">Resume</a></div>
<div class="button"><a href="gallery.html">Gallery</a></div>
<div class="button"><a href="essays.html">DIGIT 100 Essays</a></div>
</nav>CSS rules to match
nav#menu {padding:2vw; }
/* This means: style the <nav id="menu"> element. */
.button {
border:2px;
border-style:solid;
border-color:red;
padding:2vw;
background-color:#E6E6FA;
color:yellow;
width:10%;
display:inline;
border-radius: 20px;
}
/* This means: style ANY element that as an @class set to button, as in */
/* <li class="button"> or <p class="button"> or <div class="button">. */
<nav id="menu">
<div class="button"><a href="index.html">Home</a></div>
<div class="button"><a href="resume.html">Resume</a></div>
<div class="button"><a href="gallery.html">Gallery</a></div>
<div class="button"><a href="essays.html">DIGIT 100 Essays</a></div>
</nav>You could also write it like this:
#menu {padding:2vw; }
/* This means: style the <nav id="menu"> element. */
.button {
border:2px;
border-style:solid;
border-color:red;
padding:2vw;
background-color:#E6E6FA;
color:yellow;
width:10%;
display:inline;
border-radius: 20px;
}
/* This means: style ANY element that as an @class set to button, as in */
/* <li class="button"> or <p class="button"> or <div class="button">. */
# means @id, . means @class
<nav id="menu">
<div class="button"><a href="index.html">Home</a></div>
<div class="button"><a href="resume.html">Resume</a></div>
<div class="button"><a href="gallery.html">Gallery</a></div>
<div class="button"><a href="essays.html">DIGIT 100 Essays</a></div>
</nav>or, like this (no spaces between element name and . or #)
#menu {padding:2vw; }
/* This means: style the <nav id="menu"> element. */
div.button {
border:2px;
border-style:solid;
border-color:red;
padding:2vw;
background-color:#E6E6FA;
color:yellow;
width:10%;
display:inline;
border-radius: 20px;
}
/* This means: style ANY element that as an @class set to button, as in */
/* <li class="button"> or <p class="button"> or <div class="button">. */
# means @id, . means @class