XPath Intro
Patricia O'Connor

Oxygen Version

XPath Scope
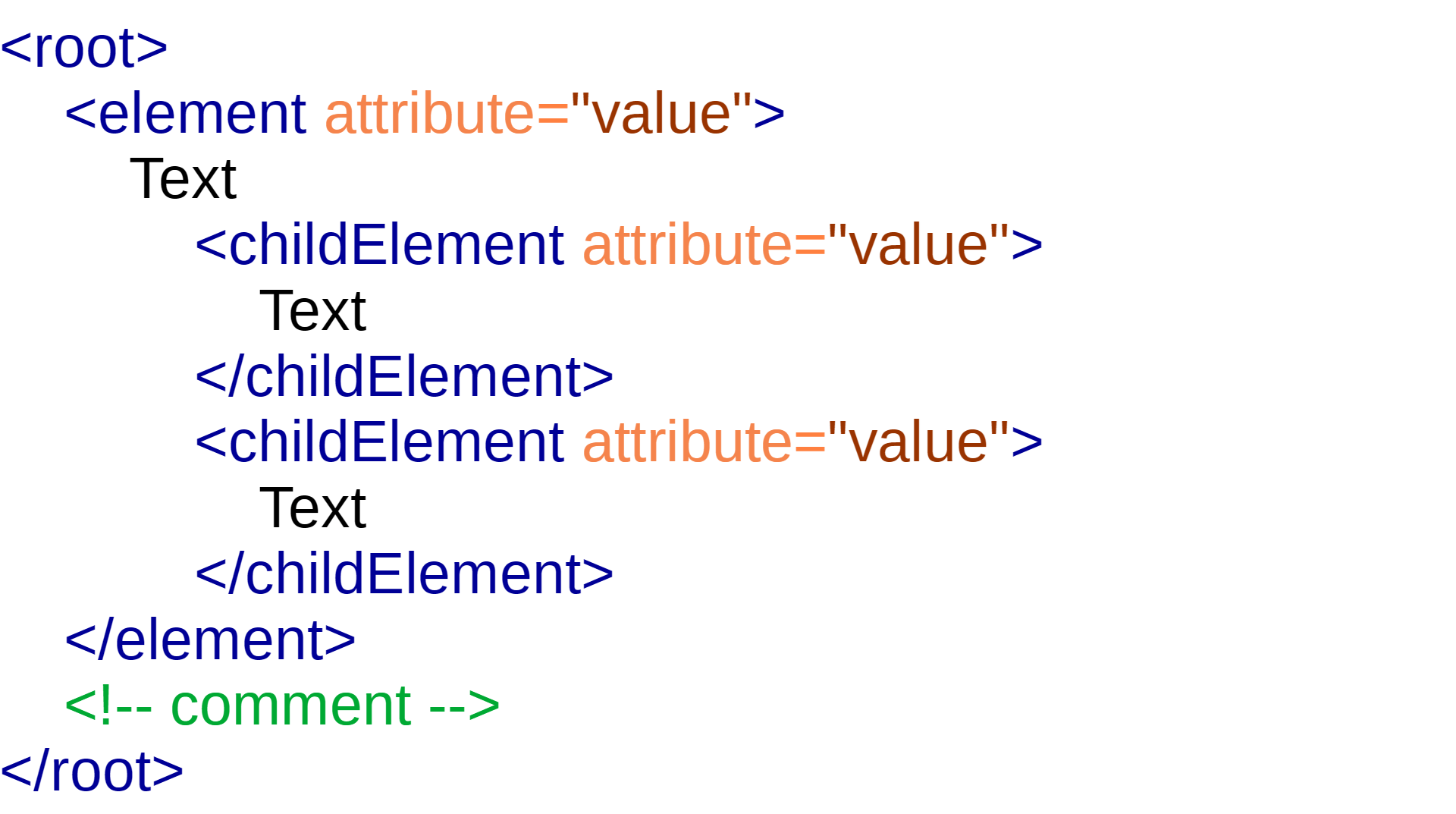
XML Tree Structure
An XML file starts from "the root", and branches out in complex ways to the "leaves".
Parent
Siblings

ancestor
children
siblings
grandchild
children
children

ancestor
children
siblings
descendent
children
children
ancestor
immediate child of TEI
immediate child of TEI
5 children of teiHeader
child of text
child of text
child of body
children of div
What is XPath?
XPath is a syntax/language that we write to select parts (or nodes) of an XML document
An XPath expression enables a user to describe, find, and navigate to information inside an XML document
XML languages that employ XPath to find and manipulate information in XML documents:
XSLT (eXtensible Stylesheet Language Transformations)
XQuery (XML Query language)
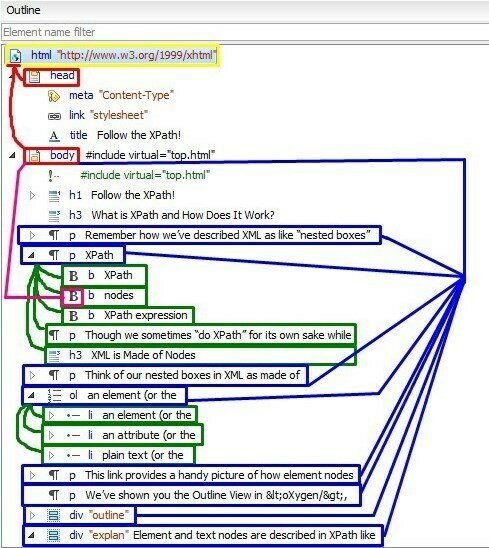
Nodes
A node is a piece of information in the XML tree, such as an element, an attribute, a string of text, or a comment.

element()
attribute()
text()
comment()
@
XPath Components
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| path expression | Describe the location of some nodes in a tree. |
| axis | An axis is part of a path expression. Describe the direction in which one looks in the tree. |
| predicate | Filter the results of a path expression. |
| function | Do something with the information retrieved from the document instead of just returning it as received. |
Path Expressions
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| nodename | Selects all nodes with the name "nodename" |
| / | Selects from the root node |
| // | Selects nodes in the document from the current node that match the selection no matter where they are |
| . | Selects the current node |
| .. | Selects the parent of the current node |
| @ | Selects attributes |
| Describes the location of some nodes |
|
Axes
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| ancestor:: | The ancestor axis sends you to parents and above, all the way up to the root node. |
| . or self:: |
The self axis designating the current context node and the current location in a path. |
| .. or parent:: | The parent axis sends you up a short distance, to the immediate parent of the context node |
| / or child:: | The child axis (the default) sends you down to the immediate child of the context node. |
| // or descendant:: | The descendant axis sends you down to the children and their children etc. |
| @ or attribute:: | The attribute (@) axis for locating attributes and attribute values |
Predicates
Predicates are always embedded in [ ]
Filter the results of path expressions
Predicates are used to find a specific node or a node that contains a specific value.
Predicates
Remember: Predicates are always embedded in sqaure brackets
How do we find the first paragraph of a div?
Predicates are used to find a specific node or a node that contains a specific value.
//div/p[1]
//div/p
Predicates
How do we find a element node called div that has an attribute called type and a value of "letter"?
//div[@]
//div[@type]
//div[@type="letter"]
//div[ ]
Predicates
How do we find the first paragraph of a div with a type attribute value of "letter"?
//div[@type="letter"]
//div[@type="letter"]/p[ ]
//div[@type="letter"]/p
//div[@type="letter"]/p[1]
Predicates
How do we find the first personal name mentioned in the first paragraph of a div with a type attribute value of "letter"?
//div[@type="letter"]/p[1]
//div[@type="letter"]/p[1]/persName
//div[@type="letter"]/p[1]/persName[ ]
//div[@type="letter"]/p[1]/persName[1]
Predicates
How do we find the personal name with a reference to Chaucer?
//persName[@ref]
We need to filter for ref attributes using @ref
//persName[@ref="#Chaucer"]
We need to specify the value of @ref
Predicates & Axes
//persName
Find the persName elements with a parent title element
//persName[parent::]
//persName[parent::title]
//title/persName
Predicates & Axes
Find the persName elements with a body ancestor
//persName[ ]
//persName[ancestor::]
//persName[ancestor::body]
Unknown Nodes
| Wildcard | Description |
|---|---|
| * | Matches any element node |
| @* | Matches any attribute node |
| node() | Matches any node of any kind |
| XPath Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| //* | Selects all elements in the document |
| //title[@*] | Selects all title elements which have at least one attribute of any kind |
Function
Do something with the information retrieved instead of just returning it as received.
Retrieve all of the <paragraph> elements in a <div> element (that has a type attribute value of "letter") but instead of returning the actual elements, return just a count of how many there are. This uses the count() function.
count(//div[@type="letter"]/p)
//div[@type="letter"]/p => count()
Functions
Retrieve all of the <persName> elements in a <div> element (that has a type attribute value of "letter") and return just a count of how many there are.
count(//div[@type="letter"]//persName)
//div[@type="letter"]//persName => count()
//div[@type="letter"]//persName
Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| distinct-values() | eliminate repetition in a list of results |
| last() | Returns the last |
|
lower-case() upper-case() |
Changes case of string |
| not() | Inverts the truth value of the argument. //p[not(q)] returns all <p> elements that do not have any <q> child element. |
| normalize-space() | normalize the white space (spaces, tabs, new lines, etc.) in text |
| string-length() | returns the length of text by counting characters. |
Functions
//div[@type="letter"]//p[1]
How do we find the last paragraph in the letter?
Remember: To find the first paragraph we used predicates or [ ]
Functions
//div[@type="letter"]//p[ ]
//div[@type="letter"]//p[1]
To find the last paragraph in the letter
//div[@type="letter"]//p[last()]
Using the last() function
Functions
How do we remove repetition from the results for persName?
//persName=>
//persName
//persName=> distinct-values()
Functions
//div[@type="letter"]//persName=>distinct-values()
How do we remove repetition in the results of persName in the letter?
//div[@type="letter"]
//div[@type="letter"]//persName
Functions
[not(@ref="#Webb_Mary_younger")]
//div[@type="letter"]//persName
//div[@type="letter"]//persName[not(@ref="#Webb_Mary_younger")]
The not() function
Simple Map & Arrow
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| ! | The simple map operator (!) means do the thing on the right once for each item on the left. |
| => | The arrow operator (=>) means apply the function on the right to the entire sequence (all at once) on the left. |
Simple Map & Arrow
//* ! name() => distinct-values()
//* ! name()
The name() function returns a string representing the QName of the first node in a given node-set.
Comparison Operators
| Value | General | Description |
|---|---|---|
| eq | = | equal to |
| ne | != | not equal to |
| gt | > | > greater than (may also be written >) |
| ge | >= | greater than or equal to (not less than; may also be written >=) |
| lt | < | less than (may also be written <) |
| le | <= | less than or equal to (not greater than; may also be written <=) |
//p[count(persName) > 10]
//p/persName
//p[persName]
//p/count(persName)