ECF5560
Winter term, 2023
Policy effects
Cost benefit analysis & economic decision making
Dr. Emilia Tjernstrom
Session 2: spreadsheets
Session 3: applying economics to
real-world topics
Session 1: questions
1. Price ceiling
2. Price floor
3. Taxes
https://flux.qa/GFDENE

0. The sheets
-
PriceCeiling PriceFloor
Taxes
Policy analysis worksheet | the sheets
- experiment with demand & supply curves
- analyse the impact that price ceilings
& price floors have on markets
- examine how price elasticities influence
the incidence of taxes
Policy analysis worksheet | the sheets
As we know, governments can intervene in markets in many ways
Here, we focus on two common policy instruments:
- price restrictions
- per-unit taxes
Policy analysis worksheet | the sheets
As we know, governments can intervene in markets in many ways
Here, we focus on two common policy instruments:
- price restrictions
- per-unit taxes
price ceilings
price floors
persistent shortage
persistent surplus
1. Price ceilings
Price ceilings
What are some examples of price ceilings?
Price ceilings
When you open the sheet, it initiates with a price ceiling of $50
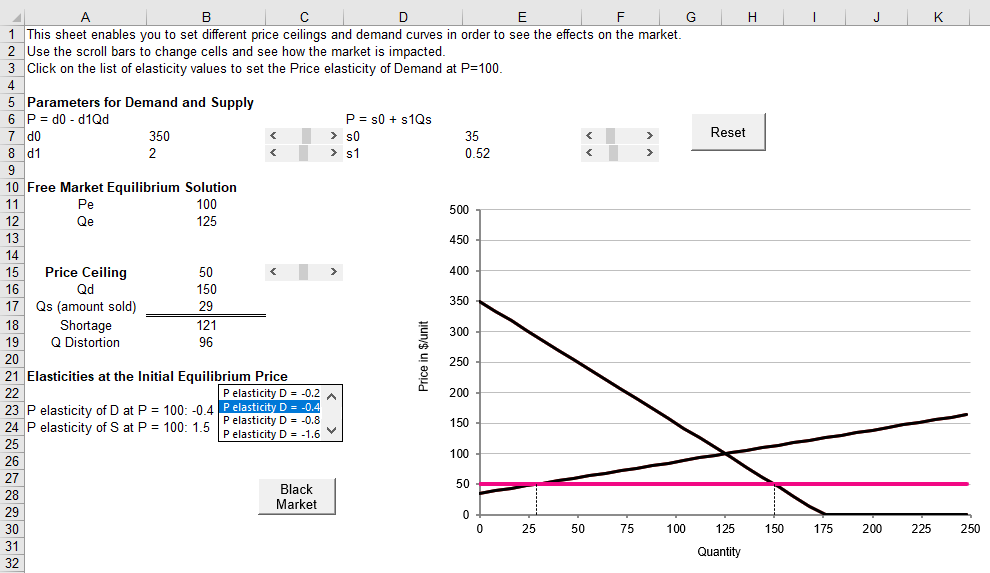
Price ceilings
The free-market equilibrium price is $100, quantity is 125 units

Price ceilings
With the price ceiling of $50, producers only supply 29 units

Price ceilings
- Calculate the distortion generated by the price ceiling at $50
- Use the scroll bar to increase the price ceiling to $80
What is the distortion now? Is this better or worse than $50? - Use a figure (can be a screenshot) & your ability to change the price elasticity of demand (PEoD) to explain the relationship between the size of the distortion and the PEoD
- How is price elasticity of supply related to the size of the distortion?
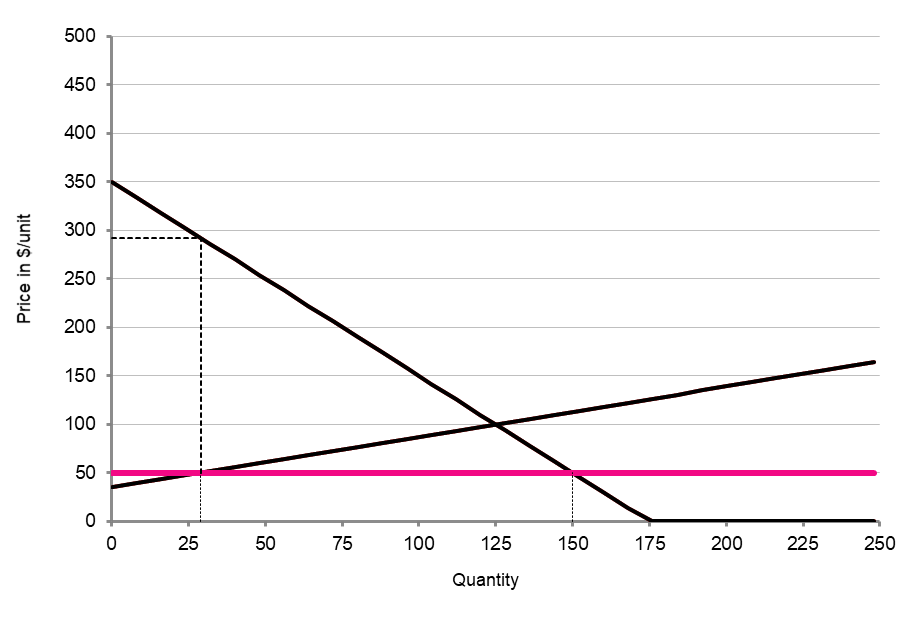
Price ceilings
- Calculate the distortion generated by the price ceiling at $50
- Use the scroll bar to increase the price ceiling to $80
What is the distortion now? Is this better or worse than $50? - Use a figure (can be a screenshot) & your ability to change the price elasticity of demand (PEoD) to explain the relationship between the size of the distortion and the PEoD
- How is price elasticity of supply related to the size of the distortion?
distortion = 96 units
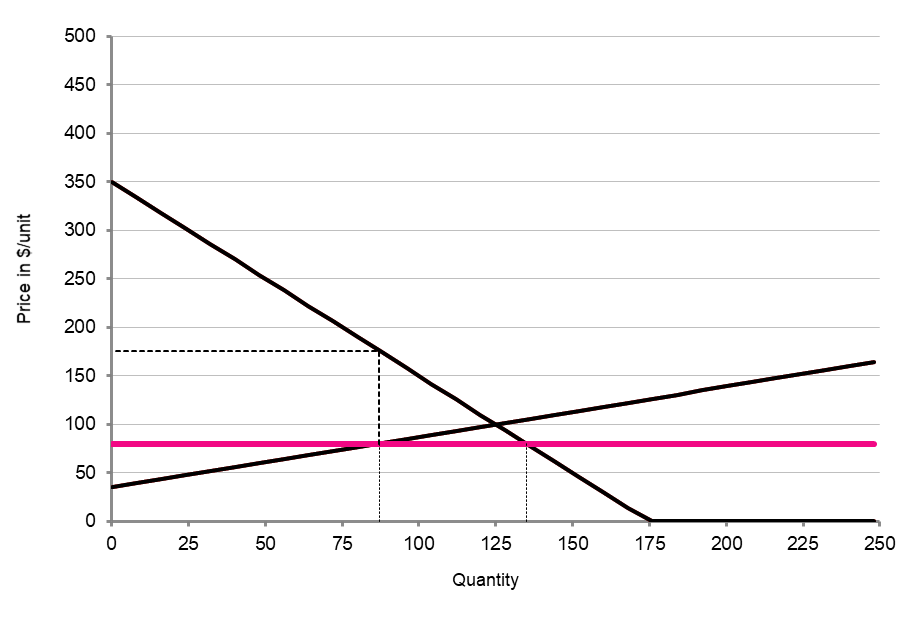
Price ceilings
- Use the scroll bar to increase the price ceiling to $80
What is the distortion now? Is this better or worse than $50?
- Use a figure (can be a screenshot) & your ability to change the price elasticity of demand (PEoD) to explain the relationship between the size of the distortion and the PEoD
- How is price elasticity of supply related to the size of the distortion?
Price ceiling: $50
Distortion: 96 units
Price ceilings
- Use the scroll bar to increase the price ceiling to $80
What is the distortion now? Is this better or worse than $50?
- Use a figure (can be a screenshot) & your ability to change the price elasticity of demand (PEoD) to explain the relationship between the size of the distortion and the PEoD
- How is price elasticity of supply related to the size of the distortion?


Price ceiling: $80
Distortion: 38 units
Price ceilings
- Use a figure (can be a screenshot) & your ability to change the price elasticity of demand (PEoD) to explain the relationship between the size of the
distortionshortage and the PEoD - How is price elasticity of supply related to the size of the distortion?
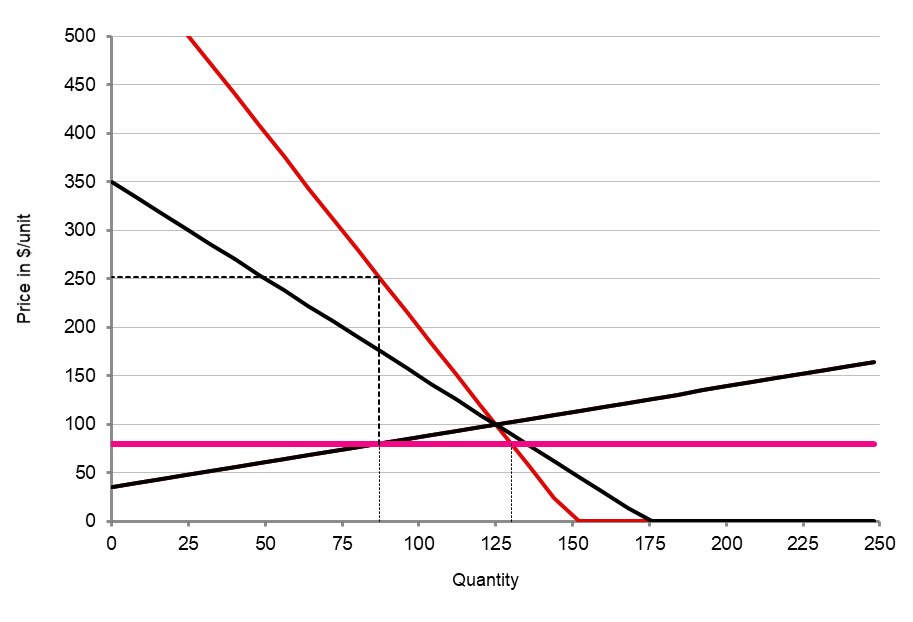
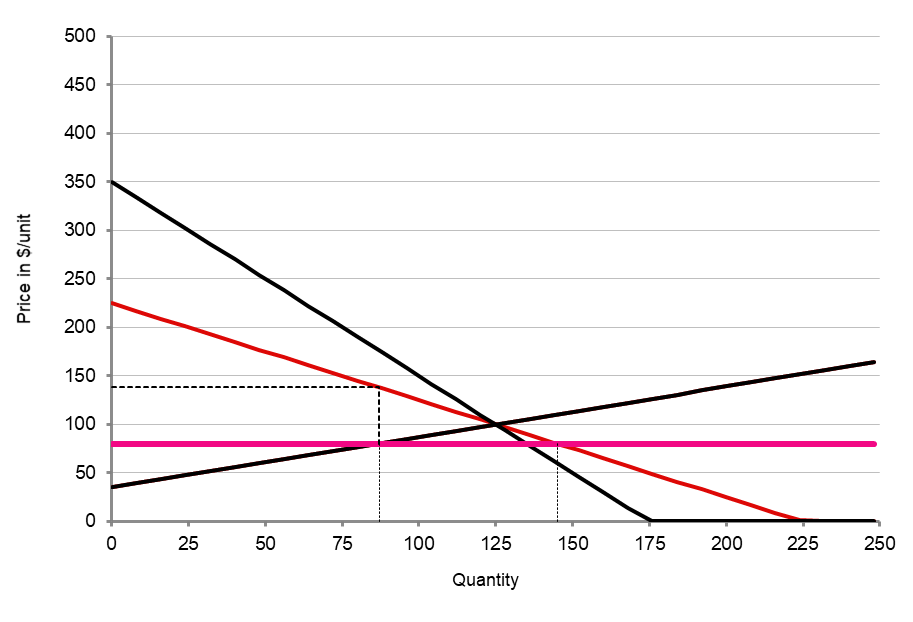
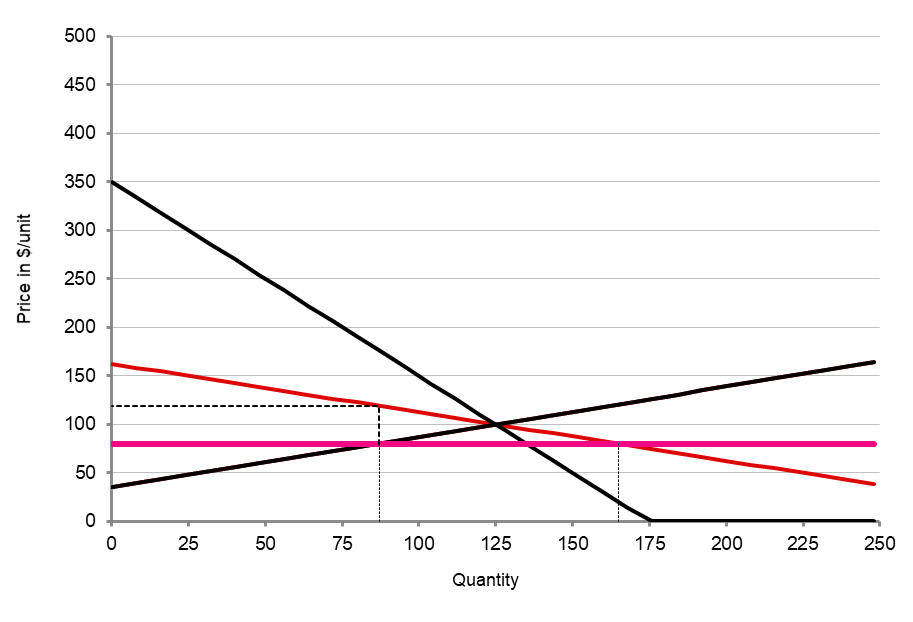
The size of the distortion doesn't change with PEoD

...but the shortage does!
...but the shortage does!

...but the shortage does!

What about the price elasticity of supply?

Let's talk about rents!
Rental caps
Identify the different arguments
- in favor of rent freezes/caps
- against rent freezes/caps

Find at least 3 sentences that are (implicitly) about price elasticities & shortages
- PEoD
- PEoS
- ...or a combination!
Rental caps
Identify the different arguments
- in favor of rent freezes/caps
- against rent freezes/caps
Find at least 3 sentences that are (implicitly) about price elasticities & shortages
- PEoD
- PEoS
- ...or a combination!
Are there assumptions that we can (safely) make about the market for housing / rental properties?
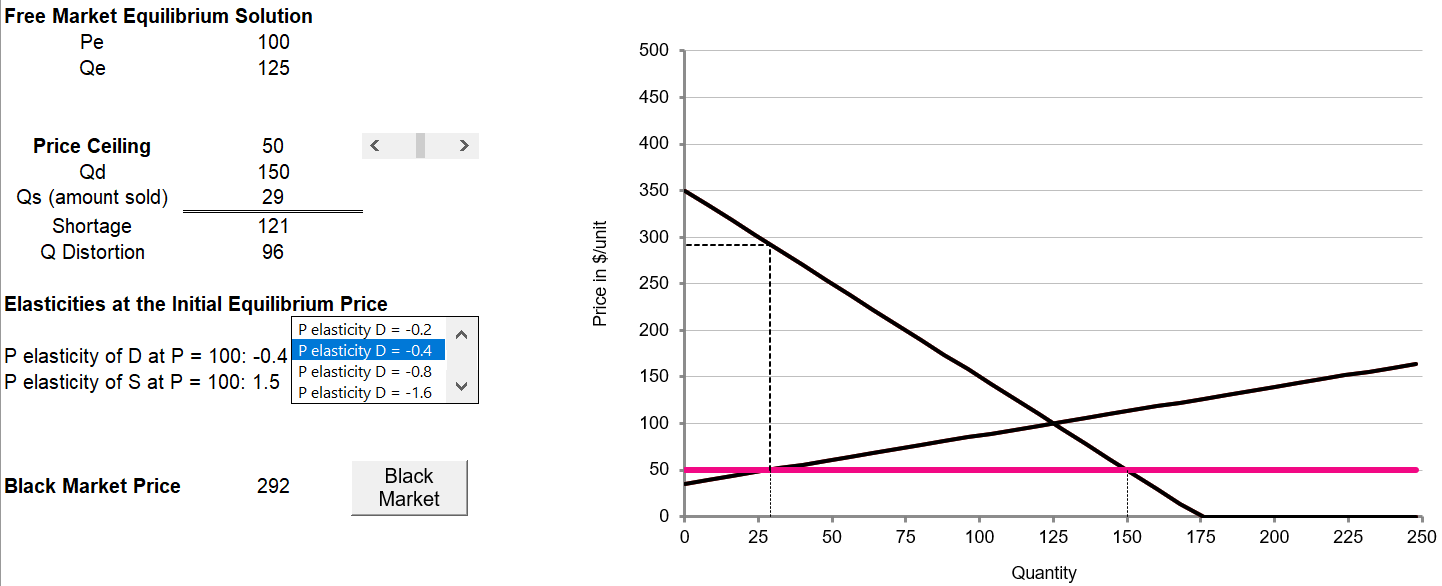
Price ceilings & cheating
Click reset to go back to the original $50 price ceiling
Click the Black market button to reveal the black market values
- Compute the difference between the price ceiling and the black market price as a percentage of the price ceiling value
- Compute the extra revenue that producers would gain if they cheated and sold all that they produce at the black market price
- Use a figure to show the relationship between the black market price and the PEoD
Price ceilings & cheating
- What is the relationship between the PEoS & the black market price?
- What does this all suggest about the overall costs and benefits of price ceilings?
2. Price floors
Price floors
- What is the size of the distortion caused by the price floor (@$125)?
- Set the price floor at $150. How does this compare with above?
- Reset the price floor to $125 and show the relationship between PEoD and the surplus caused by the price floor
- How would you (the policy-maker) keep a price floor at the desired level? In other words, why doesn't the market adjust to eliminate the distortion?
Price floors
- What is the cost of whatever you answered in 4)?
- If you were a government considering price floor policy, would you want demand to be price elastic or inelastic?
Examples?

A) Read the article
What are the arguments in favour?
What are the arguments against?
What questions do you have?
Are there any perspectives missing?
B) Form an opinion
What would you need to know evaluate whether the policy's successful?
Successful: the benefits > the costs
What data could you bring to bear?
3. Taxes
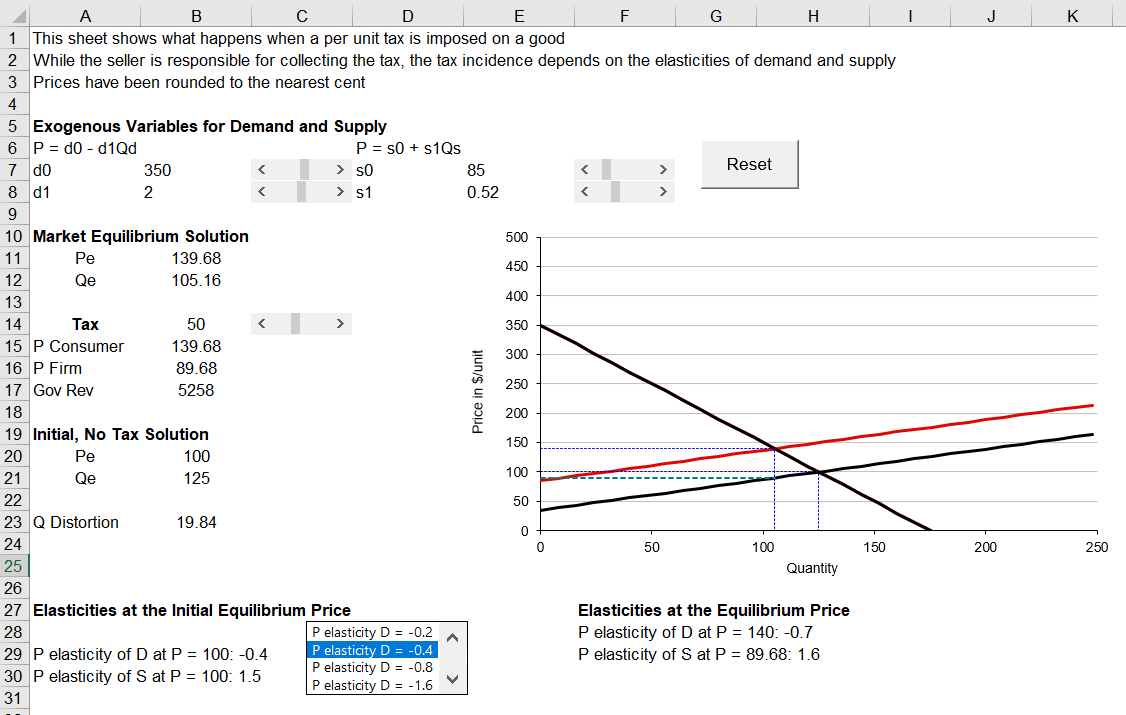
Taxes
Use the scroll bar to set a tax of $50 dollars per unit on the good
Taxes
Use the scroll bar to set a tax of $50 dollars per unit on the good
- While we illustrate the impact of a per-unit tax as a shift left
(or up) of the supply curve, what is actually happening? Describe the forces that push the market to its new equilibrium. - What are the drawbacks of a per-unit tax? Do these drawbacks depend on the efficiency of the market prior to the tax?
- Who bears the burden of the $50 tax?
Consumers? Producers? How do we measure this?
Taxes
- Keeping the tax at $50 per unit, change the PEoD to -1.6
- Is the distortionary effect of the per unit tax greater now than compared to the initial situation?
-
What can you conclude about the effect of the PEoD on the distortion created by per-unit taxes?
-
For a per-unit tax of $50, compare
-
the government revenue when the PEoD = -0.4 and -1.6
-
the incidence of the tax when the PEoD = -0.4 and -1.6
-