

Microcontrollers
Written by: Igor Korotach
What are microcontrollers?
A microcontroller (MCU for microcontroller unit) is a small computer on a single metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) chip.
Distinctive features
Energy
- Consumes less energy
- Has mostly battery lifespan
- Has a very energy efficient deep sleep mode
Programming & Computing
- Doesn't have an Operating System built-in
- Requires special compilers
- Code is mostly written in C/C++
- Doesn't have a lot of RAM
- Might have a single core
Cost
- Cost may vary from less than $1 to >250$
- Requires modules to operate in full potential
- Needs battery recharge and metal-case disassembling
Popular microcontrollers
Arduino
Raspberry

ESP8266/ESP32

Programming
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(F("BME280 test"));
bool status;
// default settings
// (you can also pass in a Wire library object like &Wire2)
status = bme.begin(0x76);
if (!status) {
Serial.println("Could not find a valid BME280 sensor, check wiring!");
while (1);
}
Serial.println("-- Default Test --");
delayTime = 1000;
Serial.println();
}
Programming
String getValues() {
auto temperature = bme.readTemperature();
auto pressure = bme.readPressure() / 100.0F;
auto alt = bme.readAltitude(SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA);
auto humidity = bme.readHumidity();
String message = "{\n";
message += " \"temperature\": "; message += temperature; message += ",\n";
message += " \"pressure\": "; message += pressure; message += ",\n";
message += " \"altitude\": "; message += alt; message += ",\n";
message += " \"humidity\": "; message += humidity; message += "\n";
message += "}";
// Convert temperature to Fahrenheit
/*Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(1.8 * bme.readTemperature() + 32);
Serial.println(" *F");*/
Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
return message;
}Message queues
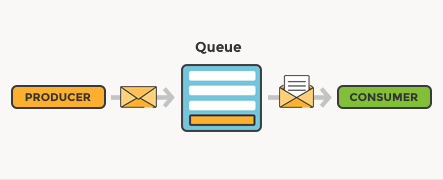
In computer science, message queues and mailboxes are software-engineering components typically used for inter-process communication (IPC), or for inter-thread communication within the same process. They use a queue for messaging – the passing of control or of content.
Message queue
Why MQTT?
MQTT advantages
- Low bandwidth
- Low energy consumption
- Easy to implement
- Uses TCP
MQTT architecture
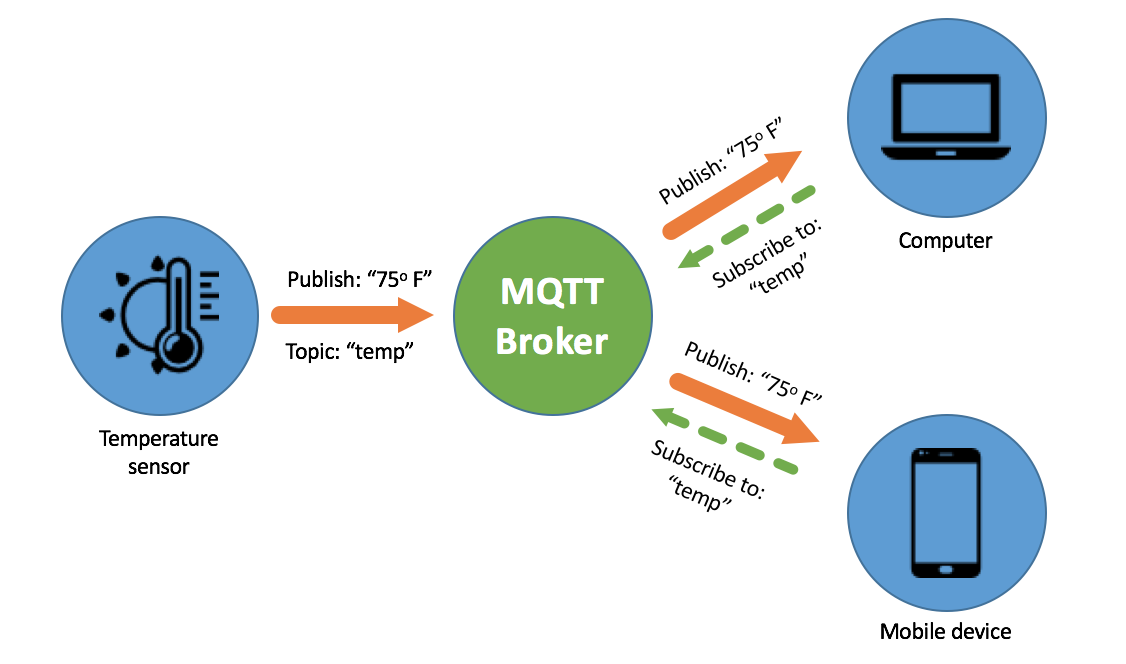
MQTT programming
#define TOPIC String("YOUR_NAME_SURNAME/lab4_topic/YOUR_DEVICE_NAME")
EspMQTTClient client(
"WIFI_HOTSPOT_NAME",
"WIFI_HOTSPOT_PASSWORD",
"MQTT_SERVER_IP", // MQTT Broker server ip
"MQTT_LOGIN", // Can be omitted if not needed
"MQTT_PASSWORD", // Can be omitted if not needed
"DEVICE_NAME", // Client name that uniquely identify your device
1883 // The MQTT port, default to 1883. this line can be omitted
);
void setup() {
client.enableDebuggingMessages(); // Enable debugging messages sent to serial output
client.enableHTTPWebUpdater(); // Enable the web updater. User and password default to values of MQTTUsername and MQTTPassword. These can be overridden with enableHTTPWebUpdater("user", "password").
client.enableLastWillMessage("TestClient/lastwill", "I am going offline"); // You can activate the retain flag by setting the third parameter to true
}MQTT programming
void onConnectionEstablished()
{
// Publish a message to "mytopic/test"
client.publish("mytopic/test", "This is a message"); // You can activate the retain flag by setting the third parameter to true
}
void loop() {
auto msg = getValues();
client.publish(TOPIC, msg);
client.loop();
delay(delayTime);
}
Thanks for your attention. You've been awesome!
Questions?
Presentation link: https://slides.com/emulebest/microcontrollers-mqtt
Mail: igorkorotach@gmail.com
Telegram: @emulebest
